Showing 190 items
matching anaesthetic
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Boyle's gas anaesthesia apparatus, circa 1937
This is an early example of the Boyle's Anaesthetic Machine which was to become widely used throughout the world. The plaque on the wooden plinth suggests it was a display model from the medical equipment distributor Charles A King of London.The gas anaesthesia apparatus is mounted to a rectangular wooden base. It comprises two long, vertical glass cylinders held in place with metal brackets which are connected to a glass chloroform vaporiser container via metal tubes and associated valves and connections. The bottom of the glass flasks have outlet connections and inscriptions on the glass to measure volume. The chloroform vaporiser and adjacent glass ether vaporiser also have volume measurements etched on the glass, and the latter is the same height as the former but is larger in diameter. Both are connected via metal tubes and include outlet pipes that have associated cork stoppers. The maker's details are provided on a brass plaque attached to thewooden platform.A. Charles King Ltd. London, W1.henry edmund gaskin boyle, vaporiser, rotameter, chloroform, ether, anaesthetic apparatus, charles king ltd, plenum, sectioned, dr geoffrey kaye -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Portable dental and midwifery anaesthetic machine, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd, circa 1950
This gas anaesthesia machine comprises a four yolk manifold, two circular metal components for nitrous oxide and two for oxygen. It is mounted atop a four pointed stand on casters for portability. In addition to reducing valves and regulators, the main stand also supports a cream-coloured, cylindrical Austox fractional rebreather and an ether vaporiser with variable bypass control within a circular glass container. portable, anaesthesia, midwifery, dentistry, obstetrics, oxygen, nitrous oxide, commonwealth industrial gases ltd, cig, austox fractional rebreather, ether vaporiser, variable bypass control, 1950 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Anaesthetic machine, Minnitt, 1930 - 1937
This Minnitt machine was owned by Dr Mary Clementina DeGaris. Dr DeGaris qualified from medicine, MB BS, at the University of Melbourne in 1905. She continued her studies, becoming only the second woman in Victoria to qualify MD, in 1907. With the outbreak of war, DeGaris attempted to enlist as a doctor with the Australian Army but was refused. Undeterred she travelled to England, where she joined the Scottish Women's Hospitals for Foreign Service, a medical group made up entirely of women. After the war, she returned to Australia and set up practice as an obstetrician in Geelong, Victoria. Subsequently, the Geelong Hospital named a wing after her, "DeGaris House", which is now part of Geelong Private Hospital. DeGaris was awarded the St Saba medal, 3rd class, for her work during WWI. Robert James Minnitt introduced the concept of self-administered analgesia, using an apparatus designed and built in conjunction with London scientific instrument-maker, Charles King. The Minnitt apparatus met with considerable success and led to further modifications, including the introduction of the Queen Charlotte gas-air analgesia apparatus in 1936.Brown leather suitcase with brass locks and leather handle. Inside the case is metal equipment, with arms for attaching cylinders. On top of the case, located underneath the handle, is a small brass plate, bearing the name of the owner in black printed script on a piece of card or paper held inside the plate.Printed in black ink on name plate: Dr Mary C. De Garis.minnitt, geelong, scottish women's hospitals, world war i, obstetrician -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Kelene, Gilliard, Monnet & Cartier, 1890
Kelene is the proprietary name used for ethyl chloride in France which became synonymous with the agent in Europe. The manufacturer, Gilliard P. Monnet and Cartier of Lyon, also supplied Redard with his ampoules in 1890. Ethyl chloride was discovered by the French chemist Guillaume-Francois Rouelle in 1759; however it was not until 1901 that Frederic-Henri Basse manufactured sufficient for scientific study. Marie Jean-Pierre Flourens, Professor Comparative Anatomy at the University of Paris, first reported the effect of the inhalation of ethyl chloride after some experiments with and other agents in dogs. He described three experiments in which the dogs died, however death followed a period of insensibility as with ether although of much faster onset.Ten large glass phials containing 3g Kelene (Ethyl Chloride) stored in their original packaging. The box originally had twelve phials with now only ten remaining. Of the ten, 8 still contain the Kelene, 1 phial is empty but intact and 1 phial is broken. The cardboard box has a maroon paper cover, removable top with the product label and literature pasted across the base and top of the package. All product information is in French.ethyl chloride, kelene, local anaesthetic, gilliard p. monnet and cartier, france -
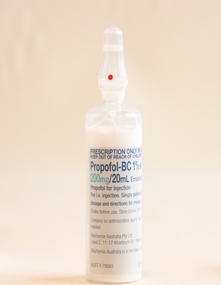 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Ampoule, Propofol, Biochemie Australia (Novartis)
Propofol is an induction agent for anaesthesia and also used in intensive care to induce unconsciousness. Propofol doesn't dissolve in water so it comes in a white, oily solution and must be refrigerated before it’s used. The solution consists of soybean oil, fats purified from egg yolks, and glycerol. Propofol is used as an “induction agent”—the drug that causes loss of consciousness— for general anaesthesia in major surgery. In lower doses it is also used for “conscious sedation” of patients getting procedures on an outpatient basis at ambulatory surgery centres. The main reason propofol is the agent of choice is because it allows for very rapid recovery, is the perfect drug for insertion of laryngeal masks and is the agent of choice for infusions. It has largely replaced thiopentone, the original drug of choice, but this is still available in Australia and used in specific situations. Propofol was linked to the death of Michael Jackson. Large clear glass ampoule with adhered manufacturer's label blue on white label containing the milky liquid of Propofol BC, 20mls.propofol, local anaesthetic, intensive care, jackson, michael, biochemie australia (novartis) -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Vial, Ketalar, Parke Davis
Ketamine is useful for inducing anaesthesia in shocked patients. It is also commonly used in low doses or infusions for the management of chronic pain. It can produce a state of 'dissociative anaesthesia', where patients are pain free, but not necessarily unconscious. Three small glass vials with different colour print labels on each containing 10ml Ketalar (Ketamine Hydrochloride).local anaesthetic, ketalar, ketamine hydrochloride, shock, parke davis -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Bruck, 1908
The Bruck Inhaler is a modification of the Clover Inhaler, designed by Lambert Bruck. Bruck added a glass dome which enabled the level of ether to be monitored during administration. This was a revolutionary change as it removed guess work from the process.The Bruck Inhaler is a historically, aesthetically and scientifically significant piece. The basic design is based on the Clover Inhaler, but with a rounded bottom. The idea of a glass viewing window was possibly inspired by Wilson-Smith Inhaler. The Bruck Inhaler is historically significant as it is the first inhaler to be made with a completely clear lower glass section. This improved the usability for the ether administrator, and eliminated much of the guesswork associated with dosage and ether levels, which in turn improved the patient experience. This piece provides a strong local link to both anaesthetic and general medical practice at the turn of the century. The design is credited to Ludwig Bruck of Sydney, and was presumably manufactured in the same area. Bruck, as the attributed designer, holds much relevance to the significance of the object, as connected with him is much historical information about the social context of medical practice. Ludwig Bruck was a prominent figure in the medical industry. He started his medical career in Sydney as a Medical Transfer Agent, and later owned a shop at 16 Castlereagh Street, Sydney. This business is listed in the 1903 Register of Firms as a Medical Agent and Importer of Medical Instruments and Books. Bruck was vocal as a journalist and published analyses of medical statistics, as well as the well known Australasian Medical Dictionary and Handbook, which included the “List of Unregistered Medical Practitioners”. Ludwig Bruck was an immigrant. He was of German descent, which placed him in a precarious position within Sydney society during the turn of century. Bruck conducted several public conversations with prominent members of the Australian Natives Association through the Sunday News in regards to his disagreement of the employment of medical practitioners by the ANA specifically to corroborate their health insurance policies. He was also a stalwart supporter of the Australian arm of the British Medical Association, being the publisher of the first and subsequent editions of The Australian Medical Gazette. Bruck chose to end his life with a combination of poison and chloroform on 14 August 1915, after being accused of trading with the enemy during World War One. His suicide note stated his horror at leaving his business partner to deal with the tarring of his reputation as the reason for his decision. The Bruck Inhaler has aesthetic significance as it is a beautiful example of turn of the century surgical design and craftsmanship. Aseptic methods of surgery were well known by 1909, and the aesthetic design of the Bruck Inhaler conformed to these principles. The ability for the surgeon to unscrew, clean and sterilize each part of the Inhaler contributes to the streamlined design of the piece. The Buck Inhaler holds scientific significance. There is the capacity for further research to be undertaken on the object. Geoffrey Kaye often collected multiple examples of equipment, usually one for reverse engineering and another for teaching. There are currently two examples of the Bruck Inhaler in the collection, presenting an opportunity for further technical research on the object. The inhaler is oval shaped with one half made of glass to allow observation of the ether level. A vertical cross tube, 22mm in diameter passes between the face-piece and the bag [missing]. There is a stopcock for admission of oxygen or nitrous oxide opposite the bag attachment. There is a central tube, 28mm in diameter, with controllable ports on either side. There is also a tear-drop shaped fask mask.Hand engraved on side of base: L. Bruck / Sydneyclover, joseph, bruck, lambert, inhaler, rebreather, nitrous oxide, oxygen, williams, probyn -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMedal - Medal, Dean, c. 1986
Robin William Smallwood was Dean of the Faculty of Anaesthetists at the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons from 1986 - 1987. Smallwood died 6 October 1987 after a brief illness. Smallwood completed medicine at the University of Melbourne in 1958 and decided on anaesthesia as a career, attaining his FFARACS in 1964. The Orton Medal was awarded posthumously.Gold coloured oval shaped medal with the Faculty of Anaesthetists coat of arms on the obverse in relief. The owner's name has been engraved into the reverse. There is a thick, ribbed, navy blue ribbon connected to the medal by a circular ring at the top. The medal and ribbon are encased in a black velvet box with white satin lining on the inside of the lid and a red velvet cushion resting in the base.Engraved on reverse of medal: R.W. SMALLWOOD / 1986 - 1987medal, medallion, dean, anaesthetist, anaesthesia, anaesthetic history, royal australasian college of surgeons -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Vaporiser, Penthrane, Cyprane Ltd, c. 1982
This vaporiser has a main cylindrical body with a step up to the dial plate with a small red latch to lock dial in to place.On the front of the body sits a square gauge to indicate the level FULL along with a long rectangular shape.There is an Inlet and outlet valve that sits behind the metal dial.There is a manufacturers plate sitting on top of the dial and the inlet/outlet valve. Inscribed on top plate: KEEP UPRIGHT/ PENTEC 2/ WHEN CHARGED •Inscribed on inlet & oulet valve plate: PENTEC 2/ SERIAL NO 252939/ PATENTS PENDING •MADE IN / ENGLAND BY/ CYPRANE LTD / KEIGHLEY •Metal dial has inscribed: OFF/.2 .5 1 1.5 2 Max •Inscribed on front plate in green writing: USE ONLY/ PENTHRANE/ (METHOXYFLURANE)penthrane, vaporizer, anaesthesia, anaesthetic machine -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing Archive
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing ArchiveBook - Illustrated book, Alfred Hospital heritage committee, Alfred Hospital - faces and places volume III, 2004
Contains biographies and photos of Alfred Hospital staff. Also includes history of emergency and anaesthetic departments, war service of Alfred staff and information about Chevron Hotel.Paperback book, photos of Alfred Hospital on front and back cover. 380 pages with many blacka and whit photosnon-fictionContains biographies and photos of Alfred Hospital staff. Also includes history of emergency and anaesthetic departments, war service of Alfred staff and information about Chevron Hotel.alfred hospital, ahnl, nurses, doctors, emergency department, chevron hotel, war service
