Showing 296 items
matching geological surveys
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - The Tasman fold belt system in Victoria : geology and mineralisation of proterozoic to carboniferous rocks, A.H.M. Vanden Berg, 1976
... to carboniferous rocks A.H.M. Vanden Berg Geological Survey of Victoria ...A scientific analysis of the development of the sequence of geological events and processes which contributed to the building of southeastern Australia landforms as part of the Tasman Fold Belt System.non-fictionA scientific analysis of the development of the sequence of geological events and processes which contributed to the building of southeastern Australia landforms as part of the Tasman Fold Belt System.geology victoria, landforms victoria, tasman fold belt -
 Federation University Historical Collection
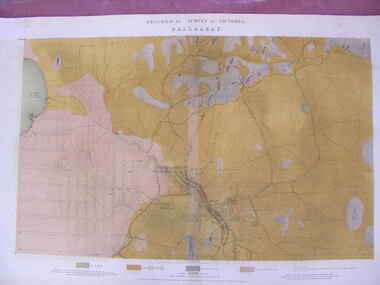
Federation University Historical CollectionMap - Geological Survey, J. Phillips, Geological Survey of Victoria - Ballarat, 1857, 10/1858
... featuring four colours. Geological Survey of Victoria - Ballarat ...Geological map of the Ballarat District featuring four colours.ballarat, geological, geology, geological plan, main road, camp, golden point, pennyweight hill, clayton hill, ballaarat cemetery, bakery hill, specimen hill, soldiers hill, nightingale lead, native youth black hill flat, white flat, mining, mines, eureka lead, old post office hill -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap - Map - Geological, Geological Survey of Victoria - Ballarat, 09/1858
... W.E. extent: 5km NS extent: 3 km Geological Survey of Victoria ...Coloured Geological Map of Ballarat, edged with masking tape. The map show alluvial silt, gold drift, geological orders, volcanic, and gold workings. Scale is 8 chains to an inch. WGS 84 Centroid: 37 degrees 33 feet 33 inches south 143 degrees 52 feet 02 inches east W.E. extent: 5km NS extent: 3 kmballarat, ballaarat, geology, goldfield, phillips, j. phillips, mining, alfred selwyn, ferguson and mitchell -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Chalcopyrite
... as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 ...This specimen was recovered from Mica Schist, Canada. Chalcopyrite is a copper iron sulfide mineral with a chemical composition of CuFeS2. Its name derives from the Greek words for copper (chalco-) and brass (pyrite). It can be found in shades of yellow, green and grey, and, when exposed to acid, it can change to purple, blue, violet and yellow tones. Weathering can cause loss of its metallic luster and its brass-yellow colour. Chalcopyrite forms under various conditions, with the most significant deposits being hydrothermal in their origin. It is known globally as the most important ore of copper for thousands of years, and is thus considered a very important mineral formation. Given its golden appearance, it is often confused for the mineral gold, earning it the popular reputation as 'fool's gold' or 'yellow copper'. However, it can be straightforwardly distinguished from gold; the latter is soft, with higher specific gravity and a yellow streak, whereas chalcopyrite is brittle, easily scratched by a nail, and has a greenish grey streak. Copper was the first metal that was used by people. It was discovered by the Neolithic man about 9,000 years ago and it gradually replaced stone as it was easier to be shaped. In Australia, search for copper began after the European settlement, leading to the discovery of substantial deposits, like the one at the Olympic Dam in South Australia, which is regarded as one of the largest copper deposits in the world. Chalcopyrite has been used for copper since smelting processes began approximately five thousand years ago. Although by no means rare, this the specimen of this mineral can be used to reflect a wider history of industrial uses of copper for a significant portion of human history. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized copper iron sulfide mineral of brass yellow, often with an iridescent tarnish, with greenish-black streak and submetallic luster. Chalcopyrite can be formed in several ways, including crystalizing from accessory minerals in igneous rocks, or from magma or within volcano sulfide deposits. Most commonly, chalcopyrite are found in hydrothermal conditions, where it forms in hydrothermal veins. As a member of the tetragonal crystal system, it often takes the shape of tetra-headed crystals, often with striations along the sides of the crystals. #18 Copper pyrites/(chalcopyrite) in/Laurentian Slate/(page 315 of inventory)/page missing from/descriptive catalogue/ Other label: 81 /fool's gold, chalcopyrite, mineral, rock, geology, geological, hydrothermal, neolithic, european settlement, olympic dam, south australia, stone, deposits, specific gravity, greenish grey streak, brittle, mineral gold, metallic luster, cufes2, greek words -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Final recommendations Ballarat Study Area Land Conservation Council, Victoria, 1982, 1982
Yellow soft covered report of 95 pages . The contents of the report include: Parks, reference areas, wildlife reserves, water production, harwood production, softwood production, flora Reserves and Flora and Fauna reserves, bushland reserves, historic area and reserves, rivers and streams, Roadside conservation and Highway parks, Education areas and School Plantations, Lake Reserves, geological reserves, recreation, scenic reserves, agriculture, mineral and stone production, utilities and survey, township land, Uncommitted Land, military training, other reserves and public land. Maps include: The Study area 1: 250 000 Supplementary Mapsland conservation authority, ballarat, endowment plantations, pine plantations, langi ghiran state park, mount buangor state park, enfield state park, ballarat-creswick regional park, rossbridge, black lake, flax mill swamp, dereel lagoon, lake bolac, lake wongan, langi ghiran reservoir, gong gong reservoir, pincotts reservoir, beales reservoir, wilsons reservoir, moorabool reservoir, korweinguboora, korweinguborra reservoir, learmonth bores, sago hill, illabarook reservoir, ballarat water commission, dunneworthy, mount cole, mont lonarch, ben major, waterloo, trawalla, linton, ross creek, canadian, shepherds flat, lal lal, mount doran, raglan, chute, carngham, buninyong, watsons hill, enfield, cape clear, illabrook, rokewood junction, mount warrenheip, nerrina, jubilee, golden stream, australasian deep lead mine, happy valley school, piggoreet, berringa, bulldog, ballarat common, wildlife, water, timber, flora, rivers, geology, agriculture, warrenheip, biodiversity -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Olivine Crystals, Unknown
... as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 ...Olivine is mostly found on the Earth's surface in igneous rocks that are dark-coloured. It is common at divergent plate boundaries and at warm spots, such as volcanic areas. It crystalises and forms during the cooling of magma. Olivine is used in refractory sand, bricks, and gemstones. Olivine has been found on a number of meteorites, which might have originated from large asteroids or the mantle of a now-destroyed planet. This olivine crystal is thought to originate from Mount Noorat, with speculation that it could have originated from Mount Shadwell. Mount Noorat is a dormant volcano cone located in the Newer Volcanics Province of Victoria. Mount Noorat belongs to the Kirrae Wuurong people, who used the Mount as a place for meetings and gatherings prior to European settlement. Contact was first made between European settlers and the Indigenous people in 1841. The Mount has mostly been used for cattle and sheep grazing. Mount Shadwell is a well-known source of olivine and is the highest of a gathering of volcanic cones. The New Volcanic Province is located in South East Australia and covers 15000 square kilometres. It contains 400 explosive vents and small shield volcanoes. The last eruption is thought to have occurred 5000 years ago at Mount Gambier and Mount Schank. This olivine crystal has been identified as a volcanic bomb, which is a molten rock which was pushed out and ejected into the air when a volcano reupts. A rock needs to be larger than 65 mm in diameter to be classified as a volcanic bomb. This olivine volcanic bomb and its locality is historically and socially significant. The olivine was found in the Newer Volcanic Province, an area which contains over 400 dormant volcanoes. This olivine is one part of a volcanic bomb, which would have ejected when magma erupted out of a volcano. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid iron-magnesium silicate mineral with shades of green and brownburke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, olivine, igneous rock, volcanic, gemstones, volcanic bomb, meteorites, asteroids, plantes, mount noorat, mount shadwell, indigenous, kirrae wuurong people, newer volcanics province, victoria, european settlement, eruption -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Native Sulphur, unknown
... collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria ...Native Sulphur in its solid form is a yellow crystalline mineral that forms near volcanic vents and fumaroles where it is the solid form of hot gases. It is also frequently found in the subsurface as a by-product of sulphide ore mineralization. In all its forms, sulphur is one of the most commonly occurring minerals on the planet, especially in natural gases, and is key to the make-up of a range of other minerals. It is essential to continuing life on earth, and was used in ancient societies as part of medical care, religious rites, and entertainment, and was key to the invention of gunpowder by the Chinese. Native Sulphur in its solid form is a yellow crystalline mineral that forms near volcanic vents and fumaroles where it is the solid form of hot gases. It is also frequently found in the subsurface as a by-product of sulphide ore mineralization. In all its forms, sulphur is one of the most commonly occurring minerals on the planet, especially in natural gases, and is key to the make-up of a range of other minerals. It is essential to continuing life on earth and was used in ancient societies as part of medical care, religious rites, and entertainment, and was key to the invention of gunpowder by the Chinese. The exact site of extraction for this specimen is unknown, but it was probably collected in New Zealand in the 1850s. Sulphur is significant both for its historical and current uses, and for its nature as one of the most abundant minerals on the planet. Sulphur's importance comes both from its abundance and its role in ensuring survival, creating other minerals, and daily human life. This specimen is significant as representative of sulphur's solid properties. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid, small, crystalline mineral specimen that is largely bright yellow, with some darker spotting. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, sulphur, native sulphur, new zealand, native sulphur specimen, sulphur specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Thunderegg agates, Unknown
... collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria ...Thunderegg Agates are formed within rhyolite volcanic ash layers. They are rough spherical shapes, varying in size from less than an inch to over a metre long. Thundereggs usually contain centres of chalcedony which may have been fractured followed by deposition of agate, jasper or opal, either uniquely or in combination. A unique characteristic that these specimens have is the fact that they often look like ordinary rocks on the outside, but slicing them in half and polishing them may reveal intricate patterns and colours. These particular specimens are examples of thunderegg agates. Agate is a variety of chalcedony, a cryptocrystalline form of quartz. The agate component contributes to the intriguing internal patterns of the specimens. The specific locality of these specimens is unknown but they can be found in flows of rhyolite lava. They are formed in gas pockets in the lava, which act as moulds. These specimens can be found globally, with specific locations in Germany being particularly abundant. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Two small solid specimens with pale, sandy-coloured exteriors and fractured internal patterns. burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, thundereggs, thundereggs agate, agate, rhyolite, rhyolite lava, volcanic ash, chalcedony, cryptocrystalline -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Fossil Leaves
... were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey ...A fossil refers to any remains or traces of past life that are preserved in the rock. It could be remains of plants or animals. Fossil leaves are commonly found on different types of rocks. These fossils can go as far back as the Triassic Age just like the series of fossil plants collected at Denmark Hill, Ipswich in Queensland. Fossils leaves are formed when dead plants get buried by sediments like mud, sand, or volcanic ash. Often, it gets detached cleanly from stems along a special layer of weak cells, then twigs, and, less commonly, cones of conifers and fruits and seeds of flowering plants. Over time, the leaves or pieces of leaves get buried by more sediments and eventually gets 'lithified' or hardened into a rock. Erosions and mining can cause the rocks to break and reveal the fossils buried in it. Fossilisation frequently takes place at sites in the lowlands where deposits of clay, silt, sand are found. This is usually due to weathering and erosion of rocks. Fossil leaves can provide information about ancient Australia's way of living. It contributes to Victorian biodiversity records and its botanical collections. It also contributes information on the geographical profile of Victoria as fossilisation usually occur at estuaries and deltas of rivers, river flood plains, ponds and lakes. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Piece of light brown rock with fossilised leaves in shades of golden yellow and brown.Existing label: Fossil Leaves / Locality unknown / might be worth checking if this is Glossopteris, a Permian age plant. / C. William 16/4/21 geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, fossil leaves, fossilization, 1868 geological survey of victoria, lithified, rocks, fossilised leaf, rock, fossils, leaves -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ventifact (wind- or ice-shaped) pebble
... to those found on earth. The Geological Survey of Victoria ...Ventifacts are sand-blasted rocks that are typically faceted and often display parallel grooves carved by wind-blown sand. They are useful indicators of wind direction and strength in environments such as deserts, mountains, and coastal areas because they are usually not hidden by later sediment, soil or vegetation cover. In Antarctica ventifaction is strongly related to the composition or type of rock. Ventifacts are important because they provide evidence for abraders such as sand, dust or snow and ice crystals, and offer a unique understanding of past wind processes that are effective in the reconstruction of past wind flow conditions and can provides clues to weather and climate changes in the past. Interestingly ventifacts have also been found on the surface of Mars. They were a threat to the NASA rover due to the sharp angles of the facets, created by the Martian wind over the course of millions of years. These Martian ventifacts act like weathervanes for past wind and weather patterns on the red planet in a similar manner to those found on earth.The Geological Survey of Victoria was instigated in response to the Victorian Gold Rush which began around 1851 in the Beechworth, Castlemaine, Daylesford, Bendigo and Ballarat areas. The survey was conducted by Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn from his arrival in December 1852 until his resignation in 1869and during this time he trained many notable geologists, e.g. Aplin, Wilkinson, Daintree, who went on to other State survey senior positions. This specimen was among those donated to the Burke Museum in 1868.A hand-sized solid mineral specimen in shades of dark and light browns with light lines visible in all configurations and a groove on configuration 2.light lines visible in all configurations and a groove on configuration 2burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, ventifact, antarctic region, antarctic, alfred richard cecil selwyn, alfred selwyn, wind direction, wind strength, abraders, wind flow, climate change, reconstruction of wind flow conditions, weather change, mars -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Galena (with quartz), unknown
... collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria ...Galena is the natural compound of lead and classed as a sulphide, it crystallises in a cubic pattern and its chemical formula is PbS. Galena is a primary source of both lead and silver. This specimen of Galena comes from Broken Hill. Broken Hill has one of the world’s largest and most significant deposit of ore for the production of lead. Mining of Galena at Broken Hill began with the staking of land by Charles Rasp in 1883. By the following year, in 1884, Rasp and six others had formed Broken Hill Mining Company. Broken Hill Mining Company eventually evolved into BHP group limited and is currently the largest mining company in the world and the largest company in Australia. There is archaeological evidence from artefacts discovered in Turkey that humans have been extracting lead from galena by the process of smelting since at least 6500 BCE. This specimen also has quartz on the top surface which is frequently discovered alongside Galena. This mineral specimen is of historic significance as a sample of Galena extracted from Broken Hill during the 19th century. Mining for Galena in Broken Hill begin in 1883 by Charles Rasp and evolved into the world’s largest mining company – BHP Group Limited. Broken Hill is one of the world’s most significant deposits of ore for the production of lead. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A flat, hand-sized, grey sulphide specimen that is the natural compound of lead with a quartz formation on the top surface. Existing Label: GALENA / (with quartz) / Locality: Broken Hill / N.S.W 120 x 70 x 29geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, galena, galena quartz, quartz, charles rasp, broken hill mining company, bhp group limited, bhp, lead, ore, lead sulphide, sulphide, silver, broken hill -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Mangan Hedenbergite
... is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens ...This specimen was recovered from Broken Hill, NSW. It was given the name Mangan Hedenbergite in 1819 by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in honor of Mr. Anders Ludvig of Hedenberg who was the first to define hedenbergite as a mineral. Hedenbergite, belongs in the pyroxene group having a monoclinic crystal system. The mineral is extremely rarely found as a pure substance. Mangan Hedenbergite is a manganese bearing variety of Hedenbergite. Manganese is the world’s fourth most used mineral after iron, aluminium, and copper primarily because it has no satisfactory substitute in its major applications. Globally, the steel industry is the primary user of manganese metal, utilizing it as an alloy to enhance the strength and workability of steel and in the manufacture of tin cans. Manganese is a key component of certain widely used aluminium alloys and, in oxide form, dry cell batteries used in electric vehicles. These batteries are in high demand. Another potential use for manganese may as an additive to help coat and protect a car’s engine. Manganese is also used for non-metallurgical purposes such as plant fertilizers, animal feed, and colorants for bricks. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A hand-sized mineral specimen in shades of silver and blackmanganese, open cut mine, manganese ore processing, bell bay, tasmania, northern territory, steel industry, zinc-carbon batteries, alkaline batteries, tin cans -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, List of Subjects
School of Mines Ballarat is predecessor of Federation University Foolscap sized list of Subjects from Ballarat School of Mines with handwritten names.8S3S in large writng on the back school of mines ballarat, practical chemistry, mr. walker, theoretical chemistry, theoretical agricultural chemistry, practical agricultural chemistry, technical chemistry, metallurgy, alfred mica smith, metallurgical calculations, metallurgy of gold and ore dressing, assaying practical, assaying dry, mr. murphy, ore dressing practical, mining, mining geology, mineralogy, geology, petrology, botany, applied mechanics, mr hart, mine surveying, land surveying, steam and gas engines, mr gilchrist, elementry electricity & magnetism, electrical technology, mr sutherland, turning and fitting, mr connon, engineering drawing, mr kerr, geometry, algebra, trigonometry, physics, conics, calculus, mr whitington, building construction, plane and solid geometry, plumbing grade, mr hall, mr mullins, carpentry, wool classing, materia medica, mr gutheil, technical arithmatic, mr hutchison, telegraphy, mr williams, sloyd, mr slater, photography, mr campbell, manual training, cyanide, mr deane, mr brittain, mr martell, english, astronomy, list of subjects -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupBook, Paul Hicks, Berwick-Pakenham Corridor: Historical Survey, 1991
Shows early Geological maps of Berwick area, Squatting runs, Aboriginal tribal boundaries, early house, townships and early landmarksnon-fictionShows early Geological maps of Berwick area, Squatting runs, Aboriginal tribal boundaries, early house, townships and early landmarkscounty of mornington, early houses of berwick, westernport squatting runs -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - PLAN GENERAL SURVEY MALMSBURY PORCUPINE INN, FOREST CREEK TO GOLDEN POINT. ALEXANDRA RANGE 1853
Colour Copy of Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing (sic) the Alexandrian Range also Sawpit Gully Bendigo and Bullock Creeks. Handwritten note under the title a follows '' Forwarded to the Colonial Secretary with my letter No A 53/105 dated 30th March 1853 for transmission to the Geological Surveyor. R Hoddle Surveyor General. ' Stamped by Department of Mines Victoria with record#123 in Top right Hand corner. Also contains a catalogue number 2053/M/2. Part of the Contents of a DVD entitled 'Mapping Great Change' - Archival Maps, produced to support an exhibition in the Post Office Gallery Bendigo. A description of the Map, its history and implications for both historical and future discussions is contained in an Essay 'Mapping Great Changes' : The landscape of central Victoria by Gerry Gill.R. Hoddlemap, bendigo, country lands -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupBook, AM Cooney, Geological Survey Report: 1977/12 Engineering geology of the Berwick area, 1979
... of the Berwick area 76 p.; 27 cm Geological Survey Report: 1977/12 ...A report on the engineering geology of the Berwick area76 p.; 27 cmnon-fictionA report on the engineering geology of the Berwick areaberwick (vic.), geology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Azurite, Unknown
... obtained as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria, which ...Azurite is a secondary copper mineral made by the weathering of copper sulphide ore deposits. Azurite is formed from copper, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. There are over 45 forms of azurite that are more well-known, however over 100 forms have been found. Azurite is also commonly found together with Malachite, and Azurite is often psuedomorphed to Malachite. This specimen was found at the Great Cobar Copper Mine in New South Wales, which was founded in 1870. At the time it was one of the largest mining operations in the world. It was the largest copper mine in Australia and housed the southern hemisphere’s tallest chimney stack. The international price of copper collapsed at the end of World War 1 which led to the closure of the Great Cobar Mine on March 16th 1919. A year later on March 10th 1920 an underground fire in the CSA (Cornish, Scottish, Australian) mine started and burned for 16 years. The closure of the mine and the fire left thousands jobless and many people left the area. These were factors in Cobar facing a long stretch of poverty, until a boom in the 1960s led to the reopening of the mine. The mine still operates today, obtained by Metals Acquisition Limited in June 2023. Azurite is considered an uncommon mineral. Named for its deep blue colour, azurite was historically used for pigment making and as a gemstone, despite its softness. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 as part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens. Many of the specimens in this collection were obtained as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria, which started in 1852. The Survey aimed to map the scientific makeup of the earth.A solid copper mineral with shades of darker blues almost covering it.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, cobar mines, great cobar copper mine, cobar mining, new south wales, azurite, azurite specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Quartz veining in Breccia Conglomerate, Unknown
... as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria which begun in 1852 ...Quartz is one of the most common minerals in the world. It is formed by a 3d structure of silicon and oxygen. While it is a simple mineral, it can come in a variety of shapes and colours. When quartz is pure it is colourless, transparent and can appear glass-like. Better known and more rare variations of quartz include amethyst and smoky quartz. This specimen is a vein of quartz in Breccia Conglomerate. Breccia is coarse-grained clastic rock which is made up of broken rock fragments and held together by mineral cement. The locality of this specimen is unknown. While quartz is a very common mineral and does not have rarity, it is an important material in industrial settings. One of it's physical and chemical properties is that it is piezoelectric, which means it can be used to generate an electric charge. This has made it useful in the manufacturing of timekeeping devices. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 among a larger collection of geological specimens. It was collected as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria which begun in 1852 as a response to the Gold Rush. Collections were distributed to organisations across Australia to encourage the further study of the scientific makeup of the Earth. A solid egg-shaped rock with a mineral vein forming a ring around the rock in shades of brown and beige.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, 1852 geological survey of victoria, mineralogy, quartz, breccia, breccia conglomerate, conglomerate -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Green Feldspar (orthoclase)
... is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens ...Feldspar, derived from the German word feldspat, is a group of minerals which is the most common mineral group found on Earth, making up more than half of the planet's crust. The major rock-forming minerals in the Feldspar group include albite, anorthite, orthoclase and microcline. (Mindat, Feldspar Group). Orthoclase is part of the Feldspar Group subgroup, Alkaline Feldspar, which are known to be poor in calcium, and mostly rich in potassium. It is further also considered to be a K Feldspar, a subgroup of Alkaline Feldspar that are Potassium-dominant with variable crystal symmetry and Al-Si ordering state. Orthoclase are most commonly Colorless to white, Greenish white, Grayish yellow, or Pale pink and transparent to translucent with slightly pearly cleavage. The mineral rates at a 6 on the Mohs Hardness Scale. (cannot be scratched with a knife, but scratches glass with difficulty). The stronger green colour of this particular specimen is distinctive to the Broken Hill region (where it was found), and due to a small amount of lead. (BB) Its qualities find it misidentified at times as as microcline variety amazonite. Broken Hill is one of the world’s richest lead-zinc-silver deposits. The huge, 300-million-tonne orebody was discovered in 1883 and the superb mineral specimens attract collectors from around the world. (Australian Museum, Minerals from Australia: Australian mining regions)While feldspar is not by any means rare, this particular specimen has qualities distinctive to the Broken Hill mining district, with these properties leading at times to the mineral's misidentification. This creates potential for further study and identification of these mineral deposits through methods such as microscopic twinning, or using the position of certain d values in XRD patterns to calculate the degree of disorder of a K-feldspar, as discussed on the Mindat website (Mindat.com, Orthoclase:About Orthoclase). This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid small aluminosilicate mineral composition which is primarily pale green and blue-grey in colour with traces of beige and white throughout. Note: green plumbian orthoclase (aka green feldspar) is an indicator mineral for the Broken Hill style lead-zinc deposits.N/Abroken hill mine, geological specimen, minerology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Olivine with Chromian diopside (dark green), Unknown
... of the Geological Survey of Victoria, initiated in 1852 during the Gold Rush ...This specimen was donated in 1868 by Alfred Selwyn. Olivine is typically found in basic and ultra-basic igneous rocks around the world, in a variety of colours including yellowish green, olive green, greenish black and reddish brown with a transparent to translucent diaphaneity. The luster of the specimen is vitreous, the luminescence non-fluorescent and when fractured the mineral is very brittle producing small, conchoidal fragments. Chromian diopside is normally found in small sizes as the larger the size of the mineral the darker the colour is, almost black rather than green. Chromium is the element that gives chromian diopside and emeralds their rich green colour. Diopside is found across the world in multiple colours however gem-quality chromian diopside is mined in Siberia, Russia and prominent within the jewellery industry as a more affordable substitute to emeralds. Chromium-bearing diopside has been located across Australia. Chromium-bearing Diopside is located across the world found in North America, parts of South America, and across Australia, Africa, Europe and Asia. Chromium-bearing Diopside is mined in Siberia, Russia and is sold as a commercial substitute for emeralds. The stone is often turned into jewellery. This item is one of many geological and mineral specimens that constitute a broader collection obtained from various regions across Australia (as well as some international locales) and generously contributed to the Burke Museum between 1868 and 1880. A significant portion of these specimens originated from Victoria and were acquired as a result of the Geological Survey of Victoria, initiated in 1852 during the Gold Rush era. The primary objective of this survey was to investigate and chart the geological characteristics of Victoria. The procurement of geological specimens played a vital role in advancing our comprehension of the Earth's scientific composition and was instrumental in supporting research and educational institutions throughout Australia, including the Burke Museum, in their efforts to foster further exploration and study. A solid mineral specimen in shades of green, grey and brownburke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Garnet crystals in galena, Unknown
... collecting of the geological surveyers in Victoria and Australia ...Majority of Galena in Australia is found in hydrothermal deposits emplaced around 1680 million years ago which have been heavily metamorphosed. Galena is the natural mineral form of lead sulfaide. It occurs generally as fine to large crystals due to syntectonic remobilization at low temperatures and moves to a suitable location. The colour is a shining lead and silvery gray with high specific gravity between 7.2 and 7.6 gms/cm3 and contains 86.6 lead sulfaide in its purest form. Its cyrstal system is cubic with perfect cleavages, and contract penetration and lamellar twinning. This particular specimen is from the Broken Hill mine, it is one of the largest lead mines located in Western New South Wales and still has ore reserves amounting to 20.9 million tonnes of ore grading of 7.4% lead, 9.4% zinc, and 61.5 million oz of Silver. Throughout its history, it has produced over 200 million tonnes of ore throughout its 127 years of mining history dating back to 1885. Galena mineral ore found in Australia is considered rare, as it is only currently found in the Broken Hill Mine of Western New South Wales. It represents heritage value through the systematic collecting of the geological surveyers in Victoria and Australia during the early to late 19th Century. The fact that it is only found in one mining area of Australia, shows that this specimen is rare for examples of Australian Galena. This mineral specimen is one part to a larger collection, aquistion, and distribution of Garnet in Galena around Australia and parts of the world and donated to the Burke Museum between 1860-1880. While this specimen was not found by the Victorian Geological Survey, it shows the historical need for mapping geological areas around the Gold Rush region to further identify areas of precious metal and gem aquisition. Additionally, collecting these specimens was an important part of mapping the scientific make up of the earth's surface. Many were sent to institutions for further contribution to research and scientific knowledge of the specimens. A solid coin-sized lead and zinc sulphaide and zinc silicate ore mineral in shades of black and red with shiny black points. GARNET CRYSTALS in / GALENA (lead sulphide), / SPALERITE (zinc sulphide), / WILLEMITE (zinc silicate) ore. / Locality: Broken Hill, NSWburke museum, #beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineral, galena, galena quartz, broken hill mine, broken hill, nsw -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Pyrite crystals in black slate, Unknown
... of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected ...Pyrite also known as iron Pyrite or fools gold is an iron sulfide with a chemical formula of FeS2 and is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Its metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold for which its nickname of Fools Gold comes from. There are a number of iron pyrite mines in Victoria and many would have been mined during Victoria's Gold Rush revolution in the 19th century. As it's lustrius yellow metallic look closely resembles gold, it is likely that it was often mistaken for gold as real gold was also often found in similar metamorphic and sedimentary rock. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these collections were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush). Collecting these specimens was an important part of Australia's early Geoplogical scientific discovery for mapping the earth's surface. It is unknown where in Victoria this specimen was mined from however; it shows strong provenance connections to Victoria's gold mining history and represents through larger economic and cultural structures the impact the Gold Rush had on Victoria during the 19th century. A solid coin-sized Pyrite crystal in black slate in shades of beige with tiny crystal structures. Pyrite / crystals / BB / in black slate / probably / victoria / (nice specimen)geology, geological specimen -
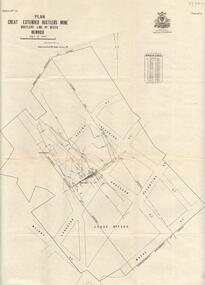 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - GREAT EXTENDED HUSTLER'S MINE - PLAN OF THE GREAT EXTENDED HUSTLER'S MINE
... Latham & Watson's Shaft Geological Survey of Victoria Underground ...Plan of the Great Extended Hustler's Mine. Bulletin No 33, Plate No XI. Shows No 2 Shaft, Latham & Watson's Shaft, levels and their depths and some geographical features. Geographical Survey of Victoria emblem and signed by H A Whitelaw, Underground Survey Office, Bendigo, September 1913. Has reference to photos.mining, parish map, great extended hustler's mine, no 2 shaft, latham & watson's shaft, geological survey of victoria, underground survey office bendigo, h a whitelaw -
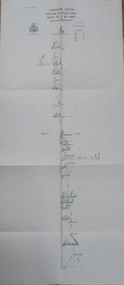 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - FORTUNA HUSTLER'S MINE - TRANSVERSE SECTION OF THE FORTUNA HUSTLER'S MINE
... Geological Survey of Victoria Underground Survey office Bendigo H ...Transverse Section of the Fortuna Hustler's Mine on the Hustler's Line of Reef, Bendigo. Bulletin No 33, Plate No III. Drawing shows poppet legs on the surface and Sill of Shaft 745.38 feet above Sea Level. Shows levels and their depths, geographical features and stone encountered. Reference table to stone and geographical features. Geographical Survey of Victoria emblem. Signed by H A Whitelaw, Underground Survey Office, Bendigo. mining, fortuna hustler's mine, hustler's line of reef, geological survey of victoria, underground survey office bendigo, h a whitelaw -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - HUSTLER'S REEF MINE - TRANSVERSE SECTION OF THE HUSTLER'S REEF MINE
... of the Hustler's Reef Mine Geological Survey of Victoria H A Whitelaw ...Transverse Section of the Hustler's Reef Mine on the Hustler's Line of Reefs. Bulletin No 33, Plate No XVIII. Shows cross-cuts and their depth, different types of stone and geological features encountered. Drawing of poppet legs at the surface and Sill of Shaft 756.39 ft above Sea Level. Reference Table shows key to the different stone and geographical features encountered. Geographical Survey of Victoria. Signed by H A Whitelaw, Underground Survey Office, Bendigo, September 1913. Thompson's Reef is also mentioned on the map. mining, hustler's reef mine, transverse section of the hustler's reef mine, geological survey of victoria, h a whitelaw, underground survey office bendigo, thompson's reef. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - HUSTLER'S CONSOLS MINE - TRANSVERSE SECTION OF THE HUSTLER'S CONSOLS MINE
... of the Hustler's Consols Mine Geological Survey of Victoria Underground ...Transverse Section of the Hustler's Consols Mine Bulletin No 33, Plate No XXXIII. Map shows poppet legs at the surface and Sill of Shaft 779.42 feet above Sea Level. Shows the different levels and their depths and the different stone and geographical features encountered. Has larger drawing of Section A - B. Geographical Survey of Victoria. Signed by H A Whitelaw, Underground Survey Office Bendigo, September 1913. mining, parish map, hustler's consols mine, transverse section of the hustler's consols mine, geological survey of victoria, underground survey office bendigo, h a whitelaw
