Showing 76979 items matching "coins-australian"
-
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Ambush and Counter Ambush, 1965
... Australian Military Forces: Ambush and Counter Ambush...Australian Military Forces ...A grey spectacled cardboard cover with a dark blue binding. Under the Australian Military Forces Insigna are the details of the booklet. The booklet has dark material down the spine.booklet, australian military forces, ambush, counter ambush -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Royal Australian Engineers, Royal Australian Engineers: Weapons Lessons Aide Memoire
... Royal Australian Engineers: Weapons Lessons Aide Memoire...Royal Australian Engineers ...A white coloured paper with black information on the front. Under the Royal Australian Engineers insignia is the description of the bookle. There are two metal staples down the left hand side.manual, royal australian engineers, weapons lessons, aide memoire -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 19
... Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 19...Australian Army ...A blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Army insignia are the details of the booklet. There are two punch holes down the left hand side.australian army, booklet, training, information bulletin -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Air Force: Firewire Elements And Accessories (Graviner)
... Royal Australian Air Force: Firewire Elements And...Royal Australian Air Force ...A yellow plastic cover with a window in the front. At the top right hand corner reads AAP 7484.013-3M which is written in black texta, Near the top of the cover there is the Royal Australian Air Force Insignia with Royal Australian Air force and Engineering Publication. Through the window is the title of the Manual. Inside a plastic sleeve on yellow cardboard are the full details of the manual. The manual is held together with a large metal slide.royal australian airforce - manuals, firewire elements, engineering -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Report On Written Examinations For Promotion to Captain and Major, Entrance To Staff College, 1977 And Briefing Materials For Written Examinations For Promotion To Captaon And Major, Entrance To Staff College 1978, 1977
... Australian Army: Report On Written Examinations For...Australian Army ...A yellowish coloured cardboard cover with black information on the cover. Under the Australian Army Insignia are the details of the boollet. At the top of the booklet writeen in ink is the name Maj A.W. Sween major aw sweeney, promotion to captain and major, written examinations, briefing materials, royal australian army medical corps, staff college, australian army -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965 (Copy 1), 1965
... Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965...Australian Military Forces ...A brown coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is bound with a black material on the left hand side of the booklet.australian military forces, patrolling and tracking -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965 (Copy 4), 1965
... Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965...Australian Military Forces ...A blu coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is bound with a black material on the left hand side of the booklet.australian military forces, patrolling and tracking -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965 (Copy 3), 1965
... Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965...Australian Military Forces ...A blu coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is bound with a black material on the left hand side of the booklet.australian military forces, patrolling and tracking -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965 (Copy 2), 1965
... Australian Military Forces: Patrolling And Tracking 1965...Australian Military Forces ...A blu coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is bound with a black material on the left hand side of the booklet.australian military forces, patrolling and tracking -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 20
... Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 20...Australian Army ...A blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Army Insignai is the description of the booklet. There are two punch holes down the left hand side of the booklet.australian army, training, information bulletin, map folding -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 22, January 1972
... Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin Number 22...Australian Army ...A blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Army Insignia is the description of the booklet. There are two punch holes down the left hand side of the book.australian army, training, information bulletin -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Meeting Minutes, Minutes of the First Adelaide Conference Australian Primary Producers' Union held in A.N.A. Hall, Adelaide on Tuesday and Wednesday, 17th and 18th September, 1946, 1946
... Minutes of the First Adelaide Conference Australian Primary...Australian Primary Producers' Union ( South Australian ...This document contains the minutes of the 1946 Australian Primary Producers Union first conference .This is a booklet of 47 pages. It has a grey cover with green linen binding and metal staples with black printing on the front cover. It has a postal stamp on the back. The pages contain black typed printingnon-fictionThis document contains the minutes of the 1946 Australian Primary Producers Union first conference .australian farmers' union, 1946 australian primary producers union, warrnambool. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1883
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1883, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side of the coin is inscribed "ONE SHILLING. The engraver of the reverse image was Jean Baptiste Merlen. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1883. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Young Head’, looking left. Reverse; crown on top of wreath. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA DEI GRATIA BRITANNIAR: REG: F: D :” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1883” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1883, queen victoria currency, colonial australia currency, wlliam wyon, jean baptiste merlen, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1885
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1885, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 3 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side of the coin is inscribed "ONE SHILLING. The engraver of the reverse image was Jean Baptiste Merlen. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1885. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Young Head’, looking left. Reverse; crown on top of wreath. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA DEI GRATIA BRITANNIAR : REG : F : D :” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1885” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1885, queen victoria currency, colonial australia currency, wlliam wyon, jean baptiste merlen, numismatics -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Air Force: Oxygen Valves (English)
... Royal Australian Air Force: Oxygen Valves (English)...Royal Australian Air Force ...A yellow coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Top right hand corner reads Australian Air Publication 7551.054-2. Above the RAAF insignia reads Royal Australian Air Force and beside the insignea there is a stamp which reads R.A.A.F. Library Copy No: 2: Base Squadron Amberly. There are three punch holes and tow metal staples down the left hand side. There are two amendments inside the manual.royal australian airforce - manuals, australian air publication, oxygen valves -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumUniform - T-shirt, Country Road, Sydney 2000 Olympic Games Casual Australian Uniform, c.2000
... Sydney 2000 Olympic Games Casual Australian Uniform ...Australian t-shirt from the Sydney 2000 Olympic Games unisex casual uniform (option 1). Designed by Country Road.White T-Shirt with Australian emblem and Sydney 2000 Olympic logo on left sleeve. AUSTRALIA SYDNEY 2000fashion, woolmark company country road, sport, the woolmark company 2000 australian olympic display - exhibition (21/12/2001 - 24/05/2002), sydney 2000 olympic games -
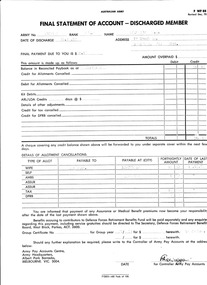 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Document, Final Statement of Account - Discharged Member of Australian Army F WF 88 ( rev Dec 1970), 20/10/1972 12:00:00 AM
... Australian Army F WF 88 ( rev Dec 1970)...Australian Army ...Proforma document of Australian Army : Final Statement of Account Discharged Member issued to PTE 3 Swainston, NE detailing monies to be paid at final discharge on 20/10/1972.payment, discharge, swainston collection -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, Australian Army, Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 1, Infantry Platoon Weapons, Pamphlet No. 6A: The General Purpose Machine Gun, 7.62mm M60, 1962, 1962
... Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 1, Infantry...Australian Army ...A brown coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Top right hand corner reads 7610-66-015-3985. Under the Australian Coat of Arms is the description of the manual.australia - armed forces - service manuals, infantry training, infantry platoon weapons, m 60 machine gun 7.62 -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 1: The Battalion, 1967 (Copy 1), 1967
... Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 1: The...Australian Army ...A speckled blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms reads Infantry Training. The booklet is held togeher with two metal screws on the inside.australian army, infantry training, the battalion -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 1: The Battalion, 1967 (Copy 4), 1967
... Australian Army: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 1: The...Australian Army ...A speckled blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms reads Infantry Training. The booklet is held togeher with two metal screws on the inside. australian army, infantry training, the battalion -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin, Number 17, Airmobile Operations (Copy 1), 1970
... Australian Army: Training Information Bulletin, Number 17...Australian Army ...A blue coloured cardboard cover with black information n the front. Under the Australian Army Insignia are the details of the booklet. There are two punch holes down the left hand side of the booklet.australian army, training, information bulletin, airmobile operations -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: The Division In Battle, Pamphlet No. 11: Counter Revolutionary Warfare. 1965 (Copy 1), 1965
... Australian Army: The Division In Battle, Pamphlet No. 11...Australian Army ...A light blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms is the description of the booklet. The booklet is held together with two metal screws on the inside of the cover.booklet, division in battle, counter revolutionary warfare -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: The Division In Battle: Pamphlet No. 2: Administration, 1966 (Copy 3), 1966
... Australian Army: The Division In Battle: Pamphlet No. 2...Australian Army ...A light blue coloured cardboard cover with the details in black on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms is the title of the booklet. the booklet is held together with two metal screw on the inside of the booklet. booklet, division in battle, australian army, administration -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 2: The Platoon, 1967 (Copy 6), 1967
... Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4...Australian Military Forces ...A blue colourer carboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is held together with two metal screws from the inside of the cover. .australian military forces, infantry training, the platoon -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 2: The Platoon, 1967 (Copy 7), 1967
... Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4...Australian Military Forces ...A blue colourer carboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is held together with two metal screws from the inside of the cover. .australian military forces, infantry training, the platoon -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 2: The Platoon, 1967 (Copy 9), 1967
... Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4...Australian Military Forces ...A blue colourer carboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is held together with one metal screw from the inside of the cover. australian military forces, infantry training, the platoon -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Military Forces, Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4, Part 2: The Platoon, 1967 (Copy 10), 1967
... Australian Military Forces: Infantry Training, Volume 4...Australian Military Forces ...A blue colourer carboard cover with black information on the front. Under the Australian Coat of Arms are the details of the booklet. The booklet is held together with two metal screws from the inside of the cover. australian military forces, infantry training, the platoon -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Medal, Australian Defence Medal
... Australian Defence Medal...Australian ...the Australian Defence Medal - the ADM was approved in 2006 to be awarded to Australian Defence Force personnel who have demonstrated their commitment and contribution to the nation by service for an initial enlistment period of four years service, whichever is the lesser.Round silver replica medal depicting Australian coat of arms. Red ribbon with two thin white stripes.The Australian Defence Medalaustralian, defence, medal -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumCurrency - Coin, Australian One Penny 1932, 1932
... Australian One Penny 1932 ...Found at POW camp 13 site post war by war time guard. Contained in a gold coloured material covered display box.Circular Commonwealth of Australia copper coin, value one penny, dated 1932. Head and shoulders impression of George V wearing a crown on reverse sideone pennycamp 13, penny coin, australian currency, 1932 australian penny -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionReport, Saunders, Cheryl, The constitutional centenary and the Australian courts : seventh AIJA oration in judicial administration, 1996
... The constitutional centenary and the Australian courts...Australian Institute of Judicial Administration ...Seventh Australian Institute of Judicial Administration (AIJA) oration in judicial administration Delivered by Profession Cheryl Saunders AO at The Melbourne Business School The University of Melbourne Friday, 23 February 1996ISBN: 1875527168constitutional law -- australia, courts -- australia, judicial review -- australia, australia -- constitutional law, constitutional centenary, high court of australia
