Showing 2501 items matching "lead"
-
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPamphlet, BUSINESS & TOURISM, BURIED RIVERS OF GOLD, 2021
MAP OF DEEP LEAD MINES, CRESWICK. WALKING TOURCOLOURED PAMPHLET FOLDED TO DL SIZE. INCLUDES MAP AND INFORMATION FOR SELF GUIDED TOUR. MAP OF THE DEEP LEAD MINES, CRESWICK, AND NOTES FOR YOUR SELF-GUIDED TOUR.gold mining, creswick -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumPhotograph, Photographer unknown, Queenscliff Customs house
Undated photo of the original Customs House building at Queenscliffe, with the adjacent steps that lead up the hill to the 'Black' high-light lighthouse.RealismBlack & white photo of the original Queenscliffe Customs House building, with the adjacent steps that lead up the hill to the 'Black' high-light lighthouse.On the reverse - NILcustoms house building, steps, lighthouse -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Alice Maud (Perry) Grinter
Teacher at Deep Lead School 712 From 1901 -1909B/W Photo. Portrait of a Lady wearing Glasses and Pearl NecklaceOn Reverse: Alice Maud (Perry) Grinter. Teacher at Deep Lead 1901, Sewing Mistress 1906, Resigned 1909.deep lead school, education -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Realia, c1860's-1880's
Reported as being with the Davidson family of Deep Lead for a long time. Who may have been the original Donors through Cliff LoatsSilver Pated Communion Set. Two wafer Plates, two challises, wine jug and serving tray. Used at Deep Lead Congregational Churchstawell, religion -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumPhotograph, Photographer unknown
Undated black & white photo of the original Customs House building at Queenscliffe, with the adjacent steps that lead up the hill to the 'Black' high-light lighthouse & Flag pole.RealismBlack & white photo of the original Queenscliffe Customs House building, with the adjacent steps that lead up the hill to the 'Black' high-light lighthouse.On the reverse - "date?", "present lighthouse 1863", "Mrs Campbell(?)"customs house building, steps, lighthouse -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This photograph depicts four men standing near a large unidentified building. This building is the entrance to a deep lead mine shaft. There is a bridge entering the building, which was used to access the elevator to the shaft. Deep lead mining involved placing large shafts into the ground which miners use to access deeper locations in order to excavate the rocks in the search for lead. Deep lead mining was highly dangerous as roofs could cave in of the soil was loose. Therefore, this particular mining considered to be highly undesirable profession as many miners did not want to work long hours nor risk their lives in the search for lead. Indigo Shire was a large area where deep lead mining took place, and thus the landscape and environment was largely impacted by these mining businesses. The Indigo Shire grew in population and wealth in the early 1850s when people came into this location in the hopes of finding gold and making a fortune. Ultimately, the accessibility and availability of gold and precious metals decreased once the gold reserves dried up and alongside this, the large population moved away. The Ovens was also heavily impacted environmentally as deep mining resulted in the change in land formation.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portray an open cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about the methods used to find gold in Indigo Shire. It also shows a location where deep mining was undertook which provides insight into the impact of deep mining on the environment at a time when it was done. This image is important for current research into the history of Indigo Shire, a region in Victoria's north-east. Therefore, this image has the capacity to be beneficial for research into society and the motivations of those living and working in this region during this period and therefore, has social significance. The Beechworth Burke Museum has additional images relating to deep lead mining and Indigo Shire which can be analysed and studied alongside images like this one.Sepia coloured retangular photo printed on gloss photographic paper.Reverse: 1997, 2510/ A02570/ Deep Lead Mining/ page 94/ 65%/ Burke Museum, Photo 44beechworth, burke museum, indigo shire, deep lead mining, mining, gold, gold mining -
 Buninyong & District Historical Society
Buninyong & District Historical SocietyPhotograph - Copy of original photo, black & white laser copy, Copy of photograph of John William Henry Austin
John William Henry Austin who emigrated with his brother Lindsay James to Australia in 1852, eventually settled in Durham Lead. He was a well known local photographer and also catered for local sporting functions including the Lal Lal races.John William Henry Austin was a well known local identity and photographer in the latter half of the 19th centuryCopy of photographed portrait of John William Henry AustinJohn William Henry Austin, Photographer, Durham Lead, 1870-1909.john william henry austin, austin family, photographer, local identity -
 Buninyong & District Historical Society
Buninyong & District Historical SocietyPhotograph - Photo of Original Photograph, John William Henry Austin, Photograph of Austin's Shoeing Forge and Coach factory, Learmonth St, c1899
historic, industryPhotograph of Austin's Shoeing Forge and Coach factory, Learmonth St. taken by John William Henry Austin, photographer of Durham Lead. on rear; "John Purcell Austin, Blacksmith, Buninyong, 1899. Took over from Caffrey. By 1906 Bourke had the forge. See p.34 Closed down 1938. JWH Austin Photographer, Durham Lead"john william henry austin, photographer, durham lead, austin shoeing forge, austin carriage factory -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - KELLY AND ALLSOP COLLECTION: SHARE CERTIFICATES - MOUNT DEDDICK SILVER-LEAD MINING CO, 14/07/1898 to 09/02/1899
Document. KELLY & ALLSOP COLLECTION. Two share certificates issued by the Mount Deddick Silver-Lead Mining Company, No Liability, Snowy River, East Gippsland. Certificate No. 1851 for 20 fully paid up shares @ 1 Pound each issued on 14 July 1898 to M.Kelly. Certificate No. 2113 for 5 fully paid up shares @ 1 Pound each issued on 9 Feb.1899 to M.Kelly of Bendigo. Capital raised was 60,000 Pounds from 60,000 shares. Each certificate signed by the Manager (signature not readable). Registered office - 31 Queen St., Melbourne.Mount Deddick Silver-Lead Mining Co.business, stockbroker, kelly & allsop, kelly & allsop collection, share certificates, mount deddick silver-lead mining co., m.kelly. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lead beater, dresser, plumbers' dresser -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPhotograph (item) - Black and white photograph, Unknown
A black and white photograph which shows two saddled horses standing at the sign that once stood near the track that lead to the base of Steavenson Falls in Marysville in Victoria.A black and white photograph which shows two saddled horses standing at the sign that once stood near the track that lead to the base of Steavenson Falls in Marysville in Victoria. The sign was destroyed in the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires. The Steavenson Falls is named after the Victorian Assistant Commissioner of Roads and Bridges, John Steavenson who arrived in Victoria in the early 1860s.STEAVENSON FALLS/ MARYSVILLE/ HEIGHT 271 FEETsteavenson falls, marysville, victoria, waterfalls, john steavenson -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Lead shot, Before 1878
The objects are a sample of medium caliber lead shot raised by Flagstaff Hill divers from the Loch Ard shipwreck site in 1976. Included in the vessel’s cargo manifest were 22 tonnes of lead shot, packed into her holds in cloth bags and wooden casks. These 49 pieces of 7 mm diameter lead shot are identical in size and smoothness. Each one also bears the same slightly raised square of residual metal left behind by the process of pouring molten lead into individual but identical moulds through a small (square) opening. These pieces of shot can be compared with contrast pieces in the Maritime Village collection, which are examples of shot tower pellet production; an industrial technique more suited to the creation of uniformly spherical balls that do not need subsequent trimming. In conventional shot tower production, lead is heated in a cauldron at the top of a 150-160 feet tower, and poured through a copper lattice that divides the metal into falling droplets. As these droplets fall, they spin into small spheres and gradually cool, before finishing in a pool of water at the bottom of the tower. However the maximum size of lead shot, and the economic efficiency of shot tower production, is limited by the practical height of the drop. Larger diameter lead shot must fall further in order to cool evenly and sufficiently to avoid shape distortion on hitting the water at the base. This sample of larger 7 mm lead shot, although mass produced, appears to have been manufactured under the traditional and more labour intensive mould system. They are therefore distinct from the other samples of smaller gauged and shot tower produced lead shot that were being imported on the Loch Ard . In terms of metallurgical technology these 7 mm shot are more closely related to an artifact in our Collection (No. 5241) — a forged set of pincers or pliers with two facing cups at the end. When the pincers are closed, the cups join to form a single mould. Molten lead is poured through a small (circular) opening left at the top of the mould. When cooled the pincers are opened, breaking the mould and releasing the lead shot. The excess metal left over from the pouring operation at the top of the ball is then trimmed off using the scissor like cutting edges on the inner side of the pliers handles. In this manner, individual shooters were able to make their own ammunition for their shotguns. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got it’s name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic.The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register Ref S 417. Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. A quantity of forty-nine (49) loose round lead shot of 7 mm diameter retrieved from the wreck of the Loch Ard. All are smooth round spheres with the same small raised square of excess lead on one face.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, shipwreck artefact, shot, lead shot, shot towers, shot mould, colonial imports, practical metallurgy -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet.13"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet. 11½"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lead beater, lead dresser, plumbers' dresser, beating mallet -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet.13"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lead beater, lead dresser, plumbers' dresser -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet. 13¼"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lead beater, lead dresser, plumbers' dresser -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionWatercolour Painting, The Rotunda in the Surrey Gardens,1966, 1966
The rotunda in the Surrey Gardens was built in 1912 and demolished in the early 1970's. The rotunda was dedicated to John Gray in appreciation of his service to the community. The watercolour was painted in 1966 by Miss Barker of Union Road. The artist may be Valerie Jean Barker of Unit 5, 246 Union Road. (REF: 1963 electoral roll). There is no knowledge of the identity of the lettering in the lower right hand corner of the painting. The medium is grey lead ink and watercolour. Framed watercolour of the rotunda in Surrey Gardens painted circa 1966. The medium is grey lead ink and watercolour.On the back: "The Rotunda in the Surrey Gardens, 1966/, Ink and watercolour by Miss Barker of Union Road, Surrey Hills/ [Could be Valerie Jean Barker, 5/246 Union Road - ref:1963 electoral roll]" -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDresser
Also called Lead Beater, Lead Dresser or Plumbers' Dresser -Wooden lead beating mallet.320mm longflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Lead line
The lead line or hand lead is a simple navigational instrument used as a depth finder to measure the depth of water under the ship’s keel and to take samples of the sea bed. The long line may be marked at regular intervals with tags of different coloured and textured fabric, such as rope, leather and cloth. Each tag was a code to represent a certain depth. The leadsman’s eyes and hands could distinguish the depth easily as he drew in the lead line, day or night and in poor weather conditions. A standard set of codes for the tags was used so that the depth of the sea could be easily and quickly read. The measurement used was a Fathom, which equals 1.83 metres. The codes were: - 2 fathoms = 2 strips of leather 3 fathoms = 3 strips of leather 5 fathoms = white duck fabric 7 fathoms = red bunting fabric 10 fathoms = leather with a hole 13 fathoms = blue serge fabric 15 fathoms = white duck fabric 17 fathoms = red bunting 20 fathoms = 2 knots The lead weight could be between 7 -14 pounds (3.5 – 6.5kg) and the rope would be approximately 25 fathoms (45m). The hollowed-out end of the weight would hold a stick substance such as tallow or wax, which would pick up samples from the sea bed which would show whether the vessel was close to, or far away from, the shore. The leadsman would stand at the front of the vessel and cast the lead line into the sea. When it hit bottom he would note the tag marker nearest the surface of the water and call out his finding. Then he would haul it up again and examine the kind of matter that adhered to the end of the weight, whether it be sand, mud, gravel, or the colour of it. This information would be given to the ship’s helmsman or navigator and would help indicate the proximity to the land.This handheld lead is an example of early marine navigational equipment used by sailors to travel the seas to measure the depth of the water and sample the nature of the seabed. It helps to understand the history and progress made from the very basic to the sophisticated technology of today.Lead line, sounding line or depth finder. The long length of rope has a heavy lead weight attached to the end. Coloured fabric tags are tied onto the rope at regular intervals, representing different depths. The concave base of weight holds sticky substances such as tallow or beeswax, providing an adhesive surface to collect samples of sea bed like sand, shells or pebbles. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, lead line, depth finder, hand lead, sounding lin, leadsmane, navigation instrument, leadline, hand lead line -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bottle Seal, circa 1843-1878
This lead sealing capsule was recovered from the tragic wreck of the sailing ship ‘Loch Ard’. It may have once been on a bottle amongst the ship's cargo, its provisions or the passengers’ personal luggage. It is now part of the John Chance collection. Bottles in the early 19th century were handmade. They were not necessarily uniform in size or shape, so sealing was not always successful. If the bottles were stored they often became contaminated by rats and mice breaking the cork or wax seals, or by insects attracted to the contents if the seal on the bottle leaked. Lead sealing capsules were used from 1843 to overcome this problem. The lead was heated until it was malleable, then moulded by hand to fit over the sealed bottle’s mouth and neck. This was more successful if wire was also used under the capsule for added security (similar to modern champagne bottles). The capsule couldn’t be re-fitted so it was discarded after the bottle was opened. Capsule designs from about 1862 used tin-plated lead foil and often had the inscriptions and trademarks of the content makers on them. Eventually it was found that the lead was toxic. The lead was replaced by tin, aluminium, and later plastic. Today’s home brewers can buy readymade plastic capsules that fit over the bottle then twist to lock it firmly into place and can be re-used. Digs at archaeological sites often reveal lead sealing capsules. These are collected and catalogued. The information gathered from inscriptions, makers’ marks, logos and descriptions of the bottle contents has provided valuable insights into the history and the dating of other items on the sites. This lead sealing capsule was made to seal a handmade glass bottle and is historically significant for representing its invention to solve a preservation and integrity issue with bottle seals in the mid-to-late 19th century. Its design has evolved and is still in use today. This sealing capsule is representative of their historical use of capsules as a tool for dating and interpreting archaeological sites around the world. The sealing capsule is also significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard in the 1960s-70s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The sealing capsule is also significant for being connected to the wreck of the Loch Ard (1873-1878), which is historically significant to both Victoria and Australia. The loss of the ship has been described as one of the ‘worst shipwreck tragedies’ and is well known in Victoria for the tragic death of 52 out of the 54 lives on board. The Loch Ard wreck's historical significance as a large international passenger and cargo clipper ship has been recognised and it is now registered on the Victorian Heritage Database, VHR S417. The wreck site is labelled as ‘one of Victoria’s most spectacular diving sites’ and the area is a popular tourist site. It is part of Victoria’s Underwater Shipwreck Discovery Trail.Bottle sealing capsule, cylindrical with thin, round top separated from thicker body (taped in place and fragile). Made from grey-white lead, uneven in thickness and shape. Remnants of a thick substance are inside the capsule.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, loch ard, bottle seal, bottle capsule, handmade bottle, antique bottle, sealing capsule, lead capsule, bottle closure, bottle foil, bottle preservation, bottle finish -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Lead nipple shields developed by Dr. Wansbrough, Dr Wansbrough, England
The changes in the metal observable on the interior of both these lead nipple shields suggests that this pair was well used. One can only imagine the long-term effects. Perhaps significantly, the lid of the box is stained with the distinctive purple of gentian violet. The underside of the lid claims “They are in no way likely to be injurious to the infant”. Allen & Hanbury’s catalogue of c1901 lists these as costing 1/- per pair.Two nipple shields, lead, moulded, 6cm diameter, with "England" impressed on inside. In original manufacturer's circular cardboard box.breast feeding -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Lead shot mould, Early 20th century
This lead shot mould would have been used by those people wanting ammunition for shotguns. The moulds were probably originally used in a blacksmith’s forge. Although it has no known local provenance, this lead shot mould is of interest as an example of an early tool. This is a metal tool with handles in the shape of calipers with a rounded ball of metal at one end. The ball is split in the middle to allow molten material to be inserted for casting into lead shot. The object is heavily rusted.‘16’history of warrnambool, vintage tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Ammunition, Before 1878
The objects are a small sample of small gauge lead shot raised by Flagstaff Hill divers from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site in 1976. Companion pieces are in the Maritime Village collection. The three masted, iron hulled, LOCH ARD was wrecked against the tall limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island in the early hours of the first of June 1878. Included in her diverse and valuable cargo were 22 tons of lead shot, packed in cloth bags and wooden casks. Bulk quantities of lead shot, uniformly round balls of dull grey metal ranging from 2mm “birdshot” to 8mm “buckshot”, were routinely exported to the Australian colonies. Shot was used mostly as projectiles fired from smooth bored guns to bring down moving targets such as wild ducks and small game. It was also useful as ballast, when a dense, “pourable” weight was required to fill cavities or establish volume within a measuring container. The production of consistently round spheres of lead shot required the pouring of molten metal through a sieve and then a long drop through the atmosphere to a water filled basin for final cooling and collection. This “shot tower” process was first patented by William Watts of Bristol in 1782. His calculation of a 150 feet fall was not only to form evenly spherical droplets through surface tension, but also to provide partial cooling and solidification to each shot before they hit the water below. The value of his innovation was the minimising of indentation and shape distortion, avoiding the expense of re-smelting and re-moulding the lead. Lead shot was already being produced in Australia at the time the LOCH ARD loaded her cargo and left Gravesend on the second of March 1878. James Moir constructed a 157 feet circular stone shot tower near Hobart in 1870, with a peak annual production of 100 tons of lead shot sold in 28 pound linen bags. However colonial demand exceeded this source of local supply. The continued strength of the market for lead shot in the Colony of Victoria prompted substantial investment in additional productive capacity in Melbourne in the next decade. In 1882 Richard Hodgson erected the 160 feet round chimney-shaped Clifton Hill shot tower on Alexandra Parade (VHR H0709) and in 1889 Walter Coop built the 160 feet square tower-shaped Melbourne Central shot tower on La Trobe Street (VHR H0067). At its peak, the Coop Tower produced 6 tons of lead shot per week, or 312 tons per annum. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A quantity of 2mm and 4mm lead shot ammunition retrieved from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site. They are concreted together by sediment. There are (6) small pieces with some single shot and a larger conglomerate of cemented shot. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, lead shot, colonial industry, melbourne shot towers, victorian metallurgy, colonial imports -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lead Ingot, circa 1878
This lead ingot was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in January 2015 by local residents who discovered the ingot in their garden after they purchased the property about 12 months ago The LOCH ARD cargo manifest lists “Pig lead 50 tons” comprising “944 pig and 37 rolls”. Subsequent classification has rendered this section of cargo as “Lead Ballast”. This could be true. The international price per ton of lead ore plunged from a high point of £17 in 1853 to a low of £8 in 1882. The cheaper price of lead at the time of the vessel’s loading in early 1878 may have meant it was considered as an alternative to other ballast material (traditionally stone) for the journey to Melbourne. Loch Line ships generally returned to Britain laden with Australian wool. Even though wool bales were “screwed in” to the hold to less than half their “pressed weight”, they still made an awkwardly light cargo for the passage around the Horn. The concentrated weight of lead pigs along the keel line would help steady and centre the ship, and perhaps the artefacts in this case were to be retained for this purpose, rather than being sold on to the ready colonial market. However this is conjecture. Demand for building materials in the gold and wool rich Colony of Victoria was high in the 1870s, and much of the LOCH ARD cargo was intended for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880, which was another example of buoyant economic conditions. In the nineteenth century lead was valued for its density (high ratio of weight to volume), flexibility (relative softness for working into shape), and durability (corrosion resistant and waterproofing properties). It was used for pipes and water tanks, roof flashing and guttering, window sealing and internal plumbing. Many large private residences and new public buildings were at planning or construction stage in the colony during this period. The LOCH ARD lead ingots could equally have been destined for this ready market. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Lead ingots (sometimes referred to as ‘lead ballast’ or ‘lead pigs), salvaged from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. Grey metal bars with flat base, rising in a curved moulded shape to form a smooth rounded upper face. The imprint of the maker runs along the upper surface in clearly legible capital lettering (height 3cm). Durable and heavy, with some marine staining, but in good condition. Stamped along curved surface, within oval border, "PONTIFEX & WOOD LONDON."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, lead pigs, lead ingots, lead ballast, pontifex and wood, london, lead smelters -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Domestic object - Pencil, 19th Century
This pencil was found in 1946 by Mr Jim Pelling when an old wall was being pulled down in Warrnambool. This type of pen would have been used in the 19th century and apparently produced good legible writing and the lead point never wore out. No information is available on Jim Pelling or the location of the wall.Although this pencil has no known provenance it is of considerable interest because of its finding in an old wall in Warrnambool and because of its antiquarian value. It is a good example of a writing tool of the past and the ivory handle is of particular interest. This is a pencil with a handle made of ivory with a sharpened point of metallic lead screwed on the end of it. The end of the handle has an ornamental column shape. The lead at the end is slightly bent. Accompanying the pencil is an extract from a 1946 Warrnambool Standard detailing the finding of the pencil and some handwriting from a later date. The newspaper extract is pasted on to a piece of cardboard (a piece of a Rice Bubbles packet).In blue handwriting: ‘Extract from 1946 Warrnambool Standard’ and ‘Given to Warrnambool Historical Society by Mr J. Pelling 1970’jim pelling, metallic lead pencil, warrnambool history -
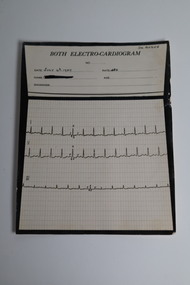 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document - "Both" Electrocardiogram printout, 4 Jul 1939
In 1932, Edward Thomas Both invented the first portable direct reading electro cardiograph. This item is a three lead electrocardiograph tracing conducted on one of Dr Angus' patients in 1939. Dr William Roy Angus (1901-1970) came to Warrnambool in 1939, purchasing the general practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson. He was the last serving Warrnambool Port Medical Officer. A health problem after the war prompted a change from general practice to ophthalmology. Dr. Angus became an important ophthalmologist , pioneering the use of the intrascleral cartilage implant which resulted in cosmetically better artificial eyes. He was an Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist at Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He was Secretary of the Victorian South West sub-division of the Australian Medical Association from 1949 to 1956 and Chairman from 1956 to 1958. His obituary in the Medical Journal of Australia (July 1970) stated he was "dedicated and devoted to both his profession and his patients" .This item provides a link to an Australian invention of medical equipment which improved diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions in the 1930's. It is an example of diagnostic recordings used by a Warrnambool doctor in 1939.This is a card record of a three lead "Both" Electrogram. The upper one third has places for the date patient details and diagnosis. There are three electrocardiogram tracings over graph paper in the bottom two thirds of the item. The reverse side has a handwritten in ink interpretation of the tracings.Front: BOTH ELECTRO-CARDIOGRAM No. Date July 4th 1939 Rate 130 Name Age Diagnosis The patient name has been blacked out. Dr. Angus is printed in the top right hand corner. Rear: The P wave in lead 1 is broadened and notched, and has a suggestive "plateau" top. This may indicate a mitral stenosis, auricular hypertrophy. E Bannondr william roy angus, both electro-cardiogram, dr angus collection -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionDomestic object - Toys - Lead Soldiers, n.d
Small collection of lead soldiers (5), lead flag and toy lead cannon parts, found at site of the 'Loch Ard' wreck. In plastic box.loch ard shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lead shot, Circa 1877
This artifact is a sample of small caliber lead shot recovered by Flagstaff Hill divers from the wreck of the Loch Ard in 1975. Included in her diverse and valuable cargo were 22 tons of lead shot, packed in cloth bags and wooden casks. Bulk quantities of lead shot, uniformly round balls of dull grey metal ranging from 2mm “birdshot” to 8mm “buckshot”, were routinely exported to the Australian colonies. Shot was used mostly as projectiles fired from smooth bored guns to bring down moving targets such as wild ducks and small game. It was also useful as ballast, when a dense, “pourable” weight was required to fill cavities or establish volume within a measuring container. The production of consistently round spheres of lead shot required the pouring of molten metal through a sieve and then a long drop through the atmosphere to a water filled basin for final cooling and collection. This “shot tower” process was first patented by William Watts of Bristol in 1782. His calculation of a 150 feet fall was not only to form evenly spherical droplets through surface tension, but also to provide partial cooling and solidification to each shot before they hit the water below. The value of his innovation was the minimising of indentation and shape distortion, avoiding the expense of re-smelting and re-moulding the lead. Lead shot was already being produced in Australia at the time the Loch Ard sinking in March 1878. James Moir had constructed a 157 feet circular stone shot tower near Hobart in 1870, with a peak annual production of 100 tons of lead shot sold in 28 pound linen bags. However colonial demand exceeded this source of local supply. The continued strength of the market for lead shot in the Colony of Victoria prompted substantial investment in additional productive capacity in Melbourne in the next decade. In 1882 Richard Hodgson erected the 160 feet round chimney-shaped Clifton Hill shot tower on Alexandra Parade (VHR H0709) and in 1889 Walter Coop built the 160 feet square tower-shaped Melbourne Central shot tower on La Trobe Street (VHR H0067). At its peak, the Coop Tower produced 6 tons of lead shot per week, or 312 tons per annum. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from "Loch Ard" a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curle & Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen, and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead, and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Lochard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy that had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost families in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce, and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Lochard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Lochard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Lochard Gorge. Cargo and artifacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artifacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artifacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collection's objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Lead shot; a group of mixed -sized lead shot. Small 2mm shot is embedded in a sea sediment clump of concretion. Also in the group are also 5 single 2mm shot and 4 single 4mm shot that are clean and free of sediment. The shot was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Nonewarrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, lead shot, loch ard, colonial industry, melbourne shot towers, victorian metallurgy, colonial imports -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook - BOOK, INFANTRY, HER MAJESTY"S STATIONARY OFFICE, INFANTRY DRILL 1893 BY AUTHORITY, C.1893
INFANTRY DRILL 1893 BY AUTHORITY - Infantry Drill Training - BritishCover - hard cover, cardboard, leather - dark red with gold print on front and spine, with gold military coat of arms above print on front. Front embossed to frame print. Pages - 269 pages, cut, stippled edges, coloured light red, off white. Block print including front and back end papers. Illustrated - black and white diagrams and illustrations. Grey lead pencil annotations throughout the book. Contents Page. greylead pencil - " ......./D Coy/69th Battalion" Throughout the book - grey lead pencil - "X"book, infantry, drill, british -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionFunctional object - STAMP, n.d
Stamp, lead, 'E.G.VIVIAN'
