Showing 9 items matching "electrostatic"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instument, Electrostatic Voltmeter, 1942
Electrostatic voltmeter, 0-12 KV, housed in a varnished wood box. Hinged front lid reveals a glass windonto a cylindical scale with with a non-linear scale, and idnetified by "M.C.C.E.S. 1942. F.G." Serial number 108scientific instrument, voltmeter -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - ARINC - Guidance For Electrostatic Sensitive Device Utilization And Protection
ARINC Report 606-1 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Spectrometer
An optical instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. Often used in astronomy and some branches of chemistry.Electrostatic spectrometer in wooden box. Measured in Kilovolts.Serial number 108 MCCES 1942 FGspectrometer, scientific instrument, electromagnetic spectrum, light's intensity, astronomy, optical instrument -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Watson, Interruptor (?)
Electrostatic precipitation device? Spark generator?A black cast iron cylindrical vessel, with unmovable top flange/cover. A variable speed electric motor with vertical shaft mounted on three bronze curved brackets centrally over the vessel. Motor shaft connected with bakelite coupling to a shaft that passes through the black top cover. The cover flange has two pairs of electric terminals posts, a shorting link and two gas cocks, all relevant to the insdie cavity.scientific instrument, interrupter, watson -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-ray Tube, Machlett
This X-ray tube was designed to provide electrostatic protection for the filament (cathode) so as to permit long life to be achieved at operating voltages in the range 100-300kV. It is not certain whether the tube was in use within the School by Professor Laby’s X-ray group or whether it was presented to the School by a medical user. It would be somewhat surprising if it fitted into this School of Physics Research Program at a date as late as 1933 when tubes with demountable anodes were in use.Glass bulbous X-ray tube attached at either end to metal electrodes. Mounted for demonstration on a wooden base. Dated1937On glass bulb: “Machlett Patent 1954016” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumElectrometer, Quadrant Elliot
Brass quadrant electrometer consists of four quarter-cylindrical brass boxes (quadrants ) each mounted on a glass insulating pillar. The whole is housed within an electrostatic shield (Faraday cage) - a beehive shaped wire cage enclosure (aka a “bird cage”). The quadrants and cage stand on a round base platform on three legs with levelling screws (tribach base?). Arising from the platform is a separate vertical rod arises from the periphery and terminates over the axis of cylindrical symmetry and from which provision is made for a conducting suspension fibre which supports the horizontal “paddle” which is free to rotate within the cylindrical cavity of the four quadrants. The suspension and paddle are unfortunately missing.Label on front: “Natural Philosophy Laboratory No. University of Melbourne” Engraved on front: “Elliott Bros London” -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Nathaniel Frank, Introduction to Electricity and Optics, 1950
Dark Blue synthetic hard caver book of 440 pages with gold lettering embossed on the spine. non-fictionelectricity, optics, force, electrostatic, charg and capacity, electric currents, magnetic field, alternating current circuits, electromagnetic waves, radiation, conduction, dielectrics, geometrical optics, interference, heat radiation, diffraction -
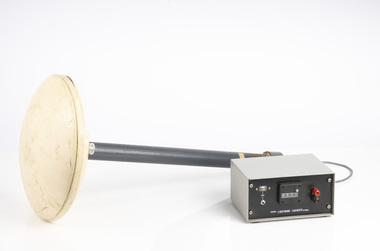 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionLightning Detector
Lightning is one of the major causes of bushfires, particularly in the remote mountains. This lightning detector system was developed by Dr. Peter Kourtz at Canada’s forest fire research institute. By 1977, some 300 were in use across the country. The small mushroom antenna could detect short-range (20-mile) changes in electrostatic field associated with lightning strikes. It needed to be placed out in the open on a hilltop and away from nearby trees. It simply counted the number of "strikes". The detector doesn't seem to have a direction finding capability or be able to distinguish between cloud-to-cloud or cloud-to-ground lightning. It's not sure how this particular unit found its way to Victoria. The Bureau of Meteorology's (BOM) current lightning detector network uses radio waves emitted by lightning to pinpoint the location of lightning strikes. The network is operated by a private company that sends data to the BOM in real time. Lightning detection systems use sensors like antennas, GPS receivers, and processing systems to detect radio waves, also known as sferics. The systems calculate the lightning's location and speed by measuring how long it takes for the radio signal to reach the different antenna stations. The BOM also has a Thunderstorm Tracker that uses weather radar data to identify areas of potential thunderstorm activity. The tracker updates every six minutes and shows the direction thunderstorms are moving, as well as their expected position in 10, 20, and 30 minutesLightning detector 1970sQ-Techforests commission victoria (fcv), weather, bushfire, bushfire aviation -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumElectrostatic Voltmeter
Round metal instrument with voltmeter (hands missing) with twisting drum inside and a metal coupling device/mount.Engraved in front plate: 'VOLTMETRE / ELECTROSTATIQUE / ABRAHAM & VILLARD / J. CARPENTIER / PARIS / 4050 D2'electrostatic voltmeter, abraham & villard, j carpentier, scientific instruments
