Showing 2547 items
matching the corporation of melbourne
-
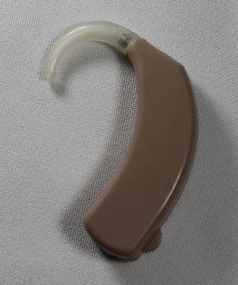 Deaf Children Australia
Deaf Children AustraliaHearing aid
The first commercial digital hearing aid was created in 1987 by the Nicolet Corporation. The hearing aid contained a body-worn processor that had a hardwire connection with an ear mounted transducer. While the Nicolet Corporation’s hearing aid was not publicly successful and the company shortly folded, it was able to start a competition between companies to create more effective hearing aids. Two years later, in 1989, the behind-the-ear (BTE) digital hearing aid was launched. In addition to the Nicolet Corporation, Bell Laboratories expanded upon the hearing aid business by developing a hybrid digital-analog hearing aid. When the hearing aid was put on in the market, it was instantaneously successful. This development helped bring major changes to the world of the hearing aid. The next major milestone was creating an all-digital hearing aid. The Oticon Company developed the first digital hearing aid in 1995, but it was only distributed to audiological research centers for research on digital technology in the realm of acoustic amplification. The Senso was the first commercially successful, all-digital hearing aid, and was created by Widex in 1996. After the success of the Senso, Oticon began marketing their own hearing aid, the DigiFocus. Presently, the digital hearing aid is now become programmable. By making the hearing aid programmable, it has allowed hearing aids to be capable of regulating sound on their own, without using a separate control. The hearing aid can now adjust itself depending on what environment it is in and often does not even need a physical volume control button.These were the first behind the ear hearing aids manufactured by the National Acoustic Laboraties (NAL) in Australia Single behind-the-ear hearing aid. -
 Deaf Children Australia
Deaf Children AustraliaCalaid Hearing Aid, National Acoustic Laboratories, 1960's
The first commercial digital hearing aid was created in 1987 by the Nicolet Corporation. The hearing aid contained a body-worn processor that had a hardwire connection with an ear mounted transducer. While the Nicolet Corporation’s hearing aid was not publicly successful and the company shortly folded, it was able to start a competition between companies to create more effective hearing aids. Two years later, in 1989, the behind-the-ear (BTE) digital hearing aid was launched. In addition to the Nicolet Corporation, Bell Laboratories expanded upon the hearing aid business by developing a hybrid digital-analog hearing aid. When the hearing aid was put on in the market, it was instantaneously successful. This development helped bring major changes to the world of the hearing aid. The next major milestone was creating an all-digital hearing aid. The Oticon Company developed the first digital hearing aid in 1995, but it was only distributed to audiological research centers for research on digital technology in the realm of acoustic amplification. The Senso was the first commercially successful, all-digital hearing aid, and was created by Widex in 1996. After the success of the Senso, Oticon began marketing their own hearing aid, the DigiFocus. Presently, the digital hearing aid is now become programmable. By making the hearing aid programmable, it has allowed hearing aids to be capable of regulating sound on their own, without using a separate control. The hearing aid can now adjust itself depending on what environment it is in and often does not even need a physical volume control button. Silver metal case with side clips and hearing aid attached. Has battery compartment for AA batteries. Volume control is the top left hand corner. "C OF A/CALAID/36778" on back of case deaf children australia, hearing aid, calaid -
 Deaf Children Australia
Deaf Children AustraliaCalaid Hearing Aid, National Acoustic Laboratories, 1960s
The first commercial digital hearing aid was created in 1987 by the Nicolet Corporation. The hearing aid contained a body-worn processor that had a hardwire connection with an ear mounted transducer. While the Nicolet Corporation’s hearing aid was not publicly successful and the company shortly folded, it was able to start a competition between companies to create more effective hearing aids. Two years later, in 1989, the behind-the-ear (BTE) digital hearing aid was launched. In addition to the Nicolet Corporation, Bell Laboratories expanded upon the hearing aid business by developing a hybrid digital-analog hearing aid. When the hearing aid was put on in the market, it was instantaneously successful. This development helped bring major changes to the world of the hearing aid. The next major milestone was creating an all-digital hearing aid. The Oticon Company developed the first digital hearing aid in 1995, but it was only distributed to audiological research centers for research on digital technology in the realm of acoustic amplification. The Senso was the first commercially successful, all-digital hearing aid, and was created by Widex in 1996. After the success of the Senso, Oticon began marketing their own hearing aid, the DigiFocus. Presently, the digital hearing aid is now become programmable. By making the hearing aid programmable, it has allowed hearing aids to be capable of regulating sound on their own, without using a separate control. The hearing aid can now adjust itself depending on what environment it is in and often does not even need a physical volume control button. Silver metal case with side clips and hearing aid attached. Has battery compartment for AA batteries. Volume control is the top left hand corner. Comes with its black case "C OF A/CALAID/101862" on back of case. "ANGUS & COOTE/Acoustics/HEARING AIDS" on inside cover of case -
 Deaf Children Australia
Deaf Children AustraliaCalaid Hearing Aid, National Acoustic Laboratories, 1955-mid 1970's
The first commercial digital hearing aid was created in 1987 by the Nicolet Corporation. The hearing aid contained a body-worn processor that had a hardwire connection with an ear mounted transducer. While the Nicolet Corporation’s hearing aid was not publicly successful and the company shortly folded, it was able to start a competition between companies to create more effective hearing aids. Two years later, in 1989, the behind-the-ear (BTE) digital hearing aid was launched. In addition to the Nicolet Corporation, Bell Laboratories expanded upon the hearing aid business by developing a hybrid digital-analog hearing aid. When the hearing aid was put on in the market, it was instantaneously successful. This development helped bring major changes to the world of the hearing aid. The next major milestone was creating an all-digital hearing aid. The Oticon Company developed the first digital hearing aid in 1995, but it was only distributed to audiological research centers for research on digital technology in the realm of acoustic amplification. The Senso was the first commercially successful, all-digital hearing aid, and was created by Widex in 1996. After the success of the Senso, Oticon began marketing their own hearing aid, the DigiFocus. Presently, the digital hearing aid is now become programmable. By making the hearing aid programmable, it has allowed hearing aids to be capable of regulating sound on their own, without using a separate control. The hearing aid can now adjust itself depending on what environment it is in and often does not even need a physical volume control button. Square, silver metal hearing aid with electronics and AA battery compartments. Has an ear piece and ear mould attached by wire, with a volume adjustment. A body level type, probably a CALAID T manufacture from 1955 to the 70's. On front "C OF A/CALAID/108499" deaf children australia, hearing aid, calaid, commonwealth of australia -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Vickers Viscount V 807 Diagrams, Vickers Viscount V 807 Diagrams New Zealand National Airways Corporation Airframe, Oxygen, Refuelling
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - PACIFIC AIRMOTIVE CORPORATION PAC-1 SPECIFICATIONS AND SALES BROCHURE, PAC-1 "THE COMMUTER AIRLINER
A4 FOLDER WITH BBOKLET AND LOOSE PAGES -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - CAC Sabre Mk.31 & Mk.32 Flight Manual, Flight Manual Sabre Mk.31 & Mk.32 Aircraft Air Publication 972 2nd Edition, August 1961
... Moorabbin melbourne Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation Sabre Mk.31 ...commonwealth aircraft corporation, sabre mk.31, sabre mk.32, cac sabre -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBooklet (collection) - Piper Aztec Owner's Handbook, Aztec Owner's Handbook Piper Aircraft Corporation
P. LangOverview of Piper Aztec Model B -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Notes On Operating The Gazelle Mark 161
Description: 75 pages. Published by Avco Corporation - Lycoming Division. Published 30/6/1964. Part No. 60299-20. Lycoming Model 10-720 Series Aircraft Engines Operator's Manual Level of Importance: World. Issued by Rolls-Royce Service Dept.( Military) -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Instruction Manual For Wolseley Aero Engines
Description: 182 pages. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. Published September 1968. Piper PA-18 & PA-18A Super Cub Aircraft Parts Catalogue Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone 9 Series R-1820-52 Engines
Description: 100 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published with materials from 1940-1945. Catalog Part No. 851653. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone Aircraft Engines Series GR-1820G-200 Level of Importance: World. Author: Editor John W. R. Taylor -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone Series 9Gc Engines
Description: SUPERSEDES PREVIOUS EDITION, PUBLISHED 1/5/1942. 134 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published 1/12/1942. Catalog Part No. 853544. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone 9 Aircraft Engines Model R-1820-52 Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone Model R1820-74W And -76 Engines
Description: 199 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published on unknown date. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone Series 9GC Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone Series 9Gc Engines Service Manual
Description: 69 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published December 1945. AN 02-35GG-4/No. 856098N1. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone Model R1820-74W and -76 Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone Series F50 Engines
Description: 121 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published January 1944. Part No. 111722-N3. Service Manual for Wright Cyclone Series 9GC Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone Model Gr-1820-G-100 Engines
Description: 120 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published with materials from 1937-1941. Part No. 87983. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone Series F50 Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Wright Cyclone 9 Engines Instructions
Description: 150 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published with materials from 1940-1941. Part No. 851361. Parts Catalogue for Wright Cyclone Model GR-1820-G-100 Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. Author: W. Baird -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Specifications Guide For Fuels, Oils And Aviation Products
Description: 120 pages. Published by Wright Aeronautical Corporation. Published May 1940. Instructions for the Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Wright Cyclone 9 Models R-1820-G, GR-1820-G and GR-1820-G-100 Aircraft Engines Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Management Control In Airframe Contracting
Description: 84 pages. Published by Shell Corporation - NATO. Published May 1968. British and US Air Forces (NATO) Specifications for Fuels, Engine Oils and Aviation Products Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Technical Manual C-130E Aircraft
Description: SUPERSEDES IB96429-1. 300 pages. Published by Radio Corporation of America. Published Octorber 1966. No. IB96429-2. Instructional Manual for AVQ-55 Avionic Weather Radar Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - Nomad De-Icing Team Uk - 1979
Description: Visit of Australian Industrial Evaluation Team, Northrop Corporation Aircraft Group. Published by Northrop Corporation Aircraft Group on the 31st of May 1979 (31/05/1979). Level of Importance: . -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa30 Twin Comanche Parts Catalogue
Description: 48 pages. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. Published January 1960. Piper Pawnee Model PA-25 Owner's Handbook for Operation and Maintenance. Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Prestwick Pioneer
Description: 231 pages. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. Published April 1966. Number 753 646. Piper PA-30 Twin Comanche Aircraft Parts Catalogue Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Handling Notes Piper Cherokee Pa-28-140 & Pa-28-180
Description: 753 690. Published May 1965, revised May 1967. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 150 pages. Piper PA32 Cherokee Six Aircraft Service Manual Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Pa32 Piper Cherokee Six Parts Catalogue
Description: Report VB-58, Manual No. 27.10-260. Published on unknown date. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 120 pages. Piper PA-32-260 Cherokee Six Approved Flight Manual Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa-28 Cherokee Parts Catalogue
Description: 753 689. Published May 1965, revised December 1965. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 148 pages. Piper PA-32 Cherokee Six Parts Catalogue Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa-31-350 Chieftain Parts Catalogue
Description: 753 582. Published August 1963, revised June 1965. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 140 pages. Piper PA-28 Cherokee Aircraft Parts Catalogue Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa23 Aztec Service Manual
Description: x61 487. Published November 1972, revised May 1984. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 568 pages. Piper PA-31-350 Chieftain Aircraft Parts Catalogue Card 1/4 Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa23 Aztec Service Manual
Description: 753 596. Published December 1966. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 64 pages. Piper PA-23-250 Aztec Model B Aircraft Owner's Handbook Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Pa31 Service Manual
Description: 753 564. Published October 1968. Published by Piper Aircraft Corporation. 400 pages. Piper PA23-250 Aztec and PA23-235 Apache Service Manual Level of Importance: World.
