Showing 7 items matching " salad rolls"
-
 Musculoskeletal Health Australia (now held by the Glen Eira Historical Society)
Musculoskeletal Health Australia (now held by the Glen Eira Historical Society)Photograph - Objects, 19/03/2002
... salad rolls... covered with a white tablecloth. The food consists of salad rolls... healthy people graded walks trial lunch salad rolls fruit platter ...On Tuesday the 19th of March 2002, a small group of people of varying ages took part in assessing the level of difficulty of some walking paths at Jells Park in Wheeler's Hill. Their assessments would inform the development of a guide of graded walks as part of the Healthy Parks, Healthy People program. Guided by two Parks Victoria rangers, the group tried out a few walking paths consisting of varying levels of difficulty. Aterwards, they enjoyed a light lunch.COL photo of various items of food. set up on a table covered with a white tablecloth. The food consists of salad rolls, a fruit and cheese platter, and a small plate of crackers. Also on the table is a glass bottle of water, two 'Healthy Parks Healthy People' branded green plastic water bottles, some glasses and various pieces of white crockery (cups and saucers, a small white milk jug, and a set of salt and pepper shakers).arthritis foundation of victoria, afv, healthy parks healthy people, graded walks trial, lunch, salad rolls, fruit platter, crackers, water bottle, 2002 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lamp, circa 1878
This Flying Angel lamp bracket was recovered from the wreck site of the steam sailing ship, "Loch Ard", which sank near Port Campbell, Victoria in 1878. It formed part of the ship's cargo. The 'flying angel' lamp was, for a time, displayed in the St Nicholas Seamen's Church at Flagstaff Hill. The design was very appropriate to the Missions to Seamen, being associated with the emblem of the 'flying angel' on the Missions' to Seamen's flag. Brief history of the Loch Ard: The vessel Loch Ard was constructed on the Clyde River in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. She sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. A century later, despite the pounding seas and the efforts of looters, the wreck site continued to provide ample evidence of the extraordinary range of goods being imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” The lamp bracket is significant for its connection with the wreck of the sailing ship, Loch Ard, in 1878. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Gas lamp, brass, single burner, wall-mounting bracket, delicately crafted. Ornate decoration features bust of an angel with up-swept wings, or 'flying angel'. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, lamp fitting, shipwreck artifact, 1878, shipwreck cargo, household effects, 19th century lighting, angel lamp, loch ard lamp, angelic lamp, lighting at sea, marine technology, ship's lighting, flying angel, gas lamp, maritime archaeology, port campbell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, Circa 1878
The artefact is a damaged brass cow bell recovered from the 1878 shipwreck of the LOCH ARD near Port Campbell. It was raised by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1973 and is in storage at the Maritime Village. The LOCH ARD was constructed on the Clyde in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. She sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman and one young female passenger. A century later, despite the pounding seas and the efforts of looters, the wreck site continued to provide ample evidence of the extraordinary range of goods being imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” From this array of objects on the ocean floor emerged the humble brass cow bell. Cow bells were common to colonial agriculture and transport, used wherever animals were turned out to graze overnight and had to be rounded up again next morning. Bells were fastened around the necks of household milking cows, domestic goats, bullock teams, horse teams, and camel teams, to help find them in the pre-dawn light. Station shepherds and cattle drovers also used them to warn of any disturbances to their flocks and herds overnight. The bells were a necessary item in a largely unfenced continent. So important, that Anthony Mongon began making his pot-bells at Yackandandah from 1861, August Menneke produced the “Wagga Pot” from 1867, and Samuel Jones started manufacturing his distinctively shaped “Condamine Bell” in 1868. However, these deeply resonant Australian bells were made from iron — Mongon and Jones were blacksmiths who simply beat old pitsaw blades into shape. Few genuinely brass cow bells were made here, the vast majority being imported from Britain where the industry of brass founding was already well established. (Some bells were also imported from the United States, but these too were nearly all of iron).This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. It was included in the cargo of the Loch Ard. Its significance is increased by being one of a collection of artefacts recovered by the Flagstaff Hill Divers from the wreck of the Loch Ard in the early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have also been recovered for Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection under a Government permit, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The cow bell is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best-known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Cow bell; a small brass bell, blunt-wedge shaped. The sides expand outwards from the smaller rectangular roof of the bell to a larger open rectangle or bell mouth. The handle, now missing, was fixed in two places at the top. A neat half-circle piece has been cut from the base on a long edge. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, eva carmichael, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, brass cow bell, colonial cow bells, 1878 shipwreck, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hill divers, cow bell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, Circa 1878
The artefact is a damaged brass cow bell recovered from the 1878 shipwreck of the LOCH ARD near Port Campbell. It was raised by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1973 and is in storage at the Maritime Village. The LOCH ARD was constructed on the Clyde in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. She sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman and one young female passenger. A century later, despite the pounding seas and the efforts of looters, the wreck site continued to provide ample evidence of the extraordinary range of goods being imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” From this array of objects on the ocean floor emerged the humble brass cow bell. Cow bells were common to colonial agriculture and transport, used wherever animals were turned out to graze overnight and had to be rounded up again next morning. Bells were fastened around the necks of household milking cows, domestic goats, bullock teams, horse teams, and camel teams, to help find them in the pre-dawn light. Station shepherds and cattle drovers also used them to warn of any disturbances to their flocks and herds overnight. The bells were a necessary item in a largely unfenced continent. So important, that Anthony Mongon began making his pot-bells at Yackandandah from 1861, August Menneke produced the “Wagga Pot” from 1867, and Samuel Jones started manufacturing his distinctively shaped “Condamine Bell” in 1868. However, these deeply resonant Australian bells were made from iron — Mongon and Jones were blacksmiths who simply beat old pitsaw blades into shape. Few genuinely brass cow bells were made here, the vast majority being imported from Britain where the industry of brass founding was already well established. (Some bells were also imported from the United States, but these too were nearly all of iron).This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. Its significance is increased by being one of a collection of artefact recovered by the Flagstaff Hill Divers from the wreck of the Loch Ard in the early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have also been recovered for Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection under Government permit, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The cow bell is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.A small brass cow bell, in poor condition. It is blunt-wedge shaped. The sides expand outwards from the smaller rectangular roof of the bell to a larger open rectangle or bell mouth. A handwritten label is attached to the bel. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Label text "["10/6/73, Brass Cow Bell, LOCH ARD, Found in the sandy hole in the centre of the wreck site. Cow bells were part of the cargo" - "10/6/73, LOCH ARD, small brass cow bell salvaged by FHMV divers"]. "LOCH ARD / PETER RONALD"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, eva carmichael, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, brass cow bell, colonial cow bells, 1878 shipwreck, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hill divers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, Circa 1878
The artefact is a brass cow bell recovered from the 1878 shipwreck of the LOCH ARD near Port Campbell. It was raised by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1973 and is in storage at the Maritime Village. The LOCH ARD was constructed on the Clyde in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. She sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. A century later, despite the pounding seas and the efforts of looters, the wreck site continued to provide ample evidence of the extraordinary range of goods being imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” From this array of objects on the ocean floor emerged the humble brass cow bell. Cow bells were common to colonial agriculture and transport, used wherever animals were turned out to graze overnight and had to be rounded up again next morning. Bells were fastened around the necks of household milking cows, domestic goats, bullock teams, horse teams, and camel teams, to help find them in the pre-dawn light. Station shepherds and cattle drovers also used them to warn of any disturbances to their flocks and herds overnight. The bells were a necessary item in a largely unfenced continent. So important, that Anthony Mongon began making his pot-bells at Yackandandah from 1861, August Menneke produced the “Wagga Pot” from 1867, and Samuel Jones started manufacturing his distinctively shaped “Condamine Bell” in 1868. However, these deeply resonant Australian bells were made from iron — Mongon and Jones were blacksmiths who simply beat old pitsaw blades into shape. Few genuinely brass cow bells were made here, the vast majority being imported from Britain where the industry of brass founding was already well established. (Some bells were also imported from the United States, but these too were nearly all of iron). This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. Its significance is increased by being one of a collection of artefact recovered by the Flagstaff Hill Divers from the wreck of the Loch Ard in the early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have also been recovered for Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection under Government permit, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The cow bell is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Brass cow bell, flat-top pyramid shape, rectangular head, shoulders flare out to a rectangular mouth. The hanging yoke is missing. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, loch ard, cowbell, great ocean road, loch line, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, cow bell, brass cow bell, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hill divers, horse bell, bell smith, vintage bell, farmer, shepherd, drover, stock bell, brass bell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, circa 1878
The artefact is a brass cow bell recovered from the 1878 shipwreck of the LOCH ARD near Port Campbell. It was raised by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1973 and is in storage at the Maritime Village. The LOCH ARD was constructed on the Clyde in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. She sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. A century later, despite the pounding seas and the efforts of looters, the wreck site continued to provide ample evidence of the extraordinary range of goods being imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” From this array of objects on the ocean floor emerged the humble brass cow bell. Cow bells were common to colonial agriculture and transport, used wherever animals were turned out to graze overnight and had to be rounded up again next morning. Bells were fastened around the necks of household milking cows, domestic goats, bullock teams, horse teams, and camel teams, to help find them in the pre-dawn light. Station shepherds and cattle drovers also used them to warn of any disturbances to their flocks and herds overnight. The bells were a necessary item in a largely unfenced continent. So important, that Anthony Mongon began making his pot-bells at Yackandandah from 1861, August Menneke produced the “Wagga Pot” from 1867, and Samuel Jones started manufacturing his distinctively shaped “Condamine Bell” in 1868. However, these deeply resonant Australian bells were made from iron — Mongon and Jones were blacksmiths who simply beat old pitsaw blades into shape. Few genuinely brass cow bells were made here, the vast majority being imported from Britain where the industry of brass founding was already well established. (Some bells were also imported from the United States, but these too were nearly all of iron). This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Cow bell, brass, covered in encrustation, handle missing from the top.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, glenample, eva carmichael, tom pearce, flagstaff hill divers, cow bell, horse bell, bell smith, vintage bell, farmer, shepherd, drover, stock bell, brass bell -
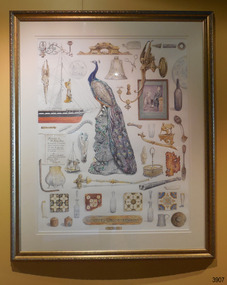 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageArtwork, other - Framed poster, Tim Walker, Loch Ard Shipwreck, circa 2010
Tim Walker’s work is an eye-catching array of shipwreck artefacts and associated items. They help tell the story of the 19th century ships that travelled across the world full of people and cargo that are now part of our history. The work was commissioned especially for Flagstaff Hill and highlights the famous story of the 1878 ‘Loch Ard’ shipwreck. The images also include two small items from the 1981 ‘Fiji’ shipwreck. Local professional artist Timothy “Tim” Walker was born in Britain in 1970. He was self-taught had the desire to use his talents for full-time work. He specialised in painting local scenes, landscape and people of Warrnambool and district after he moved there in 1990. As he worked at the location of his subjects, people often told him interesting and amusing stories. He soon became involved in the Warrnambool and District Artists’ Society, where he has served for a period as President. In 2010 Warrnambool Art Gallery hosted an exhibition “Nine Lives” with works from nine local artists including Tim Walker. The ‘LOCH ARD’ 1873-1878 - brief history The clipper ship ‘Loch Ard’ was a built in Scotland in 1873. In 1978 the ship was sailing to Melbourne with 54 people on board as well as a mixed cargo of items, some of which were bound for the 1880 International Exhibition in Melbourne. On June 1st 1878 it was very close to its destination when it crashed into Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell. Only two people survived. The wreck was re-discovered in 1967, almost a century later, and the site continues to provide evidence of the range of goods imported into the Colony of Victoria in the post-Gold Rush era. Flagstaff Hill divers in the 1970s reported finds of “Bottles of champagne, window panes, rolls of zinc, barrels of cement, iron rails, clocks, lead shot, corrugated iron, lead, marble, salad oil bottles, ink bottles, copper wire, gin bottles, rolls of carpet, floor tiles, copper rivets, gas light fittings, pocket knives, toys, crystal chandeliers, beer mugs, cutlery, candles sticks, wick scissors, cow bells, and sauce bottles.” The famous Loch Ard Peacock was also on board. The ‘FIJI’ 1875-1891 – brief history The barque ‘Fiji’ was built in Ireland in 1875. The sailing ship left Hamburg in May 1891, bound for Melbourne with a crew of twenty-five plus the captain. The ‘Fiji’ had almost reached her destination after a trip of 100 days at sea when, on September 5th 1891, she struck rock 300 metres from the shore at Moonlight Head, near Cape Otway. Eleven men lost their lives but with the help of locals including members of the Rocket Rescue Crew, the rest of the men were saved. In anticipation of Christmas, the cargo had included a wide variety of children’s toys, amongst which were dolls with china limbs, wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, and red and white rubber balls. There were also cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits, sailcloth, tobacco, fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos, concertinas and other musical instruments, artists’ supplies, porcelain, furniture, china and candles. This artwork has historical significance as it shows a small sample of the variety of items on board the late 19th century ships bound for Australia in the Colonial and late God Rush period. The cargo contained personal luggage, items intended as gifts, and goods ordered for domestic, commercial or industrial use. The wreck sites of both vessels, ‘Loch Ard’ and ‘Fiji’ are classified on the Victorian Heritage Register as significant and are now protected by government law. The sites are popular with divers and provide interpretive material regarding social and maritime history. Framed poster of a watercolour painting by Tim Walker, gilt frame, behind glass. Subject is a group of objects, most of which are connected with the 1878 shipwreck Loch Ard, such as items recovered from the shipwreck and the famous ‘Loch Ard Peacock’. Two items are from the wreck of the ‘Fiji’. Inscriptions on ingot, a handwritten letter, bell, clear bottle, and small plaque.On ingot: “PONTIFEX & WOOD. LONDON”. On letter: “Presented to Mr. Thomas Pearce”. On small ingot: “TIM WALKER”. On bell: “LOCH ARD”. On clear bottle “THE SINGER MANUFACTURING COMPANY“. On plaque: TIM WALKER”.warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, flagstaff hill, loch ard, fiji, watercolour, timothy walker, tim walker, warrnambool & district artists’ society, warrnambool art gallery, poster, henna street picture framers, cargo, print
