Showing 5 items matching "allied subjects"
-
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, Ministry of Defence: Physical Training In The Army: Pamphlet No.7: Allied Subjects (Group C), 1966
... : Pamphlet No.7: Allied Subjects (Group C)...Allied Subjects... Allied Subjects Basket Ball Gymnastics Fencing A brown coloured ...A brown coloured cardboard cover with what looks like water marks on it. Under the British Insigna are the details of the booklet. The bottom right corner has torn away. There are three punch holes down the left hand side of the booklet. the spine of the booklet has some tear marks on it.ministry of defence (army), british army, physical training, allied subjects, basket ball, gymnastics, fencing -
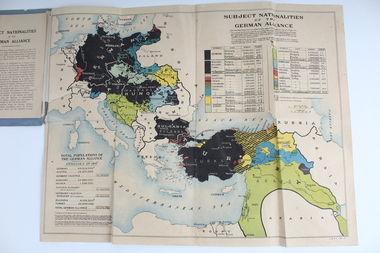 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchBooklet With Map, Cassell and Compnay Limited, Subject Nationalities of the German Alliance, 1917
Map Produced for Allied ForcesMap of German Alliance as to which nationalities were aligned with GermanyGrey Booklet containing Coloured map of the German AllianceGrey Booklet Subject Nationalities of the German Alliance (With a coloured map from German Sources) Cassell and Company Limited London New York Toronto Melbourne 1917 Price 2d -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchLetter, Dwight D Eisenhower, 1 January 1944
Letter is signed by Dwight D Eisenhower from the Allied Force Headquarters, Office of the Commander-in-Chief, and addressed to all those serving in the Allied Forced during WWII.Letter with subject "Farewell Message". A4 size paper with black print. Printing press, not typewriter.Header: "ALLIED FORCE HEADQUARTERS / Office of the Commander-in-Chief" Subject: "Farewell Message" To: "All men and women serving in or with Allied Forces in the Mediterranean Theater" Handwritten signature, "Dwight D Eisenhower"dwight eisenhower, allied forces, 1944, wwii, mediterranean theater -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Isaac Butt, c1864, 1864
An Irish barrister, politician, Member of Parliament (M.P.), and the founder and first leader of a number of Irish nationalist parties and organisations, including the Irish Metropolitan Conservative Society in 1836, the Home Government Association in 1870 and in 1873 the Home Rule League. (Wikipedia) After being called to the bar in 1838, Butt quickly established a name for himself as a brilliant barrister. He was known for his opposition to the Irish nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell's campaign for the repeal of the Act of Union.[4] He also lectured at Trinity College, Dublin, in political economy. His experiences during the Great Famine led him to move from being an Irish unionist and an Orangeman[5] to supporting a federal political system for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that would give Ireland a greater degree of self-rule. This led to his involvement in Irish nationalist politics and the foundation of the Home Rule League. Butt was instrumental in fostering links between Constitutional and Revolutionary nationalism through his representation of members of the Fenians Society in court. (Wikipedia) He began his career as a Tory politician on Dublin Corporation. He was Member of Parliament for Youghal from 1852 to 1865, and for Limerick from 1871 to 1879 (at the 1852 general election he had also been elected for the English constituency of Harwich, but chose to sit for Youghal). The failed Fenian Rising in 1867 strengthened Butt's belief that a federal system was the only way to break the dreary cycle of inefficient administration punctuated by incompetent uprisings.[6] In 1870 he founded the Irish Home Government Association. This was in no sense a revolutionary organisation. It was designed to mobilise public opinion behind the demand for an Irish parliament, with, as he put it, "full control over our domestic affairs."[6] He believed that Home Rule would promote friendship between Ireland and her neighbour to the east. In November 1873 Butt replaced the Association with a new body, the Home Rule League, which he regarded as a pressure-group, rather than a political party. In the General Election the following year, 59 of its members were elected. However, most of those elected were men of property who were closer to the Liberal cause.[7] In the meantime Charles Stewart Parnell had joined the League, with more radical ideas than most of the incumbent Home Rulers, and was elected to Parliament in a by-election in County Meath in 1875.[8] Butt had failed to win substantial concessions at Westminster on the things that mattered to most Irish people: an amnesty for the Fenians of '67, fixity of tenure for tenant-farmers and Home Rule. Although they worked to get Home Rulers elected, many Fenians along with tenant farmers were dissatisfied with Butt's gentlemanly approach to have bills enacted, although they did not openly attack him, as his defence of the Fenian prisoners in '67 still stood in his favour.[9] However, soon a Belfast Home Ruler, Joseph Gillis Biggar (then a senior member of the IRB), began making extensive use of the ungentlemanly tactic of "obstructionism" to prevent bills being passed by the house. When Parnell entered Parliament he took his cue from John O'Connor Power and Joseph Biggar and allied himself with those Irish members who would support him in his obstructionist campaign. MPs at that time could stand up and talk for as long as they wished on any subject. This caused havoc in Parliament. In one case they talked for 45 hours non-stop, stopping any important bills from being passed. Butt, ageing, and in failing health, could not keep up with this tactic and considered it counter-productive. In July 1877 Butt threatened to resign from the party if obstruction continued, and a gulf developed between himself and Parnell, who was growing steadily in the estimation of both the Fenians and the Home Rulers.[10] The climax came in December 1878, when Parliament was recalled to discuss the war in Afghanistan. Butt considered this discussion too important to the British Empire to be interrupted by obstructionism and publicly warned the Irish members to refrain from this tactic. He was fiercely denounced by the young Nationalist John Dillon, who continued his attacks with considerable support from other Home Rulers at a meeting of the Home Rule League in February 1879. Although he defended himself with dignity, Butt, and all and sundry, knew that his role in the party was at an end.[11] Butt, who had been suffering from bronchitis, had a stroke the following May and died within a week. He was replaced by William Shaw, who in turn was replaced by Charles Stewart Parnell in 1880. (Wikipedia)Image of a man known as Isaac Butt. -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyUniform, WRANS uniform, 1942-1944
This uniform belonged to Marion Elaine Caffrey, nee Bullock (1920-1993). Marion was born and lived in Begonia Road, Gardenvale and attended Star of the Sea College with her younger twin sisters, Hilary and Margaret Bullock. Their family had been living in the district since 1892 when their grandfather, James Stewart, settled first at Brighton Beach before building a new home in Gardenia Road, Gardenvale in 1910. On leaving school, Marion took a job with the T&G Insurance Company in Collins Street. However, as the threat of invasion by Japan loomed closer following the bombing of Pearl Harbour and the fall of Singapore, in 1943 she volunteered to join Australia's war effort as part of the Women's Royal Australian Naval Service (WRANS). She initially trained as a coder at HMAS Cerberus, followed by a posting to HMAS Magnetic in Townsville. By the time Marion arrived in Townsville in 1944 it was very much a garrison town, inhabited largely by Australian and American servicemen. Whereas in Melbourne the war in the Pacific may have felt somewhat distant, in Townsville it was very immediate. Though the town was never subjected to the heavy bombardments of Darwin, a series of small air strikes in July 1942 had made the fear of air raids quite real. The naval base HMAS Magnetic was responsible for communications, Port Examination Services and servicing of Allied warships. Marion worked as a coder, encoding outgoing transmissions and decoding incoming ones either manually or using a Typex cipher machine. In 1945, she completed additional training to attain the rank of Leading Coder. Her keenness for the work is evident in a note on her service record: although no WRANS women were ever sent to active warzones, Marion volunteered for overseas service. Marion later recalled her time with the WRANS as one of the happiest and most personally fulfilling times of her life. Like many Australian women, she embraced the opportunity to serve her country and take on roles traditionally reserved for men. She completed her three years' service at HMAS Harman in Canberra where she was de-mobbed in 1946. Afterwards, she secured a job with Metro Goldwyn Mayer, where she worked until her marriage to Hugh Caffrey in 1947.Second World War WRANS uniform consisting of a dark navy blue serge blazer (.1), skirt (.2) and hat (.3). The blazer features six buttons. The left arm features a black patch embroidered with a red anchor wrapped in a length of rope (a fouled anchor) with a single red chevron beneath, denoting the rank of Leading Wran (equivalent to Leading Seaman). The right arm features a black patch embroidered with red crossed flags over the letter 'C'. The pencil skirt is lined and fastens at the side with a button and snap fastenings. The navy felt hat features a round brim and a black ribbon band machine embroidered in gold with the words "H.M.A.S. HARMAN".Maker's label in collar of blazer reads "N491 / 1942 / SIZE [indistinct] / MADE IN AUSTRALIA" The label features a pen inscription, "BULLOCK". Size label in back of skirt: "2". Label inside the hat: "N18 / 1944 Size 20½ / MADE IN AUSTRALIA"1940s, marion elaine bullock, marion elaine caffrey, second world war, military uniform, wrans, women's royal australian naval service
