Showing 9 items matching "break of gauge"
-
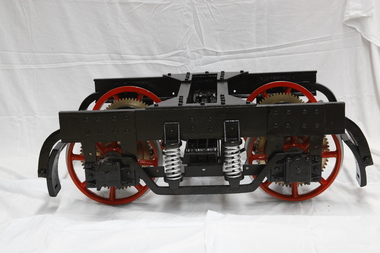 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayBogie - Break of Gauge, Circa 1920
... Bogie - Break of Gauge...break of gauge... Government into ways of solving the break of gauge problem. Breaks...Break of Gauge Bogie made of iron and wrought iron & brass... the break of gauge problem. Breaks or changes in railway gauges ...Designed and built in the early 1920’s by Charles Robert Prosser , a Melbourne Engineer, for an enquiry by the Commonwealth Government into ways of solving the break of gauge problem. Breaks or changes in railway gauges existed at most state borders of Australia during the first half of the 20th century. Upon completion of this model, it was placed on display in the Federal Parliament then located in Parliament House, Melbourne. Patents on the Break of Gauge Bogie Application number Title Applicant(s) Inventor(s) Filing date 1921000390 Improved means of adjusting the wheels of rolling stock to suit railway tracks of different gauges Charles Robert Prosser Charles Robert Prosser 1921-02-01 1917004843 Improvements in and connected with railway or other ticket supply tubes Charles Robert Prosser Charles Robert Prosser 1917-08-09 1915016191 IMPROVEMENTS IN AND CONNECTED WITH THE ADAPTATION OF RAILWAY ROLLING STOCK TO DIFFERENT GAUGES Charles Robert Prosser Charles Robert Prosser 1915-05-01 1915015980 Improvements in and connected with the adaptation of railway rolling stock to different gauges Charles Robert Prosser Charles Robert Prosser 1915-04-09 1914012931 Improvements in and connected with the adaptation of railway rolling stock to different gauges Charles Robert Prosser Charles Robert Prosser 1914-04-20 The Sydney Morning Herald Fri 2 Sep 1921 Page 6 BREAK OF GAUGE DEVICE. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article28088233 Historic - Railway Invention Break of Gauge Bogie Break of Gauge Bogie made of iron and wrought iron & brassboggie, break of gauge, puffing billy -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Wilson, John, The Break Of Gauge: A Social History, 2024
... The Break Of Gauge: A Social History...."--Publisher's blurb. index, ill, maps, p227. The Break Of Gauge ...Tells the story of the gauge problem in Australia, how it happened, why it happened and why there has been faliure to fix the problem and the consequences of the ongoing problem. "From the early days of Australia’s rail networks in the 1850s, different colonies adopted various rail gauges for their own reasons. Even after the Federation on January 1, 1901, the new nation’s leaders missed the chance to create a unified national policy for rail gauges and chose to avoid addressing the issue. This book, generously supported with photographs, timelines, and insights from seasoned rail industry experts, covers a span of 170 years. It examines the political and social attitudes of the time and highlights the missed opportunities to resolve the rail gauge problem dating back to the 1880s."--Publisher's blurb.index, ill, maps, p227.non-fictionTells the story of the gauge problem in Australia, how it happened, why it happened and why there has been faliure to fix the problem and the consequences of the ongoing problem. "From the early days of Australia’s rail networks in the 1850s, different colonies adopted various rail gauges for their own reasons. Even after the Federation on January 1, 1901, the new nation’s leaders missed the chance to create a unified national policy for rail gauges and chose to avoid addressing the issue. This book, generously supported with photographs, timelines, and insights from seasoned rail industry experts, covers a span of 170 years. It examines the political and social attitudes of the time and highlights the missed opportunities to resolve the rail gauge problem dating back to the 1880s."--Publisher's blurb.railroad gauges -- social aspects -- australia -- history, railroad gauges -- australia -- history. -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Michael "Mick" Mulqueeney Stock Agent, Wodonga
... shipped owing to the break of gauge from N.S.W, into Victorian... shipped owing to the break of gauge from N.S.W, into Victorian ...Mick Mulqueeney was born in Kilmore and arrived in Wodonga in 1886, when it was Australia's greatest store cattle market. It was not unusual to see 10,000 cattle sold in a single day. For a few years he spent time overlanding large mobs of cattle from Queensland and the back country of N.S.W He settled in Wodonga and began business as a stock and station agent at Wodonga. He was the Wodonga representative of Edward Trenchard and Co, and other Newmarket stock agents but also conducted auctions on his own account. For several years, he was in partnership with Mr A. L. Wright. Following the retirement of Mr. Wright in 1902, Mick Mulqueeney then joined with Harry H Peck under the trade name of Peck Sons and Mulqueeney. This partnership was dissolved after about 10 years and Mick was bought out by New Zealand Loan. Later he continued in stock and station agency on his own. During this time, he also conducted a very extensive stock forwarding agency where tens of thousands of stock of all classes were shipped owing to the break of gauge from N.S.W, into Victorian trucks and vice versa. He was regarded by stock owners as a genius among stock. Michael also had a sound knowledge of land in the Wodonga district and when the settlement of returned soldiers onto the land was taking place he was appointed valuer of properties being considered by the Repatriation Department. Mick also became a Government stock inspector on the Victorian side of any stock crossing the border. At this time his forwarding agency was carried on by his son, Mr. Jack Mulqueeney. Michael Mulqueeney died on 19th June 1929 and was buried at Yackandandah, VictoriaThis photo is significant because it depicts an important member of the Wodonga community and an vital industry in Wodonga.Two black and white images showing a portrait photo of Michael Mulqueeney and the Mulqueeney family home.michael mulqueeney, stock agents wodonga, livestock sales wodonga -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayZeehan & North East Dundas Tramway Bogie 1896, wagon bogie, 1896
... . There was a break-of-gauge with the mainline 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) system... the falls. There was a break-of-gauge with the mainline 1,067 mm (3 ...Zeehan & North East Dundas Tramway Bogie 1896 The North East Dundas Tramway (NEDT) was a 2 ft (610 mm) narrow gauge tramway on West Coast Tasmania that ran between Zeehan and Deep Lead (now Williamsford). It was part of Tasmanian Government Railways. The line was opened in 1896 to carry ore from the Williamsford mines to Zeehan where it would be loaded onto another train for shipment to Burnie. The narrow-gauge (2 ft) was chosen because of the extremely difficult terrain that the railway crossed, requiring several big trestle bridges, including one at the foot of Montezuma Falls. After some rain the engine and carriages would get soaked by spray from the falls. There was a break-of-gauge with the mainline 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) system at Zeehan. The railway was closed in 1932. The rolling stock for the Tramway was built in the Launceston Railway workshops, and comprised twenty five eight-wheel low-side trucks, tare 3 tons 1 cwt. 1 qr., load 10 tons; six eight-wheel flat trucks, tare 2 tons 18 cwt. 1 qr., load 10 tons; two four-wheel bolster trucks, for carrying long timber, tare 1 ton 19 cwt., load 5 tons; and four passenger cars, each with six cross-seats with reversible backs, to carry eighteen passengers, also a locker for mails and parcels. All trucks and cars have cast-steel wheels 21 inches in diameter and are fitted with automatic vacuum brakes. The trucks have side levers and the cars have hand-screw brakes. The vacuum brake can be worked from the engine or from the passenger cars, which act as brake vans. When this brake was introduced, one effect was to accelerate the journey speed by about 10 minutes owing to more even running on down gradients. Historic - Industrial Narrow Gauge railway - Bogie used on the Zeehan & North East Dundas Tramway, Tasmania, Australia Bogie made from steel, iron and wrought ironZN & NTDS ML TRAM 1896 Griffinpuffing billy, bogie, zeehan & north east dundas tramway bogie, zeehan & north east dundas tramway, industrial narrow gauge railway, gauge: 2' (610 mm) -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Lead shot, Before 1878
The objects are a sample of medium caliber lead shot raised by Flagstaff Hill divers from the Loch Ard shipwreck site in 1976. Included in the vessel’s cargo manifest were 22 tonnes of lead shot, packed into her holds in cloth bags and wooden casks. These 49 pieces of 7 mm diameter lead shot are identical in size and smoothness. Each one also bears the same slightly raised square of residual metal left behind by the process of pouring molten lead into individual but identical moulds through a small (square) opening. These pieces of shot can be compared with contrast pieces in the Maritime Village collection, which are examples of shot tower pellet production; an industrial technique more suited to the creation of uniformly spherical balls that do not need subsequent trimming. In conventional shot tower production, lead is heated in a cauldron at the top of a 150-160 feet tower, and poured through a copper lattice that divides the metal into falling droplets. As these droplets fall, they spin into small spheres and gradually cool, before finishing in a pool of water at the bottom of the tower. However the maximum size of lead shot, and the economic efficiency of shot tower production, is limited by the practical height of the drop. Larger diameter lead shot must fall further in order to cool evenly and sufficiently to avoid shape distortion on hitting the water at the base. This sample of larger 7 mm lead shot, although mass produced, appears to have been manufactured under the traditional and more labour intensive mould system. They are therefore distinct from the other samples of smaller gauged and shot tower produced lead shot that were being imported on the Loch Ard . In terms of metallurgical technology these 7 mm shot are more closely related to an artifact in our Collection (No. 5241) — a forged set of pincers or pliers with two facing cups at the end. When the pincers are closed, the cups join to form a single mould. Molten lead is poured through a small (circular) opening left at the top of the mould. When cooled the pincers are opened, breaking the mould and releasing the lead shot. The excess metal left over from the pouring operation at the top of the ball is then trimmed off using the scissor like cutting edges on the inner side of the pliers handles. In this manner, individual shooters were able to make their own ammunition for their shotguns. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got it’s name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic.The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register Ref S 417. Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. A quantity of forty-nine (49) loose round lead shot of 7 mm diameter retrieved from the wreck of the Loch Ard. All are smooth round spheres with the same small raised square of excess lead on one face.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, shipwreck artefact, shot, lead shot, shot towers, shot mould, colonial imports, practical metallurgy -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayTool - Rail bender
Railway tracks are produced straight. They may appear to be easy to bend and may appear flexible, but are required to be bent for curves, at rail joins on curves and at point (turn-out) junctions. For a safe transition around curves and in the finer areas of the point, this was required to be done with a manual rail bender. Sometimes referred to as a Jim Crow, the rail bender attaches its two claws to the rail. In the middle of the two claws is a screw that is slowly tightened using a crow-bar to bend the rail. Tightening the screw too fast or too tightly may not give the structure of the rail time to redistribute and the rail may break if not done properly.Victorian Railways Permanent Way and Works track equipment Light Rail Bender narrow GaugeCast iron semi-circular tool, with hooked ends and central screw shaft.puffing billy, rail bender, jim crow -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Eric harding, Uniform railway gauge, 1958
... The story of the break in railway gauge in Australia and the various ...The story of the break in railway gauge in Australia and the various attempts that have been made to overcome it.Index, bib, ill, map, p.114.non-fictionThe story of the break in railway gauge in Australia and the various attempts that have been made to overcome it.railway gauge - australia, railways - australia - history -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncNewsletter - Victorian Railways April 1961
... and Albury due to the break of gauge in gauge between the two railway ...This booklet is one of a series featuring news items from Victorian Railways from the early 1960s until the late 1980s. During this period the corporate name changed to VLine and the newsletter continued to be published as VLine Newsletter. This issue from April 1961 features an article "Wodonga Links the States" which explains the complexity of operations of the railways at Wodonga and Albury due to the break of gauge in gauge between the two railway networks. The article was written to acknowledge the work carried out by the railway at both stations prior to the opening of the standard gauge track. Until this time Victorian trains operated on 4’ 8½” tracks whilst New South Wales were 5’ 3” wide. With an overall stall of 241, Wodonga railmen prepared, serviced and manned 14 "up" and 11 "down" trains as well as specials each day. Special migrant trains to Bonegilla were often a feature at this time as well as transport of heavy equipment to the Snowy Mountain Scheme.A small booklet of 14 pages including articles and images.This booklet is one of a series featuring news items from Victorian Railways from the early 1960s until the late 1980s. During this period the corporate name changed to VLine and the newsletter continued to be published as VLine Newsletter. This issue from April 1961 features an article "Wodonga Links the States" which explains the complexity of operations of the railways at Wodonga and Albury due to the break of gauge in gauge between the two railway networks. The article was written to acknowledge the work carried out by the railway at both stations prior to the opening of the standard gauge track. Until this time Victorian trains operated on 4’ 8½” tracks whilst New South Wales were 5’ 3” wide. With an overall stall of 241, Wodonga railmen prepared, serviced and manned 14 "up" and 11 "down" trains as well as specials each day. Special migrant trains to Bonegilla were often a feature at this time as well as transport of heavy equipment to the Snowy Mountain Scheme.wodonga railways, victorian railways, victorian railways wodonga -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Fischer, Tim, Steam Australia: Locomotives That Galvanised the Nation, 2021
... or 'The Ghan'. Special topics feature things such as Albury's 'break ...In 'Steam Australia', Tim Fischer takes readers into the fascinating story of steam transportation over ten vital decades of transformation in Australia's history. The book also covers the great named express trains hauled by steam locomotives over the decades, such as 'Puffing Billy', Robert Gordon Menzies or 'The Ghan'. Special topics feature things such as Albury's 'break of gauge' platform (where two state track systems met), the Amiens branch line (running through Pozieres and Passchendaele stations in Queensland), some important characters such as C.Y. O'Connor and many more. The book is illustrated with over 300 exciting images from the superb National Library John Buckland collection of photography, many never seen before. Steam locomotives continue to operate as a key part of rail heritage tourism in Australia, demonstrating the ongoing legacy of these engines. The great age of steam in Australia and Fischer's salute to steam locomotion and all that it has achieved for this country is fascinating and captivating to both train novices and enthusiasts alike. A history of the steam train in Australia.index, ill, maps, p.254.non-fictionIn 'Steam Australia', Tim Fischer takes readers into the fascinating story of steam transportation over ten vital decades of transformation in Australia's history. The book also covers the great named express trains hauled by steam locomotives over the decades, such as 'Puffing Billy', Robert Gordon Menzies or 'The Ghan'. Special topics feature things such as Albury's 'break of gauge' platform (where two state track systems met), the Amiens branch line (running through Pozieres and Passchendaele stations in Queensland), some important characters such as C.Y. O'Connor and many more. The book is illustrated with over 300 exciting images from the superb National Library John Buckland collection of photography, many never seen before. Steam locomotives continue to operate as a key part of rail heritage tourism in Australia, demonstrating the ongoing legacy of these engines. The great age of steam in Australia and Fischer's salute to steam locomotion and all that it has achieved for this country is fascinating and captivating to both train novices and enthusiasts alike. A history of the steam train in Australia.steam locomotives - australia - history, railroads -- australia -- history
