Showing 638 items matching "magazine article"
-
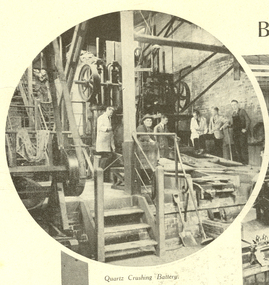 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Newspaper, Ballarat School of Mines and Industries and Junior Technical School double page newspaper article, 25/08/1934
The Ballarat School of Mines was the first school of technical education in Australasia.Double page, double sided, newspaper article from The Weekly Times with 10 images and captions depicting scenes within the School of Mines and Industries, Ballarat Technical Art School and Junior Technical School, Ballarat. Verso: Top Half page: 5 photographs on Callawadda, A pastoral district near Glenorchy Verso Bottom Half page: large photograph of boys attending the Junior technical school at Ballarat Verso Right hand page: 7 "Intersting photographs from England, Scotland and The United StatesSide A: Magazine- Section 8, The Weekley Times, Heading and captions, torn lower left corner to centre, small tears throughout especially left hand side and centre fold, Side B: the weekly times, school of mines and industries, scientific instruments, junior technical school, ballarat, smb, ballarat school of mines, university of ballarat, 1934, callawadda, glenorchy, boys, hutchings, mr j. c. hutchings j.p., state school, bryn avon homestead, broadcasting, mrs hutchings, sheep, xray, cancer treatment, northern belle, loch lomond, oxford college, red lion brewery, aldershot tattoo, siege of namur, battleship, idianapolis battleship, new york, quartz crushing battery, machine shop, pottery, electrical engineering, art department, dressmaking, building, woodwork, assaying, laboratory, architectural drawing, engineering drawing, drawing, assay, drawing from the antique, plaster casts, assay room, ballarat technical art school, bicycles -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Craft book, Norma Benporath, Tatting, circa 1940's
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doilies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. This book has photographs and detailed instructions for a wide range of tatted edgings and insertions suitable for household linens such as towels, doilies and tablecloths as well as patterns for whole mats. Stanley E. Mullen (a businessman) developed Semco Pty Ltd which began as a Melbourne based importation company in 1907. The first three letters of Semco's name were his initials. In 1915 it began manufacturing women's apparel, whitework and transfer patterns. In 1924 the company moved to Black Rock, Victoria and continued to produce an extensive range of needlework patterns and handcraft instruction booklets, threads etc. up until the late 1970's. Semco had a staff that included many young women. It was noted by E.J. Trait (editor of the local newspaper "Standard News") that the firm provided them with good working conditions and the correct rate of pay for women in a time of war - the starting rate for 15 year olds, mainly girls at Semco was 25 shillings per week. During World War 2, Manpower Regulations could be used to coerce workers to move into jobs that supported the war effort, but Trait argued that being employed at Semco could make this unlikely as the firm made some goods essential for the war effort. He even suggested that women be encouraged to produce needlework items (and play a part in the war effort) by sending them as presents, to the troops up north. He also heaped praise on the Semco workplace - noting that no Saturday work was the norm, allowing employees to shop and have "hair-do's" before enjoying a relaxing weekend! Semco also had a female cricket side in the women's Saturday association. After the war the firm stayed in production until the early 1990's when it was taken over by Coates-Paton Pty Ltd. Norma Benporath (1900 - 1998) was an expert in tatting techniques and taught and published extensively on the subject. She was born in New Zealand with impaired sight but cataract surgery restored 50% vision to one eye. She was inspired to learn tatting whilst watching her aunt tat and being told that tatting did not require as much sharp vision as embroidery. She quickly learnt to design her own patterns and published over 1000 tatted lace patterns between 1929 and 1952. She became a regular contributor to magazines (such as Home Beautiful) and newspapers across Australia. Her designs were also published in New Zealand, South Africa as well as the U.K. and U.S.A. When Semco, a thread manufacturer, noticed a rise in the sale of fine crochet threads, they realized they had an untapped market to explore. Norma designed a collection of tatting patterns for Semco that were used to help promote their threads. Norma also worked with Semco to produce a line of threads and shuttles specifically suited to tatting. In 1997, Norma was inducted into the "Order of Australia" for "Service to the craft of tatting as a designer and through the international publication of her patterns".This item is an excellent example of the needle work being enjoyed by women in the 1940's in Australia and the skills of the Australian designer, Norma Benporath. It is also an example of the trend that emerged for craft companies such as Semco to publish pattern books in order to advertise their own materials.A 32 page soft cover instruction book with green front and back covers showing two tatted doily designs. The book includes black and white photographs and written patterns by Norma Benporath.Front cover - "TATTING" "For / EXPERTS/ and / BEGINNERS" "By/Semco" "SEMCO INSTRUCTION BOOK" "No. 16" "WITH ILLUSTRATIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS" "9" Back cover - "FOR INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING SEE PAGE 22" "Published by Semco Pty. Ltd." "BLACK ROCK, 29, VIC"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, tatting, tatting instruction book, tatting patterns, tatting shuttle, semco, semco pty ltd, norma benporath, needlework, handcrafts, household linen, craftwork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Tatting Designs, circa 1940's
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read. This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered, 16 page instruction book titled "Tatting Designs". It has black and white photographs and detailed patterns for tatted doilies, a tray mat, a chairback and arm rests, a cheval set, a luncheon set, collars and edgings for an underskirt, gloves and handkerchief. It is published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "Paragon's No 105" "PRICE 1/3" "Tatting Designs" "Household Linens * Personal Wear" Plus a stylized drawing of a deerflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, tatting book, tatting patterns, craft, handiwork, handcraft, needlework, shuttle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Learn to Tat, circa 1940's
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read.This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered 16 page instruction book with black and white photographs and detailed instructions explaining how to tat and eight tatting projects including how to make a collar and handkerchief edgings, published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "PARAGON BOOK NO. 104" "PRICE 1/3" "Learn to/ TAT' Back Cover - "36/D5 E/A DO2" - handwritten in pencil flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, tatting, tatting pattern book, tatting instructions, handicraft, needlework, shuttle, tatting shuttle, paragon needlecraft, paragon craft book -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Tatting Shuttle, Aero Needles Group Ltd, Mid to late 20th century
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots.The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century.Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic (as is item 8535.1). The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound (e.g. item 8535.2). The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace. One type of tatting shuttle produced by "Aero" from the 1930's to the late 1960's was an anodized grey coated aluminium shuttle with a sharp pick at one end. In the 1970's it was superseded by the grey plastic "Aero" which has a removeable bobbin which you can put on the end of the shuttle to make thread winding easier and an embedded crochet hook for joining picots. The "Aero" company developed in Redditch, England - a town renowned as a centre for manufacturing needles. Firms run by Henry Milward and Abel Morrall were based in Redditch and by the 18th century Redditch was manufacturing one million sewing needles per year. Abel Morrall Ltd launched the "Aero" brand in 1936 and greatly expanded the firm's product line to include tatting shuttles and knitting needles. The classic plastic "Aero" tatting shuttle was manufactured in England from the early 1970's until the 1990's. These items are significant as examples of easily accessible handiwork tools that enabled women in the 1930s -1960s to be able to decorate and personalize their household linen and clothing.Shuttle no. 8535.1 is a beige, boat shaped plastic shuttle with enclosed ends, small round central indentations on both sides and an enclosed black removeable bobbin. The shuttle has a grooved point at one end to hold a bobbin and a small metal crochet hook at the other end. Shuttle no. 8535.2 is a beige, boat shaped metal shuttle with pointed ends that are open but snug, small round central indentations and two smaller circular markings (on both sides) and two internal posts with cream thread wound around.Shuttle no. 8535.1 - "AERO" / "ENGLAND" Shuttle no. 8535.2 - "AERO' / "ENGLAND" "39c" (written in ball point pen)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, tatting shuttle, aero company, handwork, handwork tool, craft, handcraft, needlework, tatting -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph (black & white), Ferdinand Moritz Krause
Civil engineer and geologist Ferdinand Moritz Krause lecturered at the Ballarat School of Mines from 1880 to 1895. He was born at Kassel, Germany on 24 February 1841, the youngest son of Frederich Wilhelm Krause. Ferdinand Krause married Amy Augusta Dimock. He died in South Africa 16 June 1918. In June 1880 Krausé was appointed to the Ballarat School of Mines as lecturer in 'geology, palaeontology, mineralogy, electricity, magnetism, scientific mining, geological and topographical surveying' and as museum curator. In 1881 he was appointed Professor of Geology and in 1892 was elected president of the Staff Association. He was held in high repute by his students and also known as a keen musician. He resigned from the School of Mines to be lecturer in mining at the University of Melbourne from June 1895 to January 1897. Whilst at Ballarat in 1887-90 he had completed geological maps and reports on the parishes of Haddon, Carngham, Scarsdale, Lillerie, Smythesdale and Comeralghip; these were published in 1898. The Institute of Surveyors elected him a member in 1891. His Introduction to the study of Mineralogy for Australian readers was published in Melbourne in 1896. In January 1897 he became manager of the General Gordon mine near Kalgoorlie. In 1900 he contributed an article to the Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine on the mining geology of Kalgoorlie. Invited by a former student, George Denny, Krausé left for South Africa in 1901. His last work was a geological map of the Barberton area, Transvaal, published in March 1918. He died on 16 June, survived by his wife, three sons and a daughter. (http://adb.anu.edu.au/biography/krause-ferdinand-moritz-3971, accessed 20 November 2018) Black and White photograph of the head and shoulders of Professor Ferdinand Krause of the Ballarat School of Mines.ballarat school of mines, ferdinand krause, geology, fm krause, krause, ballarat school of mines museum -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine, Sporting Shooter
Two copies of the Magazine 'Sporting Shooter' dated April 1999 and May 2005. .1) April 1999. Eighty page magazine with articles such as looking after your hunting dog, Australia's Toughest Game, Pigs in Mud, Black Panthers in Oz, scoring Trophy Heads, Hunting in New Zealand. .2) May 2005. 106 page magaine including an article called "Big Cats in the Bush? by Rebecca Lang.australian animal folklore collection, black panthers, panther, mittagong, merimbula, , thylacoleo carnifex, puma, feral cats -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine, Nature, 1910, 22/12/1910
This magazine was taken to Antarctica by Richard W. Richards, a member of Shackleton's expedition. Richards was a member of the Ross Sea Party. The item was returned to Dick Richards after L. Quartermain found it above Richards' bunk in Cape Evans in 1961 when a party were sent down by the New Zealand Government to clear the hut of ice. Richards later gave it to the donor because of the article on the swerve of cricket balls.This copy of Nature was used by Dick Richards when he was marooned at Cape Evans during the Shackleton Antarctic Expedition. The hut used by Richards and his party was also used by Captain Scott. The magazine dates before the use of the hut by Captain Scott so it may be assumed that it belonged to Scott or one of his party. In 1960, during ice being cleared from the hut, the magazine was found above Dick Richards' bunk and returned to him in 1961. It is therefore a remnant of the Shackleton Antarctic Expedition..1) A magazine called 'Nature', a weekly magazine of science, featuring beautiful advertisements and illustrations. .2) A note on a piece of cardboard written on by Dick Richards .3 An envelope addressed to Leslie B. Quartermain of the New Zealand antarctic Society, with the hand written note 'This copy of "Nature" was found embedded in ice in my bunk at C. Evans in Dec 1960..2) This copy of Nture was brought back from above my bunk in Cape Evans by L Quartermain in 1961. his party were sent down by NZ Govt to clear the hut of ice (250 tons removed) and restore to the condition when Scott and ourselves lived in it in 1911 - 12 and 1914 - 17. It contains an article by J.J. Johnson on swerve in cricket tennis and golf balls etc & settles an argument I often had re lat dip in of a ball [pist?]. The black is due to oily blubber smoke which permeated everything at Cape Evans. antarctica, ross sea, cape evans, nature, richards, dick richards, richard w. richards, scott, robert falcon scott, robert scott, scott of the antarctic, holioake, cricket, r.w. richards, microscope -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Ivoryflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
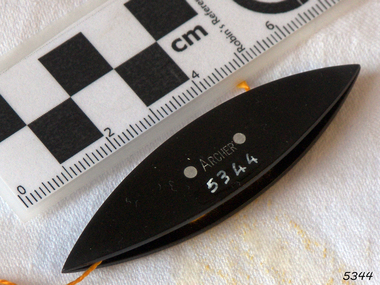 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Black plastic, "ARCHER" inscribed. "ARCHER" inscribed.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, tortoise-shellflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, ivory, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, black plastic flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1935, 1935
List of Full Course Students' 1935, Editorial, Obituary - J. B. Robinson, Personal Column, Personal Column, Editor's Notes, Old Boys: Personal, The "Head" - An Appreciation, The Late Dean - W. F. Tucker, A Tribute - J. M. Bickett, An Attitude to War, Some Impressions by a New Comer to New Guinea, Fumes from the Lab, Arts & Crafts Gossip, Sport, Commercial Notes, The Junior TecsYellow soft covered magazine of 70 pages, including advertisements. Artworks * Blocks and Inks supplied by F.T. Wimble and Co. Ltd Sydney - Printed by students of printing class School of Mines Ballarat * Mr G - By Valma Jenson * Miss G - By E.Shaw * Joker of the pack by Gilda Gude * Oh Mother - By Valma Jensen * Man Praying - By A.P. * Swell - By Valma Jensen * In his element - By E.Shaw * Our jazz band - By Valma Jensen * Spaghetti - By E.Shaw * The Peter Pan statue in Kensington Gardens - By Gilda Gude * Hunted - By Valma Jensen * Bridget & Vic - By Valma Jensen * Lady pointing a statue - By Gilda Gude * Hi first solo flight - By Dorothy Woolcock * Dear Me - a millionth of a milligram out ! - By E.Shaw * Marley & Paul - By Valma Jensen * Green Plan Print - By Hunt * Yes, but it doesn't read, it doesn't read - By E.Shaw * The Big Noise - By Valma Jensen * Bashful Barney - By Valma Jensen * Willowy Verna - By E.Shaw * Margaret - By Valma Jensen * Don - By Valma Jensen * Cyril - By Gilda Gude * Jack - By Gilda Gude * Nancy - By Valma Jensen * Off to English - By Valma Jensen * "A mag article today please or six tomorrow" By E. Shaw * "Oh you boys are awful" - By E. Shaw * Maureen - By Valma Jensen * Geggy - By Valma Jensen * Aw crikey - By Valma Jensen * The wheelbarrow crate reaches Africa - By J.W * Lady Dean - By Valma Jensen * Margery - By Valma Jensen * Bubba - By Lorna Bailey * Chook - By Marjorie John * Bunny - By Valma Jensen * Sixa - By Valma Jensen * Fish Print - By Hunt * Betty - By Lorna Bailey * Bessie - By Lorna Bailey * Janette - By Lorna Bailey * Butcher - By Valma Jensen * Minnow - By F.J.Hballarat school of mines, magazine, f. t. wimble & co. ltd., sydney, j. woolcock, a. nye, d. shore, d. taylor, j. elliott, b. saunders, w. williams, a. moodie, v. hunt, j. shelton, r. warnock, dr. j. r. pound, g. procter, g. merlin, j. b. robinson, james pound, peter wilson, mr alexander, mr creelman, mr crouch, h. steane, j. sutherland, a. bell., a. max wilson, g. f. eric rumpff, r. mcconnell, t. byrne, c. r. king, p. marshman, a. f. heseltine, w. f. tucker, j. m. bickett, a. m. wilson, f. whitworth, w. tierney, r. leigh, g. berriman, a. sneddon, a. collins, h. maddern, d. flynn, n. bayly, m. rickey, w. calaghan, d. wright, e. wallace, b. lamb, s. wise, r. quick, i. leviston, b. chaplin, j. coates, n. dunstan, d. mcarthy, d. henderson, j. mathes, g. leviston, e. mcdonald, k. blackie, j. mouton, n. jelbart, r. brown, k. mathes, a. pickering, j. mcghie, r. white, w. dawson, j. forrest, m. hamill, w. martin, m. jeffs, k. waller, d. nolan, l. baxter, r. knight, l. moy, m. hunt, j. henry, a. goldby, j. menhennet, mr king, w. nice, k. pattie, f. capuano, l. g. r. crouch, gilda gude, valma jensen, e. shaw, lorna bailey, marjorie john, dorothy woolcock -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White, Junior Technical School Athletics Team, 1920, 1920
Photograph is of the Ballarat Junior Technical School Athletic Team, holders of the "winner's cup" in Victorian Inter-Technical Schools' Annual Competition, 1920. Photograph and article published in SMB Students' Magazine, 1921.Photograph mounted on cardPhotographers name - Richards & Co -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionNewspaper - Clipping, The Ballarat Bonanza in Parade, September 1956, 09/1956
A two page article on Ballarat from the magazine 'Parade' ballarat, con trencks, amasa delano, george gipps, william branwhite clarke -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Royal Historical Society of Victoria 45th Annual Report and Financial Statement of Council, 06/1954
The RHSV was established in 1909.14 page annual report of the Royal historical Society of VictoriaFront cover "Mr Keith Rash Golden Point Ballarat" "Your article will be published in the 100th magazine".royal historical society of victoria, annual report -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPrint, Tribute to Allan Ballard Carter MBE (1924-2006) in the Yarra Valley Grammar , Kalinda Road, Ringwood, magazine
Allan Carter, Richard Carter's Father was a prominent business man and resident of Ringwood . The article describes how he was intrumental in obtaining the land for the school as one of the Formative Committee members. Also a member of the school's first Council and then the Chairman of the Building Fund. Richard Carter followed in his Father's footsteps in the Real Estate business. He was also the President of the Ringwood Historical Society for many years.Grey page with text and photographs torn from the school magazine. No date -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION: 'LANCEWOOD' DIARY
(1) A black hard covered diary concerning the running of the male student hostel 'Lancewood' in 1952. Also included is a type written article on the hostel 'Comersdale' and an outline of the opening ceremony of 'Lancewood' in April 1952. (11) A type written article by J.C. Burnett titled ' In Touch with the Rest of the World' for the 'Embers' magazine 27/05/71.bendigo, education, bendigo teachers' college, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, bendigo teachers' college, teaching, students, bendigo, education, hostel, ms. j.c. burnett, teachers -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Magazine - HORWOOD COLLECTION: OLD MACHINERY MAGAZINE
Magazine 'The Old Machinery Magazine' Issue no 180. page 23 article 'Horwoods Foundry Bendigo 1860' 67 pages overall. Article is by John Horwood. Attached to front cover: business card of John Horwood, Director of Aqua Vic, natural water purification systems.bendigo, industry, horwoods foundry -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - THE GENEALOGIST
The Genealogist Family History Magazine, June 2016, soft cover 39 pages with black and white & coloured photographs, includes an article on collecting historical Women's dresses 1820-1940 by Ann Dixon.Australian Insitute of Genealogical Studies Incbook, magazine, clothing -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - RAILWAYS COLLECTION: STEPHENSON LOCOMOTIVE NAMED BENDIGO
Railways collection Photocopied A4 re article on Stephenson locomotive named Bendigo extracted from The Australian Historical Railway Society Bulletin No. 487 - May 1978.The article has a photo of a Stephenson - built 2-4-0 Loco (see 6857) this photo is shown with the caption Contractors (Bruce & Cornish).magazine -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Magazine - RAILWAYS COLLECTION: BULLETIN 727 ARTICLE MAY 1998, 1998
Railways Collection--Bulletin 727 article May 1998 - A Job For Life - by Graham Thomas. 13 x A4 loose pages photocopied from 'The Bulletin' - In this article Jack Thomas records his memories of Bendigo North Workshops during 31 years he was employed there as a boilermaker's assistant and the events that led him to seek permanent employment with the Victorian Railways in 1946. Black and white photos include The South Nell Gwynne mine, various photos of the workshops, the original D3 658, D3 619, K171, J Class and R727 steam locomotives, There is a photo of a Coffee Pot crane Locomotive.Graham Thomas.magazine -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BADHAM COLLECTION: VICTORIAN RAILWAYS CENTENARY 1854-1954 100 YEARS OF SERVICE BOOKLET
Victorian Railways Centenary 1854-1954 100 years of service booklet. Printed in glossy paper, page 1 contains article of 'condensed from a history of the Victorian Railways' which compiled by L.F. Harrigan. The contents include topics of Early private railways (1846-1878), The Melbourne and Hobsons Bay Railway Company - Gala opening, The Victorian government railways four periods of time (during 1856-1864, 1865-1911, 1883-1954, 1950 -1960). Photos inside include the seal of the Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company, South Yarra station 1874, opening of the Geelong and Melbourne railway June 25 1857, a hotel advertisement of 1857 featuring the Geelong and Melbourne railway - showing 'the British hotel Corio St Geelong, Spencer St station in 1872, the Taradale viaduct, on the Bendigo line in 1864, Harcourt station in 1865, Spirit of Progress, train on the Gembrook line. 1908 steam trains between Flinders St and Richmond the first electric train in Australia on a test run 6.10.1918, moving wheat by train 1901. The aircraft fuselages at Newport workshops during WWII, Bren gun carrier. Newport workshops at Queen Elizabeth Spencer St station 1954. The newsletter published by the Victorian Railways Public Relations and Betterment Board by the direction of the Commissioner.book, magazine, victorian railways, victorian railways / compiled by l.f. harrigan / -the melbourne and hobsons bay railway company - gala opening / south yarra station 1874 / published by the victorian railways public relations and betterment board by the direction of the commissioner -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Magazine - BADHAM COLLECTION: VICTORIAN RAILWAYS NEWSLETTER JANUARY 1969
Victorian Railways Newsletter January 1969. Newsletter printed in glossy paper with colour photos on front. The contents include photos of Melbourne's West Tower signal box also a related article, Powelltown in 1919, horse train on Sanderson's line at turn of the century. Printed at the Victorian railways printing works Laurens St North Melbourne.magazine, government, victorian railways -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION: BOOK ''DARLINGHURST NIGHTS'' BY KENNETH SLESSOR & VIRGIL REILLY
Book. ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION. 47 page soft cover magazine type booklet of verse. 'Darlinghurst Nights and Morning Glories / Being 47 strange sights / Observed from eleventh storeys, / In a land of cream puffs and crime, / By a Flat-roof Professor; / And here set forth in sketch and rhyme / by Virgil and Kenneth Slessor.' Illustrated with B & W drawings. Published about 1932 by Frank C. Johnson, Sydney and printed by Clark & Dunstan Ltd. Catalogue sticker ''2132 SLE'' on front cover. Handwritten in ink on first page ''A. H. Chisholm with regards Ken Slessor Jan.1932'' 2 page article from The Bulletin, April 20 1963 ''My King's Cross'' by Kenneth Slessor placed inside front cover.Kenneth Slessor & Virgil Reillybooks, collections, poetry, alec h chisholm collection, kenneth slessor, virgil reilly, poetry -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - SHAMROCK HOTEL COLLECTION: SOUVENIR MAGAZINE
Shamrock Hotel, Pall Mall, Bendigo - The Gazette Shamrock Hotel Souvenir Newspaper Supplement 8.4.1981 showing excellent photo of the hotel - dating back to the 1850's - on the front with an article from Premier Hamer.newspaper -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - GOLDEN SQUARE LAUREL STREET P.S. COLLECTION: BENDIGO MAGAZINE ISSUE 9 SUMMER 07/08
Bendigo Magazine Issue 9 Summer 07/08. Contains an article written by Sharon Greenaway about Violee Myer-Davey OAM which mentions her life and education in Bendigo. Book also contains other articles about Bendigo, its people and businesses.government, local, city of bendigo, golden square laurel street p.s. collection - bendigo magazine issue 9 summer 07/08, violee myer-davey oam -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newsletter - Senior constable Webb's watch
Richard John Webb (c. 1832-1906) was the Senior Constable of the Chinese Constabulary in Bendigo in the 1850's. He was promoted to Dunolly and the rank of Sergeant in late 1860. In 1864 he was made the keeper of the gunpowder magazine at Dunolly. He married Kate Corbett in 1867 and they had 3 children; James Ramsay (1868-1929),Annie Harriet (1869-1950) and Kate Margaret Irene (1874-1963). Neither of the girls married and James became a doctor. Following his time at Dunolly, Webb was transferred to Eaglehawk and thence to Gippsland where he served at Bairnsdale. He retired as a Superintendent of Police and died in Melbourne. He was made an inspector in the Metropolitan Police District in 1888 and the Inspector of Licensing for Gippsland in 1894.Article by Carol Holsworth that appeared in the newsletter of the golden dragon museum in April 2006 titled "Senior constable Webb' watch". Also, a letter from relatives and six photographs of the gold watch and a silver teapot.constable webb, watch, chinese museum -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MELBOURNE HOTELS - 14 ARTICLES BY R. K. COLE, 1952 to 1962
... ? Ballarat Publication dates written in biro on each article ...Magazine articles. Photocopies of 14 historical articles by R K Cole on Melbourne hotels. Photocopied from the publication 'What's Brewing ?' by the Carlton Brewery. List of articles include. Dates of publication are handwritten in biro at the bottom of the first page of each article. Article (g) entitled 'Some Early Goldfields Inns' is mainly about Ballarat hotels.Publication dates written in biro on each article.organization, business, hotel, melbourne hotels, r.k.cole, what's brewing?, ballarat
