Showing 18 items matching "murray river trade"
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Riverboats and Rivermen, William Drage & Michael Page, 1976
... Murray River Trade... on the Murray River paddle steamers. Murray River Murray River Trade ...A story of the great days of riverboats on Australia's inland rivers written from personal recollections of the author. He spent most of his working life on the rivers. William Drage worked as deckhand, barge hand, mate, and master. Life on the rivers was full of drama and variety, strange characters and unexpected adventures. William Drage's story of the boats he served and the men he knew is a lively description of a vanished world: a nostalgic glimpse into a way of life that was uniquely Australian and disappeared forever.A volume of 221 pages featuring text and images.A story of the great days of riverboats on Australia's inland rivers written from personal recollections of the author. He spent most of his working life on the rivers. William Drage worked as deckhand, barge hand, mate, and master. Life on the rivers was full of drama and variety, strange characters and unexpected adventures. William Drage's story of the boats he served and the men he knew is a lively description of a vanished world: a nostalgic glimpse into a way of life that was uniquely Australian and disappeared forever.murray river, murray river trade, murray riverboats -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
Taken between 1928 and 1930, depicted is the Bethanga Bridge under construction. The Bridge was completed in 1930 and was built to assist residents of the Bethanga district to travel to Albury. Other bridges would become submerged by the backed-up water of the Murray and Mitta Rivers so the Bethanga bridge was built two miles above the Mitta Weir. The Bethanga Bridge was built north of the future Hume Dam which would be completed in 1936. At 2430 feet long, Bethanga Bridge was the longest road bridge in Australia at the time of its completion. The Bridge is 20 feet wide and made up of nine 270 feet long spans. Materials used include ten tons of paint for the steel works; 1600 tons of steel; 900 tons of timber for the decking; and reinforced concrete for the piers. The tender for the construction was awarded to C. Ruwolt Pty. Ltd., engineers who were located on Victoria Street, West Richmond. The contract was awarded for £71,890. It was predicted between 250 and 300 men would find employment on the project. The news was well received by trade unions at the time as there had been a drop in available engineering work.This photograph is historically significant as it depicts the progress of the Bethanga Bridge construction, which was important infrastructure for the area. It is also a good example of methods used in the area to assist in travel over the river prior to the construction of the Hume Dam.Black and white rectangular photo printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: 1997 3186 / 84-19-3 / This is the bridge. / It is not yet open to traffic / yet. will not be completed / until May next / It is a wonderful bridge the / pillars are 100 feet high. / KODAK PRINT Envelope Obverse: Peterson PHOTO / Hume Weir Envelope Reverse: BMM 84-20-1,2+3. bethanga bridge, lake hume, hume dam, hume weir, murray river, bridge, bethanga, albury -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Maxwell Pemberton, 23 June 2000
Mr Maxwell Pemberton was born in Goulburn, NSW in 1923 and moved to Beechworth as a child just before the Great Depression. Mr Pemberton's father was a baker who opened a grocery store in Beechworth to support his seven children. The store, which competed with eight other grocery traders in Beechworth for finite local business, delivered goods by horse and cart to customers all over the district, including the hamlet of Stanley. Mr Pemberton's oral history testifies to the sorts of economic struggles faced by the majority of Beechworth's residents during the depression years. Mr Pemberton worked in many different industries in and around Beechworth, including in his father's grocery store, which he later took over with his brother; the Zwar Tannery, where he served as a union representative; and at the Ovens and Murray Hospital for the Aged, formally the Ovens Benovolent Asylum, established in 1862 for care of the district's destitute, disabled and aged people from Euroa to the Murray, among them, homeless people Mr Pemberton referred to as 'river-bankers'. The hospital's founding in the 1860s was driven by a committee headed by the notable figure, G.B Kerford. Beechworth's institutions were a major source of local employment in the twentieth century. Mr Pemberton joined the Australian Navy during WWII and served at Port Moresby in Papua New Guinea. During his period of service, he received an honorary award from the Royal Humane Society of Australia for aiding and saving a drowning civilian at risk to his own life. Mr Pemberton's oral history also touches on the complex relationship between Australian forces and local Papuan people during the war. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Mr Maxwell Pemberton's oral history recalls many aspects of life in Beechworth and the Oven's district during the twentieth century and enriches our understanding of the effects of the periods of socio-economic decline and renewal that unfolded as the century progressed. His singular account of his various jobs and colourful memories of life as a youth and young man in Beechworth, and abroad as a serviceman, contributes to our understanding of society's attitudes and expectations regarding ideals of masculinity and Australian national identity. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which would have been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mr Max Pemberton /twentieth century beechworth, benevolent asylums, wwii, beechworth's institutions, local employment, government institutions, listen to what they say, oral history, burke museum, maxwell pemberton, ovens and murray hospital for the aged, zwar tannery, beechworth grocers, australian navy, port morseby, papua new guinea, trade unions, welfare services, homelessness, 'river bankers', aged care, g.b kerford, ovens benevolent asylum, ovens benevolent home -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaPhotograph - Black & white photograph of boats tied up at Morgan Wharf, Boats tied up at Morgan Wharf, 19/09/1984
... Shows the extent of the River trade in the Murray Darling... the extent of the River trade in the Murray Darling River basin ...Shows the extent of the River trade in the Murray Darling River basin in the early 20th Century.Helps show the extent of river trade in the Riverland area of South Australia in the early 20th Century.Copy of an original photograph of a wharf scene with moored river boats. possibly of Morgan c. 1900.Written on back in pencil."boats tied up at Morgan-?"murray river, paddle steamers, river boats, morgan. south australia., riverland -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaBlack and white photograph, 21.09.1984
Black and white photograph of the P. S. Gem moored by the river bank. Recorded as being holed on Mildura slip. For statistical on the P. S. Gem see registration no.10 from The River trade, Wool & Steamers by G. Painter , pp.55, 66. Details of the paddle steamer can be located in The Register of Australian & N. Z. Shipping.The P. S. Gem is a large paddle steamer of historical and social significance. It has 3 levels including what appears to be many cabins.Black and white photograph of P. S. Gem moored by river bank. Recorded as being holed on Mildura slip. Copy of an original photograph taken 1954.On reverse of photo in pencil: Gem 1954, holed on Mildure slip.p. s. gem, mildura slip -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaBlack and white photograph
... to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system... to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system ...P.S Decoy was built in Scotland and reassembled in 1878 in Melbourne. It steamed to Goolwa, arriving in July 1878. It was used on the Darling River, and as a South Australian tug. In 1905 it sailed to Fremantle W.A for use as an excursion vessel. It was towed back to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system in 1909. It is now a house boat at Mannum. It's owner is Dick Bromhead.( Ref; Parsons, Ron. "Ships of the inland Rivers. P. 65.)The P.S Decoy is significant because it worked as a passenger vessel as well as a transport vessel. It was built in Scotland and reassembled in Melbourne. It was built to use coal, but when it started work on the inland rivers system it was converted to wood fuel.Two black and white photographs ( P000385.1 is missing) of the P.S Decoy passing under a bridge. There are high banks behind the boat and there are nine people on board.On the boat is the word 'Decoy' written on the bow and under the wheelhouse.p.s decoy, darling river, murray river, goolwa, mannum, passenger vessel, bromhead, dick -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaBlack and white photograph, Early 20th Century
... to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system... to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system ...P.S Decoy was built in Scotland and reassembled in 1878 in Melbourne. It steamed to Goolwa, arriving in July 1878. It was used on the Darling River, and as a South Australian tug. In 1905 it sailed to Fremantle W.A for use as an excursion vessel. It was towed back to work on the inland river trade on the Darling -Murray system in 1909. It is now a house boat at Mannum. It's owner is Dick Bromhead.( Ref; Parsons, Ron. "Ships of the inland Rivers. P. 65.)The P.S Decoy is significant because it worked as a passenger vessel as well as a transport vessel. It was built in Scotland and reassembled in Melbourne. It was built to use coal, but when it started work on the inland rivers system it was converted to wood fuel.A black and white copy of a photograph of the P.S Decoy tied up to a riverbank with a barge alongside . The banks are high and there are buildings on the top of the banks.On the boat is the word 'Decoy' written on the bow .p.s decoy, darling river, murray river, goolwa, mannum, passenger vessel, bromhead, dick -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayDouble Headed Rail, circa 1872 - 1883
Double Headed Rail from Ravenswood Station Siding which was dismantled circa 1987 the two rails were stored for a time at Maldon before being donated to Puffing Billy Museum Bearing makers marks of Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield, North East Derbyshire, England from 1872 - 1883 Double-headed rail In late 1830s Britain, railway lines had a vast range of different patterns. One of the earliest lines to use double-headed rail was the London and Birmingham Railway, which had offered a prize for the best design. This rail was supported by chairs and the head and foot of the rail had the same profile. The supposed advantage was that, when the head became worn, the rail could be turned over and re-used. In practice, this form of recycling was not very successful as the chair caused dents in the lower surface, and double-headed rail evolved into bullhead rail in which the head was more substantial than the foot. Info from Wikipedia - Rail Profile https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_profile The first records of double headed rail being used In Victoria by Victorian Railways was in 1859, the rails, chairs, oak and trenails were imported from UK. After the 1870’s the Victorian Railways went over to using flat bottom rails, but they still needed replacement double headed rail for lines already laid and this continued up to at least 1883 Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield England from 1872 - 1883 Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway The Melbourne, Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway Company received parliamentary assent in February 1853 to build Victoria's first inland railway from Melbourne to Williamstown, and Melbourne to Bendigo and Echuca. Construction commenced in January 1854 with work on a pier at Williamstown but lack of funds slowed progress, eventually prompting the company to sell out to the government. The 100-mile (162 km) section to Bendigo opened in October 1862. Its cost of £35,000 per mile made it the most expensive railway ever built in Australia. In 1864, the line was extended to Echuca, tapping into the booming Murray-Darling paddlesteamer trade. info from Museums Victoria - Victorian Railways https://museumsvictoria.com.au/railways/theme.aspx?lvl=3&IRN=450&gall=456 1863 Ravenswood Station open on the 1st Feb 1863 Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Ravenswood Siding When the Victorian Railways were established in 1856 they adopted one of the popular British permanent way standards - heavy 80lb (36.3kg) double-headed rail held up right in cast iron chairs attached to transverse timber sleepers by wooden pegs called trenails. The Ravenswood Railway siding was constructed in 1862 with 12 feet wrought iron double-head rail held in cast iron chairs with Ransom and May patent compressed keys. Trenails held the chairs to the sleepers and the joints were secured in joint chairs. Joints were subsequently joined using fish plates. It formed part of the Melbourne to Echuca rail line, initially known as the Melbourne, Mt Alexander and Murray River Railway. George Christian Derbyshire, the first Engineer-in-Chair of the Victorian Railways was responsible for the design and construction of the works. No new lines were built in Victoria using double-headed rail after 1870. The siding was disconnected from the main line in 1988. The Ravenswood Railway Siding demonstrates the original 1856 philosophy of the Victorian Railways to adopt British permanent way technology. The siding demonstrates significant aspects in the development of permanent way technology in England and Victoria over the period from the 1830's to the 1880's. The chairs in the Ravenswood siding are physical evidence of early railway technology rendered obsolete 120 years ago, namely joint chairs at rail joints and trenails to secure the chairs to the sleepers. The double-headed rail demonstrates an important stage in the evolution of British rail technology in the 1830s. The old fish plates, square headed bolts and square nuts demonstrate the success of fishing the rail joins. The Ravenswood siding demonstrates the earliest form of rail joint technology developed in England, and existing in Australia, the joint chair. In part of the siding the sequence of joint and intermediate chairs is consistent with the 1856 specifications, that sequence is rare with the joints secured in joint chairs. The survival of chairs in this sequence is rare and almost certainly demonstrates that they remained in continuous use at the same location from 1862 to 1988. This remnant of the Ravenswood siding has survived 126 years. The siding has proved to be the most significant of extant remnant double-headed sidings in Victoria, containing a rare combination of early permanent way technologies. Construction dates 1862, Info from Ravenswood Railway Siding Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4693/download-report The remaining section of this siding is significant at the State and National levels in that it demonstrates the use of chaired rail by the Victorian Railways Department for the Trunk Lines and, more particularly, the following stages in the evolution of this long obsolete method of permanent way construction: a) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs at regular intervals inferring that the original wrought iron rail lengths were 12 feet, as is known through documentary sources to have been the case. The survival of chairs in this sequence is unique and almost certainly demonstrates that they have remained in continuous use at the same location and in the same sequence from 1862 to 1988 . b) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs designed for use with trenails. c) The use of later intermediate chairs designed for use with steel pins and the use of fished joints with steel double head chaired rail, representing a second method of constructing the permanent way using chaired rail technology. info from Ravenswood Siding - Melbourne/Echuca Railway Line - Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/70103/download-report Addition to Citation for Melbourne to EchucaRailway Line 1/10/1990 Double Head Rail The surviving lengths of double head rail with chairs on this railway compare with one surviving similar remnant on the Geelong to Ballarat railway and are representative of permanent way construction techniques applied exclusively to the two trunk railways of the 1860's. In this respect they are rare survivors and may be unique at the national level and of technical importance at the international level to the extent that they enhance contemporary understanding of early railway building technology. Surviving lengths of chaired double head rail survive at Kyneton, Ravenswood and Bendigo on this railway and include a number of different types of cast iron intermediate and joint chairs with hardwood keys and metal pins. The Ravenswood siding is of special significance for the diversity of chair types and for the sequence of chairs recalling rail lengths known to be associated with construction of the line in 1862. Construction of the Railway Tenders closed on 24 March 1858 with no less than 133 tenders being received. A contract was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937 to commence work on 1 June 1858 and complete the line by 31 July 1861. Cornish and Bruce made quick early progress with the Melbourne to Sunbury section being officially opened on 13 January 1859. The line was officially opened to Bendigo (Sandhurst) on 20 October 1862 by the Governor of Victoria, Sir Henry Barkly. A great banquet was held for 800 guests and this was followed by a grand ball. The extension of the line to Echuca was a relatively simple matter as that part of the line was across plain country without any significant engineering challenges. Tenders were called for the work in 1863 and the work was completed in 1864 by contractors Collier and Barry Apart from the line contractors, other firms directly involved were J Shire law and Co (sleepers), R Fulton, Langlands Brothers and Co, William Crossley (water supply), B Moreland, Langlands Brothers and Co (platelayers lorries), E Chambers (iron pins, traversers), Miller and McQuinstan (luggage vans and steam engines) and various contractors for building works. Info from Engineers Australia Engineering Heritage Victoria Nomination for Recognition under the Engineering Heritage Australia Heritage Recognition Program for the Goldfields Railways - Melbourne , Bendigo & Echuca Railway Page 25 - .2.9.2 Statement from National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Listing number B5323 for Mt Alexander/Murray Valley Rail Line: Page 69 - Theme 3 https://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/portal/system/files/engineering-heritage-australia/nomination-title/Melbourne_%20Bendigo_Echuca%20Railway%20Nomination.pdf The Melbourne, Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. It was established on 8 February 1853 to build a railway from Melbourne to Echuca on the Victorian-NSW border and a branch railway to Williamstown. The company struggled to make any progress and on 23 May 1856, the colonial Government took over the Company and it became part of the newly established Department of Railways, part of the Board of Land and Works. The Department of Railways became Victorian Railways in 1859. Construction of the Bendigo line commenced in 1858, but this private consortium also met with financial difficulties when it was unable to raise sufficient funds, and was bought out by the Victorian colonial government. The design work was then taken over by Captain Andrew Clarke, R. E., Surveyor-General of Victoria, with bridge designs completed by Bryson and O'Hara The contract for the first stage of the line from Footscray to Sandhurst (now Bendigo), was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937.2s.2d ($6.714 million) with work commencing on 1 June 1858. Completion of the permanent way was to be by 31 July 1861 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melbourne,_Mount_Alexander_and_Murray_River_Railway_Company Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Victorian Railways : report of the Board of Land and Works November 1862 GP V 1862/63 no. 21 (2.8 MB) https://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1862-63No21.pdfHistoric - Victorian Railways - Double Headed rail Ravenswood Railway Station and Siding Victorian Heritage Database Reports Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1100 Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1786 National Trust VHR H1100 Mount Alexander and Murray River Rail way Line National Trust2 rail lengths of Double Headed Rail made of Iron makers marks : Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel and 20 joint chairs with metal rail pins Makers mark Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel (possible date 187? very hard to read ) puffing billy, double headed rail, wilson & cammell - dronfield - steel works, ravenswood station siding, melbourne to echuca rail line, initially known as the melbourne, mt alexander and murray river railway. -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Aldo Massola, Journey to Aboriginal Victoria, 1969
Looks at the Aboriginal community from the time of white contact, across many parts of Victoria. Chap.1; Melbourne - early missions, camp of Native Police, corroboree trees, canoe trees, grave &? headstone of Derrimut; quarries at Keilor, excavation sites at Green Gully &? Keilor; quarry at Mt. William, notes on inheritance of quarries Coranderrk settlement - Barraks grave, notes on his life; Chap.2; Geelong - Yawangi group of the Wothowurong tribe, camping grounds in area quarries; Notes on William Buckley, Gellibrand (a notable Aboriginal), graves in the Western Cemetery; Chap.3; Colac - war between Colac &? Geelong tribes; Mission at Birregurra, reason for failure of Buntingdale Mission; brass plate to Coc-coc-coine; reserve at Elliminyt, native ovens, camp sites, initiation site &? ritual; quarry sites, axegrinding factory, rock pecking &? engraving; dried hand &? 3 Aboriginal skulls found; Chap.4; The south-west coast - middens, camp sites notes on Framlingham Stn., fish traps at Tyrendarra; Chap.5; The far west - massacres of Aborigines near Casterton; camp sites, oven mounds; the first cricket team formed; Aboriginal cemetery; Chap.6; Hamilton - camps; Mount Rouse Station, axegrinding grooves at Nareeb Nareeb, shelters described, fish traps, massacre at Lake Condah; mission; canoes; Chap.7; Camperdown - legend about Lake Bullen Merri; obelisk erected in memory of Aborigines of district especially chief Wombeetch Puyuun; Jarcoort tribe; fish weirs, camps, intertribal fights between Booluc-burrers, Jarcoorts &? Ellengermote groups; bartering place at Mount Noorat; articles traded, legend of Flat-Top Hill; Chap.8; Ballarat - camp at Lake Wendouree; White Stone Lagoon; legends concerning Mt. Buninyong &? waterfalls at Lal-lal; camp sites; pygmy-type implements near Meredith, quarry at Glue Pot Rocks near Durdidwarrah; brass plate of King Billy; Chap.9; Ararat - Tjapwurong territory; camp sites, quarries, shield &? canoe trees; Bunyip belief at Lake Buninjon of Muk-jarawaint &? Pirtkopen-noot tribes, gives legend; stone implements; mill stones; fish weirs; stone arrangement near Lake Wongan; ground drawing of a bunyip, paintings in rock shelter near Mt. Langi Ghiran; Chap.10; Maryborough - camps, oven mounds, rock wells, stone arrangement at Carisbrook; camp sites at Mt. Franklin; Chap.11; Charlton - belief in Mindye (snake); canoe trees, ovens, camp sites, water holes, rock wells, stone implements; method of rainmaking; Chap.12; Horsham-Stawell, The Wimmera - Wotjobaluk land; camps, fish traps at Toolondo; Black Range cave paintings, Flat Rock shelters (detailed account of these paintings); Bunjils Cave; Chap.13; Horsham-Stawell, The Mallee - camp sites, implements; Ebenezer Mission, Willie Wimmera taken to England by Rev. Chase to become a missionary, died in England; Chap.14; The Murray River, Mildura Swan Hill - Battle of the Rufus; ceremonial ground, Lake Gol Gol, canoe &? shield trees; stone implements; camp sites, fire place arrangements; fish traps; oven mounds; Chap.15; The Murray River, Swan Hill-Echuca - legend about Lake Boga; camps, oven mounds, the Cohuna skull, Kow Swamp, method of burial; Chap.16; Shepparton ovens; brass plates of King Paddy of Kotupna &? King Tattambo of Mulka Stn., native well, camps; Chap.17; Wangaratta -camps, quarry, rock holes, the Faithful massacre; grinding rocks at Earlston; Chap.18; The High Plains - Ya-itma-thang; camps, Bogong moth feasts, native paths for trade &? intertribal fights, articles traded; painted shelters; Koetong Ck. Valley, near Mt. Pilot &? near Barwidgee Ck.; Chap.19; Dandenong - water holes, list of 8 holes in Beaumaris - Black Rock area; camps, middens, stone implements (microliths), legend of Angels Cave, stone axes, Native Police Force, Narre Narre Warren Station, legend about rocks on Bald Hill, kangaroo totemic site; Chap.20; Wonthaggi- Yarram - natives visit Phillip Is., murder of William Cook and Yankee by five Tasmanians (listed as Bon Small Boy, Jack Napoleon Timninaparewa, Fanny Waterpoordeyer, Matilda Nattopolenimma and Truganini) near Cape Patterson, men; camp sites, middens, legend of White Rock; Chap.21; Sale - Bairnsdale, The Lakes Country middens, camps; legend at Wulrunjeri; story of a white woman supposedly living with with the Tutangolung tribe, efforts made to prove story; canoe trees; Chap.22; Sale-Bairnsdale, The Inland Braiakolung tribe, camps, implements, canoe &? shield trees; Ramahyuck Mission, grinding rocks, fights with Omeo tribe; native tracks, death through enemy magic - procedure, belief in ghosts; Chap.23; Lakes Entrance and the Country to the east - Kroatungolung people, legend of Kalimna Valley; camps, stones of Nargun, bunyip, devils at Lake Tyers, excavation at Buchan, carbon dates; middens, ochre at Cape Conrad, stone fish-hook file at Thurra River; note on Bidwel tribe; Each chapter gives historical details, early contacts, relationships with settlers; Aboriginal place names and detailed description of sites and geographical features.b&w photographs, b&w illustrations, colour illustrationsgeelong, colac, hamilton, camperdown, ballarat, ararat, maryborough, charlton, horsham, stawell, murray river, shepparton, wangaratta, dandenong, wonthaggi, yarram, sale, bairnsdale, lakes entrance -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Berndt, Ronald, A World That Was : The Yaraldi of the Murray River and the Lakes, South Australia, 1993
The book's range is encyclopedic and engrossing. It encompasses relations between and among individuals and clan groups, land tenure, kinship, the subsistence economy, trade, ceremony, councils, fighting and warfare, rites of passage from conception to death , myths, beliefs and practices concerning healing and the supernatural. Not least it is a record of the dramatic changes following European colonization.xv-xvii; 624P.; plates; appendices; bib.; indes; tables; figs.; maps; 25 cm.The book's range is encyclopedic and engrossing. It encompasses relations between and among individuals and clan groups, land tenure, kinship, the subsistence economy, trade, ceremony, councils, fighting and warfare, rites of passage from conception to death , myths, beliefs and practices concerning healing and the supernatural. Not least it is a record of the dramatic changes following European colonization.ngarrindjeri (australian people) -- social life and customs. | ngarrindjeri (australian people) -- cultural assimilation. | aboriginal australians -- murray river estuary (n.s.w.-s.a.) | aboriginal australians -- south australia. -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionBook, Paddle wheels of the past
The discovery of inland waterways during the early settlement of Victoria and South Australia led to trade being plied up and down the rivers.An A4 80 page comb bound book.paddlewheels, paddlesteamers - murray river (nsw- sa), boats, punts, barges -
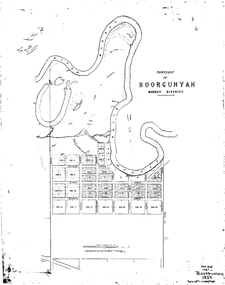 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMap - Boorgunyah - "The Town that never was"
At the height of the river trade, there was a town surveyed and laid out, and streets were named. This town was to house the workers at the river port of Red Bank when the paddle steamers plied the Murray River as far as Albury, carrying produce such as wool and wheat to the various towns along the river in the 1800s. As the river trade died away, this town never went ahead – one might say, “The town that never was.” A lone gum tree stands on the site today.This item is significant because it documents plans which were made for the early development of Wodonga.A black an white map depicting the proposed location of the township. The map is based on a sketch and is not to scale,early wodonga, boorgunyah - "the town that never was", wodonga heritage -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaPlaque - Timber sign, Murray River Sawmills, 1926
... barges built as the Murray River timber trade was declining ...This large wooden sign was originally attached to the barge D26 which was one of the 4 barges used to carry logs behind the PS Adelaide. The D indicated that it was the fourth barge to be built in 1926 by Murray River Sawmills. The number represented the year it was built.This original timber piece, salvaged from the D26 barge is an important relic from an original outrigger logging barge from the early 20th century, one of the last logging barges built as the Murray River timber trade was declining. The barge was restored by the Port's chief shipwright Kevin Hutchinson with assistance from Laurie Rendle and Alan Battsch. and the PS Adelaide is also a significant feature in the Port's collection. Large red gum timber signD 26d26, barge, logging industry, murray river sawmills, ps adelaide -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionWork on paper - Vertical file, Sarovich
... along the Murray River and they met at this time. They moved... along the Murray River and they met at this time. They moved ...Christopher Joseph Sarovich married Susannah Botley. There are a number of spellings of his surname. He was involved in trade along the Murray River and they met at this time. They moved to Melbourne and the Sarovich family had a furrier family business in Port Melbourne, but resided in Surrey Hills. They owned a number of houses along Whitehorse Road, including the site of the Balwyn Community Centre. The last remaining property in family hands was sold to the Camberwell Council by Mrs Margaret (Peg) Grossman, nee Sarovich. Peg was a member of the Surrey Hills Historical Society.Vertical file of information related to members and descendants of the Sarovich (Sharowich) family: 1. Certificate of marriage of C.J. Sharowitch and Susannah Botley 11.2.1882 (1 page). NB/ Spelling as per marriage certificate. 2. Notes on Louisa Smith by June Peka 21.11.2016 (2 pages); photos of family and staff in Australia and N.Z., no dates (7 pages) and emails between June Peka and Sue Barnett 11/2016 (2 pages). 3. Margaret Grossman funeral service 28.4.2014 at St. Barnabas Anglican church, Balwyn. NB/ Margaret nee Sarovich (miss) susannah botley, (mr) christopher joseph sharowich, (mr) christopher joseph sarovich, (mrs) susannah sarovich, (miss) alice botley, (mr) john nicholls, (miss) louisa botley, (mrs) louisa smith, (mr) james smith, (miss) margaret sarovich, (mrs) margaret grossman -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaInstrument - Steering Wheel, PS Success, 1877
This steering wheel is from the PS Success. The PS Success was built in Moama in 1877 by GB Air for Westwood & Air. The Success towed barges of sawn red gum, wool & other cargo along the Darling and Murray Rivers as well as running as a passenger boat from Swan Hill to Mildura during 1915-16. The Success ended her working life in 1957 and was put up on the bank at Neds Corner, 80kms west of Mildura. The PS Success was donated to the Riverboat Historical and Preservation Society of Mildura with plans for full restoration but with funds becoming extremely difficult to secure, the Shire of Campaspe was approached to take ownership in 2009 to enable further restoration when possible. The Riverboat Preservation Society also donated this original steering wheel.The PS Success was an important vessel built in the Echuca area during the height of the Riverboat trade in the 1870s. She had a long, colourful history towing barges on the Murray River and in particular in the Mildura, Wentworth and Ned's Corner regions. Importantly, the Success was the last paddlesteamer to be working on the river system right up until the 1956 floods rescuing sheep and wool. The steering wheel is an important original element of the PS Success and her hopes for restoration one day. Red metal steering wheel with 10 spokes sitting on a heavy iron wheel stand. -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaFunctional object - Paddlesteamer, George Linklater, P.S. Adelaide, 1866
Built in 1866 in Echuca, the PS Adelaide is the oldest wooden hulled paddle steamer still operating as a passenger vessel in the world. Engines made in Melbourne by Fulton and Shaw. JG Grassie was the original owner who was looking for a wool carrying boat as a commercial venture with the arrival of the rail at the Port of Echuca making the future look bright. Seutonius and Charles Officer of Murray Downs Station joined Grassie in financing the venture and they used the boat for 6 years before David Blair and partners (Echuca sawmillers) bought the Adelaide in July of 1872 and she began her long working life as a logging boat providing a shuttle service between the forests around Barmah and the mill, usually towing up to 3 or 4 barges. The paddle boxes were rebuilt from round to a square configuration in approximately 1924 by Charles Felshaw, local Echuca shipwright. The Adelaide had unusual strength for her size. Her career ended in the mid 1950s where she lay idle tied up near the mill at Echuca wharf. For a short time she was sold to Mildura but fortunately the Apex Club raised funds to buy her back to be a reminder of the riverboat days at the Port. She was lifted out for safekeeping into Hopwood Gardens where she remained on show for nearly 25 years. After restoration by Port shipwright Keven Hutchinson OAM, she returned to the waters of the Murray River on Sunday March 4th 1984 at 5.20pm. After further restoration, in 1985 the Prince and Princess of Wales re-commissioned PS ADELAIDE in a ceremony on their tour of the region. The world's oldest wooden hulled paddle steamer still operating as a passenger vessel today built in Echuca in 1866. It is often considered the flagship of the operational fleet of the Port of Echuca given its age and known provenance to Echuca. The Adelaide is an iconic symbol of the riverboat timber and cargo trade that worked on the Murray River from the mid 1800s. Remarkably, PS ADELAIDE still operates with its original Fulton and Shaw engines.Composite hull, side wheeler with two single cylinder steam engines, producing a total of 36hp. Currently cream and burgundy moored at the Echuca Wharf. 49 passenger capacity.P.S. Adelaide signage on wheelhouse and port and starboard bow.p.s. adelaide, paddle steamers, echuca boat builders, charles felshaw -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - The Living Murray 2002 - A discussion paper on resourcing the health of the River Murray, Murray-Darling Basin Ministerial Council, July 2002
This paper provides an introduction to the issue of environmental flows in the River Murray. It explores the health of the River and ways it might be improved. It identifies possible consequences, benefits and concerns and was intended to guide the discussion of relevant issues, including water trade and access rights to water. It outlined a process for community engagement to discuss and address these issues and improve the overall health of the river.non-fictionThis paper provides an introduction to the issue of environmental flows in the River Murray. It explores the health of the River and ways it might be improved. It identifies possible consequences, benefits and concerns and was intended to guide the discussion of relevant issues, including water trade and access rights to water. It outlined a process for community engagement to discuss and address these issues and improve the overall health of the river.murray river, environmental issues, environmental conditions., water use murray river -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaDecorative object - Permewan Wright Vase
Permewan Wright & Co Ltd were one of the biggest shipping agents on the Murray in the 2nd half of the 19th century. They were a cartage company established in 1856 in Geelong, who opened one of its twenty Victorian branches at Echuca in 1875. The company dominated the river trade in Echuca during the 1880s and 1890s, operating a fleet of steamers on the Murray, Murrumbidgee and Edwards Rivers.Off White Vase with blue decorative Permewan Wright Co Flag. Thin blue lines encircled at top and middle. Slightly scalloped opening.Decorative Scrolls embossed on one side. permewan wright, river transport, permewan wright building, permewan wright flag
