Showing 1406 items
matching bushfire
-
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionTimber moisture meter adapted for forest fuels
Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Adaption of a timber moisture meter made by the FCV radio lab to measure fuelforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFuel Mincer
Used to mince fuel samples to measure moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Fuel mincer Made at Altona as an alternative design to the commercial Spong Mincer With wooden plug to push fuel into the mincer and glass jar to collect sampleforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionElectric Fuel Mincer
Used to mince fuel samples to measure moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Battery operated Fuel mincer. Plugs into 12 volt car cigarette lighter socket Adaption using parts from commercial food processor Made at Altona as an alternative design to the commercial Spong Mincer Glass jar to collect sampleforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionDelton Moisture meter
Used to measure moisture content by electric current resistance Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Commercial timber moisture meter used to measure fuelDCR9-Tforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionMarconi Moisture meter
Used to measure fuel moisture content Representative samples of fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced and the moisture measured The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Adaption of a commercial timber moisture meter measure fuelTF 933 Cforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionRelative Humidity Meter
Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many factors including temperature, relative humidity (RH), forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), as well as fire size, shape and direction. Temperature and relative humidity have major impacts on fuel dryness and therefore upon the availability of fuel for combustion. The amount of fine fuel available can increase rapidly from nearly zero when fuel moisture content is more than 16% after rain or a heavy morning dew, to many tonnes per hectare as fuel dries out later in the day and the moisture content drops below 9%. This explosive escalation in the amount of available fuel can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. This device is used for determining air temperature and relative humidity. It contains two thermometers, one of which is covered with a wick saturated with ambient temperature liquid water. These two thermometers are called dry bulb and wet bulb. Once the thermometers to reach equilibrium temperatures the two thermometers are quickly read. The figures are then used to convert the dry bulb temperature TDB and the wet bulb temperature TWB into humidity information. The wet bulb temperature is approximately equal to the adiabatic saturation temperature. Relative humidity meter in wooden box two stainless steel tubes contain wet and dry thermometers A small clock drives a fan motor in the base to circulate airforests commission victoria (fcv), weather, bushfire -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumMap - CLUNES 1987, CHARLES FENTON, 1987
.1 .2 A MAP OF CLUNES TOWNSHIP - ORIGINAL AND COPY - 1987. ALL STREETS AND BIRCH'S CREEK MARKED WITH ALLOTMENT NUMBERS. .3 SAME MAP SHOWING PATH OF BUSHFIRE IN 1944CLUNES 1987local history, document, maps, clunes township -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupNewspaper - Ash Wednesday 1983 Bushfires, The Herald and Weekly Times Limited, 1983
A large newspaper sized magazine remembering the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983. The magazine/newspaper was produced by The Herald and The Sun newspapers in conjunction with the Geelong and Bendigo Advertisers. It was produced to raise money for the State Disaster Appeal.Printed newspaper sized magazine. The front cover has a burnt out house with Ash Wednesday printed in white with a red background at the top of the page and 1983 Bushfires at the bottom of the page. non-fictionA large newspaper sized magazine remembering the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983. The magazine/newspaper was produced by The Herald and The Sun newspapers in conjunction with the Geelong and Bendigo Advertisers. It was produced to raise money for the State Disaster Appeal. ash wednesday, the dandenongs, mount macedon, the otways, framlingham, cockatoo, upper beaconsfield, -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Ringwood Rifle Club. Remains of the club hut after the bushfires of January 1962
Black and white photographTyped on back of photograph- "Ringwood Rifle Club. Remains of the club hut after the bushfires of January 1962. Bruce Mitchell in foreground." -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionSpong Fuel Mincer
Used to prepare fuel samples to measure their moisture content. Representative samples of fine fuel such as bark, leaves, twigs etc were minced first through a course mincing plate, then a fine plate and the moisture content measured with a Speedy moisture meter or other device. The availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Spong No 10 food mincerforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BADHAM COLLECTION: NEWSLETTER FEBRUARY1969 SPECIAL REPORT ON BUSHFIRES
Victorian Railways Newsletter February 1969 Special report on bushfires. Glossy paper with colour photos on front of bushfires in relation to railway property. The contents include photos of effects of the fire to VR property, closure of State coal mines, photos of fire destroyed bridge at Diamond Creek, Molesworth, the Powlett River Coal Field in 1910 (Wonthaggi), and Kirrak Mine. Printed at the Victorian railways printing works Laurens St North Melbourne.magazine, government, victorian railways, victorian railways newsletter / photos of effects of the fire to vr property/ closure of state coal mines / photos of fire destroyed bridge at diamond creek / molesworth/ the powlett river coal field in 1910 ( wonthaggi) / kirrak mine / printed at the victorian railways printing works laurens st north melbourne -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Information folder - Fire Safety
Folder containing fire safety pamphlets. Contents: -"Bushfire safety in urban fringe areas", Insurance Council of Australia -"Belgrave Heights & South Volunteer Fire Brigade Fire Information Pamphlet", 2 copies. -CFA recruitment pamphlet, Belgrave Heights & South FB/Home Safety Awareness, CFA -"Ordinary People, Extraordinary job", CFA recruitment pamphlet. -"Living In The Bush", CFA booklet. -"Bushfire, Recognise The Risks", CFA, 3 copies. -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionRakehoe (McLeod Tool)
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Rakhoeforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFire beater (canvas)
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Fire Beater (canvas) 1930s designforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPulaski
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Pulaski Fire Tool Combines an axe and a grubbing hoe. Digging end and cutting end with short wooden handleforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard, H D Bulmer, Bulmer's/Black Friday, 1/01/1939 12:00:00 AM
Black and white postcard of Bulmers shop taken during the Black Friday bushfires showing businesses almost hidden in dense smoke from nearby fires Esplanade Lakes Entrance Victoriabusinesses, township, bushfires -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Ringwood Rifle Range after the bushfires of January 1962
Black and white photographWritten on back of photograph- "Ringwood Rifle Range after the bushfires of January 1962. Scene looking towards the hut at 300 yard mound." -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPacific Marine pump Type Y
The Pacific Marine company was based in Seattle on the west coast of America and manufactured its first satisfactory portable fire pump 1925. These early Type N pumps were replaced in 1933 by the more familiar Type Y pumps. The updated pumps proved popular with the US Forest Service, and a large number were purchased by the Forests Commission as part of the equipment upgrade program in the wake of the 1939 bushfires. The Pacific Marine had a 9.8 Hp, two-cylinder, two-stroke petrol motor running with a high oil mix ratio of 16:1, so it blew vast clouds of blue smoke as the motor screamed at 4500 rpm. Part of its unique design was the water-cooled engine and muffler. But if the flow of water was interrupted the engine would quickly overheat and seize, so it needed constant monitoring and attention. Water was driven through a pair of bronze impeller gears which also needed a constant flow of water otherwise they would also self-destruct. When running properly, a Pacific Marine could pump 63 US gallons per minute, or about enough to fill a 200-litre drum. But its main feature was its high pressure of up to 225 psi. Pacific Marine pumps were often mounted on top of departmental fire tankers and used to spray water into the tops of burning trees. Compared to other pumps of the era it was light weight at only 70 pounds and was often mounted on a wooden stretcher frame. But they were cantankerous things to start with the rope pull and many exasperated novices came away with skinned knuckles. Modern Honda motors, which were more reliable and smoother running, replaced the Pacific Marines as the pump of choice for forest firefighters in the 1980s.High pressure Pacific marine Pumpforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhoto - Early photo of Bogong Township x2
Bogong Village was built for the workers of the State Elecricity Commission of Victoria who were employed to construct the Kiewa Hydro electric Scheme. This photo shows their homes and offices etc., Lake Guy and the spillway during construction days.Bogong village was built as part of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme. This photo gives a view of the village when it was at its peak. Large photo of Mt Bogong Township with snow on the mountain in the background and the spillway over-flowing in the foreground. Some small trees amongst those burnt by the 1939 bushfire. (2 photos - one an enlarged copy)bogong village. kiewa hydro electric scheme. s.e.c.v.. lake guy. -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBook, Bushfires Royal Commission, 2009 Victorian Bushfires Royal Commission, Interim Report, Executive Summary, 2009
Interim report of Bushfires Royal Commission on the 2009 Victorian bushfires26 p. : col. ill., maps ; 30 cm.ISBN 978192337765 -
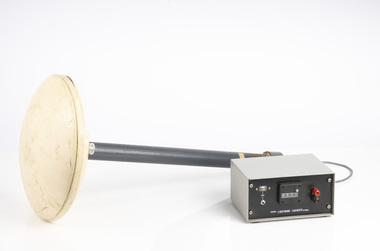 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionLightning Detector
Lightning is one of the major causes of bushfires, particularly in the remote mountains. This lightning detector system was developed by Dr. Peter Kourtz at Canada’s forest fire research institute. By 1977, some 300 were in use across the country. The small mushroom antenna could detect short-range (20-mile) changes in electrostatic field associated with lightning strikes. It needed to be placed out in the open on a hilltop and away from nearby trees. It simply counted the number of "strikes". The detector doesn't seem to have a direction finding capability or be able to distinguish between cloud-to-cloud or cloud-to-ground lightning. It's not sure how this particular unit found its way to Victoria. The Bureau of Meteorology's (BOM) current lightning detector network uses radio waves emitted by lightning to pinpoint the location of lightning strikes. The network is operated by a private company that sends data to the BOM in real time. Lightning detection systems use sensors like antennas, GPS receivers, and processing systems to detect radio waves, also known as sferics. The systems calculate the lightning's location and speed by measuring how long it takes for the radio signal to reach the different antenna stations. The BOM also has a Thunderstorm Tracker that uses weather radar data to identify areas of potential thunderstorm activity. The tracker updates every six minutes and shows the direction thunderstorms are moving, as well as their expected position in 10, 20, and 30 minutesLightning detector 1970sQ-Techforests commission victoria (fcv), weather, bushfire, bushfire aviation -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Drop Chute
From the early 1960s, the Forests Commission had pre-season arrangements in place with local aeroclubs and pilots across regional Victoria. Air observers from FCV districts routinely flew during the summer months in small, fixed-wing aircraft on fire spotting missions and to map fire boundaries. The information was often needed quickly by crews on the ground or in the control centre and these small chutes were used to drop messages and maps from the reconnaissance aircraft on a low pass above a cleared area like a football field. About 3-foot long when fully extended, they had a small pouch secured with a press stud for the map or package. The chutes were made from tough canvas with a small, weighted sandbag at one end and a long yellow streamer tail on the other to help direct its fall and locating it on the ground. Drop chutes were still in common use in the 1990s, but the increased availability of helicopters combined with improved digital data transfer made drop chutes redundant. Simple, but now redundant technologyAerial drop chute"Return to Forests Comm Vic" stenciled on sidebushfire -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Driptorch - Firebug (hand held), c 1985
The origins of the humble handheld driptorch have been lost in time. They are widely used for ignition in controlled burning operations in forest and grasslands. The “Pacific Forester“ with its short central wand and somewhat leaky ball-valve was made by the American Wajax company in the 1940s. The Pacific Forester is slightly different in design from the more robust and common “Panama” driptorch first manufactured in 1933 and used extensively by Queensland cane farmers. The Panama is closely related to the current “Firebug” used in Victoria which is manufactured by Rodney Industries in Brisbane and has an offset wand design which gives it good balance. The fuel is a mixture of petrol and diesel and every FCV District had their own closely-guarded secret formula ... 2:1, 3:1, 1:1, 4:1 or 3:2 ratio. There was also the choice of 91, 95 or 98 octane petrol mixed with summer or winter diesel. Occasionally some of the old Avgas or Jet-A1 lying around the depot was added with a splash of engine oil to make the mixture stick to the fuel to be ignited. The fuel mixed also varied between autumn or spring, heathland, mixed forest, or high-intensity slash burnsCommon driptorch used throughout AustraliaDrip torch with handle Wand has loop and valve. The loop is designed to assist with even flow of fuel which flows out onto the burning head of the wand. Pressure equalising value in top of aluminum fuel container which holds 4 litres of burner mix. Gravitational feed of the driptorch allows the unit to drip fire, making it simple and quick to operate. Instructions for use. CF+L written with texta pen.bushfire -
 Federation University Art CollectionWe are living in a climate emergency. This work references the Black Summer Bushfires (2019-2020) and the devastating impacts upon habitat and wildlife, specifically the endangered Kangaroo Island Glossy Black Cockatoo. Created with mixed media, including charcoal from the Black Summer fires. Wach piece feratures the charcoal as a potent reminder of the reality of the event. This body of work acts as both a memorial, and a warning for the future. bushfire
Federation University Art CollectionWe are living in a climate emergency. This work references the Black Summer Bushfires (2019-2020) and the devastating impacts upon habitat and wildlife, specifically the endangered Kangaroo Island Glossy Black Cockatoo. Created with mixed media, including charcoal from the Black Summer fires. Wach piece feratures the charcoal as a potent reminder of the reality of the event. This body of work acts as both a memorial, and a warning for the future. bushfire -
 City of Whittlesea Art Collection
City of Whittlesea Art CollectionWork on paper - Pastel on paper, Caroline Lewallen, Natural Beauty
bushfire -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPhotograph (police motorcycle)
Police motorbike riding through a bushfire zone between Cockatoo and Belgrave around the time of the Ash Wednesday fires. In the background is a signpost that has been relatively untouched but melted into a twisted shape by the heat of the fire. Circa 1983.police vehicles; motor transport branch; motor transport section; wireless patrol; motor cycle patrol; police motorcycles -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Peter WEGNER (b.1954 NZ - a.1958 AUS), Peter Wegner, The Blanket (from the 'Black Saturday' series), 2009
The 'Black Saturday' bushfires were a series of bushfires that ignited across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009. It was Australia's worst ever natural disaster. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire-weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest ever loss of life from a bushfire: 173 people died and 414 were injured as a result of the fires.This work is by a local contemporary artist with a national and international reputation for figurative and portrait works. The 'Black Saturday' series is a powerful investigation of emotion and grief as experienced by many Nillumbik residents during the 2009 'Black Saturday' bushfires. A cluster of bronze figurines either stand alone or embrace in groups. Their expressions and gestures of despair are made more pertinent with the raw like application and surface treatment of the material used. The 'Black Saturday' series is a challenging work, but one that encourages healing, connection and empathy. Solitary male figure wrapped in a blanket, clutched to his chest and over his head. Surface treatment is textured. Metallic brown colour with base starting to turn a green patina. Sticker underside of sculpture 'WEGNER THE BLANKET AG205642'wegner, bronze, figurine, black saturday, sculpture -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Peter WEGNER (b.1954 NZ - a.1958 AUS), Peter Wegner, Man in Shock (from the 'Black Saturday' series), 2010
The 'Black Saturday' bushfires were a series of bushfires that ignited across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009. It was Australia's worst ever natural disaster. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire-weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest ever loss of life from a bushfire: 173 people died and 414 were injured as a result of the fires.This work is by a local contemporary artist with a national and international reputation for figurative and portrait works. The 'Black Saturday' series is a powerful investigation of emotion and grief as experienced by many Nillumbik residents during the 2009 'Black Saturday' bushfires. A cluster of bronze figurines either stand alone or embrace in groups. Their expressions and gestures of despair are made more pertinent with the raw like application and surface treatment of the material used. The 'Black Saturday' series is a challenging work, but one that encourages healing, connection and empathy. Solitary male figure wearing a long hooded coat clutching his hands underneath his chin in shock. Surface treatment is textured. Dark metallic brown colour. Hand carved on base, back of figure '2/6 WEGNER 10'wegner, bronze, figurine, black saturday, sculpture -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Peter WEGNER (b.1954 NZ - a.1958 AUS), Peter Wegner, The Embrace (from the 'Black Saturday' series), 2011
The 'Black Saturday' bushfires were a series of bushfires that ignited across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009. It was Australia's worst ever natural disaster. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire-weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest ever loss of life from a bushfire: 173 people died and 414 were injured as a result of the fires.This work is by a local contemporary artist with a national and international reputation for figurative and portrait works. The 'Black Saturday' series is a powerful investigation of emotion and grief as experienced by many Nillumbik residents during the 2009 'Black Saturday' bushfires. A cluster of bronze figurines either stand alone or embrace in groups. Their expressions and gestures of despair are made more pertinent with the raw like application and surface treatment of the material used. The 'Black Saturday' series is a challenging work, but one that encourages healing, connection and empathy. Two men embrace in despair. One man throws his arms around the other man's shoulders. The other man holds the other's back. Surface treatment is textured. Dark metallic brown colour with figures starting to turn a green patina. Note stuck with tape underside of sculpture 'Savage Art Prize Peter Wegner (phone number) The Embrace 2011'wegner, bronze, figurines, black saturday, sculpture -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Peter WEGNER (b.1954 NZ - a.1958 AUS), Peter Wegner, Disbelief (from the 'Black Saturday' series), 2010
The 'Black Saturday' bushfires were a series of bushfires that ignited across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009. It was Australia's worst ever natural disaster. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire-weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest ever loss of life from a bushfire: 173 people died and 414 were injured as a result of the fires.This work is by a local contemporary artist with a national and international reputation for figurative and portrait works. The 'Black Saturday' series is a powerful investigation of emotion and grief as experienced by many Nillumbik residents during the 2009 'Black Saturday' bushfires. A cluster of bronze figurines either stand alone or embrace in groups. Their expressions and gestures of despair are made more pertinent with the raw like application and surface treatment of the material used. The 'Black Saturday' series is a challenging work, but one that encourages healing, connection and empathy. Solitary figure sitting on rock/log with elbows resting on knees and hands on head. Face looking down in despair. Surface treatment is textured. Dark metallic brown colour with figure starting to turn a green patina.Sticker underside of sculpture 'No. 205640 (AP)'wegner, figurine, bronze, black saturday, sculpture
