Showing 2953 items
matching the flag
-
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, c 190
Weatherboard hotel, two-storey turret, flag pole on top. Lantern light above entrance door with name of hotel. single storey left of turret. Trees on right and left of photograph. Victorian house tucked behind trees on right. Wood and wire fencing in foreground.Pier Hotel from the ReserveThe Rose Series P.700 copyrightlocal history, photography, photographs, slides, film, pier hotel, black & white photograph, miss elms san remo -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Tram 38 decorated for Royal Visit, Ken Magor, 1954
The photo, shows tram 38 decorated for the 1954 Royal Visit, crossing the railway tracks at Ballarat Station in Lydiard St North. The tram has the destination of Sebastopol. In the background is the railway signal gantry, Reids Coffee Palace and the Post Office. Many of the buildings are flying flags.Yields information about the 1954 Royal Tram.Photograph, black and white - plain black with Ken Magor stamp and negative number written on the rear.Ken Magor Negative Number - "3427" tramways, trams, royal visit, decorated trams, tram 38, lydiard st nth, level crossings -
 Disability Sport & Recreation Victoria
Disability Sport & Recreation VictoriaStickers, Stickers and sheets from first Commonwealth Paraplegic Games, Perth 1962, 1962
The 1962 Commonwealth Paraplegic Games, held in Perth, were the first edition of the Commonwealth Paraplegic Games.Approximately 100 stickers, both loose and attached in original sheets.Red image and text, in white/cream background. Drawing of a male wheelchair athlete throwing a javelin, in front of an Australian flag. Text underneath: FIRST COMMONWEALTH PARALYMPIC GAMES. Perth. 10-17 November 1962commonwealth paraplegic games, disabled sports, wheelchair sport, 1962 commonwealth paraplegic games, perth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel, H.M.A.S. Warrnambool J202, 1941-1947
This photograph is connected to the first HMAS Warrnambool J202, which was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with Royal Australian Navy and its vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (j202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWIIPhotograph, black and white, HMAS Warrnambool J202 in water with land and buildings in background. Ship is flying a dark flag with Union Jack in corner and star below it. Lifeboat suspended above deck in centre of ship. Top of funnel has a black band. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, ship’s bell, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Phillip island Football Club Seconds 1959, 1959
HistoricalBlack & white team photograph. Back row standing with arms folded, front row sitting, one sitting at front with ball. Umpire in white coat holding flag, standing at left. Taken on oval with cypress trees and parked cars in background.1959 Phillip Island Football Club - Seconds phillip island football club seconds 1959, local sporting teams, j. drennan, cleeland, morgan-payler, k mcilwraith, jeffrey, m. toovey, h. lacco, b. robb, g. anderson, p. curtin, m. de la haye -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumSouvenir - BELT BUCKLE
Buckle was created for the 1988 Reunion in Melbourne for Vietnam Veterans. 300 of these buckles were made for sale at the Reunion.Silver Belt Buckle of heavy metal. On front "Vietnam Veteran" across top. Image of 3 Service personal and a helicopter. At the bottom on top of the image of some flags. At back is a folding buckle and a hook stud to clip into belt holes. Shape is rectangular.Inscribed on front "Vietnam Veteran". On back inscribed "Vietnam Veterans International Reunion Melbourne 1988". Also "Made in Australia by Blandon Australia Pty Ltd". Also an Acclamation included under notes. Inscribed on back: "We Veterans do not gather to justify or dispute the rights of wrongs of War because it is not a dispute for those of us who Served to Answer. This buckle is in Remembrance of our International Veterans Community Celebration, A Community Strong of Heart, Strong with Love. The Tide is Turning". vietnam veterans, buckle -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumCertificate - CERTIFICATE, CHARTER BENDIGO DISTRICT RSL, Bendigo, Kangaroo Flat, Eaglehawk RSL's, October 2000
The formation of the Bendigo District RSL Sub Branch was an amalgamation of the 3 RSL Sub Branches in Bendigo, Bendigo, Kangaroo Flat and Eaglehawk. In 1978 a "Servicemen's Club" was formed by the 3 Sub Branches as a Social venue which included lawn bowls. In year 2000 this venue became the Bendigo District RSL Sub Branch INC of the 3 Sub Branches. Kangaroo Flat retained their own Sub Branch HQ same as Eaglehawk, Bendigo’s HQ became the Sub Branch at the venue instead of the SMI at Pall Mall.Charter, timber framed with gold edging, the charter is various colours with the RSL badge central at the top with the flag either side with the word Charter in big letters under followed by the wording to establish a Sub Branch. A red seal is at the bottom RH side.The main points are, "Bendigo District RSL Sub Branch Inc" Dated 26th day of October 2000" "Bruce Ruxton State President" "John Deighton State Secretary"brsl, smirsl, charter -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook, CPN Publications Pty Ltd, 'We have not forgotten' Yass and Districts War 1915 - 1918, 1998
Softcover, cardboard, quarto bound, red print on front cover and spine. Black and white photo of child with flags on front cover, inset on sepia background of an enlarged section of the B&W photo. 343 pages, illustrated, with black and white photos.Handwritten in black on front end paper "For Bendigo & District RSL Museum / (?) / Richard S Reid / 6 April 2006"books- military history, yass, rememberance -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumCertificate - CERTIFICATE WW1, J Jenkin, Buxton & Co / Rialto, c.1915
For King and Country certificate - Australian Commonwealth Military Forces. Enlisted / sailed / served the Empire in the Australian Imperial Forces / Company / Battalion / Brigade. God Save The King. Verse by CHC Montrose.Cardboard rectangle with map of Australia in gold print, 2 red, blue, white flags. Oval cutouts with block & white photographs of 2 individual soldiers in uniform inserted, black print verse. Rising Sun badge depicted in gold print.“1st Nov 1916 / 16th Dec 1916 / W A Reid / 14th / 4th”, handwritten in red ink. “5th June 1915 / 8th Nov 1915 / W Robinson / 21st & 59th”, handwritten in blue ink.documents - certificates, military history -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook, Derrick V.C
Authors history on back of dust cover. Book part of N. DALEY Collection. Hard cover, pink colour, title and author in white lettering on spine. Mediterranean Ops map inside front cover. Derrick bike trip to Berri map inside with Australian flag. Printing of soldier and medal on front. Illustrated - 205 pages.N. DALEY Bendigo 1985 inside front cover.books, biography, military history -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook, A Guest of the Emperor, 1995
Book hardcover - front cover is coloured red and black. Stylized imperial Japanese flag. Image of rail track in central foreground. Rising sun at top. Writing is in white ink. Japanese writing on left. Pages 141. Illustrated with maps and photos."Donated by BGO YMCA". "Bill 0 with my best wishes - RUSSELL SAVAGE October 1995" Thailand Hellfire Pass - Ex POW Project. books-military-history, japan -
 Montmorency/Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency/Eltham RSL Sub BranchSouvenir - Framed Embroided Handkerchief, WW2 embroidered handkerchief, Estimated date 1941
Framed World War Two souvenir embroidered silk handkerchief. A soldier aiming his rifle, done in black, is in the bottom left hand corner and an inscription with the Australian flag in the top right hand corner is done in black and red. The background is yellow.Souvenir to Australia. Army in Syria and Lebanon. AIF 1941.world war two, australia, army, aif, 1941, souvenir, silk, handkerchief, embriodery, syria, lebanon -
 Montmorency/Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency/Eltham RSL Sub BranchPostcard, 1914 - 1918
Typical hand embroided post card. One of 5 in this display. Embroided rectangular card featuring large “1917” made up from national flags of United Kingdom, Belgium, France, USA, Russia and Portugal. Beneath is embroided “Souvenir de France” in silver (?). “I’m thinking of you” printed at base of card. Reverse details TBAcard -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionSouvenir - Envelope - First Day Cover, First Fleet Reenactment, Mar-88
Envelope, 1st Day Cover, First Fleet Reenactment Fleet. White envelope, coloured depiction of HMAS 'Bounty' on left, 37cent comm stamp, showing raising of flag, cancelled Melbourne, 21 March 1988. Envelope carried on HMAS 'Bounty'.stationery, first day cover, stamps, 1988 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Anne Beggs Sunter, Eureka: The First Australian Republic?, 1997, 1997
The Eureka Stockade took place on 03 December 1854. The 1997 exhibition commemorating the Eureka Stockade toured over six venues. Soft covered booklet of 6 pages, with an image of the Eureka Flag on the cover. It is a catalogue of a joint exhibition between the Ballarat Fine Art Gallery and the Public Record Office Victoria, and includes an essay "Eureka - The First repubic?" bu Anne Beggs Sunter.eureka, eureka stockade, ballarat, ballarat fine art gallery, beggs sunter, republic, democracy -
 Snuff Puppets
Snuff PuppetsPrint, Andy Freer, Front Cover for Snuff Puppets 1993 Promotional Book, 1993
Between 1992 and 1998 Snuff Puppets was housed on the third floor directly above the Melbourne Museum of Printing at the old Bradmill Cotton Mills building on Moreland St in Footscray. Museum proprietor Michael Isaacsen was keen to share his resources and gave Snuff Puppets carte blanche to use his Museum. Nearly all the promotional posters and materials from this time were printed in limited edition runs at the Museum using scrounged paper, odds and ends of ink, lead type, wooden type, lino cuts and an old press. A4 linocut print in two colours. Black background. Right side of page has a skeleton walking on hill waving his left hand and holding a red flag with letters "SP". The iconic fish skeleton logo in top right corner. art, flag, print, snuff puppets, lino cut, puppetry, andy freer, melbourne museum of printing, puppets, footscray, theatre, performing arts, promotional book, skeleton -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Uniform - Cloth patch, US Veteran
Cloth patch Yellow bordered on white background with seven red horizontal stripes left corner flue flag with 25 white embroidered stars. large black VET in centre of patch with part of E letter in green, yellow & red embroidery.PM0387 patch-Vietnam USA on bar code lable on reverse side of patchcloth badge, insignia -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Poster, Laminated Poster, 1965
(shortened version) Poster with American flag and words. I am a citizen of the USA I not speak your language. Please take me to someone who can protect me. My government with reward you. Written in many languages underneath.Published by aeronautical chart and informationcentre US Airforce. Lithographed Dec 1965 406825 South East Asia - West central Pacificposter -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchFramed photograph of two soldiers
It is believed Private C SMITH is one of the soldiers featured in this photograph. Private John Claude SMITH 2020 was born 2/8/1893 at Wangaratta He was employed by the Railways and trained in Liverpool, NSW. He enlisted on 8/2/1915 and embarked on 9/8/1915 from Sydney on the "Runic". He served with the 18th battalion on the western front and was discharged on 27/5/1919. Many soldiers going off to the war had a photograph taken of themselves in uniform, often a studio portrait taken by a professional; many also carried a photograph of a loved one with them. But most people were still rather formal and camera-conscious, and smiling for the camera was not usual. Timber frame containing image of two soldiers within a map of Australia below a crown in top centre position with Union Jack and Red Ensign flags in the background. Back has been re-mounted with chipboard. Has wire hangings on the back.ww1, north wangaratta, 18th battalion -
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph, 1913 c
Baang Yarnda formerly Carpenter's bucket dredge called Wombat. Photo possibly 1913 at relaunching as Baang Yarnda.Black and white photograph showing Baang Yarnda on slips. Boat painted dark colour, Union Jack flag hanging on bow, number of men on deck, large crowd of adults with children in front, trees right hand background. Paynesville Victoriatownship, tourism -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Banner - GOLDEN SQUARE P.S. LAUREL ST. 1189 COLLECTION: SCHOOL FLAG
Golden Square Primary School 1189, Laurel Street, school flag. Blue material, yellow text, gold fringe on bottom. Text ' Golden Square' box shape in centre ' GS PS 1189' Either side of box ' Laurel Street'.education, primary, golden square laurel st p.s. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. THE GOLD LICENCE, c1853
Diggers & Mining. The gold licence. The Government Camp. Goldfields Police and Diggers, 1853. Slide also shows a miner in the background and mines, and what would be the Commissioners tents with the flag flying. Markings: 37 994.LIF. 4. Used as a teaching aid.Hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
 Williamstown Botanic Gardens- Hobsons Bay City Council
Williamstown Botanic Gardens- Hobsons Bay City CouncilPhotograph - Williamstown Botanic Gardens, 1952
Images collected by donor for Williamstown High School archives and scanned by Lindy Wallace for Botanic Gardens archiveThe images demonstrate the social value of the Gardens to the local community and how they used as a place for meeting, playing and celebrating with friends and family.Black and white image of Williamstown High School students at the Gardens. 12 boys sitting and kneeling on the grass. Flag pole, trees and another group of students are in the background. The group includes James Morton, Ian Porter, Tom Radford, Douglas Henderson. williamstown botanic gardens, hobsons bay city council, williamstown high school, 1952 -
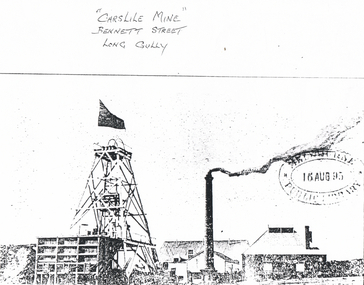 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - LONG GULLY HISTORY GROUP COLLECTION: CARSLILE MINE
Copy of a photo of the Carslile Mine. Photo shows chimney, poppet legs with flag flying and buildings. An oval stamp on the photo has an unreadable name and a date 16 Aug 95. Written at the top is - Carslile Mine Bennett Street Long Gully.bendigo, history, long gully history group, the long gully history group - carslile mine -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumNegative, Wal Jack, 3/03/1954 12:00:00 AM
Black and white negative, by Wal Jack, of PCC decorated for the Royal Tour of 1954 ascending the Collins St hill. The Conductor is standing in the back cab. Has the Regent Theatre with a large English flag, in the background, Zercho's Business College and the Metro Theatretrams, tramways, royal visit, collins st, conductors, tram 980, pcc class, mmtb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, distant signal, signal, maritime signal, ball signal, signal shape, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal ball, day signal ball, ball signal, ball day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897
