Showing 225 items
matching collapsable
-
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2010
Mediating conflict in the age of Native Title Peter Sutton (The University of Adelaide and South Australian Museum) Mediators have played roles in managing conflict in Aboriginal societies for a long time. This paper discusses some of the similarities and differences between older customary mediator roles and those of the modern Native Title process. Determinants of tribunal outcomes for Indigenous footballers Neil Brewer, Carla Welsh and Jenny Williams (School of Psychology, Flinders University) This paper reports on a study that examined whether football tribunal members? judgments concerning players? alleged misdemeanours on the sporting field are likely to be shaped by extra-evidential factors that disadvantage players from Indigenous backgrounds. Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australian Football League (AFL) players, matched in terms of their typical levels of confidence and demeanour in public situations, were interrogated in a mock tribunal hearing about a hypothetical incident on the football field. The specific aim was to determine if the pressures of such questioning elicited behavioural differences likely to be interpreted as indicative of testimonial unreliability. Mock tribunal members (number = 103) then made judgments about the degree to which a number of behavioural characteristics were evident in the players? testimonies. Under intense interrogation, Indigenous players were judged as presenting less confidently and displaying a greater degree of gaze aversion than non-Indigenous players. These behavioural characteristics are commonly ? and inappropriately ? used as cues or heuristics to infer testimonial accuracy. The paper discusses the implications for Indigenous players appearing at tribunal hearings ? and for the justice system more broadly. Timothy Korkanoon: A child artist at the Merri Creek Baptist Aboriginal School, Melbourne, Victoria, 1846?47 ? a new interpretation of his life and work Ian D Clark (School of Business, University of Ballarat) This paper is concerned with the Coranderrk Aboriginal artist Timothy Korkanoon. Research has uncovered more about his life before he settled at the Coranderrk station in 1863. Evidence is provided that five sketches acquired by George Augustus Robinson, the former Chief Protector of Aborigines, in November 1851 in Melbourne, and found in his papers in the State Library of New South Wales, may also be attributed to the work of the young Korkanoon when he was a student at the Merri Creek Baptist Aboriginal School from 1846 to 1847. Developing a database for Australian Indigenous kinship terminology: The AustKin project Laurent Dousset (CREDO, and CNRS, Ecole des Hautes Etudes en Sciences Sociales), Rachel Hendery (The Australian National University), Claire Bowern (Yale University), Harold Koch (The Australian National University) and Patrick McConvell (The Australian National University) In order to make Australian Indigenous kinship vocabulary from hundreds of sources comparable, searchable and accessible for research and community purposes, we have developed a database that collates these resources. The creation of such a database brings with it technical, theoretical and practical challenges, some of which also apply to other research projects that collect and compare large amounts of Australian language data, and some of which apply to any database project in the humanities or social sciences. Our project has sought to overcome these challenges by adopting a modular, object-oriented, incremental programming approach, by keeping metadata, data and analysis sharply distinguished, and through ongoing consultation between programmers, linguists and communities. In this paper we report on the challenges and solutions we have come across and the lessons that can be drawn from our experience for other social science database projects, particularly in Australia. A time for change? Indigenous heritage values and management practice in the Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes region, South Australia Lynley A Wallis (Aboriginal Environments Research Centre, The University of Queensland) and Alice C Gorman (Department of Archaeology, Flinders University) The Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes in South Australia have long been recognised under the Ramsar Convention for their natural heritage values. Less well known is the fact that this area also has high social and cultural values, encompassing the traditional lands and waters (ruwe) of the Ngarrindjeri Nation. This unique ecosystem is currently teetering on the verge of collapse, a situation arguably brought about by prolonged drought after decades of unsustainable management practices. While at the federal level there have been moves to better integrate typically disparate ?cultural? and ?natural? heritage management regimes ? thereby supporting Indigenous groups in their attempts to gain a greater voice in how their traditional country is managed ? the distance has not yet been bridged in the Coorong. Here, current management planning continues to emphasise natural heritage values, with limited practical integration of cultural values or Ngarrindjeri viewpoints. As the future of the Coorong and Lower Murray Lakes is being debated, we suggest decision makers would do well to look to the Ngarrindjeri for guidance on the integration of natural and cultural values in management regimes as a vital step towards securing the long-term ecological viability of this iconic part of Australia. Hearts and minds: Evolving understandings of chronic cardiovascular disease in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations Ernest Hunter (Queensland Health and James Cook University) Using the experience and reflections of a non-Indigenous clinician and researcher, Randolph Spargo, who has worked in remote Aboriginal Australia for more than 40 years, this paper tracks how those at the clinical coal-face thought and responded as cardiovascular and other chronic diseases emerged as new health concerns in the 1970s to become major contributors to the burden of excess ill health across Indigenous Australia. The paper cites research evidence that informed prevailing paradigms drawing primarily on work in which the clinician participated, which was undertaken in the remote Kimberley region in the north of Western Australia. Two reports, one relating to the Narcoonie quarry in the Strzelecki Desert and the other concerning problematic alcohol use in urban settings.maps, b&w photographs, colour photographs, tablesstrzelecki desert, native title, timothy korkanoon, merri creek baptist aboriginal school, austkin project, coorong, lower murray lakes district, south australia, indigenous health -
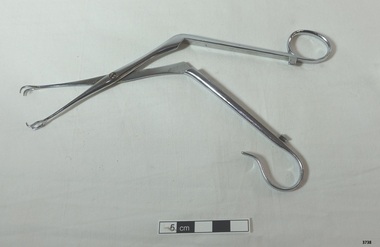 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928. Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community. They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine, administration, household equipment and clothing from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from W.R. Angus Collection. Stainless steel, elbow shape in middle, hollow claw shape ends, one handle is open circle, handles clip together. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, department of defence australia, australian army, army uniform, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, forceps, surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. They are part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. These are bonney forceps, often used when closing up after surgery. Blunt nose ends with V shaped teeth on each side that mesh together. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, medical equipment, surgical instrument, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, forceps, bonney forceps -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. Various types of forceps are still in common use today in modern surgery. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. 'STAINLESS" & "LONDON MADE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hillflagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w.r. angus, surgical instrument, forceps, dr ryan, medical equipment, surgical instrumentt.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, ear nose throat surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. Various types of forceps are still in common use today in modern surgery. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, heavy duty, from the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, ear nose throat surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th Century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection.Stamped "2" and crown, staff and snake insignia.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel punch forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. Ring on one end of tip and scoop on opposite side, angled handle.Stamped 'Ramsay'.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection.'2' stamped on two parts.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection."ALLEN & HANBURYS" & "LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel angled forceps with scoop shaped ends.Inscribed "MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT": & "R" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Angled handles, crocodile teeth ends. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Inscribed "RERL" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Marked 'Stainless Steel' on both parts.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Inscribed "SURGI _ _ _ _ " & '1'flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaPhotograph, Original photo c.1920
The iron bridge was completed in 1878 and was used by the Deniliquin and Moama Railway company for goods trains only - it was another year before passengers were included in the transport service. On 4 March 1879 citizens of Echuca and Moama stormed the bridge, opened the gates and declared it open for their use.At the turn of the century the railway line carried produce from southern New South Wales & the Riverina to Melbourne, with goods trains being a very important mode to transport. When the bridge was being constructed, six workmen were killed and another maimed when a pile on the Moama bank collapsed. After the storming of the bridge by local people in March 1879 it was declared open for use of local residents traveling between the towns of Echuca and Moama. The bridge was shared by rail, road and pedestrian traffic.An image of the iron bridge at Echuca, taken looking East from Victoria bank.Verso: "Iron bridge"murray river bridge , echuca, murray bridge, echuca, iron bridge, echuca -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchBook, The Great World War Volume VII, 1919
Historical timeline of events from 1915 - 1917, Formal record of the Great WarThe Great World War Volume VII Dark green hardcover and spine. Faded gold text on spine. Maps, illustrations photographseve of russian revolution, the fall of tsardom in russia, the entry of america, minor naval operations, british battles on the hindenburg line, italy's double offensive, the last russian effort, battle of messines, passchandaele, the collapse of russia -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Kambrook Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/43737 - re 26 Kambrook Road and 345 Balaclava Road corner building: A prominently situated two-storeyed complex of late Victorian buildings consisting of "Wybar's Buildings" occupying the Balaclava Road/ Kambrook Road corner and the "Caulfield Bakery" facing Kambrook Road, separated by a driveway from a single storeyed shop. The main building has a comer splay and balustraded parapet with curved pediments, the words "Wybar's Buildings 1887" having been obliterated but "Caulfield Bakery 1887" with the characteristic wheatsheaf surviving in raised cement work. The walls are stuccoed and richly ornamented with bracketed cornices and keystones with masks extending to the Bakery. The main building is further distinguished by the Masonic symbol of the mason's dividers in the pediment whilst the upper level of the bakery is in overpainted brickwork. The single storeyed shop incorporates the bracketed cornice and consoles characteristic of the main buildings and is in other respects a utilitarian structure. https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/35413 - re 16 Kambrook Road A small late Victorian Italianate villa distinguished by its parapeted window bays either side of a small verandah with encaustic tiled floor. The parapets are balustraded with console enrichment and glazed tiles, the stuccoed surfaces being unpainted. Ornamentation is in other respects undistinguished. https://www.gleneira.vic.gov.au/services/planning-and-building/heritage/heritage-management-plan - re 9-11 Kambrook Road ... they demonstrate most of the commonly employed aesthetic devices characteristic of the Italianate Style including patterned brickwork, patterned slate roofs, cast iron lace verandahs, ornamental stucco work and ashlar boards...https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/43737 - 345 Balaclava and 26 Kambrook Roads HO91 in City of Glen Eira "Wybar's Buildings" at the corner of Balaclava Road and Kambrook Road are important as a prominent late Victorian commercial development incorporating a variety of activities including a bakery and possibly a coffee palace, the latter understood to be unique within the municipality, but characteristic of the period. It is a rare complex of its type in Caulfield and is important also as evocative evidence of the late Victorian Land Boom and the creation of a small now defunct commercial centre at this location by the George Wybrow. https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/35413 - 16 Kambrook Road HO121 in City of Glen Eira ''Hollywood'' at 16 Kambrook Road is of architectural interest for its pavilions which retain their unpainted parapets and ornamental tiles in the manner of other less imposing examples in the immediate locality possibly linked with the builder George Wybar and his son, who undertook substantial projects nearby. Its association with James Yorston, presumably is Yorston of Dickson and Yorston, important builders and estate developers at Caulfield during the Inter war period is of interest. https://www.gleneira.vic.gov.au/services/planning-and-building/heritage/heritage-management-plan - re 9-11 Kambrook Road HO152 Normanby Road/Kambrook Road, Caulfield North Statement of Significance: The Precinct is historically significant for its capacity to demonstrate standards of design and building construction in this part of the municipality during the late Land Boom years and especially just prior to the bank collapse of 1891. The housing stock is representative of the standards of amenity excepted by the middle classes of Melbourne society at the time, including artists, (horse) trainers, jockeys, managers, travellers, journalists and the like, also having a functional link with the activities of the Caulfield Racecourse which forms an important element in the history of the Municipality. The row of attached pairs at 5-11 Kambrook Road and 53-67 Kambrook Road is especially significant in this respect in that the narrow allotments are indicative of the owner/developer’s determination to maximise profits at the height of the Land Boom in 1891...Page 104 of Photograph Album with four photographs (landscape) of three different properties on Kambrook Road.Handwritten: Kambrook Road [top right] / WYBAR'S BUILDING 1887/ INC CAULFIELD BAKERY / [under top right photo] / 16 KAMBROOK ROAD / 1970 HIRST MRS J.N.[under bottom left photo] / 11-9 KAMBROOK ROAD / 1970 9-BUCKLAND MRS L.A / 11- ATKINS MRS N.E. [under bottom right photo] / 104 [bottom right]trevor hart, kambrook road, victorian, caulfield north, parapets, wybar's buildings 1887, caulfield bakery 1887, architectural features, painted bricks, balaclava road, victorian italianate style, houses, bay windows, verandahs, glazed tiles, shops, george wybar, builders, james yorston, dickson and yorston, j n hirst, l a buckland, n e atkins, patterned slate roofs, patterned bricks, cast iron work, attached houses -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Will Davies, Last one hundred days : the Australian road to victory in the First World War, 2018
In March 1918, with the fear of a one-million-man American army landing in France, the Germans attacked. In response, Australian soldiers were involved in a number of engagements, culminating in the Second Battle of Villers-Bretonneux and the saving of Amiens, and Paris, from German occupation. Then came General John Monash's first victory as the Commanding Officer of the newly formed Australian Corps at Hamel. This victory, and the tactics it tested, became crucial to the Allied victory after 8 August, the 'black day of the German Army'. On this day the major Allied counteroffensive began, with the AIF in the vanguard of the attack. The Australians, with the Canadians to the south and the British across the Somme to the north, drove the Germans back, first along the line of the Somme and then across the river to Mont St Quentin, Péronne and on to the formidable Hindenburg Line, before the last Australian infantry action at Montbrehain in early October. Fast-paced and tense, the story of The Last 100 Days is animated by the voices of Australian soldiers as they endured the war's closing stages with humour and stoicism; and as they fought a series of battles in which they played a pivotal role in securing Allied victory. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, notes, ill, p.340.non-fictionIn March 1918, with the fear of a one-million-man American army landing in France, the Germans attacked. In response, Australian soldiers were involved in a number of engagements, culminating in the Second Battle of Villers-Bretonneux and the saving of Amiens, and Paris, from German occupation. Then came General John Monash's first victory as the Commanding Officer of the newly formed Australian Corps at Hamel. This victory, and the tactics it tested, became crucial to the Allied victory after 8 August, the 'black day of the German Army'. On this day the major Allied counteroffensive began, with the AIF in the vanguard of the attack. The Australians, with the Canadians to the south and the British across the Somme to the north, drove the Germans back, first along the line of the Somme and then across the river to Mont St Quentin, Péronne and on to the formidable Hindenburg Line, before the last Australian infantry action at Montbrehain in early October. Fast-paced and tense, the story of The Last 100 Days is animated by the voices of Australian soldiers as they endured the war's closing stages with humour and stoicism; and as they fought a series of battles in which they played a pivotal role in securing Allied victory. Collapse summary world war 1914- 1918 - campaigns - western front, western front - australian participation - 1918 -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Craig Deayton, The battle of Messines : 1917, 2017
On 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, ill (col), p.172.non-fictionOn 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summary world war 1914-1918- campaigns - western front, battles of messines - australian participation - 1917 -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Paul Ham, Passchendaele : requiem for doomed youth, 2016
Passchendaele epitomises everything that was most terrible about the Western Front. The photographs never sleep of this four-month battle, fought from July to November 1917, the worst year of the war- blackened tree stumps rising out of a field of mud, corpses of men and horses drowned in shell holes, terrified soldiers huddled in trenches awaiting the whistle. The intervening century, the most violent in human history, has not disarmed these pictures of their power to shock. At the very least they ask us, on the 100th anniversary of the battle, to see and to try to understand what happened here. Yes, we commemorate the event. Yes, we adorn our breasts with poppies. But have we seen? Have we understood? Have we dared to reason why? What happened at Passchendaele was the expression of the 'wearing-down war', the war of pure attrition at its most spectacular and ferocious. Paul Ham's Passchendaele- Requiem for Doomed Youth shows how ordinary men on both sides endured this constant state of siege, with a very real awareness that they were being gradually, deliberately, wiped out. Yet the men never broke- they went over the top, when ordered, again and again and again. And if they fell dead or wounded, they were casualties in the 'normal wastage', as the commanders described them, of attritional war. Only the soldier's friends at the front knew him as a man, with thoughts and feelings. His family back home knew him as a son, husband or brother, before he had enlisted. By the end of 1917 he was a different creature- his experiences on the Western Front were simply beyond their powers of comprehension. The book tells the story of ordinary men in the grip of a political and military power struggle that determined their fate and has foreshadowed the destiny of the world for a century. Passchendaele lays down a powerful challenge to the idea of war as an inevitable expression of the human will, and examines the culpability of governments and military commanders in a catastrophe that destroyed the best part of a generation. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, notes, ill (maps), p.565.non-fictionPasschendaele epitomises everything that was most terrible about the Western Front. The photographs never sleep of this four-month battle, fought from July to November 1917, the worst year of the war- blackened tree stumps rising out of a field of mud, corpses of men and horses drowned in shell holes, terrified soldiers huddled in trenches awaiting the whistle. The intervening century, the most violent in human history, has not disarmed these pictures of their power to shock. At the very least they ask us, on the 100th anniversary of the battle, to see and to try to understand what happened here. Yes, we commemorate the event. Yes, we adorn our breasts with poppies. But have we seen? Have we understood? Have we dared to reason why? What happened at Passchendaele was the expression of the 'wearing-down war', the war of pure attrition at its most spectacular and ferocious. Paul Ham's Passchendaele- Requiem for Doomed Youth shows how ordinary men on both sides endured this constant state of siege, with a very real awareness that they were being gradually, deliberately, wiped out. Yet the men never broke- they went over the top, when ordered, again and again and again. And if they fell dead or wounded, they were casualties in the 'normal wastage', as the commanders described them, of attritional war. Only the soldier's friends at the front knew him as a man, with thoughts and feelings. His family back home knew him as a son, husband or brother, before he had enlisted. By the end of 1917 he was a different creature- his experiences on the Western Front were simply beyond their powers of comprehension. The book tells the story of ordinary men in the grip of a political and military power struggle that determined their fate and has foreshadowed the destiny of the world for a century. Passchendaele lays down a powerful challenge to the idea of war as an inevitable expression of the human will, and examines the culpability of governments and military commanders in a catastrophe that destroyed the best part of a generation. Collapse summary world war 1914-1918 - campaigns - western front, france - campaigns - passchaendaele -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Frontline Books, Battle Group : German Kamfgruppen Action in World War Two, 2014
The German army in the Second World War sought to fight and win swift, decisive victories in a succession of short campaigns - blitzkrieg, or lightning war. Flexibility was as essential as the will to win. Battle groups, or shock troops, were created from miscellaneous, and often disparate military units to undertake a specific local operation; it was the army's skill in combining superior numbers, aggressive tactics and the battle group commander's ability to exploit the changing situation on the ground which brought success on the battlefield. The actions described here cover all theatres of the war, and include battle groups large and small, deployed usually to smash a breach in the enemy line or seal off an enemy penetration. It covers operations in the first dynamic years when Wehrmacht forces defeated the armies of one European country after another in fast campaigns, through to the years after Stalingrad and Africa as they moved towards defeat. The battle groups' contribution to Wehrmacht fortunes offer powerful lessons in the tactics of battle management and this book by James Lucas, a military historian known for his close studies of the German soldier, is considered to be one of the most detailed and authoritative accounts on the subject. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, maps, ill, p.173.non-fictionThe German army in the Second World War sought to fight and win swift, decisive victories in a succession of short campaigns - blitzkrieg, or lightning war. Flexibility was as essential as the will to win. Battle groups, or shock troops, were created from miscellaneous, and often disparate military units to undertake a specific local operation; it was the army's skill in combining superior numbers, aggressive tactics and the battle group commander's ability to exploit the changing situation on the ground which brought success on the battlefield. The actions described here cover all theatres of the war, and include battle groups large and small, deployed usually to smash a breach in the enemy line or seal off an enemy penetration. It covers operations in the first dynamic years when Wehrmacht forces defeated the armies of one European country after another in fast campaigns, through to the years after Stalingrad and Africa as they moved towards defeat. The battle groups' contribution to Wehrmacht fortunes offer powerful lessons in the tactics of battle management and this book by James Lucas, a military historian known for his close studies of the German soldier, is considered to be one of the most detailed and authoritative accounts on the subject. Collapse summary germany - armed forces - history, germany - regimental histories -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Big Sky Publishing, Combat medic : an eyewitness account of the Kibeho massacre, 2008
On the 22nd of April 1995 more than 4,000 Rwandans were massacred and thousands more injured in a place called Kibeho. Terry Pickard, a seasoned soldier and medic, was one of a 32-strong force of Australian UN peacekeepers in Kibeho on that terrible Saturday. While the United Nations’ presence prevented the death toll from being even worse than it was, the massacre continues to haunt him. The rules of engagement that stopped him from intervening in the senseless slaughter, and the life and death decisions he was forced to make when dealing with the injured condemned him to more than a decade of recurring nightmares and debilitating flashbacks. The horror and unimaginable tragedy of the Kibeho Massacre still looms large in the lives of Rwandans and the people sent to help the African country. No one who walked away from that day was ever the same again. Combat Medic is a personal account of one Australian soldier who found himself at the centre of events that shocked the world, and the personal toll that he paid. Terry Pickard’s army career spanned nearly 20 years. More than 25 years after Rwanda he continues to struggle with post traumatic stress triggered by his experiences. Collapse summaryIll, maps, plans, p.181.non-fictionOn the 22nd of April 1995 more than 4,000 Rwandans were massacred and thousands more injured in a place called Kibeho. Terry Pickard, a seasoned soldier and medic, was one of a 32-strong force of Australian UN peacekeepers in Kibeho on that terrible Saturday. While the United Nations’ presence prevented the death toll from being even worse than it was, the massacre continues to haunt him. The rules of engagement that stopped him from intervening in the senseless slaughter, and the life and death decisions he was forced to make when dealing with the injured condemned him to more than a decade of recurring nightmares and debilitating flashbacks. The horror and unimaginable tragedy of the Kibeho Massacre still looms large in the lives of Rwandans and the people sent to help the African country. No one who walked away from that day was ever the same again. Combat Medic is a personal account of one Australian soldier who found himself at the centre of events that shocked the world, and the personal toll that he paid. Terry Pickard’s army career spanned nearly 20 years. More than 25 years after Rwanda he continues to struggle with post traumatic stress triggered by his experiences. Collapse summary united nations - peacekeeping forces - rwanda, rwanda - civil war - atrocities -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Indra Publishing, Best we forget, 1998
Donkey Simpson, a typically naive young Australian, thrust into uniform by his country, sets out on the adventure of a lifetime -- or so he thinks. But Vietnam is not what he expected. It's a horror story. It's a story over which he has no control, at first a 'typical Army stuff-up' which wrenches him this way and that, like a puppet soldier on a string, and then something far more dangerous and sinister threatens to destroy him -- but who's pulling the strings? This is the story of Simpson and his mates, caught in a war between powerful ideologies which none of them understood. They walk the fine line of sanity, swinging wildly between love and hate, pathos and humour, patriotism and treason, life and pointless death. Donkey Simpson's story is centred around the Public Relations Office of the Australian contingent, and a spy in the nearby Intelligence Office -- a spy of unclear loyalties, working for the South Vietnamese allies, working for the enemy, or working only for survival? The novel has its ugly aspects -- most soldiers' lack of respect for the Vietnamese, whether ally or enemy, the callous disregard for human life, and the treachery practised on both sides. Collapse summaryp.390.fictionDonkey Simpson, a typically naive young Australian, thrust into uniform by his country, sets out on the adventure of a lifetime -- or so he thinks. But Vietnam is not what he expected. It's a horror story. It's a story over which he has no control, at first a 'typical Army stuff-up' which wrenches him this way and that, like a puppet soldier on a string, and then something far more dangerous and sinister threatens to destroy him -- but who's pulling the strings? This is the story of Simpson and his mates, caught in a war between powerful ideologies which none of them understood. They walk the fine line of sanity, swinging wildly between love and hate, pathos and humour, patriotism and treason, life and pointless death. Donkey Simpson's story is centred around the Public Relations Office of the Australian contingent, and a spy in the nearby Intelligence Office -- a spy of unclear loyalties, working for the South Vietnamese allies, working for the enemy, or working only for survival? The novel has its ugly aspects -- most soldiers' lack of respect for the Vietnamese, whether ally or enemy, the callous disregard for human life, and the treachery practised on both sides. Collapse summary vietnam war 1961-1975 - fiction, vietnam war 1961-1975 – personal recollections – australia -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Allen & Unwin, The battle of Long Tan : as told by the commanders to Bob Grandin, 2004
This is the first time that those in direct command of Delta Company have shared their memories of the most significant battle fought by Australians in Vietnam, the Battle of Long Tan. Each of the commanders shares the experiences that brought them to Vietnam, and describes how the company commander, Harry Smith, drove Delta Company to become one of the most outstanding units in the Australian forces. Delta's superb military discipline, and its commanders' ability to think outside the square were decisive in holding a vastly superior number of enemies at bay. Each platoon played a crucial role in Delta Company's survival. The artillery's commitment in providing an unbroken wall of metal through which the enemy had to advance is told from the perspectives of both the forward controller and the gun positions. We fly with the RAAF helicopter pilots whose ammunition resupply was the turning point of the battle, and experience the carnage of the battlefield through the eyes of those in the relieving APCs. Delta Company's trauma on returning to the battlefield to claim their fallen was lightened only by the miraculous survival of two of their wounded. The trauma of the battle did not end with the action, however, as politics began to play their part in the drama. The valour of those directly involved in the battle has never been duly recognised - in some cases it has been belittled, in others denied. The ongoing efforts of the Long Tan commanders to right the many wrongs perpetrated in the wake of the battle, and their own journeys from the events of August 1966 draw the reader into a compelling dialogue on the aftermath of Vietnam. Collapse summaryIndex, ill, maps, p.332.non-fictionThis is the first time that those in direct command of Delta Company have shared their memories of the most significant battle fought by Australians in Vietnam, the Battle of Long Tan. Each of the commanders shares the experiences that brought them to Vietnam, and describes how the company commander, Harry Smith, drove Delta Company to become one of the most outstanding units in the Australian forces. Delta's superb military discipline, and its commanders' ability to think outside the square were decisive in holding a vastly superior number of enemies at bay. Each platoon played a crucial role in Delta Company's survival. The artillery's commitment in providing an unbroken wall of metal through which the enemy had to advance is told from the perspectives of both the forward controller and the gun positions. We fly with the RAAF helicopter pilots whose ammunition resupply was the turning point of the battle, and experience the carnage of the battlefield through the eyes of those in the relieving APCs. Delta Company's trauma on returning to the battlefield to claim their fallen was lightened only by the miraculous survival of two of their wounded. The trauma of the battle did not end with the action, however, as politics began to play their part in the drama. The valour of those directly involved in the battle has never been duly recognised - in some cases it has been belittled, in others denied. The ongoing efforts of the Long Tan commanders to right the many wrongs perpetrated in the wake of the battle, and their own journeys from the events of August 1966 draw the reader into a compelling dialogue on the aftermath of Vietnam. Collapse summary vietnam war 1961-1975 – australian involvement, vietnam war 1961-1975 – battles – long tan -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Transworld et al, We were soldiers once -and young : Ia Drang : the battle that changed the war in Vietnam, 2002
In November 1965, some 450 men of the 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry, under the command of Lt. Col. Hal Moore, were dropped by helicopter into a small clearing in the Ia Drang Valley. They were immediately surrounded by 2,000 North Vietnamese soldiers. Three days later, only two and half miles away, a sister battalion was chopped to pieces. Together, these actions at landing zones X-Ray and Albany constitute one of the most savage and significant battles of the Vietnam War. The Americans faced what seemed to be certain destruction. How these men persevered - sacrificed themselves for their comrades and never gave up - makes a vivid portrait of war at its most inspiring and devastating. General Moore and Joe Galloway, the only journalist on the ground throughout the fighting, have interviewed hundreds of men who fought there, including the North Vietnamese commanders. The result is a story of unparalleled human interest. We Were Soldiers Once... and Young also brings the war back home with unforgettable stories of those who lost family members to combat. This devastating account rises above the specific ordeal it chronicles to present a picture of men facing the ultimate challenge, dealing with it in ways they would have found unimaginable only a few hours earlier. It reveals to us, as rarely before, man's most heroic and horrendous endeavor. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, notes, ill, maps. p.483.non-fictionIn November 1965, some 450 men of the 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry, under the command of Lt. Col. Hal Moore, were dropped by helicopter into a small clearing in the Ia Drang Valley. They were immediately surrounded by 2,000 North Vietnamese soldiers. Three days later, only two and half miles away, a sister battalion was chopped to pieces. Together, these actions at landing zones X-Ray and Albany constitute one of the most savage and significant battles of the Vietnam War. The Americans faced what seemed to be certain destruction. How these men persevered - sacrificed themselves for their comrades and never gave up - makes a vivid portrait of war at its most inspiring and devastating. General Moore and Joe Galloway, the only journalist on the ground throughout the fighting, have interviewed hundreds of men who fought there, including the North Vietnamese commanders. The result is a story of unparalleled human interest. We Were Soldiers Once... and Young also brings the war back home with unforgettable stories of those who lost family members to combat. This devastating account rises above the specific ordeal it chronicles to present a picture of men facing the ultimate challenge, dealing with it in ways they would have found unimaginable only a few hours earlier. It reveals to us, as rarely before, man's most heroic and horrendous endeavor. Collapse summary vietnam war 1961-1975 – us involvement, vietnam war 1961-1975 – battles – ia drang valley -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Brolga Publishing, Mary in the morning, 2013
A Vietnam Soldier K.I.A. and His True Love... is the unique true story of a Vietnam soldier who was killed in action on his first wedding anniversary. Based on the life of Pte C W Roost, the book tackles the horrors of war and in particular the loss of a loved one in the duty of service to his country. An exceptional love story written from a woman's perspective, this book puts a human face to the controversial war in Vietnam. At just 20 years of age Chris, like so many Australian young men, was conscripted into the army as a National Serviceman. After marrying his childhood sweetheart, Mary, Chris was posted to Vietnam in June 1968. This book follows Chris' adventures through training, marriage and war. It shares his thoughts through his precious letters to his family, and tells the incredible story of the impact of war on our young Aussies. Chris was killed in action on December 23rd 1968 - his first wedding anniversary. He lives on in this book. Collapse summaryIll, p.192.non-fictionA Vietnam Soldier K.I.A. and His True Love... is the unique true story of a Vietnam soldier who was killed in action on his first wedding anniversary. Based on the life of Pte C W Roost, the book tackles the horrors of war and in particular the loss of a loved one in the duty of service to his country. An exceptional love story written from a woman's perspective, this book puts a human face to the controversial war in Vietnam. At just 20 years of age Chris, like so many Australian young men, was conscripted into the army as a National Serviceman. After marrying his childhood sweetheart, Mary, Chris was posted to Vietnam in June 1968. This book follows Chris' adventures through training, marriage and war. It shares his thoughts through his precious letters to his family, and tells the incredible story of the impact of war on our young Aussies. Chris was killed in action on December 23rd 1968 - his first wedding anniversary. He lives on in this book. Collapse summary vietnam war 1961-1975 – personal recollections – australia, soldiers - australia - biography -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Oxford University Press, The Oxford companion to Australian military history, 1995
This landmark book explores the richness and diversity of Australian military history, which has had a profound impact on the development of Australia. The two world wars - destructive yet often ennobling commitments for the young nation - have been the most important experiences for several generations of Australians, but military considerations and obligations have had a pervasive influence throughout Australian history. Just as it would be impossible to form a proper understanding of that history without due consideration of Gallipoli, the Kokoda Track, and conscription, it would be difficult to exaggerate the abiding influence of the 'digger' and the Anzac legend. From the beginnings of European settlement and the violence that accompanied it, to the more recent engagement of Australian forces in the Gulf War and peace-keeping operations in Africa, military questions have been a constant theme in the story of Australia. Anzac and Gallipoli are well-known names in the consciousness, but they can only be fully appreciated if examined in a wider context. This book does just that, providing a detailed analysis of Australian military achievements and an assessment of the importance of war in Australian history. The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History covers all aspects of this complex and fascinating subject. It contains more than 800 individual entries, written by leading military historians. All the major campaigns and battles are examined, along with significant military and civilian figures, such as Thomas Blamey, John Monash, John Curtin, Albert Jacka and Charles Bean. There are articles on weapons and weapons systems and on the development of the individual services and their component parts. The roles of industry, science and technology are analysed, and a series of essay-length articles discusses key aspects of our military legacy, including military humour and the impact of war on Australian film, television and literature. Here, then, is the most comprehensive guide to Australian military history, ranging from the colonial period to the 1990s. The Companion is supplemented by 100 photographs and by more than 30 maps. It is an indispensable source for students, specialists and general readers alike. Collapse summaryBibliography, ill, maps, p.692.non-fictionThis landmark book explores the richness and diversity of Australian military history, which has had a profound impact on the development of Australia. The two world wars - destructive yet often ennobling commitments for the young nation - have been the most important experiences for several generations of Australians, but military considerations and obligations have had a pervasive influence throughout Australian history. Just as it would be impossible to form a proper understanding of that history without due consideration of Gallipoli, the Kokoda Track, and conscription, it would be difficult to exaggerate the abiding influence of the 'digger' and the Anzac legend. From the beginnings of European settlement and the violence that accompanied it, to the more recent engagement of Australian forces in the Gulf War and peace-keeping operations in Africa, military questions have been a constant theme in the story of Australia. Anzac and Gallipoli are well-known names in the consciousness, but they can only be fully appreciated if examined in a wider context. This book does just that, providing a detailed analysis of Australian military achievements and an assessment of the importance of war in Australian history. The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History covers all aspects of this complex and fascinating subject. It contains more than 800 individual entries, written by leading military historians. All the major campaigns and battles are examined, along with significant military and civilian figures, such as Thomas Blamey, John Monash, John Curtin, Albert Jacka and Charles Bean. There are articles on weapons and weapons systems and on the development of the individual services and their component parts. The roles of industry, science and technology are analysed, and a series of essay-length articles discusses key aspects of our military legacy, including military humour and the impact of war on Australian film, television and literature. Here, then, is the most comprehensive guide to Australian military history, ranging from the colonial period to the 1990s. The Companion is supplemented by 100 photographs and by more than 30 maps. It is an indispensable source for students, specialists and general readers alike. Collapse summary australia - armed forces - history, australia - armed forces - encyclopaedias -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, St Ermin's, The secret history of PWE : the Political Warfare Executive, 1939-1945, 2002
Of all Britain's secret intelligence organizations, the least known is the Political Warfare Executive, developed to conduct psychological warfare against the Nazis. The PWE's history has now been declassified by the Cabinet Office and released, 50 years after it had been completed and consigned to Whitehall's secret archives. David Garnett's book tells of how such resourceful intellects as Richard Crossman, Sefton Delmer, Leonard Ingrams and Valentine Williams waged a covert campaign against the enemy, using such unorthodox, ingenious methods as black propaganda and "false flag" radio broadcasts. It also reveals the internal conflicts with the BBC, Special Operations Executive and the Secret Intelligence Service. Once completed, PWE's history was considered too explosive to release to the public, and even circulation within Whitehall was strictly limited because of the document's sensitivity. At best a handbook of how to undermine an adversary and at worst a tale of breathtaking incompetence and political infighting, this volume aims to add a missing dimension to recent disclosures of Britain's covert wartime operations. --Publisher. Collapse summaryIndex, bib, ill, p.496.non-fictionOf all Britain's secret intelligence organizations, the least known is the Political Warfare Executive, developed to conduct psychological warfare against the Nazis. The PWE's history has now been declassified by the Cabinet Office and released, 50 years after it had been completed and consigned to Whitehall's secret archives. David Garnett's book tells of how such resourceful intellects as Richard Crossman, Sefton Delmer, Leonard Ingrams and Valentine Williams waged a covert campaign against the enemy, using such unorthodox, ingenious methods as black propaganda and "false flag" radio broadcasts. It also reveals the internal conflicts with the BBC, Special Operations Executive and the Secret Intelligence Service. Once completed, PWE's history was considered too explosive to release to the public, and even circulation within Whitehall was strictly limited because of the document's sensitivity. At best a handbook of how to undermine an adversary and at worst a tale of breathtaking incompetence and political infighting, this volume aims to add a missing dimension to recent disclosures of Britain's covert wartime operations. --Publisher. Collapse summary world war 1939-1945 - propaganda, world war 1939-1945 - secret service -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Hodder and Stoughton, German boy : a refugee's story, 2002
In the Third Reich young Wolfgang Samuel and his family are content but alone. The father, a Luftwaffe officer, is away fighting the Allies in the West. In 1945 as Berlin and nearby communities crumble, young Wolfgang, his mother Hedy, and his little sister Ingrid flee the advancing Russian army. They have no inkling of the chaos ahead. The boy and his mother must prevail over hunger and despair, or die." "In Strasburg, a small town north of Berlin where they find refuge, Wolfgang begins to comprehend the evils the Nazi regime has brought to Germany. As the Reich collapses, mother, son, and little sister flee again just ahead of the Russian charge.Ill, p.357.non-fictionIn the Third Reich young Wolfgang Samuel and his family are content but alone. The father, a Luftwaffe officer, is away fighting the Allies in the West. In 1945 as Berlin and nearby communities crumble, young Wolfgang, his mother Hedy, and his little sister Ingrid flee the advancing Russian army. They have no inkling of the chaos ahead. The boy and his mother must prevail over hunger and despair, or die." "In Strasburg, a small town north of Berlin where they find refuge, Wolfgang begins to comprehend the evils the Nazi regime has brought to Germany. As the Reich collapses, mother, son, and little sister flee again just ahead of the Russian charge.world war 1939-1945 - refugees, wolfgang samuel - biography -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Big Sky Publishing et al, Long Tan : the start of a lifelong battle, 2016
On the afternoon of 18 August 1966, just five kilometres from the main Australian Task Force base at Nui Dat, a group of Viet Cong soldiers walked into the right flank of Delta Company, 6 RAR. Under a blanket of mist and heavy monsoon rain, amid the mud and shattered rubber trees, a dispersed Company of 108 men held its ground with courage and grim determination against a three-sided attack from a force of 2,500 Viet Cong and North Vietnamese Army troops. When the battle subsided, 18 Australian soldiers lay dead and 24 had been wounded. Battlefield clearance revealed 245 enemy bodies with captured documents later confirming the count at over 500 enemy killed and 800 wounded. These men were led by a gruff and gusty perfectionist, Major Harry Smith. Now, some 47 years after the battle, Harry tells his story for the first time. But Long Tan is more than just an account of a historic battle. Harry Smith takes his readers on an extraordinary journey - one that ultimately reveals a remarkable cover-up at the highest military and political echelons. Long Tan is also Harry's life story and portrays his many personal battles, from failed marriages to commando-style killing; from a horrific parachute accident through to his modern-day struggles with bureaucracy for recognition for his soldiers. Harry's battles are tempered by his love of sailing, where he has at last found some peace. Long Tan portrays the wrenching, visceral experience of a man who has fought lifelong battles, in a story that he is only now able to tell. Harry can still hear the gunfire and smell the blood spilt at Long Tan. For him, the fight continues. Collapse summaryIll, maps, p.336.non-fictionOn the afternoon of 18 August 1966, just five kilometres from the main Australian Task Force base at Nui Dat, a group of Viet Cong soldiers walked into the right flank of Delta Company, 6 RAR. Under a blanket of mist and heavy monsoon rain, amid the mud and shattered rubber trees, a dispersed Company of 108 men held its ground with courage and grim determination against a three-sided attack from a force of 2,500 Viet Cong and North Vietnamese Army troops. When the battle subsided, 18 Australian soldiers lay dead and 24 had been wounded. Battlefield clearance revealed 245 enemy bodies with captured documents later confirming the count at over 500 enemy killed and 800 wounded. These men were led by a gruff and gusty perfectionist, Major Harry Smith. Now, some 47 years after the battle, Harry tells his story for the first time. But Long Tan is more than just an account of a historic battle. Harry Smith takes his readers on an extraordinary journey - one that ultimately reveals a remarkable cover-up at the highest military and political echelons. Long Tan is also Harry's life story and portrays his many personal battles, from failed marriages to commando-style killing; from a horrific parachute accident through to his modern-day struggles with bureaucracy for recognition for his soldiers. Harry's battles are tempered by his love of sailing, where he has at last found some peace. Long Tan portrays the wrenching, visceral experience of a man who has fought lifelong battles, in a story that he is only now able to tell. Harry can still hear the gunfire and smell the blood spilt at Long Tan. For him, the fight continues. Collapse summary vietnam conflict - australian involvement, vietnam war 1961-1975 – battles – long tan
