Showing 26 items matching "fire shovel"
-
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumFire Irons - Shovel
... Fire Irons - Shovel...fire shovel...Fire Irons - shovel with ornate brass handle... shovel brass Fire Irons - shovel with ornate brass handle Fire ...Fire Irons - shovel with ornate brass handlefire irons, fire shovel, brass -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomFunctional object - Fire-tools, Fire-shovel
... Fire-shovel... and broken shovel end Fire-shovel Functional object Fire-tools ...Metal Shovel - 59cm. Rusted cast iron with ornate handle and broken shovel end -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Tool - Fireside implements, 000190.1 Shovel : 000190.2 Tongs
... fire shovel.... Warrnambool courthouse fire tongs fire shovel fire spade Warrnambool ...Initial court cases for the Western district were held and controlled for some time by Rutledge in Port Fairy. The first courthouse was built around 1854 and was in service until the stone building was built next to it in 1870. These two implements were used until around 1970 when heating was installed in the courthouse. They were decommissioned by Mr Ellis Roberts, Public Works Department Inspector.These implements have a strong connection to a public building which has a long association with the town and surrounding area. The courthouse of 1863 was the scene of an infamous murder of Constable O’Boyle in front of the fireplace. Shovel has barley sugar twisted handle with eight sided domed top. It is flared at the bottom to hold the spade which is attached with two metal rivets. Spade contains a number of holes cut into oval shape in centre and has fluted side edges. The tongs consist of two parts held together below a short handle with a metal rivet and two metal discs. Both pieces have decorative mouldings on the handles and remnants of black paint. warrnambool courthouse, fire tongs, fire shovel, fire spade, warrnambool -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumFire irons
... fire shovel... poker fire shovel 00062.1 : Brass fire tongs - ornate handle ...00062.1 : Brass fire tongs - ornate handle. 00062.2 : Brass poker - ornate handle. 00062.3 : Brass shovel - ornate handle.brass, fire tongs, fire poker, fire shovel -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomFunctional object - Fire-tools
... Metal Tongs - 70cm. Rusted cast iron. Metal fire-shovel...-country Metal Tongs - 70cm. Rusted cast iron. Metal fire-shovel ...Metal Tongs - 70cm. Rusted cast iron. Metal fire-shovel - 59cm. Rusted cast iron. -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumEquipment - Fire implements
... 4 brass implements: fire poker, fire shovel handle, shaft... implements 4 brass implements: fire poker, fire shovel handle, shaft ...The wreck site of the Earl of Charlemont is historically and archaeologically significant for the remains of its cargo and passengers' belongings from an international immigrant ship of the gold rush period, representing the cultural material being bought out to Australia in a typical immigrant ship. It is socially significant for the descendants of the many immigrants who made it ashore safely, and who have erected a memorial cairn to their forbears on Point Flinders.4 brass implements: fire poker, fire shovel handle, shaft and head of unknown implement, piece if fire tongs. 1 copper dumpship wrecks, earl of charlemont, fire implements -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyletter, September 1 1909
... and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented... and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented ...When early settlers began to arrive on the Snowy River somewhere in the 1880s, the land was mostly swamps and heavily timbered jungle on the river frontages. The swamps were drained bit by bit using hand tools. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented with such as hops, hemp and maize. Maize grew particularly well and became the main crop of the district. (info. from October 2006 ODHS Newsletter) The Argus was a morning daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia that was established in 1846 and closed in 1957. It was considered to be the general Australian newspaper of record for this period.Maize-growing has been an important agricultural industry in the Orbost district since early settlement. This item is associated with that history.A typed letter sent to a local maize farmer requesting information on maize growing. The letter has the "Argus" letter head. The name of the recipient is unknown.maize agriculture-orbost correspondence-argus -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyPhotograph, 1930s
... and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire... and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire ...Maize has been grown on the Orbost flats for at least 70 years. When early settlers began to arrive on the Snowy River somewhere in the 1880s, the land was mostly swamps and heavily timbered jungle on the river frontages. The swamps were drained, bit by bit, with short handled shovels working in mud and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented with such as hops, hemp and maize which grew particularly well and became the main crop of district. The problem then was to thresh and deliver the product to the market. A small single cob machine was brought here and one man turned the handle, while the boy or Mum fed the cobs singly into the machine. A good day’s work would thresh about 50 bushels or about 12 bags (4 bushels). The task then was to cart the maize to market. For a few years this was done by horses and dray carrying about 60 bushels to Mossiface, where it was loaded onto river boats to Lakes Entrance, and then by ocean boats to Melbourne. (information from NEWSLETTER OCTOBER, 2006)The growing of maize in the Orbost district contributed significantly to the economy of the township for many years, The many maize cribs once seen on the surrounding farms have now disappeared and this photograph is a pictorial record of that significance.A small sepia photograph with six men in front of a wooden barn. They are bagging maize. In the foreground are two rows of filled bags. On the right is a lifting machine to take the bags to the top storey. On the far right is a water tank on a stand"on back - "Thrashing Maize"maize-orbost agriculture-maize industry -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph
... , bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working..., bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working ...Maize,has been grown on the Orbost flats for at least 70 years. When early settlers began to arrive on the Snowy River somewhere in the 1880s, the land was mostly swamps and heavily timbered jungle on the river frontages. The swamps were drained, bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working in mud and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented with such as hops, hemp and maize, the latter grew particularly well and became the main crop of district. The problem then was to thresh and deliver the product to the market. A small single cob machine was brought here and one man turned the handle, while the boy or Mum fed the cobs singly into the machine. A good day’s work would thresh about 50 bushels or about 12 bags (4 bushels). The task then was to cart the maize to market. For a few years this was done by horses and dray carrying about 60 bushels to Mossiface, where it was loaded onto river boats to Lakes Entrance, and then by ocean boats to Melbourne. Later it was taken to Bairnsdale by foot and loaded onto the trains to Melbourne. (more information in Newsletter October 2006)The growing of maize in the Orbost district contributed significantly to the economy of the township for many years, The many maize cribs once seen on the surrounding farms have now disappeared and this photograph is a pictorial record of that significance.A black / white photograph of a man unloading maize from a horse-drawn wagon into a maize crib. Another man is standing by the horse.maize-crib-orbost agriculture maize-corn-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, late 19th century - early 20th century
... and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented... and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented ...Maize, or corn as it is called in America and New South Wales, has been grown on the Orbost flats for at least 70 years. When early settlers began to arrive on the Snowy River somewhere in the 1880s, the land was mostly swamps and heavily timbered jungle on the river frontages. The swamps were drained, bit by bit, by stout hearted men with short handled shovels and working in mud and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented with such as hops, hemp and maize, the latter grew particularly well and became the main crop of district. The problem then was to thresh and deliver the product to the market. A small single cob machine was brought here and one man turned the handle, while the boy or Mum fed the cobs singly into the machine. A good day’s work would thresh about 50 bushels or about 12 bags (4 bushels). The task then was to cart the maize to market. For a few years this was done by horses and dray carrying about 60 bushels to Mossiface, where it was loaded onto river boats to Lakes Entrance, and then by ocean boats to Melbourne. ( from NEWSLETTER OCTOBER, 2006) This is a pictorial record of farming practices in Orbost in the early 20th century.A black / white photograph of a horse team hauling a wagon loaded with bags of maize.A man is sitting on the edge of the wagon.farming-orbost agriculture maize corn transport -
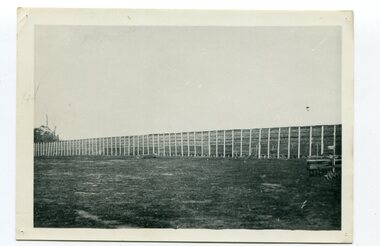 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, Vogt, Stanley, 1918
... , bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working..., bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working ...Maize,has been grown on the Orbost flats for at least 70 years. When early settlers began to arrive on the Snowy River somewhere in the 1880s, the land was mostly swamps and heavily timbered jungle on the river frontages. The swamps were drained, bit by bit, by men with short handled shovels and working in mud and water. The frontages were cleared by axe and shovel and fire. Several kinds of crops were experimented with such as hops, hemp and maize, the latter grew particularly well and became the main crop of district. The problem then was to thresh and deliver the product to the market. A small single cob machine was brought here and one man turned the handle, while the boy or Mum fed the cobs singly into the machine. A good day’s work would thresh about 50 bushels or about 12 bags (4 bushels). The task then was to cart the maize to market. For a few years this was done by horses and dray carrying about 60 bushels to Mossiface, where it was loaded onto river boats to Lakes Entrance, and then by ocean boats to Melbourne. Later it was taken to Bairnsdale by foot and loaded onto the trains to Melbourne. (more information in Newsletter October 2006) This crib, measuring seven chains, sixteen feet, contained 10,000 bags of maize cobs which were grown by Linc Timmons on Peter Irvine's farm (Fairlea?) in Orbost, East Gippsland. The growing of maize in the Orbost district contributed significantly to the economy of the township for many years, The many maize cribs once seen on the surrounding farms have now disappeared and this photograph is a pictorial record of that significance.A black / white photograph of a large maize crib full of maize in a paddock. There is a large framed copy of the original.agriculture-orbost farming-maize-orbost maize-crib-orbost -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyShovel head - Fainter Falls
The Fainter Falls Walking Track was originally accessible via a fire fighting access trail, which was used by fire-fighters putting out spot fires caused by lightening strikes. The fires in the summer of 2003, highlighted the beauty of this area and provided the residents with the opportunity to consider the redevelopment of the trail. Work to establish a 700 metre grade 2 walking trail with a 50 metre grade 3 extension trail to the Falls began in 2005. It also includes 3 observation decks, a bridge over a creek crossing, car parking and interpretative signage.The shovel was found during work on the Fainter Falls track. It was left there some time ago by a previous visitor to the Falls indicating that the Falls were accessible and attracted visitors many years ago.Rusty metal shovel head curved on each side and rounded at the front. At the back of the blade it is attached on top with 3 nails to the top piece. The top metal piece overlaps the blade by 6.5 cm longitudinally x 5 cm across. On the back the metal piece overlaps the blade by 12 cm both longitudinally and across the handle end but tapers to a point. It has 6 nails attaching it. Both metal pieces are attached to the blade and curve parallel and around so that a wooden handle would fit between them. This would have 2 nails passing through both metal pieces and the handle. (The handle is missing.) shovel. fainters falls. bogong. walking track. fire track. water. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire iron stand
... , shovel, poker. Domestic object Fire iron stand ...Fire iron stand; black, all metal stand with a singular spine attached to rectangular base. below the handle on the spine is a horizontal 'U' shaped rack with a hook at each end and a hook at the centre back of the 'U' for hanging tools. Decorative metal handles on tools and rack. 4 parts; stand, brush, shovel, poker. Impressed into underside of stand "B1O2" and " ATWN"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, fire iron stand, fire iron, fire tools, fireplace set, fire iron set, domestic ware, heating -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumFire irons
... utensils - Long poker, short poker, tongs, shovel Fire irons ...Brass stand in shape of a cobra, with four brass fireplace utensils - Long poker, short poker, tongs, shovelirons, fire, domestic, utensil -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumTool - TOOLS FIRESIDE
... TONGS SHOVEL LAURA HUDSON FIRE TOOLS .1 TONGS, KNOP HANDLE, TONG ...FIRE TOOLS .1 TONGS, KNOP HANDLE, TONG ARMS ATTACHED TO CIRCULAR FITTING, MANUALLY OPERATED .2 SHOVEL, SMALLER, KNOB HANDLES PATTERN CUT IN SPADE .3 SHOVEL LARGER, KNOB HANDLE, PATTERN CUT IN SPADEfiretools, tongs, shovel, laura hudson -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Rakut - Fire rake, Unknown FCV District, c 1952
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts.Fire tool used before the introduction of RakehoesRakut - Fire Rake and cutting toolGreen and red coloured handle and 020 marking indicated which FCV District the tool belonged tobushfire -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Fire Beater - Canvas, c 1930s
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. This canvas hose beater was based on a century-old design which used lengths of canvas fire hose rivetted together and lashed with wire to a broom handle. The hose was be soaked in water to improve its effectiveness. If the flames were more than a metre or so the user was generally not able to get close enough to extinguish the fire It's recommend that users lift no more than above knee height to conserve energy and let the beater to the work. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts and later RakehoesEarly firefighting toolBushfire beater - Canvas with wooden handleR P PWD (Public Works Department) The handle has painted markings which indicate which FCV District it belonged to.bushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Fire Beater - Leather, c 1940s
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. This leather beater was based on a century-old stockman's design which used green cow hide leather lashed to a broom handle. It's recommend that users lift no more than above knee height to conserve energy and let the beater to the work. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts and later RakehoesEarly firefighting toolBushfire beater - Leather with wooden handlebushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaFunctional object - Locomotive Type Fire Tube Boiler, 1927
This Johnson Bros. (USA) Locomotive Type Boiler was from a steam shovel (that moved on rails) that excavated rock and soil during the construction of Stevens Weir near Deniliquin NSW in 1934. It has a working pressure of 100psi. This is an example of a fire tube boiler where the fire from the fire box heats the water surrounding the fire tubes running through the boiler, smoke escapes out the smoke stack and the steam is captured in the dome and sent through pipes toward other engines in the Port of Echuca Steam Display. Two glass gauges are fitted on the side of the firebox. Two safety valves are fitted at the top of the boiler to maintain the correct and safe pressure. It still functions today for visitors most days of the week.A good example of the technology and industrial history of the Riverina region of southern NSW and northern Victoria. It is an integral part of the Port of Echuca Steam Display running secondary engines off the steam produced within this boiler. Large cast iron, fire tube boiler with 124 fire tubes, fire box, steam dome and exhaust chimney. boiler, johnson bros, steam display, kevin hutchinson steam shed -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - PURDY COLLECTION: WILFRED WATSON ARTICLE
Newspaper article: 'Years in the Mines". Article details the life of an Eaglehawk man who spent 22 years working in Bendigo mines and who is celebrating his 80th birthday (no date on article) Wilfred worked at the Unity Mine in Long Gully, when the Prince of Wales, visited it. He also worked at the Red White and Blue, Big Deborah and South Virginia (between 1920 and 1942) He stated worked as a shoveler and then learnt to bore holes and fire with explosives. At the South Virginia, there were three shifts working the shaft. Each shaft shift had two miners and one shoveller and the mine has 20 or 30 workers.bendigo, mining, wilfred watson -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFire Scoop
... Scoops Shovels Silver painted fireplace shovel or scoop ...Silver painted fireplace shovel or scoop.scoops, shovels -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionRakehoe (McLeod Tool)
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Rakhoeforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Fire Irons, 20th c
Sets of vintage fire irons or tools were used to maintain a fire and clean a fireplace. They usually consisted of three or four items, sometimes on a vertical stand.A 20th century set of four wrought iron fire irons hanging on a heavy steel base square stand with the main rod riveted to the base. All have turned lined brass handles with a knob at the top. Included are: one poker with a pointy end, one dustpan or shovel, one wire brush and a pair of tongs. 1. Taiwan -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFire beater (canvas)
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Fire Beater (canvas) 1930s designforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPulaski
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.Pulaski Fire Tool Combines an axe and a grubbing hoe. Digging end and cutting end with short wooden handleforests commission victoria (fcv), hand tools, forest harvesting, bushfire -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Rakehoe, McLeod Tool (American)
Bushfire perimeter rather than bushfire area is the main control problem for firefighters on the ground. A conundrum rapidly compounded by spot fires. A small 5 ha fire can be nearly 1 km around the perimeter. That's a long way to build a control line by hand in rough bush. Dry firefighting techniques by hand were mostly confined to “knocking down” or “beating out” the flames, as well as "digging out". Digging or raking a “mineral earth” trail down to bare dirt proved most effective in forest fuels which, unlike grass, tend to retain heat and smoulder. Early tools were whatever happened to be close at hand. They were simple and primitive and included shovels, slashers, axes, hoes, beaters and rakes. A cut branch to beat the flames was often the only thing available. Farming and logging tools, developed over centuries of manual labour, and readily available at local hardware stores came into use, but little thought was given to size, weight, and balance. For years foresters experimented with combination tools. In about 1952 fire beaters and other implements were being replaced with Rakuts. However, its believed the now common Rakehoe is an Australian variation of the American McLeod Tool which was developed in 1905 by forest ranger Malcolm McLeod of the Sierra National Forest. The late Athol Hodgson advised that predecessors, Reg Torbet who had been the Chief Fire Officer for the Forests Commission from 1948-1956, along with his QLD counterpart Clive Price, went in late 1951 as Australian delegates on a 10 week fire study tour of Nth America organised by the United Nations. They came back with a couple of McLeod tools from Canada. Cam MacLeod (different spelling) had been the Head of Fire Research for the Canadian Forest Service at the time and had supplied them. The tools were ideal for deciduous forests in the eastern provinces and Clive arranged to have them manufactured in QLD. The Rakho, as it was then spelled, was first issued to FCV crews 65 years ago in 1955-56. The American Pulaski had been trialled, but never found favour with Australian firefighters.First used in 1955Rakehoe Combination of a heavy-duty six-toothed (each 9cm long) rake with a large, sturdy (25cm) hoe.bushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv)
