Showing 913 items matching "northern victoria"
-
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2009
Darkness and a little light: ?Race? and sport in Australia Colin Tatz (AIATSIS & Australian National University) and Daryl Adair (University of Technology Sydney) Despite ?the wonderful and chaotic universe of clashing colors, temperaments and emotions, of brave deeds against odds seemingly insuperable?, sport is mixed with ?mean and shameful acts of pure skullduggery?, villainy, cowardice, depravity, rapaciousness and malice. Thus wrote celebrated American novelist Paul Gallico on the eve of the Second World War (Gallico 1938 [1988]:9-10). An acute enough observation about society in general, his farewell to sports writing also captures the ?clashing colors? in Australian sport. In this ?land of the fair go?, we look at the malice of racism in the arenas where, as custom might have it, one would least want or expect to find it. The history of the connection between sport, race and society - the long past, the recent past and the social present - is commonly dark and ugly but some light and decency are just becoming visible. Coming to terms: ?Race?, ethnicity, identity and Aboriginality in sport Colin Tatz (AIATSIS & Australian National University) Notions of genetic superiority have led to some of the world?s greatest human calamities. Just as social scientists thought that racial anthropology and biology had ended with the cataclysm of the Second World War, so some influential researchers and sports commentators have rekindled the pre-war debate about the muscular merits of ?races? in a new discipline that Nyborg (1994) calls the ?science of physicology?. The more recent realm of racial ?athletic genes?, especially within socially constructed black athletic communities, may intend no malice but this search for the keys to their success may well revive the old, discredited discourses. This critical commentary shows what can happen when some population geneticists and sports writers ignore history and when medical, biological and sporting doctrines deriving from ?race? are dislocated from any historical, geographic, cultural and social contexts. Understanding discourses about race, racism, ethnicity, otherness, identity and Aboriginality are essential if sense, or nonsense, is to be made of genetic/racial ?explanations? of sporting excellence. Between the two major wars boxing was, disproportionately, a Jewish sport; Kenyans and Ethiopians now ?own? middle- and long-distance running and Jamaicans the shorter events; South Koreans dominate women?s professional golf. This essay explores the various explanations put forward for such ?statistical domination?: genes, biochemistry, biomechanics, history, culture, social dynamics, the search for identity, alienation, need, chance, circumstances, and personal bent or aptitude. Traditional games of a timeless land: Play cultures in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities Ken Edwards (University of Southern Queensland) Sports history in Australia has focused almost entirely on modern, Eurocentric sports and has therefore largely ignored the multitude of unique pre- European games that are, or once were, played. The area of traditional games, especially those of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, is an important aspect of the cultural, social and historical experiences of Indigenous communities. These activities include customs of play that are normally not associated with European notions of competitive sport. Overall, this paper surveys research undertaken into traditional games among Indigenous Australians, as well as proposals for much needed further study in this area. Culture, ?race? and discrimination in the 1868 Aboriginal cricket tour of England David Sampson As a consequence of John Mulvaney?s important historical research, the Aboriginal cricket and performance tour of Britain in 1868 has in recent decades become established as perhaps the most famous of all public events in contact history involving Aborigines, white settlers and the British metropolis. Although recognition of its importance is welcome and significant, public commemorations of the tour have enveloped the tour in mythologies of cricket and nation. Such mythologies have obscured fundamental aspects of the tour that were inescapable racial and colonial realities of the Victorian era. This reappraisal of the tour explores the centrality of racial ideology, racial science and racial power imbalances that enabled, created and shaped the tour. By exploring beyond cricketing mythology, it restores the central importance of the spectacular performances of Aboriginal skills without which the tour would have been impossible. Such a reappraisal seeks to fully recognise the often trivialised non-cricketing expertise of all of the Aboriginal performers in 1868 for their achievement of pioneering their unique culture, skills and technologies to a mass international audience. Football, ?race? and resistance: The Darwin Football League, 1926?29 Matthew Stephen (Northern Territory Archive Service) Darwin was a diverse but deeply divided society in the early twentieth century. The Commonwealth Government introduced the Aboriginals Ordinance 1911 in the Northern Territory, instituting state surveillance, control and a racially segregated hierarchy of whites foremost, then Asians, ?Coloureds? (Aborigines and others of mixed descent) and, lastly, the so-called ?full-blood? Aborigines. Sport was important in scaffolding this stratification. Whites believed that sport was their private domain and strictly controlled non-white participation. Australian Rules football, established in Darwin from 1916, was the first sport in which ?Coloured? sportsmen challenged this domination. Football became a battleground for recognition, rights and identity for all groups. The ?Coloured? community embraced its team, Vesteys, which dominated the Northern Territory Football League (NTFL) in the 1920s. In 1926, amidst growing racial tension, the white-administered NTFL changed its constitution to exclude non-white players. In reaction, ?Coloured? and Chinese footballers formed their own competition - the Darwin Football League (DFL). The saga of that colour bar is an important chapter in Australia?s football history, yet it has faded from Darwin?s social memory and is almost unknown among historians. That picture - Nicky Winmar and the history of an image Matthew Klugman (Victoria University) and Gary Osmond (The University of Queensland) In April 1993 Australian Rules footballer Nicky Winmar responded to on-field racist abuse by lifting his jersey and pointing to his chest. The photographic image of that event is now famous as a response to racial abuse and has come to be seen as starting a movement against racism in football. The racial connotations in the image might seem a foregone conclusion: the power, appeal and dominant meaning of the photograph might appear to be self-evident. But neither the fame of the image nor its racial connotation was automatic. Through interviews with the photographers and analysis of the use of the image in the media, we explore how that picture came to be of such symbolic importance, and how it has remained something to be re-shown and emulated. Rather than analyse the image as a photograph or work of art, we uncover some of its early history and explore the debates that continue to swirl around its purpose and meaning. We also draw attention to the way the careful study of photographs might enhance the study of sport, race and racism. ?She?s not one of us?: Cathy Freeman and the place of Aboriginal people in Australian national culture Toni Bruce (University of Waikato) and Emma Wensing (Independent scholar) The Sydney 2000 Olympic Games generated a national media celebration of Aboriginal 400 metre runner Cathy Freeman. The construction of Freeman as the symbol of national reconciliation was evident in print and on television, the Internet and radio. In contrast to this celebration of Freeman, the letters to the editor sections of 11 major newspapers became sites for competing claims over what constitutes Australian identity and the place of Aboriginal people in national culture. We analyse this under-explored medium of opinion and discuss how the deep feelings evident in these letters, and the often vitriolic responses to them, illustrate some of the enduring racial tensions in Australian society. Sport, physical activity and urban Indigenous young people Alison Nelson (The University of Queensland) This paper challenges some of the commonly held assumptions and ?knowledges? about Indigenous young people and their engagement in physical activity. These include their ?natural? ability, and the use of sport as a panacea for health, education and behavioural issues. Data is presented from qualitative research undertaken with a group of 14 urban Indigenous young people with a view to ?speaking back? to these commentaries. This research draws on Critical Race Theory in order to make visible the taken-for-granted assumptions about Indigenous Australians made by the dominant white, Western culture. Multiple, shifting and complex identities were expressed in the young people?s articulation of the place and meaning of sport and physical activity in their lives. They both engaged in, and resisted, dominant Western discourses regarding representations of Indigenous people in sport. The paper gives voice to these young people in an attempt to disrupt and subvert hegemonic discourses. An unwanted corroboree: The politics of the New South Wales Aboriginal Rugby League Knockout Heidi Norman (University of Technology Sydney) The annual New South Wales Aboriginal Rugby League Knockout is so much more than a sporting event. Involving a high level of organisation, it is both a social and cultural coming together of diverse communities for a social and cultural experience considered ?bigger than Christmas?. As if the planning and logistics were not difficult enough, the rotating-venue Knockout has been beset, especially since the late 1980s and 1990s, by layers of opposition and open hostility based on ?race?: from country town newspapers, local town and shire councils, local business houses and, inevitably, the local police. A few towns have welcomed the event, seeing economic advantage and community good will for all. Commonly, the Aboriginal ?influx? of visitors and players - people perceived as ?strangers?, ?outsiders?, ?non-taxpayers? - provoked public fear about crime waves, violence and physical safety, requiring heavy policing. Without exception, these racist expectations were shown to be totally unfounded. Research report: Recent advances in digital audio recorder technology provide considerable advantages in terms of cost and portability for language workers.b&w photographs, colour photographs, tablessport and race, racism, cathy freeman, nicky winmar, rugby league, afl, athletics, cricket, digital audio recorders -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2009
Social Engineering and Indigenous Settlement: Policy and demography in remote Australia John Taylor In recent years neo-liberals have argued that government support for remote Aboriginal communities contributes to social pathology and that unhindered market engagement involving labour mobility provides the only solution. This has raised questions about the viability of remote Aboriginal settlements. While the extreme view is to withdraw services altogether, at the very least selective migration should be encouraged. Since the analytical tools are available, one test of the integrity of such ideas is to consider their likely demographic consequences. Accordingly, this paper provides empirically based speculation about the possible implications for Aboriginal population distribution and demographic composition in remote areas had the advice of neo-liberal commentators and initial labour market reforms of the Northern Territory Emergency Response been fully implemented. The scenarios presented are heuristic only but they reveal a potential for substantial demographic and social upheaval. Aspects of the semantics of intellectual subjectivity in Dalabon (south-western Arnhem Land) Ma�a Ponsonnet This paper explores the semantics of subjectivity (views, intentions, the self as a social construct etc.) in Dalabon, a severely endangered language of northern Australia, and in Kriol, the local creole. Considering the status of Dalabon and the importance of Kriol in the region, Dalabon cannot be observed in its original context, as the traditional methods of linguistic anthropology tend to recommend. This paper seeks to rely on this very parameter, reclaiming linguistic work and research as a legitimate conversational context. Analyses are thus based on metalinguistic statements - among which are translations in Kriol. Far from seeking to separate Dalabon from Kriol, I use interactions between them as an analytical tool. The paper concentrates on three Dalabon words: men-no (intentions, views, thoughts), kodj-no (head) and kodj-kulu-no (brain). None of these words strictly matches the concept expressed by the English word mind. On the one hand, men-no is akin to consciousness but is not treated as a container nor as a processor; on the other, kodj-no and kodj-kulu-no are treated respectively as container and processor, but they are clearly physical body parts, while what English speakers usually call the mind is essentially distinct from the body. Interestingly, the body part kodj-no (head) also represents the individual as a social construct - while the Western self does not match physical attributes. Besides, men-no can also translate as idea, but it can never be abstracted from subjectivity - while in English, potential objectivity is a crucial feature of ideas. Hence the semantics of subjectivity in Dalabon does not reproduce classic Western conceptual articulations. I show that these specificities persist in the local creole. Health, death and Indigenous Australians in the coronial system Belinda Carpenter and Gordon Tait This paper details research conducted in Queensland during the first year of operation of the new Coroners Act 2003. Information was gathered from all completed investigations between December 2003 and December 2004 across five categories of death: accidental, suicide, natural, medical and homicide. It was found that 25 percent of the total number of Indigenous deaths recorded in 2004 were reported to, and investigated by, the Coroner, in comparison to 9.4 percent of non-Indigenous deaths. Moreover, Indigenous people were found to be over-represented in each category of death, except in death in a medical setting, where they were absent. This paper discusses these findings in detail, following the insights gained from the work of Tatz (1999, 2001, 2005) and Morrissey (2003). It also discusses a further outcome of this situation - the over-representation of Indigenous people in figures for full internal autopsy. Finding your voice: Placing and sourcing an Aboriginal health organisation?s published and grey literature Clive Rosewarne It is widely recognised that Aboriginal perspectives need to be represented in historical narratives. Sourcing this material may be difficult if Aboriginal people and their organisations do not publish in formats that are widely distributed and readily accessible to library collections and research studies. Based on a search for material about a 30-year-old Aboriginal health organisation, this paper aims to (1) identify factors that influenced the distribution of written material authored by the organisation; (2) consider the implications for Aboriginal people who wish to have their viewpoints widely available to researchers; and (3) assess the implications for research practice. As part of researching an organisational history for the Central Australian Aboriginal Congress, seven national and regional collections were searched for Congress?s published and unpublished written material. It was found that, in common with other Aboriginal organisations, most written material was produced as grey literature. The study indicates that for Aboriginal people and their organisations? voices to be heard, and their views to be accessible in library collections, they need to have an active program to distribute their written material. It also highlights the need for researchers to be exhaustive in their searches, and to be aware of the limitations within collections when sourcing Aboriginal perspectives. Radiocarbon dates from the Top End: A cultural chronology for the Northern Territory coastal plains Sally Brockwell , Patrick Faulkner, Patricia Bourke, Anne Clarke, Christine Crassweller, Daryl Guse, Betty Meehan, and Robin Sim The coastal plains of northern Australia are relatively recent formations that have undergone dynamic evolution through the mid to late Holocene. The development and use of these landscapes across the Northern Territory have been widely investigated by both archaeologists and geomorphologists. Over the past 15 years, a number of research and consultancy projects have focused on the archaeology of these coastal plains, from the Reynolds River in the west to the southern coast of the Gulf of Carpentaria in the east. More than 300 radiocarbon dates are now available and these have enabled us to provide a more detailed interpretation of the pattern of human settlement. In addition to this growing body of evidence, new palaeoclimatic data that is relevant to these northern Australian contexts is becoming available. This paper provides a synthesis of the archaeological evidence, integrates it within the available palaeo-environmental frameworks and characterises the cultural chronology of human settlement of the Northern Territory coastal plains over the past 10 000 years. Ladjiladji language area: A reconstruction Ian Clark and Edward Ryan In this reconsideration of the Ladjiladji language area in northwest Victoria, we contend that while Tindale?s classical reconstruction of this language identified a fundamental error in Smyth?s earlier cartographic representation, he incorrectly corrected that error. We review what is known about Ladjiladji and through a careful analysis demonstrate not only the errors in both Smyth and Tindale but also proffer a fundamental reconstruction grounded in the primary sources.ladjiladji, social engineering, dalabon, indigenous health, coronial system, radiocarbon dating -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesAudio CD, Laura Brearley et al, Gulpa ngawal : Indigenous deep listening, 2009
Introduction: In the Ngungikurungkurr language of the Daly River in the Northern Territory, the word for "Deep Listening" is 'Dadirri' (Ungunmurr, 2009) and in the Yorta Yorta language of the Murray River in Victoria, it is 'Gulpa Ngawal'. The closest we can get to describing it in English is deep and respectful listening which builds community. Deep listening draws on many senses beyond what is simply heard. It can take place in silence. Deep listening can be applied as a way of being together, as a research methodology and as a way of making a difference.CDsilcar, rmit, monash, koorie heritage trust, yorta yorta, taungurung, gunnai, gippsland, gunditjmara, richard frankland, deep listening, woolum bellum, education, art, music, indigenous research, sista girl productions -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Harold Koch, Aboriginal placenames : naming and re-naming the Australian landscape, 2009
... of Aboriginal microtoponymy in western and central Victoria: case... of Aboriginal microtoponymy in western and central Victoria: case ..."Aboriginal approaches to the naming of places across Australia differ radically from the official introduced Anglo-Australian system. However, many of these earlier names have been incorporated into contemporary nomenclature, with considerable reinterpretations of their function and form. Recently, state jurisdictions have encouraged the adoption of a greater number of Indigenous names, sometimes alongside the accepted Anglo-Australian terms, around Sydney Harbour, for example. In some cases, the use of an introduced name, such as Gove, has been contested by local Indigenous people." "The 19 studies brought together in this book present an overview of current issues involving Indigenous placenames across the whole of Australia, drawing on the disciplines of geography, linguistics, history, and anthropology. They include meticulous studies of historical records, and perspectives stemming from contemporary Indigenous communities. The book includes a wealth of documentary information on some 400 specific placenames, including those of Sydney Harbour, the Blue Mountains, Canberra, western Victoria, the Lake Eyre district, the Victoria River District, and southwestern Cape York Peninsula." -- Publisher description. Contents: Introduction: Old and new aspects of Indigenous place-naming /? Harold Koch and Luise Hercus NSW &? ACT: 1. Aboriginal placenames around Port Jackson and Botany Bay, New South Wales, Australia: sources and uncertainties /? Val Attenbrow 2. Reinstating Aboriginal placenames around Port Jackson and Botany Bay /? Jakelin Troy and Michael Walsh 3. The recognition of Aboriginal placenames in New South Wales /? Greg Windsor 4. New insights into Gundungurra place naming /? Jim Smith 5. The methodology of reconstructing Indigenous placenames: Australian Capital Territory and south-eastern New South Wales /? Harold Koch Victoria: 6. Toponymic books and the representation of Indigenous identities /? Laura Kostanski 7. Reviving old Indigenous names for new purposes /? Laura Kostanski and Ian D. Clark 8. Reconstruction of Aboriginal microtoponymy in western and central Victoria: case studies from Tower Hill, the Hopkins River, and Lake Boga /? Ian Clark South Australia &? Central Australia: 'Aboriginal names of places in southern South Australia': placenames in the Norman B.Tindale collection of papers /? Paul Monaghan 10. Why Mulligan is not just another Irish name: Lake Callabonna, South Australia /? J.C. McEntee 11. Murkarra, a landscape nearly forgotten: the Arabana country of the noxious insects, north and northwest of Lake Eyre /? Luise Hercus 12. Some area names in the far north-east of South Australia /? Luise Hercus 13. Placenames of central Australia: European records and recent experience /? Richard Kimber Northern Australia: 14. Naming Bardi places /? Claire Bowern 15. Dog-people: the meaning of a north Kimberley story /? Mark Clendon 16. 'Where the spear sticks up': the variety of locatives in placenames in the Victoria River District, Northern Territory /? Patrick McConvell 17. 'This place already has a name' /? Melanie Wilkinson, Dr R. Marika and Nancy M. Williams 18. Manankurra: what's in a name? placenames and emotional geographies /? John J. Bradley and Amanda Kearney 19. Kurtjar placenames /? Paul Black.Maps, b&w photographs, tables, word listsaustralian placenames, sociolinguistics, linguistics, anthropology, sydney harbour placenames, blue mountains placenames, canberra placenames, western victoria placenames, lake eyre placenames, victoria river district placenames, cape york peninsula placenames -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Laura Brearley et al, Gulpa ngawal : Indigenous deep listening, 2010
Introduction: In the Ngungikurungkurr language of the Daly River in the Northern Territory, the word for "Deep Listening" is 'Dadirri' (Ungunmurr, 2009) and in the Yorta Yorta language of the Murray River in Victoria, it is 'Gulpa Ngawal'. The closest we can get to describing it in English is deep and respectful listening which builds community. Deep listening draws on many senses beyond what is simply heard. It can take place in silence. Deep listening can be applied as a way of being together, as a research methodology and as a way of making a difference.colour illustrations, colour photographsyorta yorta, taungurung, gunnai, gippsland, gunditjmara, richard frankland, deep listening, woolum bellum, education, art, music, indigenous research, sista girl productions -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Judi Cooper, Needs survey of community languages 1996 : report : March 1998, 1998
Report of Needs Survey of Community Languages, including, Methodology, Victoria, NSW, Queensland, Torres Strait Islanders, Western Australia, Northern Territory and summary. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Keith & Allison Pither, 1967
Keith Pither was born at Shepparton in 1914 and grew up on a farm. Attended Otira Methodist Home Mission Training College from 1936 and by 1939 was a probation minister at Burnie (Tas.). Enlisted in the army 1939 and served in the Middle East and Northern Australia. In 1943 he was ordained in the field as a chaplain and later served in New Guinea. Married Allison (Alison?) Brown in 1945 and they had four children, Brian, Rhonda, Andrew and Howard. Completed his studies at Melbourne University 1946. Placements were Red Cliffs, Carlton Methodist Mission, Benalla, Portland, Sandringham and Ivanhoe. Died 19/6/2008.The Pithers are holding a knife about to cut an anniversary cake."Rev. K. M. Pither and Mrs Allison Pither 1967"pither, keith, red cliffs, carlton methodist mission, benalla, portland, sandringham, ivanhoe -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, 06/1984
Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra 1986. Moderator Northern Synod and Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Conference.Head and shoulders portrait."Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress"gondarra, djiniyini, uniting aboriginal & islander christian congress -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, 06/1984
Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra 1986. Moderator Northern Synod and Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Conference.Head and shoulders portrait."Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress"gondarra, djiniyini, uniting aboriginal & islander christian congress -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, 06/1984
Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra 1986. Moderator Northern Synod and Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Conference.Head and shoulders portrait."Rev. Djiniyini Gondara, Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress"gondarra, djiniyini, uniting aboriginal & islander christian congress -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1986
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe standing by a window in his office 1986.Identification of Howe. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1984
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Full-face, looking into the camera 1984 - part of an advertisement for Wesley Church's 126th anniversary 9/9/1984.Identification of Howe -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1985
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe alighting from a car at Williamstown dockyards March 1985.Identification of Howe. -
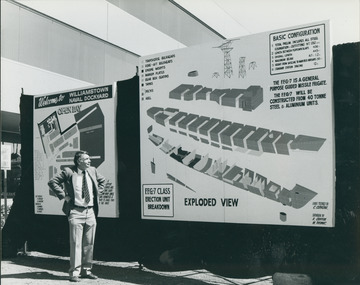 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1984
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe at Williamstown dockyard with an exploded view of a frigate September 1984.Identification of Howe.rev brian leslie howe, deputy prime minister of australia -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Reverend Greme Bence Moderator Northern Synod of the Uniting Church
Rev. Graeme Dudley Bence was born into a Methodist family on 24 December 1930 in the coal mining town of Tonyrefail, New South Wales. His family moved to Bornemouth England in 1931. He married Doreen in Bristol on 21 June 1952. Rev. Bence was ordained at East Cliff Congregational Church Bournemouth on 26 May 1953. He was commissioned to the sevice of the London Missionary Society in Papua and subsequently served in Australia starting at Hughesdale Congregational Church from 1958 to 1965 and Wyclif Congregational Chruch Surrey Hills from 1965 to 1972. In 1972 he accepted a call to the Nightcliff Church in Darwin and became Assistant Director of Mission and Service in the Uniting Church of North Australia. The Northern Synod elected Graeme Moderator from 1981 to 1983. He returned to Victoria in 1986 and retired to Rosebud in 1991. He died on 31 July 1994.Head and shoulders drawing in profile of Rev. Graeme Bence.bence, graeme -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, 1985
"Bruce Dickerdike, 29, was a teacher in the Northern Territory at Lajamanu (Hooker Creek). He did three years of study at Ridley College and was ordained deacon in the Anglican Church. After 12 months curacy he switched to the Uniting Church. In addition to the normal hall work, he's been doing further studies at La Trobe in sociology, in Aboriginal studies… (Mill Park, establishing a congregation.)"B & W head and shoulders photos of Rev. Bruce Dickerdike, Theological Hall graduate 1984.C&N identification.uniting church minister, bruce bickerdike -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, (F455-5) 1987; (F455-6) 1986; (F455-7) 1986
Reverend Dr. J. Davis McCaughey (12/07/1914 - 25/03/2005) was ordained in 1942 in Northern Ireland. He served at the YMCA, Fisherwick Belfast, United Kingdom, Professor of New Testament Studies at the Theological Hall, Master of Ormond College and retired in 1979. In 1986 he became Governor of Victoria, an office he held for six years.(F455-1) seated at table; (F455-2) head and body seated; (F455-3) head and body standing; (F455-4) seated at desk; (F455-5) seated at desk; (F455-6) head and body seated; (F455-7) head and body seated.(F455-1) "ACC 29th General Meeting Adelaide Justice Elizabeth Evatt addressed the meeting on the report on Human Relationships. Chairman of the session was the Rev Professor Davis McCaughey. Photo Rollason ACC"; (F455-2) no details; (F455-3) "Dr and Mrs McCaughey Rev Ian Steer Reg News 20 December"; (F455-4) "Rev Dr. Davis McCaughey"; (F455-5) "HE Dr Davis McCaughey, AC Governor of Victoria C&N 22/7/1987 page 19"; (F455-6) "Please return to C&N Credit Roger Mitchell Church and Nation C&N Feb 86 page1 front cover"; (F455-7) "C&N 12/2/1986 page 17".mccaughey, davis, rev., presbyterian minister, theological hall, ormond college, governor of victoria -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Reverend Chris Budden, undated
Reverend Dr. Christ Budden was ordained in 1977 and served at Lake Cargelligo, Northern Territory Synod, Board of Church and Community New South Wales, Commission for Mission, Hunter Presbytery and Adamstown.B & W head and shoulders photograph of Rev Chris Budden."Rev Chris Budden Secretary Social Responsibility and Justice"budden, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, undated c.1980s
Rosalie Rayment originally trained and worked as an Occupational Therapist. Following completion of studies in Theology she worked for 11 years with the Church in Thailand. Rosalie was ordained in 1988. Fred Vanclay B.D., Dip AgS. ordained 1964 in the Presbyterian Church. Served: Queensland 1961 - 1975; Victoria 1976 - 1985 Vermont - Parkmore; Northern Territory Tennant-Barkly Patrol 1985 - 1993. Died in 2016. Adapted from the eulogy given by his son, Jerry Vanclay One of Fred’s first placements as a minister was in Mackay, North Queensland. Mackay was a wonderful place for Fred, his wife Donna and their young family. They all loved the beaches and the bush, and the children completed a significant part of their schooling there. Whilst posted in Mackay, Fred and Donna enjoyed long road trips in their modest HR Holden sedan, with the family, to Uluru, to Broome via the Borroloola Track, and down the Birdsville Track to the Flinders ranges; along the way, developing the bushcraft that would stand them in good stead later in the Tennant-Barkly Patrol. After many years in ministry in Mackay, then in Vermont, Victoria, Fred and Donna were called to the Tennant-Barkly Patrol in the Northern Territory, where he served for eight years, probably Fred’s most satisfying years. All Fred’s parishes were welcoming and rewarding, but Fred said on more than one occasion that he had a special love for the Patrol. He felt that in an urban congregation, he ministered mainly to those who came to Church, but in the Patrol he ministered to everyone, and especially to those in need. Fred loved to get involved with the day-to-day activities of his people, to develop a deeper relationship and greater understanding. Some remarked that when Fred helped, everything took longer, but they loved him and his assistance nonetheless. Fred was proud to follow in the footsteps of his predecessor Padre Fred McKay, and sometimes joked that he was “Fred the 2nd”, not Fred McKay, but “Fred from Mackay”. During his last few weeks in hospital, Fred liked to reminisce on his time in the Patrol. He joked about how he surprised the selection panel with his knowledge of bush tracks and outstations – knowledge that he had gained on those long road trips from Mackay. He reflected that many aspects of his life were good preparation for his time in the Patrol. After their Patrol, Fred and Donna retired to Mt Waverley, in Melbourne, but they were both restless in retirement, and undertook supply ministries in Wedderburn, Kerang and North Cairns, and made several long journeys into the interior and into their beloved Patrol [in Tennant Creek] – as well as frequent visits to their eight grandchildren and two great-grandchildren, and occasional trips to Europe to reunite with distant family. They never tired of ministering and adventuring, but as age and infirmity progressively clipped their wings, they travelled more in spirit and less by car. Despite the many celebrations that he blessed – baptisms, marriages, and funerals – Fred never sought the limelight, and I think he would be surprised by our gathering today. I can almost hear him saying “Don’t make a fuss; just say a heartfelt prayer together”. – Jerry Vanclay Informal B & W gloss photo of Rev. Fred Vanclay, his wife Donna, Rosalie Rayment (later ordained) and one other unidentified person. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1892
Reverend John Gray Sterling was a Presbyterian minister who was born in Belfast Northern Ireland in 1858 and was ordained in Rockhampton in 1881. He served at Bundaberg, Maryborough Victoria and Flemington. He died in 1924.B & W waist length seated studio portrait of the Rev. John Gray Sterling. Cabinet card format -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1892
Mrs Annie Sterling was the wife of the Reverend John Gray Sterling, a Presbyterian minister who was born in Belfast Northern Ireland in 1858 and was ordained in Rockhampton in 1881. He served at Bundaberg, Maryborough Victoria and Flemington. He died in 1924.B & W waist length seated studio portrait of Mrs Annie Sterling. Cabinet card formatannie sterling, rev john gray sterling, presbyterian, minister -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1980s
Reverend Dr. J. Davis McCaughey (12/07/1914 - 25/03/2005) was ordained in 1942 in Northern Ireland. He served at the YMCA, Fisherwick Belfast, United Kingdom, Professor of New Testament Studies at the Theological Hall, Master of Ormond College and retired in 1979. In 1986 he became Governor of Victoria, an office he held for six years.B & W photograph of Rev Professor Davis McCaughey seated at the podium with Justice Elizabeth Evatt at the ACC 29th General Meeting held in Adelaide."ACC 29th General Meeting Adelaide Justice Elizabeth Evatt addressed the meeting on the report on Human Relationships. Chairman of the session was the Rev Professor Davis McCaughey. Photo Rollason ACC"mccaughey, davis, rev., presbyterian minister, theological hall, ormond college, governor of victoria, justice elizabeth evatt -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated c.1980s
Reverend Dr. J. Davis McCaughey (12/07/1914 - 25/03/2005) was ordained in 1942 in Northern Ireland. He served at the YMCA, Fisherwick Belfast, United Kingdom, Professor of New Testament Studies at the Theological Hall, Master of Ormond College and retired in 1979. In 1986 he became Governor of Victoria, an office he held for six years.B & W photograph of Rev Dr Davis McCaughey seated in an office.mccaughey, davis, rev., presbyterian minister, theological hall, ormond college, governor of victoria -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, c.1986
Reverend Dr. J. Davis McCaughey (12/07/1914 - 25/03/2005) was ordained in 1942 in Northern Ireland. He served at the YMCA, Fisherwick Belfast, United Kingdom, Professor of New Testament Studies at the Theological Hall, Master of Ormond College and retired in 1979. In 1986 he became Governor of Victoria, an office he held for six years. Rev Ian Steer: b.1929; ordained 1959 at Norlane United Charge; 1963 Broadmeadows Task Force; 1972 chaplain Essendon Grammar; 1985 Sunbury-BullaB & W photograph of Rev Dr Davis McCaughey standing between Rev Ian Steer and Mrs Jean McCaughey."Dr and Mrs McCaughey Rev Ian Steer Reg News 20 December"mccaughey, davis, rev., presbyterian minister, theological hall, ormond college, governor of victoria, rev ian steer, jean mccaughey, presbyterian, minister -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1939
Rev. Henry Griffiths was Director of Methodist Inland Missions. He was station at Katherine originally, as a patrolling unit of the Methodist Mission.Gloss, black and white, head and shoulders, studio portrait of Rev. Henry Griffiths.northern territory, inland mission, methodist, griffiths, henry -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1939
See entry for F53-1Gloss, black and white photograph as postcard of Rev. Harry Griffiths and his wife Dorothy with inscriptions.Rev. H. Griffiths, Director M. I. M., & Mrs. Griffithsnorthern territory, inland mission, methodist, griffiths, henry -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1949
See entry for F53-1Gloss, black and white photograph of Rev. Henry Griffiths, Rev. W. J. Turner and one other minister outside a building.northern territory, inland mission, methodist, griffiths, henry, turner, w.j. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, 1949
See entry for F53-1Gloss, black and white photograph of Rev. Henry Griffiths standing in the garden.northern territory, inland mission, methodist -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1939
The Rev. Henry Griffiths was Director of the Methodist Inland Mission. He was stationed at Katherine, originally, as a patrolling unit of the Methodist Mission.Gloss, black and white, head and shoulders photograph of Mrs. Dorothy Griffiths, wife of Rev. Henry Griffiths.northern territory, inland mission, methodist, griffiths, dorothy, griffiths, henry -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1930
See entry for F53-1Matte, sepia, head and shoulders portrait of Rev. Henry Griffiths and his wife Dorothy, mounted on card.northern territory, griffiths, henry, griffiths, dorothy, methodist, inland mission
