Showing 326 items matching "ivory"
-
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Thomas pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Pessary, Thomas style, made of black vulcanite. Inscribed with number "60". intrauterine device, pessary -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Thomas retroflexion pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape. Size small.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Uterine stem pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape, and in the "eyeglass" stem style.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Ringwood Bowling Club- Ladies Section, C1 Division Pennant winners Season 1970-71
Sepia photograph "Attached to photograph" Players names" Back Row- L to R: A Holliday, D Sommerville, D Ivory, P Nicks, M Westmore, L Williams, G Gabbe, M Allsop. Front Row- L to R: M Henchel, A Dixon, O Turner, M Causon, R Kofoed, S Lowry, C Montgomery. Absent R Nally. -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, W Edmends, Grade 2, Kew State School, 1915
Kew Primary School is the oldest school in Kew and was established on November 1, 1870. It predates the commencement of State education with its genesis lying in the year the colony was founded, namely, 1851. Nicholas Fenwick was recognized as the founder of Kew when he purchased an area of 122 acres (Lot 87) on which Kew Primary School now stands.Grade 2, Kew State School, 1915. One student, Ray Watson, front row, sixth from left is identified by an arrow and cross. Inscriptions front: "Kew State School. Grade 2. Year 1915. Ray Watson. Presented to the Kew Historic Society by Ray Watson, Oct 1978." Inscriptions reverse: "KH-229. Kew State School, Melbourne, Victoria. Grade 2 1915. Teacher Miss Thomas. Albert Raymond Watson. Age 7 years. Mrs Ivory's brother."kew state school, kew primary school -- peel street -- kew (vic.), schools -- kew, government schools -- kew (vic.) -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - INFANT'S IVORY COLOURED SILK DRESS
Clothing. Infant's ivory coloured waisted silk dress. High round neckline with one cm lace trim. Bodice extends to short sleeves with 2.5 cm eyelet lace at hem. Embroidered leaves and vines at centre frfont of bodice. Eyelet lace around waistline (1.5 cm) with gathered skirt. Centre back opening (22 cm) fastened at neck with one press-stud and ribbon tie at waist ( Ribbon missing).costume, children's, infant's ivory coloured silk dress -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - INFANT'S IVORY COLOURED DRESS
Clothing. Infant's ivory coloured waisted silk dress. High round neckline with one cm lace trim. Bodice extends to short sleeves with 2.5 cm eyelet lace at hem. Embroidered ribbon bow and flowers at centre front of bodice. Eyelet lace around waistline (1.5 cm) with gathered skirt. Centre back opening (22 cm) fastened at neck with one press-stud and ribbon tie at waist (Ribbon missing).costume, children's, infant's ivory coloured silk dress -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - INFANT'S IVORY COLOURED COTTON NIGHT DRESS
Clothing. Infant's ivory coloured cotton night dress.High round neckline with casing and lace frill trim (1.5 cm).Front yoke of broderie lace and horizontal strip of lace at waist with square pattern. Long straight sleeves with casing and 1 cm of broderie lace with scalloped edge. Centre back opening (30 cm) fastened with cotton tape tie through casing at neckline and one button and button hole at waistline.costume, children's, infants ivory coloured nightdress -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - INFANTS NIGHTDRESS, 1880-1900
Clothing. Infant's ivory coloured nightdress. Front yoke with 1 cm X 14 cm centre lace insert. Lace trim around neckline. Centre back opening(24cm) with tape ties at neck and waist. Lace trimmed 58cm fabric ties attached at waist at centre front. Eyelet lace trim around waist. Ribbon missing. Skirt gathered at waist. Long sleeves with lace trim at wrist. French seams.costume, children's, infants ivory coloured nightdress -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - CHILD'S IVORY COLOURED DRESS, 1880-1900
Clothing. Child's ivory coloured sleeveless yoked linen dress. High round neckline with wide fold down lace edged collar (12 cm) dipping to a V shape at centre front and on either side of the back opening. Skirt is gathered into the yoke back and front. Arm holes edged with four cm lace. Full length back opening fastened with two one cm imitation pearl buttons at top and bottom of yoke.costume, children's, child's ivory colored dress -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook, Neil Maclean, "Each a new Leviathan - Great Passenger Ships in Melbourne", 2014
"Each a new Leviathan - Great Passenger Ships in Melbourne" 174 page soft cover book about Great Passenger ships which have visited Melbourne. Author Neil Maclean. Includes some brief local history in Introductiontransport - shipping, piers and wharves - station pier, piers and wharves - princes pier, war - world war i, war - world war ii, migrants, neil maclean -
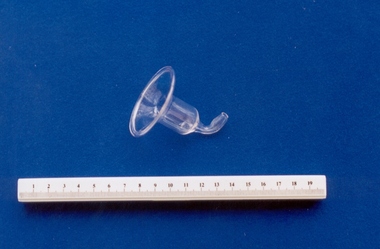 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Glass nipple shield associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
A rubber teat would be attached to the top of this nipple shield for breast feeding. From 1801 onwards, nipple shields were available in a variety of materials, such as pewter, horn, bone, ivory, wood, glass and silver. They varied in shape from a bell to a flatter, cap shaped appliance. With the application of the nipple shield, the baby was able to take milk from the breast without giving added trauma to the nipples. In the ante partum period the nipple shield could be worn to assist in drawing out flat nipples; or, as it was known during this period, for the formation of "new nipples". (Fildes, Valerie. 'Breasts, Bottles & Babies - A History of Infant Feeding', 1986) Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Glass nipple shield. Shape resembles that of a bell.infant feeding, midwifery -
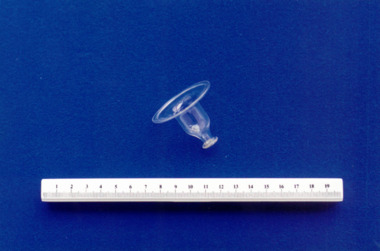 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Glass nipple shield associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
A rubber teat would be attached to the top of this nipple shield for breast feeding. From 1801 onwards, nipple shields were available in a variety of materials, such as pewter, horn, bone, ivory, wood, glass and silver. They varied in shape from a bell to a flatter, cap shaped appliance. With the application of the nipple shield, the baby was able to take milk from the breast without giving added trauma to the nipples. In the ante partum period the nipple shield could be worn to assist in drawing out flat nipples; or, as it was known during this period, in the formation of "new nipples". (Fildes, Valerie. 'Breasts, Bottles & Babies - A History of Infant Feeding', 1986) Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Glass nipple shield. Shape resembles that of a bell.midwifery, infant feeding -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Handbook of the arts of the Middle Ages and Renaissance, 1855, 1855
This book was translated from the French of M. Jules Labarte.Charcoal hard covered book with over 200 beautiful black and white woodcut illustrations. Illustrations include: Ivory chair at Ravenna - Abbey of Lorsch Martha and Mary advancing to the savior (Chichester Cathedral sculpture) The Navicella mosaic by Giotto Crown of Charlemagne (Imperial Treasury Vienna) Sword of Charlemagne (Imperial Treasury Vienna) Shrine of the Migi (Cologne Cathedral) Cup of Lapis Lazuli Iron Crown of the Lombards (Monza Cathedral) Irish Harp Bayeux TapestryLibrary cards, dates stamps, etcballarat technical art school library, library cards and date stamps, book plate, art, middle ages, renaissance -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Award - GOLDEN SQUARE STATE SCHOOL COLLECTION: BENDIGO ADVERTISER SHIELD, 1928
Golden Square State School collection, Bendigo Advertiser Shield for Bendigo Competitions School Choir Contest Section B Grade VIII & Under (Under 14 Years) finally won by Golden Square. Wooden shield with attached metal badges depicting winning schools, a ribbon with Bendigo Advertiser name and a central enamelled Lyre surrounded by a green laurel wreath, small ivory name plate at bottom reading Prescott & Dawe Silversmiths Bendigo.Prescott & Dawe Silversmiths Bendigotrophies & awards, public events, music -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Instrument - FORTUNA COLLECTION: THE MELBA ACCORDION - FORTUNA
Wooden musical instrument purportedly from Fortuna Villa.The Melba Accordion, black lacquered timber with some red leather covering, metal corner pieces which read made in Germany (G missing) buttons of ivory or bone connected to keys, pull knobs on side, bellows of grey and white paper. Contained in a black wooden box with metal hinges and handle, also in box is a small wooden piece, possible a tuner, with inserts of mother of pearl flowers & brass ends.Melba Accordion Made in Germanymusical instruments, wind, accordion -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Footwear - LEATHER BOOTMAKING TOOLS AND COMPANY STAMP OF J.M.OKEY
Okey, J M Leather Bootmaking Tools and Company Stamp. An open Wooden box of assorted Bootmakers 'Leather working'Tools.(Some appear hand-made')Some tools seem to be chisels, cutters, crimpers etc. The box is approx. 30cm x 15cm x 15cm. These include a metal Stamp that creates an oval-shaped label. 'John M Okey., Boot & shoe-maker, Kangaroo Flat'. Also included is an 'Ivory?' Chisel. Donated by 'Mr Reed' 7.8.69. -
 Bendigo Art Gallery
Bendigo Art GalleryFurniture, ERARD & Co, Napoleon III upright piano, 1877
(underside of falboard) c; ERARDdecorative arts, piano, furniture, musical instrument, keys, music, upright piano, ivory, marble, french, napoleon, erard & co, fortuna villa -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Thomas pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
This pessary was manufactured by Allen and Hanburys in three sizes - large, medium, and small. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Thomas style supportive antiflexion pessary. Pessary is made of black vulcanite and is inscribed with number "60". Pessary is thickened at distal end and tapered at proximal end.intrauterine device, pessary -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Thomas pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
This pessary was manufactured by Allen and Hanburys in three sizes - large, medium, and small. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Thomas style supportive antiflexion pessary. Pessary is made of black vulcanite and is inscribed with number "65". Pessary is thickened at distal end and tapered at proximal end.intrauterine device, pessary -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncAccessory - Woman's Visiting Card Case, 19th century
Calling cards, also called visiting cards, visiting tickets, or compliments cards, originated in their paper and ink form in France in the 18th century and their popularity quickly spread across Europe and the United Kingdom. Victorian calling cards were large and could be extremely ornate, with the names usually printed instead of handwritten. Women's cards were squarish and fairly large, usually about 2.5 x 3 inches. Men's cards were smaller and more rectangular, meant to fit in a breast pocket, while women often carried their cards in specially made cases of silver, tortoiseshell, ivory, or mother-of-pearl. (Source: Claire Green: Calling Cards and Visiting Cards: A Brief History)Nineteenth century silver, leather and silk woman's visiting card case, donated by M. Swanston MacDowell. The case has a tooled brown leather cover attached to a silver frame. The interior of the card case, used for visiting cards, is lined with maroon silk with brown leather pockets. The pocket on the left is embroidered in silk with a spray of flowers.On one of the interior leather pockets "Kew Historical Society" has been crudely inscribed in biro. A card placed in the item includes the words "Visiting Cards. M. Swanston MacDowell".visiting card case, card cases -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Digital photograph
The foundation stone of the Victorian Seamen's Institute, which is to be erected in Beach street, Port Melbourne, was laid on Wednesday afternoon by His Excellency the Governor, in the presence of Lady Loch, the Post master-General (Mr. F. T. Derham), Sir James MacBain, Colonel Sargood, and Mr. S. Fraser, M's.L.C., the Dean of Melbourne, the members of the local council, Mr. John Blyth, and a large concourse, of spectators. Captain Pasco then presented His Excellency with a silver trowel and a silver-mounted ivory mallet, whereupon the stone was lowered into position. The stone was placed in the 1937 building then given into the care of the Port Melbourne Historical and Preservation Society during the demolition in 1995. Then it was placed in the bluestone wall in front of the building with the other building stones.The 1888 Mission was sold in the 1930s when the new building, designed by Harry Norris was open in 1937. The 1888 building is still standing but is now for commercial use (restaurant). Colour photograph depicting the foundation stone of the Port Melbourne Mission to Seamen 1888.THIS MEMORIAL STONE WAS LAID BY HIS EXCELLENCY SIR HENRY B. LOCH C.C.M.C. K.C.B. GOVERNOR OF VICTORIA ON WEDNESDAY THE 5TH DAY OF SEPTEMBER A.D. 1888.lord henry brougham loch, frederick sargood, sir james mcbain, simon fraser, john blyth, captain crawford pasco, port melbourne, beach street, nott street, frederick williams, brick, frederick thomas derham, pmhps, port melbourne historical and preservation society, port melbourne mission -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDress - Wedding Ivory Satin
This dress was worn by Margaret Vyner on her wedding day to Ian Mc Kendrick. Margaret's mother's name was Rita. Margaret was living with her family at Tawonga, Ian was living at Mt Beauty.The couple were locals of the Kiewa Valley. Ian worked at the Mt Beauty Post Office and Margaret at the Tawonga & District Hospital. Their 3 children grew up in Mt Beauty.Ivory / off white satin wedding dress with a train at the back. Puffed with stiffening & padded long sleeves which come to a point at the wrist where fastened with a press stud. Ruched cross over bodice with a V neckline with a semi circular skirt. Plain back to the waist and a half self belt fastened at the back by 3 covered buttons and 3 loops. Left side as a plaquet fastened by 2 hooks and eyes. Semi circular skirt which has, at the rear, a 100 cm train with a finger loop.wedding dress; margaret vyner (mckendrick); tawonga; ladies' clothing -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: ATTENTION
Bendigo Advertiser "The way we were" from Friday, November 7, 2003. Attention: then 2nd Bendigo Cub Scout group on October 4, 1953. Pictured I. Shadforth, J. Graham, J. Samson, A. Wells, M. Tootal, J. Thomas, K. West, R. Boulton, I. Yandell, D. Woods, I. Dalrymple, R. Pocock, B. Ivory, B. Hocking, G. Dalrymple, P. Woods, G. Peacock, B. Richie, G. Gould. Other names unknown.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumCarpet Samples, Godfrey Hirst and CO. Pty Ltd, c.1990
Carpet samples created by Godfrey Hirst, a carpet mill whose history spans back to 1865 when the Victorian Woollen and Cloth Manufacturing Company began operations in Geelong and was purchased in the 1890s by the man Godfrey Hirst. Godfrey Hirst’s entrepreneurial skills and knowledge of the industry led to the great success which saw the company expand in multiple forms over the next century and a half. Today, thousands of metres of carpet are produced by Godfrey Hirst every day, and their flooring can be found in millions of homes. These 6 carpet samples date from the early 1990s and each have a unique colour pattern and design.Each carpet sample is made with a pile fibre that is 100% wool. The primary backing of the carpet is a woven polypropylene with a secondary backing a woven jute. Carpet 8102.1's colour name is Slate. It has a dark grey background with a red and blue diagonal stripe. The pattern repeats in a 10cm x 11.5cm block. Carpet 8102.2’s colour name is Terracotta. It is a mostly block pink colour with no repeating pattern. It has occasional flicks of grey. Carpet 8102.3’s colour name is Arctic Night. It has white, light blue and grey colours repeating one after another in a diagonal line. Carpet 8102.4’s colour name is Ivory. It has a brown background with a cream colour diamond. The pattern repeats in a 15cm x 15cm block. Carpet 8102.5’s colour name is Glenwood. It has a thin darker green and lighter green horizontal stripe spanning its entire width. These stripes repeat the height of the carpet. Carpet 8105.6’s colour name is also Ivory. It has a brown background with a cream colour leaf pattern. The pattern repeats in a 92cm x 92cm block.Wording on rear: Numerous. See Media.godfrey hirst, carpet, textile manufacture -
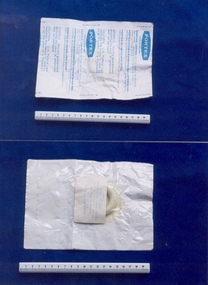 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Ring pessary associated with Dr Geoff Bishop, c. 1977, Portex Ltd, England, c1977
This pessary came from Professor Geoff Bishop's rooms, Mollison House, 386 Albert Street, East Melbourne. As well as the UK, Portex had divisions in the USA and Canada. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids. Portex brand ring pessary in original packaging. Consists of circular ring of cream vinyl, in sterile sealed pouch with transparent plastic at back. Stamped on pouch "PORTEX ENGLAND", and the text "USE BY FEB 77" and "CONTROL No F/1 505". The ring is size 700/300/056 - 56mm. A sticker on the back of pouch gives instruction for cleaning the pessary.pessary, intrauterine device -
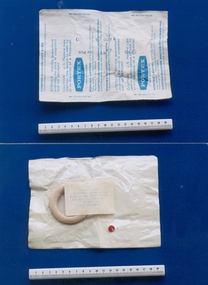 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Ring pessary associated with Dr Geoff Bishop, c. 1977, Portex Ltd, England, before 1977
This pessary came from Professor Geoff Bishop's rooms, Mollison House, 386 Albert Street, East Melbourne. As well as the UK, Portex had divisions in the USA and Canada. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient time, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Portex brand ring pessary in original packaging. Consists of circular ring of cream vinyl, in sterile sealed pouch with transparent plastic at back. Stamped on pouch "PORTEX/MADE IN ENGLAND", and the text "USE BY JAN 77" and "CONTROL No 06 88". The ring is size 700/300/065 - 65mm. A sticker on the back of pouch gives instruction for cleaning the pessary. A red dot is also stuck to the back of the pouch.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Ivory silk and tulle bridesmaid's outfit, 1874
This bridesmaid's dress was owned and first worn by Alice Frances Henty, the daughter of Francis Henty and Mary Ann (Lawrence) Henty. The outfit was worn at the marriage of her friend Miss Hopkins to Mr ST Staughnton in 1874. Alice's father, Francis Henty, was the youngest son of Thomas Henty, who with his family, their retainers and property moved to the Australian colonies between 1829 and 1832. In 1834, Francis’ older brother, Edward, sailed from Launceston in Van Diemen’s Land to what was to become Portland in the western part of Port Phillip District [Victoria]. Francis, together with the first flock of Merino sheep [in Victoria], followed some months later. The first and second generations of the Henty family established vast pastoral properties in the Western part of the Port Phillip District. Francis Henty managed ‘Merino Downs’ near Casterton, while also living in his retirement at ‘Field Place' in Kew. The Henty Collection of nineteenth and twentieth century clothing, including outerwear and underwear, was collected, stored and exhibited over time by female family members descended from Francis and Mary Ann Henty. During the twentieth century, items from the collection were modelled in two fashion parades by various descendants [1937, 1959]. The items in the collection are historically and aesthetically significant, with provenance provided by oral and written tradition within or held by the family. A number of the items in the collection are very rare survivors, and provide researchers with the evidence needed to reconstruct the lives of notable women in the Port Phillip District [later Victoria] during the nineteenth and early twentieth century.An ivory silk skirt and matching jacket worn by Alice Henty, aged 22, at the marriage of her friend Lizzie Hopkins and S.T. Staugnton in 1874. The ivory silk satin peplum jacket is boned, tailored, and fitted with many princess line panels. The front closure has handmade embroidered buttonholes and covered buttons. The collar and sleeves are decorated with gathered silk tulle frills. The peplum back features a silk cord bow decoration. The skirt with bustle and train features a central panel with hand ruching and silk satin piping. It is decorated with five rows of pleated silk tulle frills. Measurements (mm): PEPLUM JACKET Girth - Neck 317.5, Chest 914.4, Waist 698.5, Hip 965.2, Cuff 279.4, Hem circumference 1168.4. Vertical - From neck to hem 558.8, Front waist to hem 254, Back neck to hem 838.2, Back waist to hem 241.3, Sleeve length 279.4. Horizontal - Neck to sleeve head 165.1,Cross back 292.1, Underarm to underarm 393.7. SKIRT Girth - Waist 635, Hip 914.4, Hem circumference 3810. Vertical - Front waist to hem 1092.2, Back waist to hem 1701.8. fashion -- 1870s, alice frances (henty) hindson, women's clothing, bridesmaid's dresses -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Smoker's Items, 1940s
These cigarette and cigar tin boxes belonged to Dr.William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. They were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by his daughter, Bernice McDade. They are part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R. ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being a historical example of medicine from the late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.Three metal square boxes with lids, once containing cigarettes or cigars from variuos tobacco companies.Box 1: 'Pikeur Ritmeester. 20 Cigars. Made in Holland.' and Cavalier with Horse logo. Box 2: 'Cork Tipped, Trade Mark, Craven A Virginia Cigarettes. 50 Craven A Cork Tipped. ' and cat logo. Box 3: 'By Special Appointment. De Reske. The Aristocrat of Cigarettes. J Millhoff & Co Ltd Piccadiily W.' Virginias Ivory Tipped. Sole Distibutors Godfrey Phillips Ltd London & Melbourne.' and two logos.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, smoking, cigars, cigarettes, pikeur, ritmeester, craven a, de reszke, millhoff -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster, medium
This type of pessary was often used for uterine malpositions and displacements and usually made from vulcanite. This particular object is known as Hodges moulded pessary. [Source: George Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids. Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape, and medium size. "I.T.A.Y." inscribed on upper curve.pessary, intrauterine device
