Showing 286 items
matching furnishing
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - YOUNG WOMEN'S CHRISTIAN ASSOCIATION, BENDIGO - WARRIAH CLUB, 1920
Young Women's Christian Association, Bendigo - Warriah Club. For Girls over 20. Here hath dawned another blue day. Think I wilt thou let it slip useless away? General Secretary: A Louise Burton. Syllabus 1920. June 2-Readings, Members. June 9-Fancywork, Miss Sinclaire. June 16-Lofe in Honolulu, Miss Hunter. June 23-Home Cooking, Miss Leadbeater. June 30-Club 'At Home' to friends. July 7-An evening with Browning, Mrs Finster. July 14-A Cottage Farden, Mr Rumball. June 21-Demonstration of Cookery, Miss Sampson. June 28-How to take care of an invalid. Aug. 4-Personal Beauty. Aug 11-An evening in France, Sister Hunter. Aug 18-How to prepare meals, Miss Wheeler. Aug 25-A Winter Party. Sept 1-Nursing in the Home. Sept 8-How to keep youthful. Sept15-My books. Sept 22-Fancywork,. Sept 29-The teeth, and how to care for them. Oct 6-An evening with the poets. Oct 13-Open night. Oct 20-The Citizen Ideal. Oct 27-Invitation night. Nov 3-Etiquette, Members. Nov-10 China to-day. NovNov 17-How to furnish a home. Nov 24-Democracy. Dec 1-Open night. Dec 8-An evening with books. Dec 15-Christmas Party. The purpose of the Club is to unite girls in; Comradeship, Service, and Self-Development. The Club meets every Wednesday evening at 8pm, and is open to all girls over 20 years who wish to enrol. Presedent: Miss L Johns. Vice President: Miss B Marsh. Secretary: Miss R Sampson. Treasurer: Miss E Robinson.Bolton Bros. Printers. Bendigochurch, ymca warriah club, young women's christian association, bendigo - warriah club -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CONNELLY, TATCHELL, DUNLOP COLLECTION: ACCOUNTS ESTATE OF ESTHER ISABELLE CANNING, 1893 - 1895
Document. Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop - Accounts - Estate of Esther Isabelle Canning. 1 - 1893 - Acc from Oakley W H, Bridge St Bendigo. Furnishing Undertaker, Established 1853, to Mr Canning for the late Mrs Canning. Contains details of funeral expenses. Also contains receipt from Courtier? Sidney, Sexton, Kangaroo Flat Public Cemetery for Interment charges of Esther Isobel Canning. Independent Section, Label No 2221. 2 - 1895 - Acc from W Beebe & Son, Steam Granite, Marble & Stone Sawing Works, Mitchell St and Lyttleton Terrace, for supplying and fixing red gum edging etc at Kangaroo Flat Cemetery. Dated Apr 1st 1895. 3 - Blank paper titled Canning's Estate Receipts. 4 - 1894 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John. Dated Feb 6 1894. 5 - 1894 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated Mr 3 1894. 6 - 1894 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated Mar 31 1894. 7 - 1894 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning T? dated May 19 1894. 8 - 1894 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning Thomas dated Apr 21 1894. 9 - 1895 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated Jan 14 1895. 10 - 1895 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated Mar 12 1895. 11 - 1895 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated Apr 8 1895. 12 - Receipt from Connelly, Tatchell & Dunlop for allowance to Canning John dated May 7 1895.cottage, miners, connelly, tatchell & dunlop, oakley w h, mr canning, mrs canning, courtier? sidney, kangaroo flat public cemetery, w beebe & son, canning john, canning thomas -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEphemera - Ballarat, Electric Supply Co. of Vic (ESCo), "Official Time table", 1915
Timetable published by the Electric Supply Co of Victoria (ESCo) for Ballarat Tramways - dated 1/5/1915 to 30/9/1915 - winter. Provides times for each route, ticket prices, school tickets, issue and use of tokens, fares, transfer tickets, and route colours both for day and night. Also has notes to passengers and places of interest for each route. Has contact phone numbers for the Company. Manager Mr Pringle. See item 9132 for a 1914 Summer timetable. Has many adverts - from the front page: A M Palmer Chemist Hodgson - optical Snows - department store ESCo - show room in Sturt St L Casper - optician E Jermyn - feed merchant Standsfield & Smith - Decorators Briant's Red shop tea rooms A E White - tailor Ellingsen & Co - furniture Southern Cross Hotel H P Stevens & Co - fur coats Frank Williams - painter and decorator Longhurst's bread factory G Buchanan - metal ceilings Robert Hutchinson - electrical engineer and contractor G Ludbrook - furnishing undertaker A Cant - plumber, gasfitter and ironmonger Huddart Parker and Howard Smith coal merchants Precision Big 4 - motor cycles and bicycles H W Channing - Tram drivers' training school T H Richards - butcher C Ellis - furniture exchange Levecke's motor garage Frank Penhalluriack - electrical work Nankervis - store Taffy King Fred A Reed - tobacconist F & J W Gower - builder E E Hobson - decorator Walter Cornell - liver pills Irvines - wines G Warner - Ironmonger J A Reynolds - Wall papers ESCo Electric lighting Holman & Fiscalini - stables and motor garage Butler & Co - blinds Mrs Kerby - clothing reseller Rose Cosmetic - H Binzer & Co Mrs Busfield - laundry Mrs J H Dogson - registry office for servants Summerscales - stationary and postcards W J Robson - glass Porter's Boots and Shoes B G Tucker's Water Cure Electric Supply Co Rowlands drinks On the bottom of most pages - Sidar products and on the top the Coliseum Picture Palace. Demonstrates and ESCo timetable and provides information about fare systems and local businesses.Time table - booklet - 40 pages + green light card covers centre stapled with tabbed or cut pages.tramways, ballarat, timetables, esco, advertisements, fares, tickets, tokens -
 Parks Victoria - Cape Nelson Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Cape Nelson LightstationFurniture - Cabinet
The cabinet has a curved back and would have been custom‐built to fit the dimensions of the lantern room interior. It is likely to date from when the lighthouse was built in 1884 and may have been among the items delivered by the government steamer dispatch early in March which included ‘the lantern and other fittings for the Cape Nelson Lighthouse’. The Public Works Department provided a range of lightstation furnishings including office desks and cabinets, and domestic settings for keepers’ quarters, with nineteenth century items often stamped with a crown motif and the PWD monogram however the curved cupboards installed in Victoria’s lighthouse lantern rooms do not appear to display this small feature. Further research may reveal more about their manufacture and it is tempting to think that they were perhaps even supplied by Chance Bros as part of the entire lantern room installation. The company usually provided the timber battens for the lantern room paneling, and a cabinet may have been included in the assemblage. Another possibility is that the specially designed cabinet was made on site by carpenters along with other fittings. It is not known whether it is attached to the wall or movable; if attached it is considered to be a fixture and included in the Victorian Heritage Register listing for the lightstation (VHR H1773). Its location, when identified in the CMP of April 1995, was on the ‘lower lantern level’, where there was also a ‘timber step ladder’ (Argus, 6 March 1884, p6. nineteenth or early twentieth century), ‘timber framed lighthouse specification’, ‘timber framed chart’ and telephone .Residue on the furnishing indicates that it was formerly painted green, the colour of some of the other fixtures in the room, such as the original cast iron ladder. It is now partially varnished and the corner to the top’s edging on the right side has been cut off. The lighthouse also has a large curved back, two‐door cupboard. Other similar cabinets with curved backs survive at Cape Schanck, varnished wood cabinet with brass door knob, no drawers; Point Hicks, painted green with silver doors, no drawers and Gabo Island, bench top, 2‐door, no drawers, green paint removed to reveal cedar timber). Cape Nelson’s curved cabinet is unique among these examples for having drawers. The cabinet is a unique, original feature of the lantern room and has first level contributory significance for its historic values and provenance.The bench top cupboard has two drawers, each above a door, and each door is framed and beveled around a central panel. The cabinet has a curved back. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, St Patrick's College Annual Magazine, 1914, 1914
St Patrick's College is a Catholic bous secondary school in Ballarat in the Christian Brothers tradition,School Magazine of St Patrick's College, Ballarat. Includes a boarders' Roll Call. Articles include: Ireland's Freedom, The Catholic Federation, Dr Daniel Mannix Images: Physics Laboratory, Sloyd and Manual Art Room. Senior Public Class, Commercial Class, Intercollegiate Athletics, Orchestra, Rev. Dr Higgins, Br Keniry, J. Guinane of the Irish National Forresters, Gerald O'Day, P. Ryan, Frank Keys, L. Bartels, G. Hickey, T. Keys, O. Daly, J. Wolf, A. McKean, T.H. Jenkins, Football Team, Dr Devine, J. Sowersby, Chemistry Laboratory, Gerard Little, Rev. J. McHugh, Andrew Mulquiney, Bernard Heinz Advertisements: Ballarat Trustees, Heinz Brothers Butchers, Middleton and Morris, National Trustees, F. Cannon Hairdresser, G. Werner & Co, Clegg, Miller and Morrow, Rowlands, Gordon Brothers, Loreto Convent, St Alysius Junior Boys' School Portland, Coghlan Boase and Co, Briant's Red Shop Tea Rooms, Ballarat Supply Stores, Stephen Wellington furnishing undertaker, W. Cornell, Eden Photographs, W.E. Longhurst Bread, Sacred Heart Boarding School, St Anes' Ladies' College Geelong, Ballarat Brewing Company, J.S. Young Suit Builders, George Smithm, Kearns Brothers Fish and Oyster Saloon, T.G. Skewes Pharmacy, J.A. Reynolds Wal paper Wahehouse, Walter Gude Music Teacher, Snows, Auldana Wines, J. Ewins Book Store, Cowdell, Tonner and Ellis, Richards and Co, Kruse's Fluid Magnesia, Jago's Ballarat Boot Palace, R.J. Miller Undertaker, W.C. Thomas and Sons Flour Millers, Broadbent Bros, W.E. Thomas American Dentist, Harry Davies and Co., Permewan Wright, William P. Linehan, Tyler's Clothing Arcadem C. Marks and Co, Coad and Hewitson Chaff Cutters.st patrick's college ballarat, daniel mannix, rev. dr higgins, br keniry, j. guinane, irish national forresters, gerald o'day, p. ryan, frank keys, l. bartels, g. hickey, t. keys, o. daly, j. wolf, a. mckean, t.h. jenkins, dr devine, j. sowersby, gerard little, rev. j. mchugh, andrew mulquiney, bernard heinz, ballarat trustees, heinz brothers butchers, middleton and morris, national trustees, f. cannon hairdresser, g. werner & co, clegg, miller and morrow, gordon brothers, loreto convent, st alysius junior boys' school portland, coghlan boase and co, briant's red shop tea rooms, ballarat supply stores, stephen wellington furnishing undertaker, w. cornell, eden photographs, w.e. longhurst bread, sacred heart boarding school, st anes' ladies' college geelong, ballarat brewing company, j.s. young suit builders, george smith, kearns brothers fish and oyster saloon, t.g. skewes pharmacy, j.a. reynolds wal paper warehouse, walter gude music teacher, snows, auldana wines, j. ewins book store, cowdell, tonner and ellis, richards and co, kruse's fluid magnesia, jago's ballarat boot palace, r.j. miller undertaker, w.c. thomas and sons flour millers, broadbent bros, w.e. thomas american dentist, harry davies and co., permewan wright, william p. linehan, tyler's clothing arcade, c. marks and co, coad and hewitson chaff cutters, loret oconvent portland -
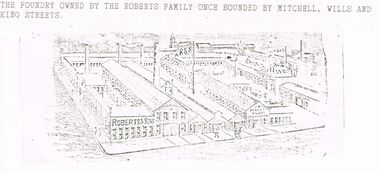 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CORNISH COLLECTION: DOCUMENTS RELATED TO VARIOUS CORNISH ENTERPRISES IN BENDIGO
Documents and copies of photos related to various Cornish enterprises in Bendigo: a. Line drawing (faint) of foundry owned by the Roberts family (Mitchell, Wills and King streets); b. copy of article from unknown source re United Iron Works with details of the firm and Roberts principals - William Roberts, Abraham Roberts and Arthur Roberts - with copies of photographic portraits (Bartlett Bros.) - bad copy with LH side of text partly illegible; c. copy of article titled 'Goyne's Battery Gratings re John Goyne and history of the business (submitted by person living at ''Rosemundy'', Goynes Road, Epsom - Goyne's home then on 20 acres); d. Photograph of old Robinson photo of Bendigo Stamper Grating Factory, Epsom and five men posed in front of large timber building (badly cut photo with LH edge missing. original photo (9 x 13) of ''Former Bendigo Cornish Fuse Factory'' (handwritten inscription on reverse) taken in recent times (hint - car in driveway); f. copy from un-named book of J Nankervis's Ham and Bacon Curing Factory, Golden Square - drawing of the establishment and a photos of winning display of small goods at the Bendigo Show (no date); g. copy from un-named book of photo of premises of A J Williams, Lily and McKenzie Streets - wooden structure with sign indicating Hardware Merchants and ??Mines Furnisher?? , showing three horse-driven small wagons (delivery?); h. copy of photo of Cornish store(1880s) at White Hills - mention of Frederick Stuckenschmidt (married Miss Mary Smith), William Mathews (original owner?) - corner brick building with family posed outside alongside horse and light cart;. reproduction of exhibit in Bendigo Spring Show, 1915 , the ''Made in Bendigo Exhibition'' - first prize awarded to Messrs H M Legg & Co. Progress Jams, preserves, tomato sauce, tomatoes products, candied peels etc. (folded and small tear).bendigo, buildings, early bendigo businesses, bendigo stamper grating factory. epsom. j. nankervic ham and bacon curing establishment. golden square. bendigo cornish fuse factory. cornish stores. messrs h. m. leggo and co. abraham roberts. arthur roberts. william roberts. goyne's battery gratings. -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, New Sutherland Home, 28 Drummond Street, Diamond Creek, c.1912
Postcard: Leader (Melbourne, Vic. : 1862 - 1918, 1935), Saturday 15 June 1912, page 48 ________________________________________ NEW SUTHERLAND HOME. OPENED BY THE PREMIER. A new home for destitute and neglected children, erected for the purpose of carrying on the work of the late Miss Sutherland, was formally opened by the Premier (Mr. Watt) at 28 Drummond-street on Thursday. The new building has been erected at a cost of £1600, of which only £300 has been provided by the Government. A similar sum has been raised by private contribution, but there is still a debt of £800 or £900, which the committee hopes to liquidate shortly - to some extent by means of a sale of gifts, which was 'opened in the building, and will be continued this afternoon and evening. The Premier, in performing the opening ceremony, said the home was a monument to the life work of one of the most distinguished social servants this country had known. (Applause.) Although Miss Sutherland was dead her good work lived on. It was too often true, as Shakespeare said, that "the evil that men do lives after them - the good is oft interred, with their bones." But the statement was contradicted by this noble building, erected for the commemoration of the work Miss Sutherland had instituted. After referring to the good work done by Mrs. Alexander Smith in connection with the building, Mr. Watt said that Victoria owed to the ladies and gentlemen who associated themselves with asylums, refuges, orphanages and homes of this sort a deep and abiding debt of gratitude. (Applause.) With no coercion from the Legislature, or from anyone, these ladies and gentlemen, were endeavouring to organise and keep alive the services that surrounded these institutions. There was no form of organised charity with which he was acquainted that deserved better of the public than this one. (Hear, hear.) Their hospitals, it was true, relieved a vast amount of suffering and affliction, but there was a sacred duty resting on any civilised community to see that those who were forsaken by their natural parents or guardians should not be left absolutely to the mercy of circumstance. The new home, which is intended as a receiving, house for destitute children - prior to their departure for the home at Diamond Creek - has living accommodation for some 20 children, but when fully furnished will accommodate more. It is plainly, but neatly, fitted up, with an abundance of light and air, and of facilities for hot and cold water. Both outside and inside it is an acquisition to the charitable institutions of the city. NEW SUTHERLAND HOME. (1912, June 15). Leader (Melbourne, Vic. : 1862 - 1918, 1935), p. 48. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article198132028 See also Sutherland Homes for Children https://wikinorthia.net.au/sutherland-homes-for-children/ Nov 29, 2012 The building was replaced by a much larger building in 1929 See NNT_107tom fielding collection, diamond creek, drummond street, miss sutherland, new sutherland home, opening, sutherland home for children -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumFramed print
Framed scan of two newspaper articles from "The Williamstown Chronicle" Article 1: "The Williamstown Chronicle 20 September 1856/ Floating dock, Williamstown. To Shipowners and Commanders./ This Dock is now in working order/ and capable of docking ships of 800 tons. Apply to DOVE and Oswald, 95/ Wharf Melbourne. 94." Article 2: "25 July 1857/ The Willaimstown Chro/ Ship Chandlery/ Nelson Parade/ Dove and Oswald/ Beg respectfully to acquaint their friends that they have bought the Stock in Trade of Messrs,/ Probert, Verdon and Co Ship CHandlers abd Proviso of Merchants Neslon Parade, Williamstown;/ stores in Melbourne have opened them as:/ SHIP CHANDLERS/ Sailmakers, Iron mongers, Grocers and Provision Merchants/ The tug steamers "Hercules," "Black Eagle" and "Samson"/ Under the charge of competent masters, are at all times available for work in the River and Bay and to/ take Vessels to or from the Heads or Geelong. Orders for the Steamers left in Melbourne,/ Willaimstown, or on board the Sir W Molesworth, hulk, will have prompt attention,// The floating dock, off Williamstown,/ Capable of Docking Vessels of 800 tons register is in efficient working order. Full particulars of charges/ will be furnished at the Office in Melbourne./ Coals/ A large supply of which is kept on board the Sir W Molesworth, hulk, can be supplied on the shortest / notice to steamers, sailing vessels or on shore; orders aken at either of the stores or by Mr/ McCallum, on board the hulk. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Cupboard, c. 1890
The materials used to build the colonial cupboard have been gathered from various sources and recycled. In those days, it was normal to keep all manner of items 'just in case' they could be repurposed for another item. The brand "Laurel" on one of the wooden panels is from the Mobil Oil company's kerosene. There In the words of the donor, Betty Stone, "Made by Ellis Dale of Latrigg Wangoom, Warrnambool c 1890. The cupboard consists of packing cases stamped with original brand names. One drawer made from a gelignite packing case is of special significance as the Dale family owned a bluestone quarry known as The Dale Bluestone Quarries at Wangoom situated about three miles east of Warrnambool. Ellis Dale, second son of William Dale and Elizabeth (nee Chamberlain) Dale, was born in Wangoom, Warrnambool on 21 November 1860. His father, William Dale, a quarryman from Saddleworth, Yorkshire migrated to Australia in 1852; seven years later - in 1859- he purchased the quarries on twenty acres of land situated in Wangoom at the corner of what is now known as Dales and Aberline Roads. Later, when his two eldest sons, William Jnr and Ellis, reached ten or eleven years of age they worked with their father in the quarries. The work was arduous and dangerous as gelignite was used to blast the bluestone. In 1890 Ellis Dale married Ann Lees, daughter of Lees and Sarah (nee Chamberlain) Lees of Wangoom, Warrnambool. Initially Ellis and Ann Dale resided in a two roomed bluestone cottage which Ellis built a little further up the hill from his parents' home on the Dale family property. A few years later, in order to accommodate their growing family, additional rooms were added making a spacious, comfortable weatherboard home situated in Dales Road which they named Latrigg. Ellis Dale constructed this cupboard soon after he and Ann first set up home in their little stone cottage in 1890. When the home was rebuilt, the home-made cupboard was moved into the larger kitchen, and although Latrigg was well furnished, it remained in the corner between the kitchen door and the large wood stove where it served its purpose very well as it was used for storing ironing utensils. The lower compartment with the hinged drop-door was designed to store the flat irons which were heated on the wood stove, while the ironing blanket and cover, iron holders and other items were stored in the drawers. The Dale quarrying and contracting business existed in Wangoom, Warrnambool for over eighty years as after William Dale’s death. Ellis Dale together with his son lvor, continued on until he died in 1940. (Note: For additional information please refer to Betty Stone’s book “Pioneers and Places - A History of three Warrnambool Pioneering Families” i.e. Chamberlain, Dale and Lees Families)This item is associated with families of Chamberlain, Dale and Lees. These families are listed in the "Pioneers' Register" for Warrnambool Township and Shire, 1835-1900, published by A.I.G.S. Warrnambool Branch.Cupboard, rare example of a Colonial Cupboard, wooden. Made by Ellis Dale from packing cases; several brand names are evident inc. Gelignite and Laurel. Cupboard is lined with newspaper and wallpaper. Panels on left side are braced by attaching a metal scraper. Comprises four compartments, three have round wooden handles, lower compartment has a hinged, drop down door. (From the Chamberlain, Dale and Lees Collection)Brands on wooden panels of cupboard include "Gelignite" and "Laurel" (Laurel is a brand of kerosene)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, chamberlain, dale, lees, stone, betty stone, warrnambool pioneers, dale bluestone quarries, wangoom, cupboard, colonial cupboard, furniture, gelignite, packing crate, ellis dale, laurel -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesLetter, Letters from Fred to Mattie, 1910-11, 1913-14, 1916, 1920
Letters sent to Martha (Mattie) dated from 1907 to 1920. Each letter is an edited version of the original pertaining to aspects of Fred Myers life as a shearer. Cobran Stn via Deniliquin Thursday Sept 1st 1910 …I got a reply from Eynesbury and a favourable reply, it starts on the 13th Oct so I will have plenty of time to get there, in fact far to much as we will finish here in a month full time so that will leave a fortnight to spare. We got rain here at last and it has put us back considerably as we only worked Monday. I have been idle ever since. We will probably start again Saturday. The weather has taken up nice and fine again…. I hope it will keep up to the cut out now I have 800 sheep shorn up to date and am fifth among thirty men so I’m doing well I think. Did you get the pound I sent? I’m sending two more this time, which I drew on Saturday. I don’t like sending too much as there is a chance of it going astray. Postcard Cobran Sept 18 1910 Just a note to let you know I am all right. I was disappointed not getting a letter yesterday, Saturday…I won’t get it now till next Saturday. We have three weeks here yet. I am sending 2 and tell me if you got the other 1. Cobran Stn via Deniliquin NSW Sunday 21st August (1911) ..I’m having a good time here, a good cook and the best of everything, no fires to lights or kettles to boil just get up and wire in but plenty of hard work. The sheep here a pretty rough but much better than Wandook. I am well among them here we had a little rain on Friday but not enough to stop us so we have got one full week in and the weather is now lovely I have been basking in the sunshine all morning and feel strong and fit as a fiddle. They are all a grand lot of men here I only knew one out of the lot but now them all pretty well now. We have a bit of a concert here every night almost. There are a few good singers here and we also had a phonograph up from the station with all the latest records. We have has two dances amongst ourselves, very boisterous affairs indeed they do make the dust fly. I have not ventured to take part in them yet and don’ think I will either. I get enough dancing all day long and besides I have to furnish the music. You ought to see them going when I rattle up the concertina they do make the dust fly. Sample of letters written by Fred Myers to his wife Mattie Myerslocal identities -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Ballarat School of Mines Invoice Book, 1870 - 1875
Scrap book containing invoices relating to accounts to be paid by the Ballarat School of Mines between 1870 until 1875. The School of Mines at Ballarat was the first school of Mines in Australia and was established in 1870. The works done to the former Ballarat Circuit Court House were overseen by Robert Davidson (architect and Surveyor) with the contractor being James Williams. Large book, green leather with red binding, numerous original invoices pasted onto the pages. The first pages of the scrapbook includes correspondence relating to the refurbishment of the former Ballarat Court House which was used as the Ballarat School of Mines from 1870. The building was demolished c1913 to make way for the Ballarat Technical Art School (still standing). * 23 August 1870 - Bateman, Clark & Co, The Ballarat Courier * August 1870 - Klug Bros. Furniture and Bedding Warehouse * April 1870 - J. Armstrong * Statement of Receipts and Expenditure from 23rd Aug. 1870 to 19 January 1871 * W. Gooch, * 1870 - William L. Mullen, Ballarat Stationery Warehouse & Printing Office, * 31Jany. 1871 - A.H. King, Iron Merchant, * 1 February 1871 - Richard Tunbridge, Timber Merchant, * January 4th 1871- Henry Gough, * 8th March 1871 William Murfet, * March 1871- Maxwell Morrow, * 1 February 1871- James Curtis, Caxton Steam Printing Works, * May 4th 1871 - William Blomeley, Iron and Brass Founder, * 4 May 1871 - Thomas Rogers, Draper, Milliner, Haberdasher & c. * May14 1871- George Shannon & Co, Importers of China, Glass & Earthenware, * May 31st 1871, Wreford & Co, Machine Printers, *1st July 1871 William McCulloch & Co,( late Reynolds and English) General Carriers to all parts of the Colony, * 1871- J.J. McDonald, Plumber and Gas Fitters, * August 29th 1871 - Eyres Brothers, Furnishing and General Ironmongers, * 1st August 1871, Frank Pinkerton,H Ben. Franklin Printing and Stationary House 18, Armstrong Street, Ballarat. * 12TH July 1871 J. Donovan, * 10th August, 1871 - Edward Rand, Wholesale Druggist & Importer, *11 Nov 1871 - Matthew Hamilton, * October 2nd 1871 - C.B. Retallack, Engineer and General Smith, *December 8 1871 - James Harrington, * June 1871 - Wayne, Wholesale Druggist * 21st Nov. 1871 - Smith Brothers, Timber Merchants. * 5 January 1872 - T. Eggington, Carpenter, * 12 January 1872 - James Fayle, Plumbers & Ironwork * January 26th 1872 - S. Stansfield, * August 10th 1872 - John H. Hammond Wholesale and Retail, Bookseller, Commercial and General Stationer, etc. etc."VOUCHER" inscribed on spine in gold Each invoice pasted into the scrapbook has a number written onto it. The numbers are in chronological order at start at 1 in each calendar year. ballarat school of mines, redmond barry, hugh gray, henry richards caselli, henry caselli, joseph flude, ballarat court house, harrie wood, clock, invoice book, robert davison, james williams, ballarat circuit court house, old ballarat court, emanuel steinfeld, j.t. sleep, c.b. retallack, john phillips, eyres bros, ballaarat gas company, national insurance company, broadbent bros, charles evans, niven and co, william johnson, william ford, george robertson, william vale, m.d. hamilton, plumbago crucible company, morgans crucibles, h.r. caselli, henry richards caselli, george evans, bateman, clark & co,, klug bros., j. armstrong, w. gooch,, william l. mullen, a.h. king, richard tunbridge, henry gough,, william murfet,, james curtis, william blomeley,, thomas rogers, george shannon, wreford, william mcculloch, j.j. mcdonald, frank pinkerton, ben franklin printing and stationary house, j. donovan, edward rand, matthew hamilton, c.b. retallack,, james harrington, smith brothers,, james fayle,, maxwell morrow,, s. stansfield, walhalla, brunswick house, t rogers -
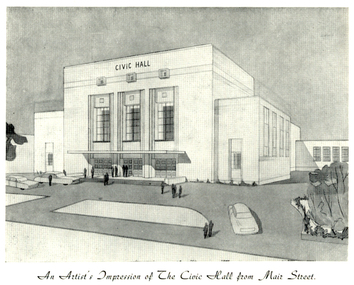 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionProgramme, The Opening of Civic Hall, 1956, 1956
The City of Ballarat unanimously resolved to erect a Civic Hall in Mair Street in 1951. The architects, Gordon Murphy, of Melbourne, and H.L. and L.J. Coburn, of Ballarat, were commissioned in 1952. The Council constructed the foundations and footings for the building under the supervision of the former City engineer, Mr L.H. Finch, in 1953. These footings are of massed concrete. The design for the building took advantage of the cross fall of the land, providing for the Small Hall to be entered from the Doveton Street frontage through a foyer under the Main Stage, the structure is steel with brick panels, with accommodation for 1,592 persons in the Main Hall and 440 persons in the Lower Hall. The front facade faces Mair Street, set back from the building line to provide for the entrance drive-ways and kerbed gardens. Tenders were invited on a firm price basis. A young Ballarat master Builter, Walter Benbow Trahar was the successful tenderer, the contract price being 139,841 pounds. the work was commenced in 1953 and has proceeded in spite of material and labour difficulties until its completion. The following statistics are of interest:- * The foundations contained 200 cubic yards of concrete. * The constructional steel work weighs approximately 270 tons. * The reinforcing steel 47 tons. * Reinforced concrete in the structure, 1,100 cubic yards. * The approximate number of bricks in the building, 580,000. * The flooring is of selected kiln-dried hard wood and totals 40,000 lineal feet. * The dimensions of the Main Auditorium, 100ft by 86 ft, including the side promenades each 82ft by 13ft. *The Main stage, of reinforced concret with parquette finish measures 62 ft by 40ft. *The floor area of the Lower Hall is 74 ft by 38 ft, and has a stage dimensions of 40ft by 20 ft. * Each hall has independent heating and ventillating systems. Where possible the material in the building was furnished from local business houses. The public address installation, which provided for additional microphones, is on the main Stage. There is inter-communication throughout the building connecting the front office, with the bioscope box, the stages in both the large and lower halls, and the Hallkeeper's residence. Local craftsmen have completed the painting, plaster work, and the electrical installation; local produced materials being used in the construction of the buildings with the exception of the timber for the Main Floor, the roofing and the structural steel. The City of Ballarat Councillors in 1956 were Councillors N. T. Callow, F.J. Cutts, K.C. Webb, W.E. Roff, O.W. Curnow, F.T. Woodward, Allan C. Pittard, A.W. Nicholson, J.A. Chisholm, G.L. Scott, F.W. Oliver, A.D. Mason. The Town clerk was H.R. Maddern and the City Engineer was G. Murrowood. A City of Ballarat Council meeting of 25 September 2013 voted to demolish the Ballarat Civic Hall. The Council heard from nearly 50 members of the public during a marathon six-hour meeting. Councilors John Birt, Des Hudson, Amy Johnson, Josh Morris, Peter Innes, John Philips supported the motion to demolish Civic Hall. Councillors Samantha McIntosh, Vicki Coltman and Belinda Coates voted against the motion.Six page souvenir Program of citizens' entertainment on the occasion of the Opening of Ballarat Civic Hall on in August 1956. The front cover features the City of Ballarat Coat of Arms. The programme starts with a message from the Mayor, Cr Neil T. Carrow. It includes the Concert Programme directed by James H. Davey, an asrtist's impression of the Civic Hall from Mair Street, and information relative to the New Civic Hall. The programme features images of the City of Ballarat Coat of Arms, Cr N.T. Callow, , James H, Davey, and an artist's impression of the Ballarat Civic Hall. Mayor Neil Callow's Message: "To-day, our citizens witness the fulfilment of the most extensive Municipal undertaking in the City's period of recent prosperity and development. Their Hall now fills a requirement of which they have been deprived since the Coliseum building was destroyed by fire over 20 years ago. The building has been designed as an all purpose structure and I am hopeful the citizens will use it and enjoy it to its fullest extent. Your Council and its Architects have planned as broadly as possible for the benefit of all to-day and for years to come. We are proud of the work executed by a Ballaarat Master Builder whose work is a monument to the City's craftsmen. I feel I should also remind this assembly that the women of Ballaarat, back in 1951, provided funds which have been applied in the purchase of a Grand Piano and two Upright Pianos which are now installed in this building. The sincere hope of myself and your Councillors is that this Hall and its amenities will prove of immense value to the development of the cultural and artistic tastes of this community and that it will be freely used for these and many other purposes. From now on this magnificent building and its furnishings and equipment will be available to all. I strongly exhort you to use and protect it. My hope is that the citizens will, for many years to come, enjoy the amenities which it has to offer. ballarat civic hall, civic hall, architecture, finch, art deco, city of ballarat, coat of arms, city of ballarat coat of arms, callow, shugg, lemke, oates, gullan, tuuri, john, robertson, sorrell, antonio, gordon murphy, walter benbow trahar, trahar, coburn, h.l. coburn, l.j. coburn, n.t. callow -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Goanna, c. early 1950s
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Mosaic, c. 1962
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Tiger Stripe, c. 1939
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Crete, 1948
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Plum Blossom, 1948
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Jungle, 1945
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Harlequin, c. late 1950s
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Staccato, c.1962
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Staccato (brown-gray), c.1962
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Tiger Lily, 1951
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Pacifica, 1954
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Magnolia, 1938-1942
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Seapiece, 1951
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Zen, c. 1965
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Lunar, 1948
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Bird and Tree, c. 1940
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, flannel flower design, c. 1955
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Hemmed, fabric square, 1950-1955
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs.
