Showing 4120 items matching "road plans"
-
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyAperture Card microfilm, Victorian Land Tiltes Office, Parish Plan Carlyle (Superseded)
... -country Town layout of Carlyle plan town boundries lots roads card ...Town layout of Carlylecard with a single microfilm insertplan, town, boundries, lots, roads -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyAperture Card microfilm, Victorian Land Tiltes Office, Parish Plan Carlyle (Superseded)
... -country Town layout of Carlyle plan town boundries lots roads card ...Town layout of Carlylecard with a single microfilm insertplan, town, boundries, lots, roads -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyAperture Card microfilm, Victorian Land Tiltes Office, Parish Plan Carlyle (Superseded)
... -country Town layout of Carlyle plan town boundries lots roads card ...Town layout of Carlylecard with a single microfilm insertplan, town, boundries, lots, roads -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyAperture Card microfilm, Victorian Land Tiltes Office, Parish Plan Carlyle (Superseded), 11/07/2000
... -country Town layout of Carlyle plan town boundries lots roads card ...Town layout of Carlylecard with a single microfilm insertplan, town, boundries, lots, roads -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Boroondara General Cemetery Gatehouse, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaBoroondara Cemetery in kew was established in 1858. It has an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. Some notable memorials include The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), The Syme Memorial (1908), The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036). Burials within the cemetery include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii'). Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. Digital images of a red brick gatehouse at Boroondara General Cemetery in Kew.cemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Boroondara General Cemetery Springthorpe Memorial, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital image of the Springthorpe Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemeterycemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, springthorpe memorial -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, Cussen Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemetery, Kew, Victoria, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital imagescemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, cussen -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Apollo Bay, Victoria, 24/01/2022
In 2021, the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) constructed two new groynes and a section of rock seawall at Apollo Bay to help manage the impacts of coastal erosion. The new 70-meter-long rock groynes run perpendicular to the shoreline and be located just south of the Milford St revetment and to the south of Milford Creek. Sections of rock seawall will be constructed between the two Groynes with an aim to protect the dune, walking path, cypress trees and road from erosion. Colour photograph of a coastal scene at Apollo Bay, featuring new rock groynes to protect the Great Ocean Road from erosion. apollo bay, beach, coast, groyne, rockwall -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Apollo Bay, Victoria, 24/01/2022
In 2021, the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) constructed two new groynes and a section of rock seawall at Apollo Bay to help manage the impacts of coastal erosion. The new 70-meter-long rock groynes run perpendicular to the shoreline and be located just south of the Milford St revetment and to the south of Milford Creek. Sections of rock seawall will be constructed between the two Groynes with an aim to protect the dune, walking path, cypress trees and road from erosion. Colour photograph of a coastal scene at Apollo Bay, featuring new rock wall and groynes to protect the Great Ocean Road from erosion. apollo bay, beach, coast, groyne, rockwall -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Sea Wall at Apollo Bay, Victoria, 24/01/2022
In 2021, the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) constructed two new groynes and a section of rock seawall at Apollo Bay to help manage the impacts of coastal erosion. The new 70-meter-long rock groynes run perpendicular to the shoreline and be located just south of the Milford St revetment and to the south of Milford Creek. Sections of rock seawall will be constructed between the two Groynes with an aim to protect the dune, walking path, cypress trees and road from erosion. Colour photograph of a coastal scene at Apollo Bay, featuring new rock wall and groynes to protect the Great Ocean Road from erosion. apollo bay, beach, coast, groyne, rockwall, sea wall -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Sea Wall at Apollo Bay, Victoria, 24/01/2022
In 2021, the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) constructed two new groynes and a section of rock seawall at Apollo Bay to help manage the impacts of coastal erosion. The new 70-meter-long rock groynes run perpendicular to the shoreline and be located just south of the Milford St revetment and to the south of Milford Creek. Sections of rock seawall will be constructed between the two Groynes with an aim to protect the dune, walking path, cypress trees and road from erosion. Colour photograph of a coastal scene at Apollo Bay, featuring new rock wall and groynes to protect the Great Ocean Road from erosion. apollo bay, beach, coast, groyne, rockwall, sea wall -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Noel and Jean Webster, 1973
Noel Webster was mayor of the City of Nunawading from 1973 to 1974. He was a founding member of the Vermont High School council and a board member of Maroondah Hospital. He was involved in U3A and was a founding member of the Early Planning for Retirement Association. Jean Webster was the president of the Nunawading Historical Society and both assisted the resettlement of Cambodian migrants. Noel Webster passed away in 2002 at the age of 77.Black and white photograph of Mayor Noel Webster, and wife Jean Websterwebster, noel, jean -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Morack Golf Course, C1970
In 1970, the area now known as the Morack Golf Course was rezoned from 'Rural' to 'Public Open Space'. This allowed planning to go ahead and by 1973 sufficient land had been acquired by the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works. The course was first open on 8 May 1976 as a nine-hole course. This was extended to 15 holes by January 1980, and to eighteen holes by 1981.Two coloured photographs a-b of the early days in the development of the Morack Golf Course. Overview of a hole plus white patches indicating where trees have been planted. Some people practicing.morack golf course -
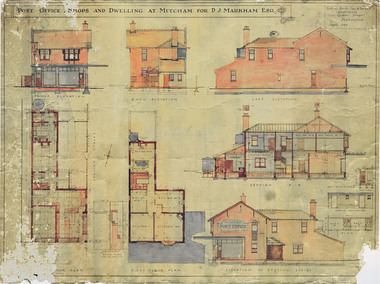 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Plan - DVD, Mitcham Post Office Architect's Plans, 1923 (Digital Copy on DVD)
DVD containing scanned images of : Post office, shops and dwellings at Mitcham for P.J. Markham Esquire, plans and elevations - Sydney Smith, Ogg and Serpelt, Architects. Original document and preservation copy are held: see ND6466.markham, patrick joseph, mitcham post office -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Hazelmere Avenue, Mitcham, No 8
Max Grant was the founder of the Mitcham Repertory Group. He performed, directed and produced 100 plays over 70 years. In 1988 he was named Nunawading Citizen of the year. He died on 22nd September 2000.12 small black and white photographs (a-m) of the erection of Max Grant's house at 8, Hazelmere Avenue, Mitcham. Plans and Specifications at ND 2873hazelmere avenue mitcham no 8, grant max, houses -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Mullauna Secondary College Staff 1989
Mitcham technical School, Blackburn Sec college, Donvale High School, later Nunawading High School merged to become Mullauna Secondary College with a $5.2 million government grant 1988.Article on plan to merge at NP3009.Coloured photograph of staff at Mullauna Secondary College 1989.Photograph taken outdoors in a treed location.mullauna secondary college staff 1989. secondary colleges -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Schwerkolt Cottage Complex - purchase of horse paddocks, 20/09/2006
Other Council and Government personnel included; local member, Tony Robinson, councillors, Sharon Ellis and Helen Harris and Whitehorse facilitator, Mark FawcettSix coloured photographs taken after the purchase of the horse paddocks by the Whitehorse Council in 2006. Victorian Minister for Planning, Rob Hull, attendingschwerkolt cottage and museum complex, hull, rob -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre. This photo relates to Blackburn Lake Primary School part of the project. Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, civic centre, blackburn lake primary school no 4860 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Vermont College's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, vermont college -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre. This photo relates to Laburnum Primary School, part of the project.Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, laburnum primary school no 4863 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre. This photo relates to Springview Primary School's part of the project. Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, springview primary school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Weedon Heights Primary School, part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, weedon heights primary school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Rangeview Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse . civic centre, ceramic tile project, rangeview primary school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Parkmore Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, parkmore primary school no. 4881 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Vermont South Special School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, vermont south special school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Old Orchard Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, old orchard primary school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Blackburn Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, blackburn primary school, no. 2923 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Mitcham Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, mitcham primary school no. 2904 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to ST Timothy's School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, st timothy's catholic primary school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project -2004-5, 1/06/2005 12:00:00 AM
See ND5890One of a set of 19 coloured photographs relating to the Ceramic Tile Project by the Nunawading Primary Schools Community Art Project which was installed in the Amphitheatre at the rear of the Nunawading Civic Centre.|This photo relates to Nunawading Primary School's part of the project.|Text, Plans & Publicity - see ND5890nunawading primary schools community art project., city of whitehorse. civic centre, ceramic tile project, nunawading primary school no. 4190
