Showing 21 items matching "anode"
-
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionPhotograph - Framed Photograph, Members of 5/6 in Op Anode
Coloured photograph with wooden frame showing soldiers before patrolling in Solomon Island during Operation Anode -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumSacrificial anode
Possibly zinc galvanic anode with a ferrous based metal attachements on both ends. Concretions still visible on underside of metal.020 has been imprinted on the concretion on the back of the anode.anode, corrosion -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
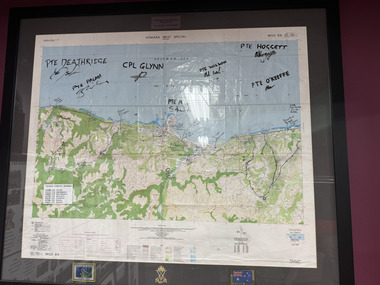
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionMap - Honiara Map, Honiara West Special used by members of 5/6
Honiara West Special signed by 7 members of 5/6 RVR who were deployed on Operation AnodeThe Map is framed in the glass frame withe the Operation Anode patch, Australian Flag and 5/6 unit symbol displayed below the Map. It has been signed by 7 members of 5/6, each member's PMKey is also displayed on the Map -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomDomestic object - Small round ashtray
Anodized ashtray round in shape -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomDomestic object - Ashtray
Anodized ashtray round in shape with purple para - 'SEPPELTS PORT' with emblem. Guard your honour -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumHeadwear - BERET & RASVY BADGE, Christies, Beret and Royal Australian Survey Corps Badge
This "Purple" Beret sold by Christies in Sydney was produced for the Queensland Ex Survey Corps Association and was not authorised for Service use. The authorised Royal Australian Survey Corps beret was dark blue. The "purple" beret was and is used extensively around Australia on ceremonial occasions such as Anzac Day.Beret, woollen, purple colour with a gold anodized badge - Crown over globe, boomerang with Royal Australian Survey Corps.uniforms - army, costume - male, headwear, numismatics-badges, military, royal australian survey corps, rasvy -
 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collection
8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental CollectionWeapon - Bayonet (French), 1914 circa
Used with Lebel Model 1886 bolt action rifle and was the basic French infantry weapon of World War 1 (1914-1918). Probably brought to Australia by a returning soldier as a souvenir. Donated to 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Collection when no longer of interest to family. Nickname 'Rosalie' by French soldiers, a reference to a popular song of the war years. Called French knitting needles by German soldiers.Fine example of World War 1 weaponry used by allied forces.French Model 1886/93 "Rosalie" bayonet, 500mm steel cruciform section blade with quillon (hook) and brass anodized handle.On Quilion "M 78124"rosalie, knitting needles, french, bayonet -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMagnetron,5cm
Copper magnetron with disc-like body has three radiating electrodes each emerging through a copper to glass tube. Two of these are arranged on one side(= filament leads) and the other larger tube (collector/anode) is arranged diametrically opposite.Handwriting on top “?A4 A98/4.9%” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-ray Tube, Machlett
This X-ray tube was designed to provide electrostatic protection for the filament (cathode) so as to permit long life to be achieved at operating voltages in the range 100-300kV. It is not certain whether the tube was in use within the School by Professor Laby’s X-ray group or whether it was presented to the School by a medical user. It would be somewhat surprising if it fitted into this School of Physics Research Program at a date as late as 1933 when tubes with demountable anodes were in use.Glass bulbous X-ray tube attached at either end to metal electrodes. Mounted for demonstration on a wooden base. Dated1937On glass bulb: “Machlett Patent 1954016” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMarconi Valve, Transmitting, with stand
Valve has wooden (possibly mahogany) display stand.On glass: “Marconi Valve, patented, Made in England Cat.2 67.5” Detached accompanying label (partially torn): “Valve Type - CAT 2, Serial No: 575 Anode? For: 5.0 Amp Emission: 9? Operate filament A? 19.2 volts 51. ?” -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumSign, Yarra Trams, Metlink, Tram Stop Sign, c2005
Tram Stop Sign - folded anodized aluminium, overlain both sides with a reflectorised backing plastic material which has been bonded to the to sign, printed with tram stop information, with Metlink and Yarra Tram logos. Has three holes in the small angled side, enabling it to be fixed to a structure at the tram stop or a pole. Tram stop - model or a sample sign for a tram stop sign in Collins at the corner of William St for Route 109, stops 47 and 441trams, tramways, tram stops, metlink, signs, route 109, collins st -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumSign, Yarra Trams, Metlink, Tram Stop Sign, c2005
Tram Stop Sign - folded anodized aluminium, overlain both sides with a reflectorised backing plastic material which has been bonded to the to sign, printed with tram stop information, with Metlink and Yarra Tram logos. Has three holes in the small angled side, enabling it to be fixed to a structure at the tram stop or a pole. Tram stop - model or a sample sign for a tram stop sign for the MCG/Vodaphone Arena, route 70, stop 7C on both sides.trams, tramways, tram stops, metlink, signs, route 70, sports, mcg, vodaphone arena -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumSign, Yarra Trams, Metlink, Tram stop sign, c2005
Tram Stop Sign - folded anodized aluminium, overlain both sides with a reflectorised backing plastic material which has been bonded to the to sign, printed with tram stop information, with Metlink and Yarra Tram logos. Has three holes in the small angled side, enabling it to be fixed to a structure at the tram stop or a pole. Tram stop - model or a sample sign for a tram stop sign for the MCG/Vodaphone Arena, route 70, stop 7C on both sides.trams, tramways, tram stops, metlink, signs, route 70, sports, mcg, vodaphone arena -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumCoolidge X-ray Tube
The investigation of the x-ray appears early on to have been a priority research topic at the University of Melbourne’s School of Physics. This interest was sparked by the appointment in 1889 of Professor T.R. Lyle. Lyle, who was head of the school until 1915, is thought to have been the first person in Australia to have taken an x-ray photograph. A copy of this photograph can be found in the School of Physics Archive. For this particular experiment Lyle actually made his own x-ray tube. His successor, Professor Laby, continued to work with x-rays. During the 1920s Laby worked on the x-ray spectra of atoms and in 1930 he co-published with Dr. C.E. Eddy, Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray Spectroscopy. Also with Eddy, Laby produced the landmark paper Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis by X-rays. Laby went on to have an x-ray spectrograph of his own design manufactured by Adam Hilger Ltd. (see cat. No. 38). School of Physics, the University of Melbourne Cat. No. 22. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 In 1913 Coolidge overcame the limitation of the narrow operating range of the gas X-ray tubes with the invention of the vacuum X-ray tube. A filament heated by an electric current directly releases electrons by thermionic emission. In thermionic emission, electrons are emitted from a metal surface directly by the application of an electric current to heat a wire filament. The electrons accelerate to the anode and produce X-rays. The anode has associated cooling fins due to the high temperatures attained by the release of kinetic energy by the electrons on colliding with the anode. Internal Glass sleeve: “A941/L2593/2821” -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumManual - SAMPLE BUTTON, GOLD COLOUR, Stokes Australasia, c.1987
Button is an example of sample used to ensure standard of manufacture among local contractors. See item 9806.Round button, gold-coloured. Shank attachment. Raised military insignia in middle of button. Paper identification tag, sealed with lead seal.Button - raised military insignia - a cross within a cog, crown at top of cross. Verso - "STOKES/MELB." impressed. Tag (handwritten) - "8455-66-025-9877" "ITEM 13" "BUTTON INSIGNIA/ARMY APPRENTICE, GOLD ANODIZED LINE 40" "STOKE (A'ASIA)/V113055)" "7-9-87/ [signature]"insignia, uniform buttons -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumRotating Anode X-ray Tube
The investigation of the x-ray appears early on to have been a priority research topic at the University of Melbourne’s School of Physics. This interest was sparked by the appointment in 1889 of Professor T.R. Lyle. Lyle, who was head of the school until 1915, is thought to have been the first person in Australia to have taken an x-ray photograph. A copy of this photograph can be found in the School of Physics Archive. For this particular experiment Lyle actually made his own x-ray tube. His successor, Professor Laby, continued to work with x-rays. During the 1920s Laby worked on the x-ray spectra of atoms and in 1930 he co-published with Dr. C.E. Eddy, Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray Spectroscopy. Also with Eddy, Laby produced the landmark paper Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis by X-rays. Laby went on to have an x-ray spectrograph of his own design manufactured by Adam Hilger Ltd. (see cat. No. 38). School of Physics, the University of Melbourne Cat. No. 22. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 A modern X-ray tube differs little from the original Coolidge tube. A minor modification is the rotating anode type that extends the life and increases the available power of the tube by presenting a new portion of the anode when required. “P125/20/40/NrF038803 (?) SIEMENS-REINIGER-WERRE AG ERLANGEN Eigen filleung (?) mind. 0,7 mm AL” On rotating shaft: “FO/33803” On cathode: “23C” -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumManual - SAMPLE BUTTON, SILVER COLOUR, Stokes Australasia, c. 1989
Button is an example of sample used to ensure standard of manufacture among local contractors. See items 9806 & 9807.Round button, silver coloured. Shank attachment. Raised military insignia in middle of button. Paper identification tag, sealed with a lead seal.Button - raised military insignia. Two (2) unfurled flags either side of a crown above a tank, all surrounded by a round wreath with a boomerang at the base. Verso - "STOKES/MELB." impressed. Tag (handwritten) - "8455-66-012-6356" "BUTTON INSIGNIA/THE ROYAL AUSTRALIAN ARMOURED CORPS SILVER ANODIZED LINE 30" "STOKES (A'ASIA)/28902188" "8-3-89/RODNEY SCOTT [signature]"military insignia, button -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTool - Knitting Pins, 1960-69
The donor (Lynn Fitzpatrick) purchased these knitting needles 20 years ago from an opportunity shop. Aero Knitting Pins are a discontinued brand that were popular in the 1960s, 70s and 80s. They are made of smooth, aircraft-quality anodized aluminium. To this day, they are a popular and sort after knitting needle. Being a long-lasting product, they are often given as heirlooms. Abel Morrall was a major needle manufacturer from Studley, a town near Redditch. In 1785, Michael Morrall who was taught the art of needle making by a maternal uncle, moved to Studley. He founded the Abel Morrall company with his brother Abel, and another unnamed brother-in-law. Within five years the company was producing 40% of the 2.5 million needles that were made each week in the Redditch area. In 1811 the company introduced the concept of creating the eyes by using a stamping press. Additional machines were invented by them throughout the 19th century leading to major improvements in the way needles were produced. Abel Morrall demonstrated their needle making machinery at the Great Exhibition of 1851 and Queen Victoria personally inspected it. The company selected the demi-griffin for its trademark in 1861, which can be seen on older products produced by the company. Set of four knitting needles stored within paper packaging. Packaging features black, red, and white ink, detailing the selling points of the Aero Knitting Pins. The packaging folds with 3 main sections, each providing different insights into the knitting needles. Examples of this are " CANNOT SOIL LIGHT WOOL", "...SPECIALLY TAPERED POINTS WHICH WILL NOT INJURE THE FINGERS" and "RUSTLESS-NON-GLITTER FINISH". As the packaging unfolds, the grey knitting needles become visible. The needles can be removed from the packaging by sliding them through small bands of paper that hold the needles secure while in transportation. The four knitting needles are a “NEUTRAL” grey colour finished in a double point style.Printed. Orange, White and Black Ink Numerous, see multimediaabel morrall, knitting needles, knitting pins, 1960s home knitting -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumGas X-ray Tube
The investigation of the x-ray appears early on to have been a priority research topic at the University of Melbourne’s School of Physics. This interest was sparked by the appointment in 1889 of Professor T.R. Lyle. Lyle, who was head of the school until 1915, is thought to have been the first person in Australia to have taken an x-ray photograph. A copy of this photograph can be found in the School of Physics Archive. For this particular experiment Lyle actually made his own x-ray tube. His successor, Professor Laby, continued to work with x-rays. During the 1920s Laby worked on the x-ray spectra of atoms and in 1930 he co-published with Dr. C.E. Eddy, Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray Spectroscopy. Also with Eddy, Laby produced the landmark paper Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis by X-rays. Laby went on to have an x-ray spectrograph of his own design manufactured by Adam Hilger Ltd. (see cat. No. 38). School of Physics, the University of Melbourne Cat. No. 22. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 The original X-ray tubes relied on low pressure operation. The electrons and positive ions are produced in the residual gas. Positive ions are accelerated towards the cathode and release electrons which on hitting the anode produce X-rays. These early gas X-ray tubes operated satisfactory only over a narrow pressure range. Stamped Label: “NATURAL PHILOSOPHY LABORATORY/ No/ UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE” Stamped: “90268 M. No. 5171[??]/No. 2156[??]/ M. No. 346585.” x-ray tubes, gas x-ray tube, laby, spectroscopy -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumGas X-ray Tube, Victor
The investigation of the x-ray appears early on to have been a priority research topic at the University of Melbourne’s School of Physics. This interest was sparked by the appointment in 1889 of Professor T.R. Lyle. Lyle, who was head of the school until 1915, is thought to have been the first person in Australia to have taken an x-ray photograph. A copy of this photograph can be found in the School of Physics Archive. For this particular experiment Lyle actually made his own x-ray tube. His successor, Professor Laby, continued to work with x-rays. During the 1920s Laby worked on the x-ray spectra of atoms and in 1930 he co-published with Dr. C.E. Eddy, Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray Spectroscopy. Also with Eddy, Laby produced the landmark paper Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis by X-rays. Laby went on to have an x-ray spectrograph of his own design manufactured by Adam Hilger Ltd. (see cat. No. 38). School of Physics, the University of Melbourne Cat. No. 22. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 The original X-ray tubes relied on low pressure operation. The electrons and positive ions are produced in the residual gas. Positive ions are accelerated towards the cathode and release electrons which on hitting the anode produce X-rays. These early gas X-ray tubes operated satisfactory only over a narrow pressure range. Manufacturer’s mark stamped: “PATENTED/ VICTOR/ TRADEMARK/ MADE IN BOSTON U.S.A./ TUNGSTEN” A white circular stamp, stamped near the manufacturer’s mark: “[illegible]TER WIGGH[illegible]” Stamped label: “NAT. PHIL. LAB./ No./ UNIV. OF MELB.” Inscription on the end face of the copper piece: “PAT. SEP 5’ 11 DEC. 30’13/ JUNE 23, 14 NOV. 30.15/ 43835” -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Tatting Shuttle, Aero Needles Group Ltd, Mid to late 20th century
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots.The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century.Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic (as is item 8535.1). The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound (e.g. item 8535.2). The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace. One type of tatting shuttle produced by "Aero" from the 1930's to the late 1960's was an anodized grey coated aluminium shuttle with a sharp pick at one end. In the 1970's it was superseded by the grey plastic "Aero" which has a removeable bobbin which you can put on the end of the shuttle to make thread winding easier and an embedded crochet hook for joining picots. The "Aero" company developed in Redditch, England - a town renowned as a centre for manufacturing needles. Firms run by Henry Milward and Abel Morrall were based in Redditch and by the 18th century Redditch was manufacturing one million sewing needles per year. Abel Morrall Ltd launched the "Aero" brand in 1936 and greatly expanded the firm's product line to include tatting shuttles and knitting needles. The classic plastic "Aero" tatting shuttle was manufactured in England from the early 1970's until the 1990's. These items are significant as examples of easily accessible handiwork tools that enabled women in the 1930s -1960s to be able to decorate and personalize their household linen and clothing.Shuttle no. 8535.1 is a beige, boat shaped plastic shuttle with enclosed ends, small round central indentations on both sides and an enclosed black removeable bobbin. The shuttle has a grooved point at one end to hold a bobbin and a small metal crochet hook at the other end. Shuttle no. 8535.2 is a beige, boat shaped metal shuttle with pointed ends that are open but snug, small round central indentations and two smaller circular markings (on both sides) and two internal posts with cream thread wound around.Shuttle no. 8535.1 - "AERO" / "ENGLAND" Shuttle no. 8535.2 - "AERO' / "ENGLAND" "39c" (written in ball point pen)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, tatting shuttle, aero company, handwork, handwork tool, craft, handcraft, needlework, tatting
