Showing 298 items
matching brickwork
-
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework, 2017
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.Colour photograph of Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stoneworkgreenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Information panel, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, 2016
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Information panel, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.Photograph of interpretation information in Greenwich Chapel and Museumgreenwich, stone, museum, chapel, stone, musuem, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Information panel, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Information panel, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Information panel, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, 2016, 2016
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.Colour photograph of a sculptural portrait. greenwich, stone, museum, chapel, portrait, sculpture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Statue, "Hope", Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.Marble statue of Hopegreenwich, stone, museum, chapel, statue, hope -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Statue, "Faith", Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Statue, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, 2016, 2016
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel, sculpture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Greenwich Chapel and Museum, England, Mason's Mark on stonework
Greenwich Palace no longer exists however archaeology had added greatly to our understanding of life at the Tudor Court at Greenwich. Since 1971 there have been well over 20 digs on the site. Many wonderful and intriguing items from gold coins to tiled floors and human skeletons have been found. The first major dig uncovered the structure of the royal apartments next to the river. Not only did it clarify the floor plan but finds included some rare Tudor ceiling decorations, a hoard of gold coins and many personal items such as dice used for gaming. Perhaps the most revealing excavations have been the most recent. In 2005 while monitoring the digging of a drainage trench archaeologists found brickwork and tiles that formed the floor of the east end of the Tudor Chapel Royal where the altar once stood.greenwich, stone, museum, chapel -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Victorian Double-fronted Brock Villa, Cotham Road, c. 1919
The Kew Historical Society's map collection includes a substantial number of real estate subdivision plans, mainly of Kew but also of surrounding suburbs in Melbourne. Most of the subdivision plans date from the 1920s and 1930s when the districts old homes and local farmland were being split up to accommodate residential growth in the postwar period. These early plans were assembled by a local firm, Jas R Mather & McMillan, which had an office in Cotham Road. Many of the plans, and sometimes photos, were annotated by the agents.Subdivision plans are historically important documents used as evidence for the growth of suburbs in Australia. They frequently provide information about when the land was sold as well as evidence relating to surveyors and real estate and financial agents. The numerous subdivision plans in the Kew Historical Society's collection represent working documents, ranging from the initial sketches made in planning a subdivision to printed plans on which auctioneers or agents listed the prices for which individual lots were sold. In a number of cases, the reverse of a subdivision plan in the collection includes a photograph of a house that was also for sale by the agent. These photographs provide significant heritage information relating house design and decoration, fencing and household gardens.The photograph may also be aesthetically significant depending o the importance of the photographic atelier.Real estate photographs of a classic double-fronted late Victorian brick villa. It central location in Cotham Road, Kew enabled the selling agent to note its proximity to the tram. With seven rooms, all ‘modern conveniences’, and land of 66×167, the house was to be sold for £1100. The villa has a number of interesting features including a pattern within the slate roof as well as the use of polychrome brickwork under the eaves and on the façade. The intricacy of the cast iron lace is emphasised by the line of projecting wooden blocks above it. The picket gate is painted a different colour to the pickets of the fence. The house has a name (illegible) that is attached to the inset cast iron lace of the central projecting gable in the veranda. Stamped on mount: "Kew. Central. Close tram. / Comfortable Brick Villa. / Containing 7 rooms / Modern conveniences: / Land 66 x 167. Sold 1100 pounds:"houses - kew, victorian villas, real estate photographs, cotham road - kew -
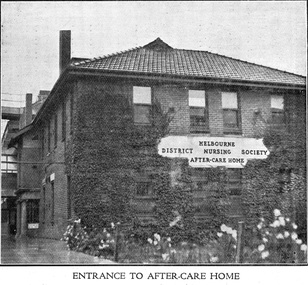 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Digital image, c.1926
The first After-Care Home in Melbourne was built by the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) in 1926 for patients of the Society who needed more nursing care than could be given at home but did not need hospitalization. Many patients from Melbourne hospitals who needed further care following discharge from hospital were nursed at the After-Care before going home. The Melbourne District Nursing Society, (MDNS), built the After-Care Home in 1926. The Home was extended and the name changed to Melbourne District Nursing Society and After-Care Hospital in 1934. It was situated at 45 Victoria Parade, Collingwood. Patients of the Society who needed more care than could be given at home, but did not need hospitalization were nursed there, along with many patients from Melbourne hospitals who needed further care before going home. Many children were nursed in the hospital, some long term, during the Polio epidemic and schooling was given to them in the hospital. In September 1930 an Ante-Natal Clinic was established. In October 1934 a Women's Welfare Clinic was opened to educate women on birth control. This was the first of its kind in Melbourne. The MDNS After Care Hospital was under District's banner until 1956. In 1957 the MDNS and the After-Care separated with the Government taking over the running of the After-Care. Melbourne District Nursing Society then became the Melbourne District Nursing Service and in 1966 was given Royal patronage and renamed Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS). Digital image of a front, and part of the left side view, of the Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home and shows the entrance. The white plaque, attached in the centre of the brickwork between the two storeys in the front of the building reads 'Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home' in black capital letters. It is a two story brick building with a tiled pitched roof, and shows two chimneys. There are four long windows running along both storeys of the front and side views. Near the rear left hand side of the building a portico can be seen and behind this part of a brick building with window runs to the left. Greenery is against part of the building and white flowers are seen in the foreground of the photograph. after- care hospital, after-care home, melbourne district nursing society, melbourne district nursing service, mdns, rdns, royal district nursing service -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - T C WATTS & SON COLLECTION: 117 QUEEN STREET,BENDIGO, 1928
BHS CollectionBlack and white photograph mounted on rectangular grey board. House, brick, porch, brick fence, small pane and lead light windows. 1 chimney. Decorative brickwork on verandah lintel and on brick fence. Stained glass windows. Written on back ' tapestry brick fireplace, dining room and kitchen, 117 Queen Street. Brick bungalow, built 1923, 5 rooms, vest, both 2 weatherboard sleep outs, toolshed, woodshed, workshop, garage, sewered. Through to King Street, 33'11 1/4' by 165'. Hot water service, electric copper, 22 points electricity, 8 power points, new gas , stainless ink, crockery cupboards, pedestal basin.t.c. watts & son, 117 queen street bendigo -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, St Margaret's Anglican Church, Pitt Street, Eltham, 30 January 2008
St Margaret’s Church of England was officially opened on December 12, 1861. It is the oldest intact church building in Eltham. At the time it was known as Christ Church until its consecration in 1871, when it was completely free of debt (£1,700 for the church and parsonage) despite the district’s poverty. This was largely due to the free labour and materials, including locally made bricks donated by local artisans and others. The church is historically significant because it is the oldest church in the former Shire of Eltham and has associations with the philanthropist and founder of Brighton, Henry Dendy (who donated the land on which the church is built), the architect Nathaniel Billing and the prominent local builder, George Stebbing. The church is architecturally and aesthetically significant because it is constructed in the Gothic Revival style with several stained-glass windows of various dates and is also a very early use of polychromatic brickwork in Victoria. Billing was one of the first Melbourne architects to employ polychromatic brickwork and an important early architect. The rear wall was intended to be temporary. A major feature of the design is the large buttresses with long, steeply graded upper faces. The overall design is well proportioned with the surface brick patterns relieving an otherwise austere design. The church is spiritually and socially significant because it has been an important place of worship for the people of Eltham for almost 150 years. The land on which the buildings stand was donated by Henry Dendy. Dendy arrived in Melbourne in 1841 after purchasing in England eight square miles at Brighton under the system of "special surveys". After this land passed out of his hands, Dendy moved about Victoria, visited England, then returned to settle in Eltham where he purchased a flour mill. Dendy chaired the meeting held in 1860 “for the purpose of devising such means as may be expedient for the establishment of a Church of England in the township of Eltham”. He became chairman and treasurer of the church committee. Unlike the establishment of many early churches in Victoria where a vicar was appointed to a parish and later a permanent church was constructed, the population at Eltham initiated action to build a church. The nearest church at that time was at Heidelberg and the Eltham settlement was part of the parish of St Johns Heidelberg. Isolation and the tedious, time consuming journey between Heidelberg and Eltham resulted in the Eltham community taking its own action. The original vicarage (Dendy House) at the rear of the church is also an important part of the cultural significance of this place because it is connected to the church and the development of the Eltham area. Together, the church and the vicarage are aesthetically significant because they form a significant streetscape feature. The mud-brick community hall designed by Robert Marshall was added in 1978. In 2014 the original temporary rear wall was removed as part of a modern extension designed by Architects Atelier Wagner and constructed by Conrad Construction and Management. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. National Trust of Australia (Victoria) State significance Victorian Heritage Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p67 St Margaret’s Anglican Church in Pitt Street, Eltham, which officially opened on December 12, 1861, is the oldest intact church building in Eltham.1 With the nearby courthouse and police station, it was one of the first permanent community buildings in the district. The church and vicarage are on the Register of the Heritage Council of Victoria and the National Trust of Australia – Victoria. The church is important as an early example of polychrome brickwork by the notable architect Nathaniel Billings. It is also notable for its historic associations with the early settlement of the Shire of Eltham and its connection with Henry Dendy, Brighton’s founder.2 Henry Dendy, who lived in Eltham much longer than at Brighton, chaired the original meeting which planned the church, and he donated the half-acre (0.2ha) site. Dendy had arrived in Melbourne in 1841 after buying eight square miles (20.7sq km) at Brighton while in England. After this land passed out of his hands, he eventually settled in Eltham where he bought a flour mill, west from the corner of Main Road and Pitt Street (then called Brewery Lane). The vicarage was named Dendy House after him. The Eltham settlers were unusual in initiating the establishment of a church. Usually in Victoria a vicar was appointed to a parish and then a permanent church was constructed. But then, the nearest church was at Heidelberg, which was a tedious and time-consuming journey. St Margaret’s builder was a local, George Stebbing, who also constructed the former Methodist, later Uniting, Church at John Street and the Shillinglaw Cottage near Eltham’s Central Park. It is believed the first Anglican Bishop of Melbourne, Bishop Perry, dedicated the church. After the ceremony he joined in the festivities at the nearby pub and a bill was sent to the parish for teas taken there by the bishop with other participants. The first vicar was the Reverend Robert Mackie from 1864 to1866. St Margaret’s Church was originally called Christ Church until its consecration in 1871, when it was completely free of debt (£1700 pounds for the church and parsonage) despite the district’s poverty. This was largely due to the free labour and materials, including local bricks, donated by local artisans and others. St Margaret’s Church is in the Gothic Revival tradition with a buttressed nave, paired lancet windows, porch and bell-cote. It was the first polychromatic brick church in Australia, using softly contrasting coloured brickwork.3 Billing was one of the first architects to introduce polychrome brickwork into Melbourne. His original drawings for St Margaret’s survive in a folio of his architectural work. However the church’s brickwork is more subdued than in his drawings. About half the windows – those in clear glass with gold borders – are original. The stained glass windows were made much later, but the one behind the altar is thought to be the oldest in the Diamond Valley. It was to be temporary until the congregation could afford to extend the church. In the early 1960s the original cedar pews were replaced by blonde timber pews and the originals were sold to restaurants and to private individuals. Eminent local sculptor Matcham Skipper created a crucifix for the church. A major addition was made in 1978, when the weatherboard hall was replaced by a mud-brick hall. Made of local material, it was designed by local architect and a former shire president Robert Marshall. The mud-brick hall reflects the style of building in Eltham of the late 1970s and for which Eltham is well-known. Perhaps because its earthy tones blend with the surrounding environment, the hall sits well with the church building. St Margaret’s membership has included economist and ABC chairman, Richard Downing; political commentator, diplomat and academic, William Macmahon Ball; Eltham civic leader, Charles Wingrove; artist, Peter Glass; and Eltham’s first postmaster, Frederick Falkiner.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, st margaret's anglican church, st margaret's church, st margarets church hall, christ church -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Watson's Eltham Hotel, Maria Street, Eltham, c.1900
Christoher Watson's Eltham Hotel, cnr Maria Street (Main Road) and Pitt Street, Eltham. Christopher Watson in centre (bareheaded). Reproduced on p60 of 'Pioneers & Painters' The hotel was constructed in the 1850s immediately following the discovery of gold in Victoria. The original founder, a Mr Warren. engaged a builder named Wallace, to erect the hotel, and being unable to finance it, the story goes, handed it over to Mr Wallace, who finished the job, and received the first licence. The building was constructed of hard basaltic blue stone, quarried in the Eltham district, and partly of bricks made at Eltham. At that time the town owned not only an hotel, but a flour mill, a brewery, a brickworks, and other important industries. The hotel was carried on for the benefit of the first owners for over 30 years and was then purchased by Mr Chris Watson. The hotel was in the early days a well-known resting place for the gold diggers during the gold rush at Woods' Point. A new hotel was erected on the same site by Mr H. Watson in 1925.This photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book,"Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as the 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.Digital imagechristopher watson, eltham, hotel, main road, maria street, pioneers and painters, pitt street, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, watson's hotel -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Watson's Eltham Hotel, Maria Street, Eltham, c.1900
Christoher Watson's Eltham Hotel, cnr Maria Street (Main Road) and Pitt Street, Eltham. Christopher Watson in centre (bareheaded). Reproduced on p60 of 'Pioneers & Painters' The hotel was constructed in the 1850s immediately following the discovery of gold in Victoria. The original founder, a Mr Warren. engaged a builder named Wallace, to erect the hotel, and being unable to finance it, the story goes, handed it over to Mr Wallace, who finished the job, and received the first licence. The building was constructed of hard basaltic blue stone, quarried in the Eltham district, and partly of bricks made at Eltham. At that time the town owned not only an hotel, but a flour mill, a brewery, a brickworks, and other important industries. The hotel was carried on for the benefit of the first owners for over 30 years and was then purchased by Mr Chris Watson. The hotel was in the early days a well-known resting place for the gold diggers during the gold rush at Woods' Point. A new hotel was erected on the same site by Mr H. Watson in 1925.Early photo of Eltham Hotel which has been on site in various forms since mid 1800sSepia photograph mounted on cardInscribed on back: "Property of Mr Albert Watson, 53 Yarra St, Heidelberg. Christopher Watson (bare headed) Given to Marion Huggett December 1977 c.1900 son of Watson Snr behind cart"christopher watson, eltham, eltham hotel, main road, maria street, pioneers and painters, pitt street, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, watson's hotel -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDrawing - Plans, J BARTRAM, CIRCA 1894
PLANS FOR THE ESTABLISHMENT OF CLUNES BUTTER FACTORY.1 2 PAGE LETTER, TYPED IN PURPLE INK .2 4 PAGES OF PAPER STAPLED TOGETHER WITH HAND HANDWRITTEN MATHEMATICAL CALCULATIONS OF THE QUANTITY OF SAWDUST OR CHARCOAL REQUIRED FOR REFRIGERATION CHAMBER .3 1 PAGE DRAWING OF THE MACHINERY ROOM AT CLUNES DISTRICT BUTTER FACTORY CO. LIMITED USING RED AND BLACK INK AND BLUE PENCIL .4 1 PAGE DRAWING OF SECTION THROUG A.B .5 1 PAGE OF WAX PAPER WITH HAND DRAWN PLAN OF BRICKWORK .6 4 PAGES OF BUFF COLOURED PAPER HANDWRITTENWITH MATHEMATICAL CALCULATIONS .7 1 PAGE OF DRAWING SECTION THROUGH A.C .8 1 PAGE OF BLUE COLOURED PAPER HANDWRITTEN WITH BLACK INK AND BLUE AND ORAGE PENCIL NOTATIONS.1 LETTERHEAD J. BARTRAM & SON 18 QUEEN STREET MELBOURN .3 MACHINERY ROOM AT CLUNES DISTRICT BUTTER FACTORY CO .LIMITED .5 SCALE: 1/1/2 INCH TO THE FOOT WRITTEN IN LEAD PENCIL .7 SCALE: 2FT TO 1 INCHj bartram & son, clunes & district butter factory co. limited, lordclyde creamery -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 30 08 1967
This photograph is of RDNS staff taken outside the RDNS Essendon Centre on the day of its opening on the 30th of August 1967. The RDNS Sisters are wearing their uniforms of a red cardigans over their grey cotton frocks. The opening of the RDNS Essendon Centre enabled Sisters to leave from this building to give nursing care in the community. They returned to this building at the completion of their shift.Gradually over the years, Melbourne District Nursing Service (MDNS, later known as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) from 1966 when they received Royal patronage, opened Centres throughout the Melbourne Metropolitan area. Their Trained nurses left from these Centres each morning to carry out their nursing visits in a specific areas (districts) taking any sterilized equipment needed with them. They returned at the end of the day to write up their patients nursing histories, clean and reset any equipment used ready for sterilization, and contact other medical personal as necessary. Most of the RDNS cars were housed at each Centre, only a few being driven home by a Sister.Black and white photograph of sixteen Royal District Nursing Service, (RDNS) staff standing in two rows outside the Essendon Centre. The Sisters are wearing uniform dark cardigans over their grey uniforms; an RDNS badge can be seen attached on the upper left hand side front of some of the cardigans. They are wearing their grey peaked uniform hats, which have a round metal silver badge with the capital letter 'RDNS' written in blue across the centre section, attached to the centre front. They are standing in front of a building, which has a flat roof with a dark fascia and below this a large windows down to a short area of brickwork. Part of a light coloured building can be seen in the background on the left hand side of the photograph.Photographers stamp. Quote No. GJ 55rdns, royal district nursing service, rdns centre, rdns uniform
