Showing 1700 items
matching concreting
-
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph, 2012
Date made December 2012Colour photograph of the railway bridge over Boggy Creek at Nowa Nowa. Bridge is built on combination of solid concrete piers, timber trestle piers on concrete to flood level, and timber piers. Nowa Nowa Victoriabridges, waterways, transport -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper nail from the Schomberg. Small piece of concretion on the nail. Nail is bent.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, nail -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Portland Harbou, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph, J.T. Somerville, Photographer, Casterton, n.d
Sourced from Casterton Town Hall (former Shire of Glenelg)Black and white photo. Wooden form work for concrete, on earth wall of gully.Back: Round, purple, photographer's stamp -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Earth Saving Dam, n.d
Sourced from Casterton Town Hall (Former Shire of Glenelg)Black and white photo. Large concrete pipe? Part of earth-saving dam -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionSlide - Slide - Construction Portland/Cashmore Airport, c. 1980
Coloured slide. Trench with narrow channel running thru it, concrete bottom in channel. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageForks
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Set of 11 dinner forks in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, dinner fork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpoons
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Set of 5 tea spoons in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, tea spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Brass Harness Ring, 1¼" dia, in concretion. Recovered from the Schomberg wreck.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, brass harness ring -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Lee Breakwater, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, lee breakwater -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - wharf, Portland, Lee BW / Tanker B, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, portland harbour, wharf, construction, trade -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Lee Breakwater / Tanker Berth, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, wharf -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Lee Breakwater, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, lee breakwater -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Lee Breakwater, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, portland harbour, wharf, construction, lee breakwater -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Lee Breakwater, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Archives Authorityport of portland archives, construction, steel, metal, girders, harbour, portland -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionSlide - Slide - Construction Portland/Cashmore airport, c. 1980
cashmore airport -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Concrete piles, No 6 Berth, n.d
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesBack: 179- pencilport of portland archives, portland harbour, no 6 berth -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionSlide - Slide - Construction Portland/Cashmore airport, c. 1980
-
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumSculpture - Mould - concrete/death mask, Death Mask, 1940's
Death mask mould found in Camp 13 POW rubbish tip by former Army Garrison guard on a return visit to the camp.Concrete casting/death mask of a face, pitted, soiled, part of nose missingdeath mask, death mask mould, camp 13 rubbish tip -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratArtwork, other - Public Artwork, Sir Walter Scott by by Stanley Hammond, c1962
A bronze statue of Sir Walter Scott, a Scottish writer, novelist, poet, historian, and biographer who lived from 5 August 1771 – 21 September 1832. The Sir Walter Scott Monument was unveiled by the Mayor Cr A. Masson in March 1962 at the Civic Hall, BallaratThe artwork is of aesthetic and historic significance to the people of BallaratBronze statue of Sir Walter Scott in seated position on sandstone and concrete plinth.sir walter scott, ballarat, stanley hammond -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratArtwork, other - Public Artwork, Gold Mill by Nicola Pammett
Sculpture erected to commemorate the Sesquicentenary of settlement in Victoria.Concrete and Corten steel sculpture depicting the circular mill wheels of a gold millTHE QUEEN ELIZABETH II ROTUNDA/ B.C.A.E GOLD MILL SCULPTURE / OFFICIALLY UNVELIED BY / THE HON. NEIL TREZISE M.P. ON THE 3RD DAY OF NOVEMBER 1985 / THE PROJECTS WERE PART OF THE SHIRE OF BUNINYONG ACTIVITIES / TO COMMEMORATE THE 150TH ANNIVERSARY / OF THE STATE OF VICTORIA.gold, mill -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratArtwork, other - Public Artwork, Belinda Woodruff, Spirit of the Ballarat Winter Festival by Belinda Woodruff, 1998
"The idea behind this artwork installation ‘Spirit of the Ballarat Winter Festival’ was to incorporate arts and cultural symbology as if it were painted like a brush stroke upon the footpath yet embedded like a time stamp within the urban streetscape. ‘Spirit of the Ballarat Winter Festival’ offers an unexpected burst of colour and vibrancy within the Ballarat CBD." This artwork was created as pert of the Ballarat Winter Festival in 1998. The Spirit of the Ballarat Winter Festival mosaic is an interpretation of the Ballarat Winter Festival logo image designed by Paul McKenna. Principal Artist Belinda (Bel) Woodruff then trading as Deevine Mosaics received Project Support from Anne Bonighton and City of Ballarat Community Arts Department staff. Vitrified glass tiles adhered to a pre-cast concrete form - installed into the footpath.SPIRIT OF THE / BALLARAT WINTER FESTIVAL / MOSAIC BY/ DEVINE ORIGINALS / SUPPORTED BY / COMMUNITY ARTS - 1998 -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO BUILDING SITE
Building Site - Pouring Concrete Date and location Unknown 3 Men in the photoFujicolorbuildings, commercial, gas and fuel -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Horse trough, Annis & George Bills, circa Dec. 1932
This horse trough is the only survivor of the two troughs originally installed in Raglan Parade, Warrnambool, in 1932. It was later moved to the Pony Club at Albert Part, near the north corner of Coulstock and Craig Streets. Over the time there its purpose was changed from a horse watering trough to a colourful garden bed of agapanthus plants. By February 2013 the horse trough had been transferred to Flagstaff Hill for display in the Maritime Village’s grounds. This trough is one of hundreds provided by the Annis and George Bills Estate Trust since 1927 for the welfare of working horses and dogs. The original concrete cap over the small compartment is still retained. There are also markings on the right side of the trough where it probably had a birdbath, tap or a dish for the horseman’s dog, similar to other troughs donated elsewhere by the Trust. Less than half of the troughs produced for the Annis and George Bills Trust still survive. In 2017 Felicity Watson, National Trust Victoria’s advocacy manager, said that the troughs were treasures and becoming rare, with more than a dozen across Victoria now being heritage protected. ABOUT ANNIS AND GEORGE BILLS The 1927 Will of George Bills included setting up the Annis and George Bills Estate Trust, which provided for hundreds of horse troughs to be supplied and installed throughout Australia, Britain, USA and other parts of the world for the welfare of horses. Town and city councils could apply to the Trustees for a horse trough for their communities. George “Joe” Bills was born in Brighton, England, in 1859. The family migrated first to New Zealand then to Australia in 1873, settling in the Echuca-Moama district. George moved to Brisbane in 1882 where he met Annis Swann, formerly from Sheffield. Both were animal lovers. George and Annis married 1885 and moved to Sydney to join George’s brother Henry in his mattress wire weaving business, later known as the Bills Brothers. They patented their own machine in 1893 and the business became very profitable. George was able to donate to charities that supported his passion to improve animal welfare. He and Annis joined the Victorian Society for the Protection of Animals and in 1924 George received a Life Membership with the RSPCA. George retired in 1908. The couple moved to Hawthorn, Victoria, in 1910, where they donated troughs for the work horses of Melbourne. During a visit to England Annis passed away. In 1927 George moved from Hawthorn to Camberwell, where he passed away at the end of that year. George had requested in his Will that a trust fund be set up from his estate "…construct and erect and pay for horse troughs wherever they may be of the opinion that such horse troughs are desirable for the relief of horses and other dumb animals either in Australasia, in the British Islands or in any other part of the world subject to the consent of the proper authorities being obtained." The troughs were to bear a plaque inscribed “Donated by Annis and George Bills, Australia”. In 1927 the cost to make a trough was about £13 (which converts to about $1079 in 2020 ), plus transport and installation costs. Most of the troughs were installed between 1930 and 1939 in Victoria and New South Wales. It is estimated that over that time around 500-700 Bills Horse Troughs were installed in Australia and another 50 overseas. Most of the troughs made in Victoria had three moulded front panels like this trough, and no panels moulded on the rear, whereas troughs made in NSW had four panels on the front and five on the back. Victorian troughs were made by a Bills’ relative, J H Phillips. Later, other manufactures for the Trust’s troughs included Rocla Concrete Pipes Ltd, in Auburn Road, Hawthorn, Victoria, who produced to the same original design. No further troughs produced after the end of World War II. A memorial to Annis and George Bills was first erected in Hawthorn in 1929. It included a drinking fountain and a dog dish. Its current location is unknown. In 1964 the George Bills RSPCA Resource Centre opened in Burwood East. This Bills horse trough is nationally significant as one of the surviving examples of the standard Bills memorial horse troughs that still has its compartment cap and evidence of it once having had attached fittings, possibly for a birdbath or dog dish. This trough has State historical significance for being produced in the early 1930s by a business in Hawthorn, Victoria. This example of a Bills horse trough is significant for being in comparatively good condition. The trough is locally significant for being the sole survivor of the two Bills horse troughs installed in the City of Warrnambool in 1932, originally installed on Raglan Parade and continued to be used in the community at the Pony Club, then finally transferred to its current location at Flagstaff Hill by early 2013. It is culturally significant as it represents the community’s dependence on horses for travel and transportation previous to motorised vehicles. It is morally significant as a generous gift from a couple concerned with the welfare of animals.Horse trough; a long narrow rectangular container used for storing water. Trough is made from pre-cast concrete with one large open compartment and a small covered compartment. The base of the small compartment is raised slightly above the base of the trough and is covered by a removable concrete cap. The design of the front of the trough includes three panels moulded into it that align with the shape of the back pediment (panel). The pediment is shaped with side arcs that step up to a wide centre arc. A rectangular concrete plaque is cast into the centre of the pediment and is engraved with the names of the original donors, Annis and George Bills. The trough was made in Hawthorn, Victoria, by J H Phillips circa 1932. “DONATED BY / ANNIS & GEORGE BILLS / AUSTRALIA”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, annis and george bills, bills trust, j h phillips, rocla concrete pipes ltd, hawthorn, water trough, watering trough, horse trough, animal welfare, bills horse trough -
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph - North Arm Bridge, Lakes Post Newspaper, 1999
Bridge was built 1917Colour photograph taken underneath the concrete North Arm bridge, shows the original four concrete piers and two piers added to widen bridge. Construction of abutments for new bridge seen in background. Lakes Entrance Victoriabridges, construction -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Watch Chains, ca 1855
The concretion of silver watch chains was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg over one hundred years later. Schomberg was a large three-masted full-ship rigged wooden ship built in 1855 by Alexander Hall and Co in Aberdeen, Scotland for James Baines' famous Black Ball Line at £43,103. The vessel was 288 feet (88 meters) in length, with a beam of 45 feet (14 meters), a depth of 29.5 feet (8.99 meters) of 2,284 tons. The mainmast was 210 feet (64 meters) high and she carried 3.3 acres of sail. The vessel was constructed with three skins. One planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). The Schomberg is one of only three clipper wrecks in Victorian waters that operated the England -to- Australia run. While the other two, Empress of the Sea and Lightning, were built by the famous American shipbuilder, Donald Mac Kay. Schomberg was an attempt to build a faster ship than Mac Kay and a vessel fast enough to break the sailing record to Australia. The Schomberg sailed on her maiden voyage from Liverpool on 6 October 1855, under the command of Captain James Forbes, on its maiden voyage to Australia with general cargo, jewellery, spirits, machinery, and 2,000 tons of iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, plus 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. There were approximately 473 passengers and a crew of 105. It was hoped that Schomberg would make Melbourne in sixty days, setting a record for the voyage, but light winds at the equator dashed those expectations. The ship sighted Moonlight Head in southwest Victoria on Christmas Day but through a deadly combination of wind, currents and unmarked sand spits, the vessel gently ran aground on 26 December 1855 on a spit that juts into Newfield Bay, just east of Curdies Inlet, and the present town of Peterborough. Fortunately, the SS Queen was nearby and managed to save all passengers and crew. The steamers Keera and Maitland were dispatched to salvage the passenger's baggage and the more valuable cargo. Other salvage attempts were made, but deteriorating weather made the work impossible, and within two weeks the Schomberg's hull was broken up and the vessel abandoned. The wrecking of the Schomberg caused quite a public stir, particularly in light of the fact the vessel was supposed to be, the most perfect clipper ship ever built. Captain Forbes was charged in the Supreme Court under suspicion that he was playing cards with two female passengers below decks when his ship ran aground. Despite a protest meeting, two inquiries and the court proceedings, he was found not guilty and cleared of all charges. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum that also displays ship fittings and equipment, and personal effects. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historically significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Conglomerated cluster of silver watch chains, encased in concretion at both ends (1 chain is separated). They were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, watch chain -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Spray Wall construction, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, portland harbour, spray wall -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Bridge Construction, 29/05/1957
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesFront: Back- 'Bridgewater road Bridge (otway street) 29/5/57' - pencilport of portland -
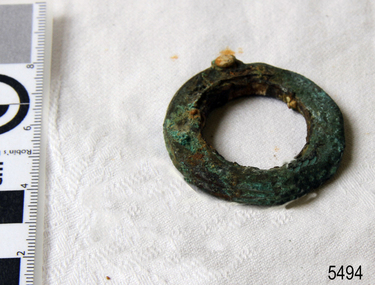 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWasher
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Flat brass washer diameter 1". Has some concretion. Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, washer, brass washer
