Showing 709 items matching "burke museum collection"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr and Mrs Don Hayes, 20th May 2000
In this interview we hear from Don and Bobbie Hayes who met and were married in Beechworth. Mrs Hayes was born in Beechworth to a blacksmith and a teacher who had moved to the area not long before she was born in 1925. She discusses her family and the struggle her mother had being a city woman relocated to the bush and into a family who didn't accept her for her Methodist religious beliefs as they were a staunch Catholic family. After working in the Tannery when they first moved to Beechworth from Melbourne, Don got a job in the 1950's at the Beechworth Mental hospital known as Mayday Hills (est. 1862) and continued working there for the next thirty six years. Starting as a nurse Don would be one of three or four staff known then as attendants, who would oversee up to forty patients in a ward taking them out to work the land and gardens or chop wood on the grounds. Mrs Hayes also worked in the Hospital and discusses the need at the time to be earning to pay for large medical bills that came from two of their children, one having a congenital heart problem which was not covered by hospital benefits and the other displaced hips that required surgery. By the end of his time working at the hospital, Don was in charge of the patient training centre where those destined for discharge would be trained on how to cope in the world outside of the hospital grounds they were so used to. Both talk openly and with heartfelt candour, recalling their years spent among the patients of the hospital community, their sense of humour and compassion are evident and although the times and the jobs were definitely hard and the wages low, this couple cared deeply about the people they worked with and sit among those people from the local area who established Beechworth as a significant social welfare region. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.The significance of this oral history lies in the firsthand accounts from two people who were directly involved in the significant nursing work undertaken at Mayday Hills Mental hospital from the 1950's. Hearing the stories from those who were there and had lived experience, adds depth and we gain valuable insight into how and what the asylum was like for those who worked there and colourful details about the kinds of patients they encountered too, it adds human and personal context to what could otherwise become statistic and abstract information about a historic site. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, mayday hills hospital, may day hills, beechworth mental asylum, mental hospital, asylum, nursing, hospital, patient training centre, patients, social welfare -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr. Vincent Makaravicius, July 2000
Vincent Makaravicius was born on the 23rd of January, 1922 in a small Lithuanian village. He was the youngest of six children and after completing his primary education he went on to study horticulture at Kaunas and Vilnius. During WWII, under the threat of Soviet occupation and conscription, Vincent travelled to Germany, before coming to Australia as a refugee after his wife in 1949 on the ship 'Victory.' Vincent eventually settled in Beechworth, working at the local tannery and the Beechworth Asylum, as well as taking on boarders in the tannery boarding house in which his wife and he lived for a number of years. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Vincent Makaravicius' story is historically and socially significant as it provides a unique insight into the trials, tribulations, hopes, and dreams of Australian immigrants during the mid 20th century. Mr Makaravicius references the turbulent political situation and lack of food in Europe as being the reason for the mass exodus from Europe that saw an influx of refugees and migrants to Australia. His personal account highlights the spirit of survival and perseverance that is quintessential of Australian settler history. His contributions to the township of Beechworth gave him a detailed understanding of the social and historical significance of the township and the people, institutions, and local businesses on which it was built, namely the Beechworth Asylum, the local tannery, and relations between migrants and the established community. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mr. Vincent Makaravicius /listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, vincent makaravicius, wwii, lithuania, kaunas, vilnius, soviet, germany, australia, victory, tannery, beechworth asylum, refugee, jennifer williams -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr Harry Mason, 13th April 2000
Mr Harry Mason was born in Stanley, Victoria, on the 23rd of July 1925, attending the primary school in Stanley and high school in Beechworth on the mail truck. His family initially moved to the area during the initial Gold Rush period. He moved to Beechworth in 1960. For seven years after school, he worked in the local orchard full time before becoming the local gravedigger, responsible for digging the graves of Beechworth residents and Asylum for 23 years. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Mr Harry Mason's account of his life in Beechworth and the local area during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of the region. He details important historical events and hardships in the region's history that had a lasting local, regional and national impact, including Australia during war time, economic struggles, and women's societal roles in a rural area. Mr Mason also discusses agricultural and gravedigging practices of the time as well as what it was like growing up in rural Australia. This first-hand account is imperative to our understanding of life during the last century. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mr Harry Madon /listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, harry mason, stanley, orchard, jennifer williams, asylum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mrs Vanessa McDonald, 9 November 2000
... and items in the Burke Museum's collection. This oral history ...Mrs. Vanessa McDonald was born in Beechworth in 1917. Christened, Agnes Bertha Collins, Vanessa changed her name in 1960. Mrs. McDonald's family's connection with gold mining in the district reach back to the first of Beechworth's gold rushes, when her great grandfather, a Dutchman who adopted the name Charles Collins, arrived in 1851-1852. Mrs. McDonald spent her childhood in the isolated hamlet of Stanley, in the area known as 'Little Scotland', where she recalls helping her mother to raise younger siblings, picking apples and walnuts on the family farm, and roaming the hills for wildflowers. As a young woman Mrs. McDonald attended religious and social gatherings in the local community. In 1940 she went to Melbourne to work as a mothercraft nurse during the Second World War. She met her husband at a Beechworth football match and was married at the Stanley Methodist Church in 1941. The gold diggings known as the 'Nine Mile' became the hamlet of Stanley, after the British Prime Minister, Lord Stanley, in 1858. By the late 1850s, Stanley boasted schools, an athenaeum, a church, a weekly newspaper and several hotels and other civic infrastructure to cater for a growing population. The area attracted large numbers of Chinese miners, whose presence was frequently resisted. Like other early Victorian mining settlements, Stanley was a hotbed of political and racial tensions during the gold rush. One side of the Nine Mile Creek was known as 'Little Scotland’, the other, 'Little Ireland'. A number of Christian denominations built congregations and churches in Stanley, including the Church of England, Methodist Church, the Catholic Church, and Presbyterian Church. Stanley became part of the United Shire of Beechworth in 1871. By 1880 timber was being cut and two sawmills were established by 1887. River-dredged gold mining consumed vast amounts of timber from the forests in the area, and in 1931 the first of several softwood plantations began. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth'. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Following the decline in the mining and associated industries during the early-mid-twentieth century, the Beechworth district experienced a period of general economic decline. On the east side of the Dingle Range, Mrs. McDonald's father, William Henry Collins, felled timber and the family were pioneer apple orchardists. The establishment of apple orchards in Stanley reflects changes to how land was used and contributes to our understanding of the historical development of rural communities following the gold rush. Mrs. McDonald's recollections are significant for understanding family and social life in a small rural town in years leading up to the Great Depression and prior to the Second World War. This oral history recording may be compared with other oral histories and items in the Burke Museum's collection. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Vanessa McDonald /listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, emigration, gold rush immigration, victorian gold rush, mining families, apple orchard, forestry, forest plantation, little scotland, stanley, twentieth century history, regional australia, rural australia, farming, harvest festival, great depression, dingle range, the nine mile, australian wildflowers, high country wildflowers, mothercraft nurse, rural and regional women, social history, collins, mrs. vanessa mcdonald, building community life, shaping cultural and creative life, fruit growers, family history, changes to land use in regional victoria -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr Jack Tully, 31 August 2000
Mr Jack Tully was born in 1927 in Box Hill Doncaster to Irish decedents. The youngest of three children, one brother and two sisters, Jack and his family took after the family orchard after his father died. After years of running the business side of the orchard Jack moved to Beechworth in 1957 purchasing an orchard and becoming a grower. Jack grew mainly apples in his orchard creating job opportunities for locals and elevating his worth in town. He speaks highly of Beechworth; he is a valued and respected member of society. He enjoyed a round of tennis with his wife. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke. Mr Jack Tully's account of his life in Beechworth and the local area during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the region's cultural heritage. He provides a unique perspective as an orchard owner within Beechworth but also as an outsider who moved and was welcomed into the town with open arms. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a more mundane insight into day-to-day life of ordinary residents during the 20th century. This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mr Jack Tully / beechworth, jennifer williams, jack tully, oral history, burke museum, listen to what they say, recording -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Fred and Bette Wyatt, 27 April 2000
Fred was born on the 1st of March 1928 and Bette in 1934, in Beechworth. Both of their families immigrated from England on convict ships in the 1800s. Fred and Bette both had large families of 9 and 5 siblings respectively, with 2 of Fred's siblings suffering from muscular dystrophy both dying at 20 years old which affected the family. Bette originally worked in multiple cafes and kitchens in Beechworth before working in "Ennals Store" which was a grocery store, for over 30 years. Fred worked as a milkman during the war before becoming an engineer at the tannery and the brewery in Beechworth. He rebuilt the factory at the brewery during the 1970s and worked there until he retired. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Fred and Bette Wyatt's account of their lives in Beechworth and the local area during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of the region. They both mention important historical events and hardships in the region's history that had a lasting local, regional and national impact, including Australia during wartime, economic struggles, and the development of Beechworth town. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Fred and Bette Wyattbeechworth, beechworth tannery, beechworth brewery, fred and bette wyatt, wyatt, wyatt beechworth, ennals store, ennals beechworth, listen to what they say, burke museum -
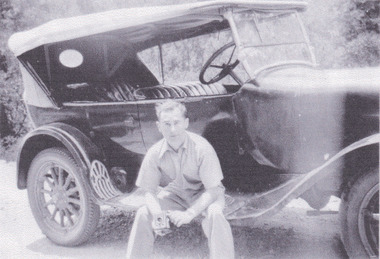 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr Desmond Zwar, 19 October 2000
Desmond was born in 1931 in Beechworth but left at age 11 (in 1944) to be educated in Melbourne at Scotch College but returned to the town for holidays and when he was finished with school. Desmond is the son of Raymond Zwar who was 1 of the 3 brothers who owned the Tannery in Beechworth. He worked there when he was 19 for a year in 1950, when the first Baltic migrants came to town. In 1951, Desmond left Beechworth to work in Albury for a newspaper called the "Border Mail" before moving to Melbourne to write for the "Melbourne Herald". He was later known for becoming a writer, having produced 17 books under his name at the time of the interview. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Mr Desmond Zwar's account of his life in Beechworth during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of the region. He details important historical events and hardships in the region's history that had a lasting local, regional and national impact, including Australia during war time, economic struggles, and the relationships of different social groups in the town. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mr Desmond Zwardesmond zwar, zwar, beechworth, burke museum, raymond zwar, zwar tannery, the tannery, zwar brothers tannery, beechworth tannery, listen to what they say, jennifer williams -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Wilma Wells, 10th February 2000
Born on the 24th of December 1912 at the Three Mile was Wilma Wells. Her mother born into English heritage bore four children, one who died shortly after birth, while her father had Irish heritage and worked at May Day Hills as a warden and a nurse. Wilma married Ted Wells when she was 23 and subsequently had two daughters. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke. Wilma Wells account of her life during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of Beechworth and the surrounding regions. She details important historical places and hardships within the region that have a lasting impact which includes but is not limited to issues with race, women's societal expectations and economic struggles. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Wilma Wells /beechworth, may day hills, oral history, burke museum, wilma wells, hospital, listen, weddings, three mile, picnic -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Unknown, possible Carnelian Agate or Chalcedony
... geology Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth indigo shire ...Although it is not known where these specimens were collected, Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole. Agate occurs when amygdales (gas pockets) form in the upper levels of basaltic lava flows. If these pockets or bubbles are iniltrated by water bearing silica in solution, the fluid dries and hardens in layers, forming round or egg shaped nodules or geodes within the rocky matrix. Agate is formed of a silica mineral chalcedony similar to quartz. The term carnelian primarily refers to the reddish shading of the stone; whether the stone is termed an agate or chalcedony type is often influenced by the degree of colour banding the specimen shows. The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.Three small geological specimens that appear visually consistent with images of rough or unpolished Carnelian Agate or Chalcedony. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, north-east victoria, gemstones, agate, carnelian -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Smoky quartz crystals, unknown
... to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage ...Quartz is an extremely common mineral to find across the world. Quartz can have two forms; Microcrystalline quartz or Crystalline quartz. Microcrystalline quartz is a fine grain quartz where crystalline quartz is often a large crystal. This specimen is a crystalline quartz. Made of silicon oxide, this specimen is called smokey quartz crystals because of its brownish colour. However, the colour of quartz can vary. In addition, quartz are formed in deep-seated igneous rocks and crystallized through hot aqueous solutions. This type of crystal can be found all over Australia, including Beechworth in Victoria. Other places quartz can be found is the Ashburton River area in Western Australia, Marlborough in Queensland, the Lune River area in Tasmania and Kingsgate in New South Wales. This specimen is significant because it is common to find this kind of mineral. While the location of where this specimen was originally from is unknown, it highlights the many places in Australia where quartz is found. It demonstrates that quartz makes up a large portion of Australia's geology. In addition, quartz itself can vary in its colour and shape. This specimen represents one of these variations. That being smoky quartz crystals. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A large hand-sized quartz mineral with shades of brown and gray throughout.Smoky quartz / crystals /locality/ unknown / (needs a wash) /BBgeological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, microcrystalline, quartz, quartz mining, quartz reefs beechworth, smokey quartz crystals, crystals, crystalline, silicon oxide, brown, colour, igneous rocks, magma, ashburton river, western australia, marlborough, queensland, lune river, tasmania, kingsgate, new south wales, nsw -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Common Opal, unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...Common Opal is a mineraloid that is non crystallising and is classed as an amorphous silicate, the chemical composition for Opal is SiO2 nH2O. Opals can develop in weathered sedimentary rock typical in arid regions where limited water enters small gaps in the rock, and the silicate is hydrated. Common opals, unlike precious opals, do not exhibit ‘play of colour’ in which the colour appears to change depending on the angle of view. While precious opals are highly valuable and cut as gemstones for jewellery, common opals can be cut into inexpensive gemstones and are also mined for various uses including as ingredients in ceramics, insulation, fillers, and abrasives. The source of this common opal specimen is unknown, but common opals are found around the world, notable deposits are found in Queensland, South Australia, New South Wales, Peru, Kenya, Nevada, Oregon, and Mexico. This common opal specimen is of historic and scientific significance due to its donation in 1868 as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria and as a typical example of uncut common opal. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A palm-sized amorphous (non-crystallising) hydrated silicate mineraloid specimen in shades of brown, orange, and white.Existing label: Common Opal / Locality unknowngeological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, common opal, opal, mineraloid, amorphous silicates, hydrated silicate -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Dolomite
... ) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage ...Dolomite is a mineral, calcium magnesium carbonate, with the chemical formula CaMg(CO3)2. It is a principle component of various rock types sometimes also referred to as dolomite, including dolostone, dolomitic marble and dolomitic limestone (according to the composition of each type). Dolomite rock is found in sedimentary basins throughout the world, comprising approximately 2% of the Earth's crust. It is formed when lime mud or limestone encounters groundwater containing magnesium. Dolomite can contain elements such as lead, zinc and copper. Dolomite and limestone are used in various construction, landscaping and agricultural processes. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum in 1868 by Alfred Selwyn as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria. It was donated to the Museum in 1868. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole. Dolomite and limestone are mined at several locations in Victoria, including sites in the North-East of the state in Bindi and Limestone Creek. There are notable dolomite deposits in most Australian states. The dolomitised form of the mineral tends to come from older limestone deposits, formed during the palaeozoic era in marine settings, so this specimen may have come from a deposit located along a coastline in Victoria or another state. The specimen is significant as an example of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Hand-sized piece of pale pink dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate) with dark grey rim and hollowed centre. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, dolomite, mineralogy, geological survey, alfred selwyn, limestone, calcium magnesium carbonate -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Kaolin, unknown
... Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth kaolin china clay ...Kaolin is also known as china clay. This specimen came from Dunolly, Victoria and was donated to the Museum in 1868 as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria. This survey helped map and study the geology of Victoria. In Victoria, Kaolin is particularly used as a filler and coating material in paper manufacture. It can also be used in paints, ceramics, rubbers and plastics. There are many kaolin deposits in Victoria but many of these have been mined out and there is not much Kaolin left. Rocks that have a high amount of Kaolinite and it can be formed through the decomposition of other materials. There are two types of Kaolin; hard and soft kaolin. Soft kaolin's are coarse but have a soapy texture. It can also break easily. The hard kaolins have an earthly texture and are finer grained. This means that they are harder to break, unlike the soft kaolin. Hard kaolin's are formed by flocculation in salt water, a process that in basic terms, bonds particles together. Kaolin is a common material in Victoria and that is why it is significant. While this specimen was mined in Dunolly, Victoria Kaolin can also be found Pittong, Pakenham, Bulla, Hallam and Ballarat as well as many other places throughout Victoria. This specimen represents the presence of Kaolin deposits in this region of Australia. It is also significant because Kaolin has many uses and is largely beneficial to many manufacturing processes in Victoria. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Two pieces of Kaolinite mineral with shades of white and graygeological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, kaolin, china clay, dunolly, geological survey of victoria, kaolinite, victoria, mining, mining deposits, geology of victoria, australia, filler, coating material, paper manufacture, paint, ceramics, rubbers, plastics, decomposition, materials, soft kaolin, hard kaolin, flocculation, particles, salt water -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Actionlite and Pyrite
... to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage ...Actinolite is usually found in metamorphic rocks, such as contact aureoles surrounding cooled intrusive igneous rocks. It also occurs as a product of the metamorphism of magnesium-rich limestones. Pyrite is usually found with other sulfides or oxides in quartz veins, sedimentary rock, and metamorphic rock, as well coal beds, and as a replacement mineral in fossils. Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral. It is named after the Greek word "aktinos" meaning “ray” in allusion to the mineral's fibrous nature. Fibrous actinolite is a type of asbestos and was once mined along Jones Creek at Gundagai, New South Wales. Pyrite or "Fool's Gold" is the most common sulfide mineral. It is named after the Greek "pyr" meaning "fire" because it can be used to create sparks needed for a fire if struck against metal or a hard surface. Due to its gold colour, pyrite can be mistaken for gold and often forms alongside it, causing small amounts of gold to be present in rocks containing pyrite. Most importantly, pyrite is an ore of gold. Pyrite is sometimes used as a gemstone but is not great for jewellery as it easily tarnishes. In some fossils of ammonites – shelled cephalopods that died ~66 million years ago – pyrite also replaces the shell. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A small-medium-sized solid specimen with the minerals actinolite (dark green fibrous) and pyrite (brassy) with shades of brown, black/grey, and white. Actinolite is an amphibole mineral in the tremolite-actinolite series of calcium, magnesium, and iron silicates. Pyrite is an iron disulfide mineral.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, geological, mineralogy, pyrite, actinolite, victoria, sewyln, alfred selwyn -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite, unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...Malachite is a water soluble, crystalline, triphenyl methylene chloride salt. It has a close relationship to copper because it is common for Malachite and copper to come from the same ore. Malachite often has shades of green, making it also known as Malachite Green. As a result of it's colour, it is known for being a dye and has been used in the dye industry, the textile industry and in medical fields. Cobar in New South Wales is well known for it's mining. This is because of the number of important deposits present in the area and include three important mining belts where most of the materials are found. These are the 'Cobar belt', the 'Canbelego belt' and the 'Girilambone belt'. The 'Cobar belt' runs underneath the main town. Copper was first discovered in Cobar in 1869 and since then, many deposits of other materials have been found, including Malachite.This specimen is significant because it comes from Cobar, NSW and represents the many deposits of materials found there. Cobar has a long history of mining and is a source of Australia's copper minerals. Malachite is often found in copper deposits meaning that it is representative of Cobar's copper production. Malachite is known for it's vivid green colour and as a result, has many uses, such as meaning used as a dye. This makes it a valuable material and highly significant. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized mineral with shades of brown , white and light green throughout.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, malachite, copper, water soluble, cobar, cobar mines, cobar mining, cobar nsw, nsw, new south wales, mining belts, ore, copper ore, malachite green, dye, green, dye industry, textile industry, desposits, canbelego, girilambone, alfred selwyn -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Oil shale
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...This particular specimen is found in Wolgan Valley, New South Wales. It could be linked to the abandoned oil shale mining sites in Wolgan Valley such as Newnes. Newnes was an industrial complex operational in the early 20th century is now partly surrounded by Wollemi National Park. It produced motor spirit, kerosene, and gas oil. Newnes's Torbanite oil shale rock contained around 350 litres of oil shale per tonne. The Torbanite was mined by the Commonwealth Oil Corporation Ltd. Oil shale is a sedimentary rock and also a form of fossil fuel. It is often formed millions of years ago and usually contain fossilised remains of plants and/or animals. Oil shale is rich in kerogen that releases hydrocarbon when heated. These hydrocarbon can be used as an alternative petroleum or natural gas. The oil-shale rock was converted into oil by "destructive distillation"; the rock being heated until it broke down to form an oily vapour and an ash residue. Oil bearing shale is one of Australia's national assets. There are many oil companies established in Australia. It reflects Australia's rich natural resources as well as connection to the Australia's engineering and oil industry. The booming oil shale extraction businesses can be traced as far back as 1920s. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Piece of dark gray oil bearing shale with shades of light brown and fossilised leavesExisting label: OIL BEARING SHALE with / FOSSILISED LEAVES / Locality: Wongan Valley, NSW / Donor: Miss M. Cambell geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, oil shale, shale, fossil fuels, alfred selwyn, wolgen valley, 1868 geological survey of victoria, rocks, sedimentary rocks, newnes, torbanite, commonwealth oil corporation ltd -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Amazonite, unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...Amazonite is classed as a Tectosilicate and is part of the Feldspar group of minerals. Amazonite forms in a triclinic crystal structure and its chemical formula is K(AlSi3O8). In appearance, Amazonite can range from shades of green to green blue to blue, and often with white streaks or veining. The greenish colour is believed to come from the small amount of lead contained in its composition. Amazonite is named after the Amazon River due to its colour and similarities to another rock found along the riverbanks, although Amazonite is not actually found at or near the Amazon. Although less commonly used in jewellery today, Amazonite has been mined and used by humans for thousands of years and Amazonite jewellery from at least 2000BCE have been discovered in North Africa. Amazonite is found in many locations around the world including Brazil, Peru, Ethiopia, Canada, Russia, Mozambique, Myanmar, Pakistan, China, Madagascar, and the United States of America. This specimen most probably comes from the U.S.A., Amazonite is found in several US states particularly in Colorado, Virginia, Pennsylvania. This specimen is of both scientific and historic significance as a striking blue green example of Amazonite mined prior to 1868 in the United States of America, most likely from Colorado, Virginia, or Pennsylvania. These three states are all locations of significant Amazonite deposits. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A palm-sized Feldspar mineral specimen from the Tectosilicate class in shades of blue-green with white veining.Existing label: green/blue Feldspar / "amazonite" / possibly USA geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, tectosilicate, amazonite, feldspar, triclinic crystal structure, amazonite usa, amazonite colorado, amazonite virginia, amazonite pennsylvania -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite in Conglomerate, Unknown
... Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth geological indigo shire ...Malachite is a green copper carbonate hydroxide mineral and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has been utilised as a gemstone and sculptural material in the past as its distinctive green color does not fade when exposed to light or after long periods of time. Malachite is formed at shallow depths in the ground, in the oxidizing zone above copper deposits. The material has also been used as a pigment for painting throughout history. Malachite is considered a rare gemstone in that the original deposits for the stones have been depleted leaving behind very few sources. In addition, the use of Malachite as gemstones and sculptural materials remains just as popular today as they were throughout history. It is quite common to cut the stone into beads for jewellery. The fact that Malachite has such a rich colour and one that does not fade with time or when exposed to light makes it particularly rare. Although there is no indication available of the locality from which the specimen was sourced, it is likely that the specimen was collected either in South Australia in the vicinity of the Burra Burra mines or in Victoria as part of programs of geological surveying undertaken in the Nineteenth and Twentieth centuries. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with quartz pebbles in red conglomorate matrix presenting shades of cream, brown and green.Existing label: Malachite / (green) in / conglomerate / (white quartz / pebbles / in red matrix /geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, geological, indigo shire, malachite, malachite specimen, australian mines, mines, geological survey, conglomorate, matrix -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Tourmaline in Quartz, Unknown
... Collection Burke Museum Beechworth indigo shire north-east victoria ...Tourmaline specimens are members of a crystalline silicate mineral group based on boron but influenced by elements including aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Specimens present a wide variety of colours and forms according to the specific mix of these elements. Tourmalines are semi-precious gemstones with many applications, including commercial jewellery production. The word 'tourmaline' derives from the Sinhalese term for the carnelian or red-shaded specimens, "tōramalli". This specimen has been classified by geologists as 'Black Schoalou/Tourmaline in quartz'. Schoalou may equate to a common black-hued type of Tourmaline associated since around 1400 with mines in Saxony, Germany near a village called Schorl (today's Zchorlau). If this specimen is part of the 'Schorl' species of tourmaline it is a member of the most common group of Tourmalines, a divalent sodium ion influenced group accounting for 95% of specimens. On assessment, it was noted that the crossed lines (XIs) of this tourmaline have been fractured and rehealed by the quartz matrix in which the tourmaline rests. This item is significant as an example of its type of gemstone and the geological processes leading to its formation. A solid medium-sized piece of Black Schoalou/Tourmaline in a cream and peach coloured quartz matrix. Existing label: Black Schoalou / Tourmaline in / quartz. / Tourmalines XIs have / been fractured and / rehealed with / quartz / C. Willman / 15/4/21 /geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, north-east victoria, tourmaline, quartz, boron, crystals, minerals, gemstones, semi-precious, black schoalou, zchorlau, schorl -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Agate and Quartz pebbles
... geology Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth agate quartz ...Agate occurs when amygdales (gas pockets) form in the upper levels of basaltic lava flows. If these pockets or bubbles are iniltrated by water bearing silica in solution, the fluid dries and hardens in layers, forming round or egg shaped nodules or geodes within the rocky matrix. Agate is formed of a silica mineral chalcedony similar to quartz. Although relatively common and semi-precious, agate has been prized since at least 1450 BC - an intricately carved agate seal was found in the 2015 excavation of a grave belonging to a Mycenaeum priest or warrior near Pylos in Greece. Agate is also used in jewellery and other decorative or ritual purposes due to its often striking appearance. Quartz is found all over Australia, including Beechworth in Victoria. It is formed in deep-seated igneous rocks and crystallized through hot aqueous solutions. It can have two forms; Microcrystalline quartz or Crystalline quartz. Microcrystalline quartz is a fine grain quartz where crystalline quartz is often a large crystal. The colour of quartz can vary. These specimens were collected in Victoria in the vicinity of the Burke Museum. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole.The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.Geological specimens of Agate and Quartz respectively; the fist-sized piece of Agate has peach/coral colouring with grey concentric patterning and the smaller piece of quartz is a uniform yellow/orange shade. Existing label: Local pebbles / (agate and / quartz / (yellowish) / egg-shaped). / BB geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, agate, quartz, north-east victoria, indigo shire, geological surveys -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - North Queensland Agates, Unknown
... geology Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth agate North ...Agate occurs when amygdales (gas pockets) form in the upper levels of basaltic lava flows. If these pockets or bubbles are iniltrated by water bearing silica in solution, the fluid dries and hardens in layers, forming round or egg shaped nodules or geodes within the rocky matrix. Agate is formed of a silica mineral chalcedony similar to quartz. Although relatively common and semi-precious, agate has been prized since at least 1450 BC - an intricately carved agate seal was found in the 2015 excavation of a grave belonging to a Mycenaeum priest or warrior near Pylos in Greece. Agate is also used in jewellery and other decorative or ritual purposes due to its often striking appearance. These specimens originated in North Queensland, which contains noted agate-fossicking regions such as in the area surrounding Forsayth. They were collected in approximately 1852 as an adjunct to the Geological Survey of Victoria. It was donated to the Museum in 1868. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole. The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century. Two solid egg-sized pieces of peach/orange toned agate (a common semi-precious chalcedony, similar to quartz) with a striped pattern, embedded in a light and dark brown matrix. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, agate, north queensland agate, 1852 geological survey of victoria, l. hufer - donor, mineralogy, agate specimen, indigo shire -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Galena (lead sulphide), Unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...Galena occurs in a range of deposit contexts, often in metalliferous veins, such as Broken Hill, Australia; Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, United States.; Clausthal Zellerfeld, Germany; and Cornwall, England. Large deposits also replace limestone, dolomite, or occasionally organic matter, or have a contact-metamorphic origin. Galena is additionally found in cavities, brecciated (fractured) zones in limestone and chert, and in coal beds. This specimen was recovered from Broken Hill NSW and is 60% lead with 8-12 oz/silver to the ton.Galena or 'lead glance' is a grey lead sulfide and the chief ore mineral of lead. It forms isometric crystals in which the ionic lattice is similar to sodium chloride. Galena is brittle and easily weathers to secondary lead minerals, with the upper part of mineral deposits often containing cerussite, anglesite, and pyromorphite. It usually contains silver, which is mined along with its lead content. Other commercially important minerals that form in close association with galena are antimony, copper, and zinc. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A small-sized solid specimen containing one mineral with a sparkly silver metallic lustre exterior and pastel-grey interior.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, galena, lead sulphide, alfred selwyn, broken hill -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Anthracite crystal, Unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...Anthracite typically occurs in geologically deformed areas due to extreme heating – with temperatures ranging from 170 to 250 °C – caused by igneous intrusions or high geothermal gradients. It is most commonly found in northeastern Pennsylvania in the United States; however, smaller amounts are also found in Australia, China, eastern Ukraine, South Africa, western Canada, and other countries. This specimen was recovered from Tasmania and is 85-95% carbon.Anthracite is the mineral name for hard coal and is the least plentiful of all coal types. It is clean to the touch and, when polished, is used for decorative purposes. Before natural gas and electricity, anthracite was used for domestic heating as it produces little dust, burns slowly, and gives off a minor amount of smoke. However, it is also limited in abundance and expensive. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A hand-sized highly metamorphosed coal mineral with a black/steel-grey shiny metallic lustre.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, geological, mineralogy, victoria, alfred selwyn, anthracite -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Greenstone, Hokitika Jade Company, unknown
... as part of the Burke Museum's Geology Collection ...New Zealand Greenstone, also called Pounamu is found on New Zealand’s South Island in riverbeds and boulders, and colours vary depending on the source, but always include green tones. It is a form of the mineral nephrite, also known as jade, and is a tough stone with a crystalline structure, made up of calcium magnesium and iron silicate. Its hardness means it is ideal for carving, and has been used for this purpose throughout history, especially by the Maori people of New Zealand. Greenstone features heavily in Maori mythology, and the traditional name for the South Island, Te-Wai-Pounamu, literally translates to waters of greenstone. Wearing of Greenstone pendants with different carvings is practiced by Maori to represent connection to land and ancestors, or to endow the wearer with certain attributes. The sticker on the base of the specimen identifies it as a product of Hokitika Jade Company. The company, which was active in the 1970s, sold jade and greenstone specimens and ornaments. Hokitika, which started life as an 1860s gold rush town, is the origin of most nephrite found in New Zealand, and the centre of the Greenstone carving industry. The object has scientific and research potential as part of the Burke Museum's Geology Collection, and as and example of New Zealand Greenstone. It also has spiritual significance for it's role in Maori beliefs and communities, where it is both traditionally worn and features in mythology. As a valuable stone regularly used in carving and jewellery, it has aesthetic significance. Sticker on base: "N.Z. Greenstone/ a product of/ Hokitika Jade Coy."geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, new zealand, greenstone, hokitika, nephrite, jade -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Common Opal, Unknown
... of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 ...It is not known where this opal originated. Common Opal is formed from silica-rich water entering the earths crust and hardening into a gel of water and silica-spheres, layered through the specimen. Common opal differs from precious opal in colouration and appearance, with precious opal including more colours, and having a translucent or glossy appearance, where common opal shows less colour and is typically opaque. It scores high on the Mohs hardness scale, and is common throughout the world, especially in Australia, where it is far more prevalent than the highly-prized precious opal. Australia is also the highest producer of opals in the modern world. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid, silica-based mineral specimen of Common Opal in shades of grey, green, and yellow, with a thick grey vein running through the centre. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, opal, common opal, gemstone, mining -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Selwynite, Unknown
... Geology Collection Burke Museum Beechworth mineralogy Heathcote ...Selwynite is a fine-grained, compact green rock made primarily of chromian muscovite (fuchsite) and diaspore. Corundum and fuchsite can occur together in the form of massive aggregates or nodules. Often, copper carbonates are found as earthy films or tiny crystals in joint planes. The mineral name honours the late A. R. C. Selwyn, founding Director of the Geological Survey of Victoria. The particular specimen, a mottled green stone suitable for carving was recovered and found in Heathcote, Victoria, Australia. The rarity and qualities of this mineral attracted commercial mining, which was not successful, but traces of the mine shafts still exist today, and it is still highly valued by mineral collectors.Selwynit is considered to be one of the rare forms of rock because it is composed of phosphate minerals containing zirconium. This is an extremely rare combination found in nature. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A fine grained rock composed of mainly of chromian muscovite (fuchsite) diaspore and corundum.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, mineralogy, heathcote, mineral collectors, selwynite, green rock, rock specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Marble, Unknown
... to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage ...A granular metamorphic rock, marble is derived from limestone or dolomite and composed of calcite or dolomite interlocking grains. Heat and pressure from overlying sediments form it from limestone buried deep in Earth's crust. Graphite, pyrite, quartz, mica, and iron oxides can affect rock texture and colour. This specimen was found in Carrara, Italy. Carrara marble is the most common marble found in Italy, and it gets its name from the region where it is located. The marble was also called Luna marble and was used as a decorative element in buildings and sculptures. It has been quarried since Roman times in the Lunigiana, the northernmost tip of Tuscany, just outside the city of Carrara in the province of Massa and Carrara.Marble is one of the most popular and expensive rocks used in sculpture, architecture, interior decorations, statues, table tops, and novelties. It is available in various colors and textures depending on the chemical composition. The strength of the rock and its ability to hold finer details have made it a favorite among designers. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand sized Marble (metamorphic rock) predominantly white with specks light grey and ochre geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, marble, carrara marble, italian marble, marble specimen, tuscany -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Fluorite (purple)
Fluorite comes in a variety of natural colours and crystal formations and glows under ultraviolet light (the word 'fluorescence' comes from the same etymological source). In its pure form, calcium fluoride, it is a colourless combination of the elements calcium and fluorine, but gains its colour from trace elements that infiltrate or replace calcium within its crystal structure during its formation. Although fluorite crystals polish well and can achieve a high level of lustre, the mineral is very soft (4 on MOHS hardness scale) so it is unsuitable for use in rings and must be handled and stored carefully if used in other forms of jewellery. Most crystals of the mineral are too coarse for decorative purposes but have been mined under the name fluorspar for a variety of commercial and industrial purposes. These include the production of hydrofluoric acid, smelting metal alloys, producing glazes and ceramic finishes and use in medical and dental products. An existing label for this specimen indicates that its origin or collection-point was 'probably USA.' Fluorspar, the form of fluorite used commercially and industrially, was mined in significant quantities in the counties of Hardin and Pope in South-Eastern Illinois throughout the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries. Fluorite was made Illinois' state mineral in recognition of its contribution to the state's identity and economy. The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.The specimen is a piece of purple shaded fluorite (also known as fluorspar), the mineral form of calcium fluoride. The unpolished specimen presents a dark purple interior with a substantial dark grey crust representing the matrix from which the specimen was obtained. Existing label: Flourite / (purple) / probably / USA / BB /burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, fluorite, flourite, calcium fluoride, hydrofluoric acid, jewellery, indigo shire, north-east victoria, mining, illinois, usa, united states, fluorine, gemstones, purple stones -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Bituminous Coal, Unknown
Bituminous coal is the most common type of coal, abundantly found in ancient coal deposits which can be dated back millions of years. Often referred to as soft or black coal, this specimen exhibits a high carbon content, ranging from 76-86%. It also holds a relatively high energy density (27 MJ/kg) meaning that it releases significant amounts of energy when burned. Bituminous coal is most commonly used for electricity generation, as well as in the production of steel. This particular piece of coal was collected as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria in the nineteenth century. It originates from Cape Paterson, a seaside village located in South Gippsland, Victoria (located on Bunurong Country). The discovery of bituminous coal in this locality was first made in 1826 by explorer William Hovell. More discoveries were gradually made over the following decades and in 1859 the Victorian Coal Company commenced the first active coal mining operations in the state by sinking a number of shafts and bores near the area of Cape Paterson. Evidence of this coal-focused past can be found today at the State Coal Mine Museum in the nearby town of Wonthaggi. This specimen is significant as it was collected from the locality of Cape Paterson in Victoria, an area that has since become historically instrumental in the mining of coal and other substances in the state of Victoria. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A solid hand-sized piece of bituminous coal with a shiny black-grey surface and jagged edges.Existing Label: BITUMINOUS COAL / Locality: Cape / Patterson, VIC. burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, state coal mine museum, wonthaggi coal mine, victorian coal company, bituminous coal, coal victoria, coal energy generation, william hovell, cape paterson, coal specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite, Unknown
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral. It has a chemical composition of Cu2(CO3)(OH)2. It often forms within limestone where a subsurface chemical environment favourable for the formation of carbonate minerals can occur. It is a substance that can be found in many different parts of the world including: Australia, USA, Russia and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Malachite has historically been used to produce copper, with mining of the mineral dating back over a period of four thousand years. Due to its beautiful green colourations, it is also commonly used for aesthetic purposes such as in the production of sculptures and jewellery. This particular specimen was collected from the town of Burra, South Australia as part of a geological survey undertaken during the nineteenth century. The locality (located on Ngadjuri Country) has a long history of mining, particularly in copper mining, as the area is rich in copper deposits. The first significant discovery of this was made in Burra (Burra Burra Mine) in 1845 and, at the time, the mine was the largest and richest of its kind in the world, producing nearly five percent of the total world copper output. This specimen is significant as it is considered to be a rare gemstone, as many of the original deposits for the stones are significantly depleted, leaving behind very few sources. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid palm-sized copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with patterns of green colourations Existing Label: MALACHITE / Locality: Burra / S. Aust. Other Label: Confirmed / as Malachite / C. Willman / 15/4/1 / + Bill Birch burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, malachite, gemstone, green gemstone, burra, burra burra mine, burra south australia, carbonate mineral, copper, copper mining, copper mining burra, carbonate hydroxide mineral, copper carbonate, malachite mining, malachite burra, monster mine
