Showing 68 items matching "peg wells"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Correspondence from SMB Girls' Ex students association
... peg wells... lorna yates denise kidd peg wells eileen hayes barbara paddle ...School of Mines Ballarat was a predecessor of Federation University.Correspondence from SMB Girls' Ex students association including letters from the secretary, invitations to attend meetings, apologies and acceptances, minutes, inaugral dinner menus and members lists. All documents vary in size.school of mines and industry ballarat, girls' ex student association, b. dulfer, g. kingsley sutton, dorothy richards, phyllis mcgregor, s. shillington, mrs a.l. arkinstall, mrs s. francis, miss ouida worthington, mrs k hale, mrs jones, mrs m mckenzie, mary green, lorna yates, denise kidd, peg wells, eileen hayes, barbara paddle, lynette atkinson, francis dowler, janet wells, rita lewis, joy mills, bonnie cody, elizabeth kinnane, beverley jennings, fay cosgrove, miss m chamberlain, gwen williams, maureen mann, nonie robertson, margaret lyttle, kathleen button, marilyn jones, rosemary paddick, nancy rimmington, mrs mary osborne, mary nolan, r. anglin, janet steele, margaret maun, mrs clare attwood, mrs d. ditchfield, heather mccallum, evelyn ditchfield, joan shearer, glenis sleeth, mrs m. mctaggart, betty hearn, mrs k. campbell, d. clemence, m. clemence, beth dalton, florence shurs, claudia mason, gwen murdoch, june murdoch, m. bailey, j. baker, j. banes, i. barr, w. beckwith, j. bilston, f. blake, v. boddinar, a. bosher, b. brookman, j. cameron, h. chasey, d. coad, r. cockburn, b. coombs, e. coombs, p. coombs, m. connell, l. cooper, m. coulter, p. crosbie, e. curnow, h. darby, d.j. davis, n. dunstan, b. elliott, o. elliott, n. eltringham, h. everleigh, m. everleigh, e. fitzgerald, m. gallie, g. gough, e. greenwood, b. guy, d. hambly, p. halse, g. harrison, h. hearn, o. hellings, d. henderson, n. henderson, m. hewitt, g. hoffman, v. hoffman, c. king, h. knox, b. lancaster, b. law, d. lawrie, g. lawry, m. lochhead, p. maloney, m. malpass, m. martin, j. matthews, morgan, g. murdock, j. murdock, b. murfett, i. murfett, c. mcilvena, e. norris, m. norris, b. patterson, h. patterson, e. prowse, l. rollan, b. ross, f. saunders, f. sheers, e. stevens, g. stevens, l. strick, v. taylor, j. trescowthick, b. veitch, j. waller, j. wallis, ms, d. williams, s.e. williams, b. william, b. willian, k. windsor, s. wyres, t. yeoman -
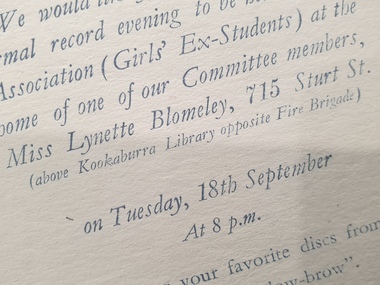 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Correspondence from SMB Girls' Ex students association
... peg wells... lorna yates denise kidd peg wells eileen hayes barbara paddle ...School of Mines Ballarat was a predecessor of Federation University.Correspondence from SMB Girls' Ex students association including letters from the secretary, invitations to attend meetings, apologies and acceptances, minutes, inaugral dinner menus and members lists. All documents vary in size.school of mines and industry ballarat, girls' ex student association, b. dulfer, g. kingsley sutton, dorothy richards, phyllis mcgregor, s. shillington, mrs a.l. arkinstall, mrs s. francis, miss ouida worthington, mrs k hale, mrs jones, mrs m mckenzie, mary green, lorna yates, denise kidd, peg wells, eileen hayes, barbara paddle, lynette atkinson, francis dowler, janet wells, rita lewis, joy mills, bonnie cody, elizabeth kinnane, beverley jennings, fay cosgrove, miss m chamberlain, gwen williams, maureen mann, nonie robertson, margaret lyttle, kathleen button, marilyn jones, rosemary paddick, nancy rimmington, mrs mary osborne, mary nolan, r. anglin, janet steele, margaret maun, mrs clare attwood, mrs d. ditchfield, heather mccallum, evelyn ditchfield, joan shearer, glenis sleeth, mrs m. mctaggart, betty hearn, mrs k. campbell, d. clemence, m. clemence, beth dalton, florence shurs, claudia mason, gwen murdoch, june murdoch, m. bailey, j. baker, j. banes, i. barr, w. beckwith, j. bilston, f. blake, v. boddinar, a. bosher, b. brookman, j. cameron, h. chasey, d. coad, r. cockburn, b. coombs, e. coombs, p. coombs, m. connell, l. cooper, m. coulter, p. crosbie, e. curnow, h. darby, d.j. davis, n. dunstan, b. elliott, o. elliott, n. eltringham, h. everleigh, m. everleigh, e. fitzgerald, m. gallie, g. gough, e. greenwood, b. guy, d. hambly, p. halse, g. harrison, h. hearn, o. hellings, d. henderson, n. henderson, m. hewitt, g. hoffman, v. hoffman, c. king, h. knox, b. lancaster, b. law, d. lawrie, g. lawry, m. lochhead, p. maloney, m. malpass, m. martin, j. matthews, morgan, g. murdock, j. murdock, b. murfett, i. murfett, c. mcilvena, e. norris, m. norris, b. patterson, h. patterson, e. prowse, l. rollan, b. ross, f. saunders, f. sheers, e. stevens, g. stevens, l. strick, v. taylor, j. trescowthick, b. veitch, j. waller, j. wallis, ms, d. williams, s.e. williams, b. william, b. willian, k. windsor, s. wyres, t. yeoman, margaret steele, r.w. richards -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyPhotograph - Image, c1950
... around a well pegged down pole, flying a flag or banner... of Girl Guides and their leader around a well pegged down pole ...Guides leader believed to be Florence Iggsten.Black and white photograph of Girl Guides and their leader around a well pegged down pole, flying a flag or banner. This is one of five photographs once mounted on a piece of paper.Paper mount has a caption for one of the other photographs: "The bride is Avis (nee Hunt) a former R'glen guide. Guard of Honour - Wangaratta guides"girl guides, florence iggsten -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Satin Bowerbird (male), 1860-1880
The Satin Bowerbird is commonly located around the eastern and south-eastern coast of Australia. They reside in wetter forests and woodlands, and nearby open areas. They feed mostly on fruits throughout the year but in summer will supplement their food supply with insects and in winter with leaves. The Satin Bowerbird is most commonly known for it's practice of building and decorating it's bower. They will often collect objects of bright blue to decorate the bower including straws, clothes peg, parrot feathers, pens, marble, string, glass and bottle tops. This decoration is done by a male Bowerbird in the effort to attract females. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This taxidermy Satin Bowerbird specimen has dark black/blue glossy plumage and a pale coloured bill of small size. The bird is of a medium size compared to other species of birds and has pale legs with short talons. The eyes are made of strikingly blue coloured glass which represents the violet-blue iris of this bird while living. The bird has a short tale and has been stylized in a leaning/crouched position with it's back arched upwards and head out long. This specimen stands on a small platform and there is some deterioration to the tail feathers which protrude beyond the platform which may have otherwise provided some protection. Donor - Mr. E.T. / BH. RO. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, bower, bowerbird, satin bowerbird -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1869-1920
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture was done by hand using one of these types of plane. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. Moulding Plane Hollow type Marked Routledge No.8 Blade Stamped JAS Burden (owner). flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood moulding Plane, Between 1869 early 20th century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture was done by hand using one of these types of plane. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. Plane, Moulding, Hollow Size No 18 Routledge Maker (Owner "J.A.S.Burden")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Plane, Richard Routledge, Late 19th to early 20th century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc, or other timber items that had to be accomplished by using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. Profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve the required decorative finish. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Rebate Moulding plane Size 1/2"Maker R Routledge Birmingham also marked Owner Jas Burdenflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Plane, Richard Routledge, Late 19th to early 20th century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc. or other timber items that had to be accomplished by using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. Profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve the required decorative finish. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Plane Moulding type size 1/8" Maker stamped R Routledge & JAS Burden (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Moulding Plane, Late 19th Century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture was done by hand using one of these types of plane. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. Moulding Plane. Stamped JAS Burden (owner) also No 2flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Moulding Plane, J Budd, Mid 19th Century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden objects. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear-resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmaker's shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other workers to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we know about J Budd is that he was a toolmaker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool believed to have been made by a known maker, J Budd given the inscription on the item of "JB" this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce an ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims, etc. or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Plane, Moulding, Ogee- PlainStamped JB No 6flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Moulding wood Plane, Richard Routledge, Mid 19th to early 20th Century
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a little known maker, this item would have been made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. At a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc. had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Moulding plane round type Marked Routledge 64 Bull Street also stamped (JAS Burden owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood moulding plane, G Davis, 1821-1876
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about George Davis is he and his successors made planes in Birmingham, England, from about 1821 to 1876. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals who worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. This item is a significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Moulding plane centre bead, also called Single Bead Reeding Plane. Stamped maker G Davis Has GM inside W (owner) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane, moulding, single bead reeding plane -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, William Bishop, 1818
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about William Bishop is that he made planes in Grey Coat St Westminster, London, around 1818. He is listed in business directories of the time but nothing before or after this date. There are many of his decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale and given that his moulding planes are vintage his wood planes are well sought after by collectors today. A vintage tool made by a little known maker, this item was made for cabinet makers and individuals who worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve the required decorative finish. This item is a significant tool from the late 18th to early 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors of vintage tools. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Plane Moulding Hollow type Marked Burden (Owner) also stamped JB and Iflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Ship's Wheel, 1871 or earlier
The ship building company E. & A. Sewall, from Bath, Maine, USA, built many ships that had wheels with the same decorative, starburst pattern on them as this particular wheel segment, including the Eric the Red. The wheel was manufactured by their local Bath foundry, Geo. Moulton & Co. and sold to the Sewall yard for $100, according to the construction accounts of the vessel. Eric the Red was a wooden, three masted clipper ship. She had 1,580 tons register and was the largest full-rigged ship built at Bath, Maine, USA in 1871. She was built and registered by Arthur Sewall, later to become the partnership E. & A. Sewall, and was the 51st ship built by this company. The annually-published List of Merchant Vessels of the U.S. shows that Bath was still the home port of Eric the Red in 1880. The vessel was named after the Viking discoverer, Eric the Red, who was the first European to reach the shores of North America (in 980AD). The ship Eric the Red at first traded in coal between America and Britain, and later traded in guano nitrates from South America. In 1879 she was re-metalled and was in first class condition. On 10th June 1880 (some records say 12th June) Eric the Red departed New York for Melbourne and then Sydney. She had been commissioned by American trade representatives to carry a special cargo of 500 exhibits (1400 tons) - about a quarter to a third of America’s total exhibits - from America for the U.S.A. pavilion at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition. The exhibits included furniture, ironmongery, wines, chemicals, dental and surgical instruments, paper, cages, bronze lamp trimmings, axles, stamped ware, astronomical and time globes, samples of corn and the choicest of leaf tobacco. Other general cargo included merchandise such as cases of kerosene and turpentine, brooms, Bristol's Sarsaparilla, Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, Wheeler’s thresher machine, axe handles and tools, cases of silver plate, toys, pianos and organs, carriages and Yankee notions. The Eric the Red left New York under the command of Captain Z. Allen (or some records say Captain Jacques Allen) and 24 other crew including the owner’s son third mate Ned Sewall. There were 2 saloon passengers also. On 4th September 1880 the ship had been sailing for an uneventful 85 days and the voyage was almost at its end. Eric the Red approached Cape Otway in a moderate north-west wind and hazy and overcast atmosphere. Around 1:30am Captain Allen sighted the Cape Otway light and was keeping the ship 5-6 miles offshore to stay clear of the hazardous Otway Reef. However he had badly misjudged his position. The ship hit the Otway Reef about 2 miles out to sea, south west of the Cape Otway light station. Captain Allen ordered the wheel to be put ‘hard up’ thinking that she might float off the reef. A heavy sea knocked the man away from the wheel, broke the wheel ropes and carried away the rudder. The sea swamped the lifeboats, the mizzenmast fell, with all of its rigging, then the mainmast fell and the ship broke in two. Some said that the passenger Vaughan, who was travelling for his health and not very strong, was washed overboard and never seen again. The ship started breaking up. The forward house came adrift with three of the crew on it as well as a longboat, which the men succeeded in launching and keeping afloat by continually bailing with their sea boots. The captain, the third mate (the owner’s son) and others clung to the mizzenmast in the sea. Then the owner’s son was washed away off the mast. Within 10 minutes the rest of the ship was in pieces, completely wrecked, with cargo and wreckage floating in the sea. The captain encouraged the second mate to swim with him to the deckhouse where there were other crew but the second mate wouldn’t go with him. Eventually the Captain made it to the deckhouse and the men pulled him up. At about 4:30am the group of men on the deckhouse saw the lights of a steamer and called for help. At the same time they noticed the second mate and the other man had drifted nearby, still on the spur, and pulled them both onto the wreck. The coastal steamer Dawn was returning to Warrnambool from Melbourne, its sailing time different to its usual schedule. Cries were heard coming from out of the darkness. Captain Jones sent out two life boats, and fired off rockets and blue lights to illuminate the area. They picked up the three survivors who were in the long boat from Eric the Red. Two men were picked up out of the water, one being the owner’s son who was clinging to floating kerosene boxes. At daylight the Dawn then rescued the 18 men from the floating portion of the deckhouse, which had drifted about 4 miles from where they’d struck the reef. Shortly after the rescue the deckhouse drifted onto breakers and was thrown onto rocks at Point Franklin, about 2 miles east of Cape Otway. Captain Jones had signalled to Cape Otway lighthouse the number of the Eric the Red and later signalled that there was a wreck at Otway Reef but there was no response from the lighthouse. The captain and crew of the Dawn spent several more hours searching unsuccessfully for more survivors, even going back as far as Apollo Bay. On board the Dawn the exhausted men received care and attention to their needs and wants, including much needed clothing. Captain Allen was amongst the 23 battered and injured men who were rescued and later taken to Warrnambool for care. Warrnambool’s mayor and town clerk offered them all hospitality, the three badly injured men going to the hospital and others to the Olive Branch Hotel, then on to Melbourne. Captain Allen’s leg injury prevented him from going ashore so he and three other men travelled on the Dawn to Portland. They were met by the mayor who also treated them all with great kindness. Captain Allen took the train back to Melbourne then returned to America. Those saved were Captain Z. Allen (or Jacques Allen), J. Darcy chief mate, James F. Lawrence second mate, Ned Sewall third mate and owner’s son, John French the cook, C. Nelson sail maker, Clarence W. New passenger, and the able seamen Dickenson, J. Black, Denis White, C. Herbert, C. Thompson, A. Brooks, D. Wilson, J. Ellis, Q. Thompson, C. Newman, W. Paul, J. Davis, M. Horenleng, J. Ogduff, T. W. Drew, R. Richardson. Four men had lost their lives; three of them were crew (Gus Dahlgreen ship’s carpenter, H. Ackman steward, who drowned in his cabin, and George Silver seaman) and one a passenger (J. B. Vaughan). The body of one of them had been found washed up at Cape Otway and was later buried in the lighthouse cemetery; another body was seen on an inaccessible ledge. Twelve months later the second mate James F. Lawrence, from Nova Scotia, passed away in the Warrnambool district; an obituary was displayed in the local paper. The captain and crew of the Dawn were recognised by the United States Government in July 1881 for their humane efforts and bravery, being thanked and presented with substantial monetary rewards, medals and gifts. Neither the ship, nor its cargo, was insured. The ship was worth about £15,000 and the cargo was reportedly worth £40,000; only about £2,000 worth had been recovered. Cargo and wreckage washed up at Apollo Bay, Peterborough, Port Campbell, Western Port and according to some reports, even as far away as the beaches of New Zealand. The day after the wreck the government steam ship Pharos was sent from Queenscliff to clear the shipping lanes of debris that could be a danger to ships. The large midship deckhouse of the ship was found floating in a calm sea near Henty Reef. Items such as an American chair, a ladder and a nest of boxes were all on top of the deckhouse. As it was so large and could cause danger to passing ships, Captain Payne had the deckhouse towed towards the shore just beyond Apollo Bay. Between Apollo Bay and Blanket Bay the captain and crew of Pharos collected Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, nests of boxes, bottles of Bristol’s sarsaparilla, pieces of common American chairs, axe handles, a Wheelers’ Patent thresher and a sailor’s trunk with the words “A. James” on the front. A ship’s flag-board bearing the words “Eric the Red” was found on the deckhouse; finally those on board the Pharos had the name of the wrecked vessel. During this operation Pharos came across the government steamer Victoria and also a steamer S.S. Otway, both of which were picking up flotsam and wreckage. A whole side of the hull and three large pieces of the other side of the hull, with some of the copper sheathing stripped off, had floated on to Point Franklin. Some of the vessels yards and portions of her masts were on shore. The pieces of canvas attached to the yards and masts confirmed that the vessel had been under sail. The beach there was piled with debris several feet high. There were many cases of Diamond Oil kerosene, labelled R. W. Cameron and Company, New York. There were also many large planks of red pine, portions of a small white boat and a large, well-used oar. Other items found ashore included sewing machines (some consigned to ‘Long and Co.”) and notions, axe and scythe handles, hay forks, wooden pegs, rolls of wire (some branded “T.S” and Co, Melbourne”), kegs of nails branded “A.T. and Co.” from the factory of A. Field and Son, Taunton, Massachusetts, croquet balls and mallets, buggy fittings, rat traps, perfumery, cutlery and Douay Bibles, clocks, bicycles, chairs, a fly wheel, a cooking stove, timber, boxes, pianos, organs and a ladder. (Wooden clothes pegs drifted in for many years). There seemed to be no personal luggage or clothing. The Pharos encountered a long line, about one and a half miles, of floating wreckage about 10 miles off land, south east of Cape Otway, and in some places about 40 feet wide. It seemed that more than half of it was from Eric the Red. The ship’s crew rescued 3 cases that were for the Melbourne Exhibition and other items from amongst the debris. There were also chairs, doors, musical instruments, washing boards, nests of trunks and fly catchers floating in the sea. Most of the goods were saturated and smelt of kerosene. A section of the hull lies buried in the sand at Parker River Beach. An anchor with chain is embedded in the rocks east of Point Franklin and a second anchor, thought to be from Eric the Red, is on display at the Cape Otway light station. (There is a photograph of a life belt on the verandah of Rivernook Guest House in Princetown with the words “ERIC THE RED / BOSTON”. This is rather a mystery as the ship was registered in Bath, Maine, USA.) Parts of the ship are on display at Bimbi Park Caravan Park and at Apollo Bay Museum. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village also has part of the helm (steering wheel), a carved wooden sword (said to be the only remaining portion of the ship’s figurehead; further research is currently being carried out), a door, a metal rod, samples of wood and a medal for bravery. Much of the wreckage was recovered by the local residents before police and other authorities arrived at the scene. Looters went to great effort to salvage goods, being lowered down the high cliff faces to areas with little or no beach to collect items from the wreckage, their mates above watching out for dangerous waves. A Tasmanian newspaper reports on a court case in Stawell, Victoria, noting a man who was caught 2 months later selling tobacco from the wreckage of Eric the Red. Some of the silverware is still treasured by descendants of Mr Mackenzie who was given these items by officials for his help in securing the cargo. The gifts included silver coffee and tea pots, half a dozen silver serviette rings and two sewing machines. The wreck and cargo were sold to a Melbourne man who salvaged a quantity of high quality tobacco and dental and surgical instruments. Timbers from the ship were salvaged and used in the construction of houses and sheds around Apollo Bay, including a guest house, Milford House (since burnt down in bushfires), which had furniture, fittings and timber on the dining room floor from the ship. A 39.7 foot long trading ketch, the Apollo, was also built from its timbers by Mr Burgess in 1883 and subsequently used in Tasmanian waters. It was the first attempt at ship building in Apollo bay. In 1881 a red light was installed about 300 feet above sea level at the base of the Cape Otway lighthouse to warn ships when they were too close to shore; It would not be visible unless a ship came within 3 miles from it. This has proved to be an effective warning. The State Library of Victoria has a lithograph in its collection depicting the steamer Dawn and the shipwrecked men, titled. "Wreck of the ship Eric the Red, Cape Otway: rescue of the crew by the Dawn". “The Eric the Red is historically significant as one of Victoria's major 19th century shipwrecks. (Heritage Victoria Eric the Red; HV ID 239) The wreck led to the provision of an additional warning light placed below the Cape Otway lighthouse to alert mariners to the location of Otway Reef. The site is archaeologically significant for its remains of a large and varied cargo and ship's fittings being scattered over a wide area. The site is recreationally and aesthetically significant as it is one of the few sites along this coast where tourists can visit identifiable remains of a large wooden shipwreck, and for its location set against the background of Cape Otway, Bass Strait, and the Cape Otway lighthouse.“ (Victorian Heritage Database Registration Number S239, Official Number 8745 USA) Segment of a ship's wheel, or helm, from the wreck of the sailing ship Eric the Red. The wheel part is an arc shape from the outer rim of the wheel and is made up of three layers of timber. The centre layer is a dark, dense timber and is wider than the two outer layers, which are less dense and lighter in colour. The wheel segment has a vertically symmetrical, decorative copper plate inlaid on the front. The plate has a starburst pattern; six stars decorate it, each at a point where there is a metal fitting going through the three layers of timber to the rear side of the wheel. On the rear each of the six fittings has an individual copper star around it. The edges of the helm are rounded and bevelled, polished to a shine in a dark stain. Around each of the stars, front and back, the wood is a lighter colour, as though the metal in that area being polished frequently. The length of the segment suggests that it has probably come from a wheel or helm that had ten spokes. (Ref: F.H.M.M. 16th March 1994, 239.6.610.3.7. Artefact Reg No ER/1.)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ship's-wheel, eric-the-red, helm, shei's wheel, ship's steering wheel -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Sword, 1871 or earlier
This wooden sword is said to “possibly be the only remaining part of the figurehead from the sailing ship Eric the Red.” It was previously part of the collection of the old Warrnambool Museum and the entry in its inventory says “Wooden sword, portion of the figurehead, held by “Eric the Red” at the bow.” A large part of the ship’s hull was found on the rocks and a figurehead may have been attached or washed up on the shore. The shipping records for E. & A. Sewall, the builders, owners and managers of Eric the Red, are now preserved in the Maine Maritime Museum. There is no photograph on record of Eric the Red but photographs of other ships built around that time by the same company show that these did not have figureheads, and there is no record found of a figurehead for Eric the Red being ordered or paid for. Further research is being carried out. The ship building company E. & A. Sewall, from Bath, Maine, USA, built Eric the Red, a wooden, three masted clipper ship. She had 1,580 tons register and was the largest full-rigged ship built at Bath, Maine, USA in 1871. She was built and registered by Arthur Sewall, later to become the partnership E. & A. Sewall, and was the 51st ship built by this company. The annually-published List of Merchant Vessels of the U.S. shows that Bath was still the home port of Eric the Red in 1880. The vessel was named after the Viking discoverer, Eric the Red, who was the first European to reach the shores of North America (in 980AD). The ship Eric the Red at first traded in coal between America and Britain, and later traded in guano nitrates from South America. In 1879 she was re-metalled and was in first class condition. On 10th June 1880 (some records say 12th June) Eric the Red departed New York for Melbourne and then Sydney. She had been commissioned by American trade representatives to carry a special cargo of 500 exhibits (1400 tons) - about a quarter to a third of America’s total exhibits - from America for the U.S.A. pavilion at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition. The exhibits included furniture, ironmongery, wines, chemicals, dental and surgical instruments, paper, cages, bronze lamp trimmings, axles, stamped ware, astronomical and time globes, samples of corn and the choicest of leaf tobacco. Other general cargo included merchandise such as cases of kerosene and turpentine, brooms, Bristol's Sarsaparilla, Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, Wheeler’s thresher machine, axe handles and tools, cases of silver plate, toys, pianos and organs, carriages and Yankee notions. The Eric the Red left New York under the command of Captain Z. Allen (or some records say Captain Jacques Allen) and 24 other crew including the owner’s son third mate Ned Sewall. There were 2 saloon passengers also. On 4th September 1880 the ship had been sailing for an uneventful 85 days and the voyage was almost at its end. Eric the Red approached Cape Otway in a moderate north-west wind and hazy and overcast atmosphere. Around 1:30am Captain Allen sighted the Cape Otway light and was keeping the ship 5-6 miles offshore to stay clear of the hazardous Otway Reef. However he had badly misjudged his position. The ship hit the Otway Reef about 2 miles out to sea, south west of the Cape Otway light station. Captain Allen ordered the wheel to be put ‘hard up’ thinking that she might float off the reef. A heavy sea knocked the man away from the wheel, broke the wheel ropes and carried away the rudder. The sea swamped the lifeboats, the mizzenmast fell, with all of its rigging, then the mainmast fell and the ship broke in two. Some said that the passenger Vaughan, who was travelling for his health and not very strong, was washed overboard and never seen again. The ship started breaking up. The forward house came adrift with three of the crew on it as well as a longboat, which the men succeeded in launching and keeping afloat by continually bailing with their sea boots. The captain, the third mate (the owner’s son) and others clung to the mizzenmast in the sea. Then the owner’s son was washed away off the mast. Within 10 minutes the rest of the ship was in pieces, completely wrecked, with cargo and wreckage floating in the sea. The captain encouraged the second mate to swim with him to the deckhouse where there were other crew but the second mate wouldn’t go with him. Eventually the Captain made it to the deckhouse and the men pulled him up. At about 4:30am the group of men on the deckhouse saw the lights of a steamer and called for help. At the same time they noticed the second mate and the other man had drifted nearby, still on the spur, and pulled them both onto the wreck. The coastal steamer Dawn was returning to Warrnambool from Melbourne, its sailing time different to its usual schedule. Cries were heard coming from out of the darkness. Captain Jones sent out two life boats, and fired off rockets and blue lights to illuminate the area. They picked up the three survivors who were in the long boat from Eric the Red. Two men were picked up out of the water, one being the owner’s son who was clinging to floating kerosene boxes. At daylight the Dawn then rescued the 18 men from the floating portion of the deckhouse, which had drifted about 4 miles from where they’d struck the reef. Shortly after the rescue the deckhouse drifted onto breakers and was thrown onto rocks at Point Franklin, about 2 miles east of Cape Otway. Captain Jones had signalled to Cape Otway lighthouse the number of the Eric the Red and later signalled that there was a wreck at Otway Reef but there was no response from the lighthouse. The captain and crew of the Dawn spent several more hours searching unsuccessfully for more survivors, even going back as far as Apollo Bay. On board the Dawn the exhausted men received care and attention to their needs and wants, including much needed clothing. Captain Allen was amongst the 23 battered and injured men who were rescued and later taken to Warrnambool for care. Warrnambool’s mayor and town clerk offered them all hospitality, the three badly injured men going to the hospital and others to the Olive Branch Hotel, then on to Melbourne. Captain Allen’s leg injury prevented him from going ashore so he and three other men travelled on the Dawn to Portland. They were met by the mayor who also treated them all with great kindness. Captain Allen took the train back to Melbourne then returned to America. Those saved were Captain Z. Allen (or Jacques Allen), J. Darcy chief mate, James F. Lawrence second mate, Ned Sewall third mate and owner’s son, John French the cook, C. Nelson sail maker, Clarence W. New passenger, and the able seamen Dickenson, J. Black, Denis White, C. Herbert, C. Thompson, A. Brooks, D. Wilson, J. Ellis, Q. Thompson, C. Newman, W. Paul, J. Davis, M. Horenleng, J. Ogduff, T. W. Drew, R. Richardson. Four men had lost their lives; three of them were crew (Gus Dahlgreen ship’s carpenter, H. Ackman steward, who drowned in his cabin, and George Silver seaman) and one a passenger (J. B. Vaughan). The body of one of them had been found washed up at Cape Otway and was later buried in the lighthouse cemetery; another body was seen on an inaccessible ledge. Twelve months later the second mate James F. Lawrence, from Nova Scotia, passed away in the Warrnambool district; an obituary was displayed in the local paper. The captain and crew of the Dawn were recognised by the United States Government in July 1881 for their humane efforts and bravery, being thanked and presented with substantial monetary rewards, medals and gifts. Neither the ship, nor its cargo, was insured. The ship was worth about £15,000 and the cargo was reportedly worth £40,000; only about £2,000 worth had been recovered. Cargo and wreckage washed up at Apollo Bay, Peterborough, Port Campbell, Western Port and according to some reports, even as far away as the beaches of New Zealand. The day after the wreck the government steam ship Pharos was sent from Queenscliff to clear the shipping lanes of debris that could be a danger to ships. The large midship deckhouse of the ship was found floating in a calm sea near Henty Reef. Items such as an American chair, a ladder and a nest of boxes were all on top of the deckhouse. As it was so large and could cause danger to passing ships, Captain Payne had the deckhouse towed towards the shore just beyond Apollo Bay. Between Apollo Bay and Blanket Bay the captain and crew of Pharos collected Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, nests of boxes, bottles of Bristol’s sarsaparilla, pieces of common American chairs, axe handles, a Wheelers’ Patent thresher and a sailor’s trunk with the words “A. James” on the front. A ship’s flag-board bearing the words “Eric the Red” was found on the deckhouse; finally those on board the Pharos had the name of the wrecked vessel. During this operation Pharos came across the government steamer Victoria and also a steamer S.S. Otway, both of which were picking up flotsam and wreckage. A whole side of the hull and three large pieces of the other side of the hull, with some of the copper sheathing stripped off, had floated on to Point Franklin. Some of the vessels yards and portions of her masts were on shore. The pieces of canvas attached to the yards and masts confirmed that the vessel had been under sail. The beach there was piled with debris several feet high. There were many cases of Diamond Oil kerosene, labelled R. W. Cameron and Company, New York. There were also many large planks of red pine, portions of a small white boat and a large, well-used oar. Other items found ashore included sewing machines (some consigned to ‘Long and Co.”) and notions, axe and scythe handles, hay forks, wooden pegs, rolls of wire (some branded “T.S” and Co, Melbourne”), kegs of nails branded “A.T. and Co.” from the factory of A. Field and Son, Taunton, Massachusetts, croquet balls and mallets, buggy fittings, rat traps, perfumery, cutlery and Douay Bibles, clocks, bicycles, chairs, a fly wheel, a cooking stove, timber, boxes, pianos, organs and a ladder. (Wooden clothes pegs drifted in for many years). There seemed to be no personal luggage or clothing. The Pharos encountered a long line, about one and a half miles, of floating wreckage about 10 miles off land, south east of Cape Otway, and in some places about 40 feet wide. It seemed that more than half of it was from Eric the Red. The ship’s crew rescued 3 cases that were for the Melbourne Exhibition and other items from amongst the debris. There were also chairs, doors, musical instruments, washing boards, nests of trunks and fly catchers floating in the sea. Most of the goods were saturated and smelt of kerosene. A section of the hull lies buried in the sand at Parker River Beach. An anchor with chain is embedded in the rocks east of Point Franklin and a second anchor, thought to be from Eric the Red, is on display at the Cape Otway light station. (There is a photograph of a life belt on the verandah of Rivernook Guest House in Princetown with the words “ERIC THE RED / BOSTON”. This is rather a mystery as the ship was registered in Bath, Maine, USA.) Parts of the ship are on display at Bimbi Park Caravan Park and at Apollo Bay Museum. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village also has part of the helm (steering wheel), a carved wooden sword (said to be the only remaining portion of the ship’s figurehead; further research is currently being carried out), a door, a metal rod, samples of wood and a medal for bravery. Much of the wreckage was recovered by the local residents before police and other authorities arrived at the scene. Looters went to great effort to salvage goods, being lowered down the high cliff faces to areas with little or no beach to collect items from the wreckage, their mates above watching out for dangerous waves. A Tasmanian newspaper reports on a court case in Stawell, Victoria, noting a man who was caught 2 months later selling tobacco from the wreckage of Eric the Red. Some of the silverware is still treasured by descendants of Mr Mackenzie who was given these items by officials for his help in securing the cargo. The gifts included silver coffee and tea pots, half a dozen silver serviette rings and two sewing machines. The wreck and cargo were sold to a Melbourne man who salvaged a quantity of high quality tobacco and dental and surgical instruments. Timbers from the ship were salvaged and used in the construction of houses and sheds around Apollo Bay, including a guest house, Milford House (since burnt down in bushfires), which had furniture, fittings and timber on the dining room floor from the ship. A 39.7 foot long trading ketch, the Apollo, was also built from its timbers by Mr Burgess in 1883 and subsequently used in Tasmanian waters. It was the first attempt at ship building in Apollo bay. In 1881 a red light was installed about 300 feet above sea level at the base of the Cape Otway lighthouse to warn ships when they were too close to shore; It would not be visible unless a ship came within 3 miles from it. This has proved to be an effective warning. The State Library of Victoria has a lithograph in its collection depicting the steamer Dawn and the shipwrecked men, titled. "Wreck of the ship Eric the Red, Cape Otway: rescue of the crew by the Dawn".The Eric the Red is historically significant as one of Victoria's major 19th century shipwrecks. (Heritage Victoria Eric the Red; HV ID 239) The wreck led to the provision of an additional warning light placed below the Cape Otway lighthouse to alert mariners to the location of Otway Reef. The site is archaeologically significant for its remains of a large and varied cargo and ship's fittings being scattered over a wide area. The site is recreationally and aesthetically significant as it is one of the few sites along this coast where tourists can visit identifiable remains of a large wooden shipwreck, and for its location set against the background of Cape Otway, Bass Strait, and the Cape Otway lighthouse. (Victorian Heritage Database Registration Number S239, Official Number 8745 USA)This carved wooden sword, recovered from the Eric the Red, is possibly the only portion of the figurehead recovered after the wreck. There are spirals carved from the base of the handle to the top of the sword. The hilt of the sword is a lion’s head holding its tail in its mouth, the tail forming the handle. The blade of the sword has engraved patterns on it. Tiny particles of gold leaf and dark blue paint fragments can be seen between the carving marks. There are remnants of yellowish-orange and crimson paint on the handle. At some time after the sword was salvaged the name of the ship was hand painted on the blade in black paint. The tip of the sword has broken or split and the remaining part is charcoal in appearance. On both the tip and the base of the handle are parts made where the sword could have been joined onto the figurehead There is a white coating over some areas of the sword, similar to white lead putty used in traditional shipbuilding. The words “ERIC the RED” have been hand painted on the blade of the sword in black paint sometime after it was salvaged.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, sword, wooden sword, eric the red, carved sword, figurehead, snake head on sword -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchKorean Currency and N.A.T.O. Forces Notes
Used during Korean War Won (1947-) Main article: North Korean won After the division of Korea, North Korea continued using the Korean yen for 2 years until the Central Bank of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea was established on December 6, 1947 and a new currency was issued. It was at the time pegged at par to the Soviet ruble. It was revalued at a rate of one hundred to one in February 1959 and new won were issued. In the following years the won faced some devaluation, caused by the subsequent devaluation and redenomination of the Soviet ruble. From 1978 to 2001, the North Korean government maintained an iconic rate of 2.16 won to the US dollar; since then banks in the country exchange at rates closer to the black market rate. However, rampant inflation has been eroding the North Korean wŏn's value to such an extent that currently it is believed to be worth about the same as the South Korean wŏn. In any case, the U.S. dollar and other currencies are still worth more in North Korean wŏn on the black market than officially. South Korean currencies[edit] Won (1945-1953)[edit] Main article: South Korean won (1945) Following the end of the division of Korea, the won was introduced to replace the Korean yen. The won was subdivided in 100 jeon. The first banknotes were issued by the Bank of Joseon in denominations ranging from 5 jeon to 100 won. In 1950 the currency management switched to the Bank of Korea and new notes were then issued, mostly with higher denominations. The first note put in circulation by the Bank of Korea in 1950 was printed in Japan by the National Printing Bureau (国立印刷局). The next year the Korea Minting and Security Printing Corporation was created and took over as printer of South Korean currency. At the time of the introduction in 1945 the won was pegged to the Japanese yen at a rate of 1 won = 1 yen. In October of the same year the anchor currency got change to the US dollar at a rate of 15 won = 1 dollar. Toward the end of the Korean War the won was devaluated at 6000 won = 1 dollar. Following that the hwan was introduced as the new currency at a rate of 1 hwan = 100 won. Hwan (1953-1962)[edit] Main article: South Korean hwan Due to devaluation of the won the hwan was introduced on February 15, 1953 at the rate of 1 hwan = 100 won. It was subdivided in 100 jeon, but they were never used. New banknotes in denominations between 10 and 1000 hwan were issued. Starting in 1959, 10 and 50 hwan coins were also issued to replace the lower denomination notes. Those were the first circulating coins in South Korea. Due to the short notice of the change in currency, the first series of the new notes was commissioned from the United States Government Printing Office. The notes were released in five denominations, all with an identical design. Some replacement notes with a more suited Korean theme were later issued, starting with the 100 hwan just a month later. The hwan suffered from inflation as well. At its introduction, it was pegged to the United States dollar at 1 dollar = 60 hwan, but toward the end of its life it was devaluated at 1 dollar = 1250 hwan. In 1962, the won was reintroduced at the rate of 1 won = 10 hwan. The 10 and 50 hwan coins were kept in circulation until March 22, 1975.5 Currency notes issued by Korean Government and R.A.A.F. denominations of 100, 100 Won and 1 shilling国立印刷局, currency korea, money korea, money korean war -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London & No 4 opposite end Stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London maker & No 6, opposite end Stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Ames is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A significant item from the mid to late 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. It also gives an insight into how many manufacturing companies bid for the rights to use prison labour to make their products at this time in our history. Complex Moulding Plane J Ames maker, No 1 at opposite end Stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Ames is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A significant item from the mid to late 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. It also gives an insight into how many manufacturing companies bid for the rights to use prison labour to make their products at this time in our history. Complex Moulding Plane Maker J Ames Stamped & No 6 & 5/16 opposite end, also J Heath (owner). flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Ames is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A significant item from the mid to late 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. It also gives an insight into how many manufacturing companies bid for the rights to use prison labour to make their products at this time in our history. Complex Moulding Plane with four screws on one sideMaker J Ames No 2 opposite end J Heath (owner) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1830-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about R Knight is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in England early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item.Complex Moulding Plane Maker R Knight, Stamped T Whlele (owner) & No 5 opposite endflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Ames is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding opposite end has 4 screws on bottomJ Ames maker, Stamped J Heath (owner) & No 7 flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Moulding wood Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London & No 12 at opposite end, stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London & No 10 opposite end, Stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London & No 14 opposite end Stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1832-1864 made in London
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about J Budd is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London between 1832 to 1864. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane J Budd London & No 12 opposite end stamped J Heath (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, j budd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, Unknown
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. The maker of this plane is unknown but probably made in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world with no makers marks however moulding planes from this era are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool made by an unknown maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item.Wood Moulding Plane Rabbet typeMarked J Heath on end, (no makers mark)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Ames is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business in London early to mid 18th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool made by a known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item.Moulding Plane one side has 4 screws heads visibleAmes J Heath (maker) stamped at end & 3/16 flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath, ames -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, 1844-1860
A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. This item is unmarked so the maker is unknown, these types of decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs are for sale around the world and these tools are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools.A vintage tool made by an un known maker, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the early to mid 18th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item.Moulding Plane J Heath (owner) stamped at one end (maker unknown)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plane moulding, moulding plane, plane, j heath
