Showing 80 items matching "pen writing-equipment"
-
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypen
... pen writing-equipment... gippsland pen writing-equipment A pearl-handled pen with the end ...A pearl-handled pen with the end in the shape of a feather. It has metal pieces along its length. There is a copper nib and a silver nib holder.pen writing-equipment -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyInk Well - Mt Beauty Post Office
... mt beauty post office. inkwell. pen. writing equipment..... writing equipment. Clear glass rectangular shaped set of two ink ...This inkwell was used by the staff of the Mount Beauty Post Office, from the late 1940's until the change from pen and ink to the use of fountain pens and then ball-point pens. The last Post Master at Mount Beauty rescued this item when the Mt Beauty Post Office was privatised in the 1990's. Ian Mc Kendrick worked at the Mt Beauty post office.Clear glass rectangular shaped set of two ink wells with a pen holder in front. Each ink well has a glass lid. Between the ink wells there is an open area for storing items such as paper clips etc. In addition it Includes a red and a black pen handle.mt beauty post office. inkwell. pen. writing equipment. -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment - Writing Equipment, Writing Case, 19th century, 19th century
... Leather pen case, containing writing equipment, possibly... Leather pen case, containing writing equipment, possibly used ...Leather pen case, containing writing equipment, possibly used by early surveyor or draftsmanCylindrical leather case containing bottles for ink and sand, holders for pens, nibs, etc. Red leather lining. Ruler, bone-spreader, ivory and brass seal, and pen-holder included. Brass external clasps.writing equipment, writing cases -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyink bottle, 1890's
An ink bottle was made of glass or ceramic and typically sat on a desk. The writer would dip the pen (or quill) into the bottle to put more ink on the pen. Because they sat on a desk, ink bottles were often decorative.We have mostly dispensed with ink bottles and quills. This item is an example of early stationery equipment commonly used in schools, households and commercial enterprises.A cylindrical brown glazed ceramic ink bottle with the neck narrowing to a pouring lip.Below the pouring lip - ANGUS & CO INK COMMERCIALcontainer ink-bottle ceramic angus-&-co writing-materials -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybottle, Probably late 19th century
An ink bottle was made of glass or ceramic and typically sat on a desk. The writer would dip the pen (or quill) into the bottle to put more ink on the pen. Because they sat on a desk, ink bottles were often decorative. We have mostly dispensed with ink bottles and quills. This item is an example of early stationery equipment commonly used in schools, households and commercial enterprises.Small, squat, brown, salt-glazed ceramic inkwell with small opening at top. It has a short neck and a round squat body. This type of inkwell is also known as a penny ink well.container ink-bottle penny-inkwell stationery writing -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyink well, 19th Century
Could have been used at home or business. An ink wellwas made of glass or ceramic and typically sat on a desk. The writer would dip the pen (or quill) into the bottle to put more ink on the pen. Because they sat on a desk, ink wells were often decorativeWe have mostly dispensed with ink bottles and quills. This item is an example of early stationery equipment commonly used in schools, households and commercial enterprises.A clear glass inkwell which is quite heavy and not easily upset. It has a concave hole in the top. ink-well writing penmanship -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyink stand, c. late 19th century
Possibly used within the Gilbert family, Orbost.We have mostly dispensed with ink bottles and quills. This item is an example of early stationery equipment commonly used in households for correspondence, creative writing and household accounting reecords.A wooden box with several small compartments, two porcelain ink well. A long space at the front is for holding pens. A small sliding door can move on top of the ink wells.The words PENS COPY RED BLACK are written into the front of the section which hold the ink wells. on front of box Ro No 347854ink-stand pen-and-ink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink well, Circa 19th century
This type of inkwell would have been used in public places such as banks, offices and on ships.Ink well, pewter, capstan design.Flat disc with ink well and pen/quill holders in centre, hinged lid to cover removable well.White ceramic ink well included. Base, well and lid are all decorated with concentric rings. Maker's stamp on base. Circa 19th century. Stamped into base "MADE IN ENGLAND" and another indentifyable symbol. warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, ink well, pewter ink well, writing equipment, stationery accessory, communication -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Artefact, Inkwell, 1920
This ink well could have been for household use but was more likely to have been used in an office or business. No information has been found on the name on the base – A.R. McLachlan. Ink wells began to be less used when fountain pens came into general use in the 1940s and went out of use completely when ballpoint pens became the popular writing instrument in the 1950s. This ink well is of interest as an example of the ink wells used early in the 20th century. It was probably used in an office or business building. This is a metal container with a circular base and an upright circular tube in which is inset a china ink well. The ink well is covered with a hinged metal lid and there are four round holes around the lid area. Both the lid and the base are etched with circular ridges. ‘A.R.McLachlan 1920’ office equipment, warrnambool, history of warrnambool -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAccessory - PEN & PENCIL SET, Onoto
Pen and pencil set presented to Flight Lieutenant Ian A. Lyons by Eaglehawk RSL on 14.11.1951. Part of the Flight Lieutenant Ian A. 'Joe' Lyons MBE Collection. See Catalogue No. 5374P for his service record..1) Blue coloured hinged presentation box with cream coloured padded lining. Brass hinges and clasp. .2) Navy blue bakelite fountain pen with gold coloured nib and cap. .3) Navy blue propelling pencil with gold coloured tip and cap..1) Printed in brown on inside lining: 'Onoto'. .2) Printed on navy blue shaft in red: ' M 9in a circle)'. Stamped on cap clip: 'TCR' Engraved on cap: 'To Ian from Ehk RSL 14.11.51" .3) Engraved on cap: 'To Ian from Ehk RSL'accessories, writing equipment, flight lieutenant ian a. lyons, memorabilia -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumCraft - CLOTH, FOLDED, 1917 - 1918
The item was bought home by James Todd No 2418, 12th Batt AIF. Refer Cat No 1340P for his service details.Cloth folder,folds in half, dark red paint on one side. Writing inside in pen: "Baron von Richthofen/ the most famous of German/ airmen killed/ in the Somme Valley/ 80 machines to his/ credit/ April 21 1 18"military equipment-air force, german, personal effects, manchester-fabric -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Early to mid 20th century
... higgins & co brooklyn n.y. stationery writing equipment pen ...This ink bottle was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The company was founded by Charles Michael Higgins (born Ireland) in New York in partnership with his brother-in-law John Gianella Snr. in 1885. It began as just Charles M Higgins in 1880. It produced a range of popular inks including India, indelible, and laundry ink, later expanding into adhesive manufacture; originally based in Brooklyn the company expanded with offices in New York, Chicago and London (106 Charing Cross Road) selling products world wide; Charles Higgins died 1929 and was succeeded by his son Tracy. It became an incorporated company in 1930. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Clear glass ink bottle with cork stopper, containing small quantity of red ink.Part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Made by Higgins of Brooklyn, New York. Impressed into base "HIGGINS BROOKLYN N.Y. INKS" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, ink bottle, ink bottle containing red ink, higgins & co brooklyn n.y., stationery, writing equipment, pen and ink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink well, early to mid 20th century
One of the daughters of Dr Angus and his wife Gladys told Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village that this glass ink well was used by her father in his office in the days when ink powder [usually supplied in paper packets] was mixed with warm water to make ink. The ink well was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Ink well, thick clear glass, bell shaped, wide and heavy base. Remnants of blue ink inside. Part of the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, ink bottle, pen and ink writing, nib pen writing supplies, ink powder writing, ink mixing -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle & Case, 1934 – Mid 1950’s
Pens, nib pens and later fountain pens, with suitable inks, were commonly used for writing communications from the 18th century to the mod 20th century. Fountain pens continue to be used and enjoyed. Dip pens with a wide variety of nibs are used for calligraphy writing, a hobby enjoyed by many people. The quality of the pen handle, the nib and the ink all work together to produce fine handwriting that expresses the character and mood of the writer. This Bakelite ink case has been specifically moulded to snugly contain an ink bottle, with just enough room to wrap the bottle with a padding or card or blotting paper. The screw top lid fits the case well and this container would be a good way to travel with ink because any spillage would be kept within the waterproof case. The Bakelite material is lightweight and strong. Ink bottle cases, or travelling cases, have been made as an accessory for nib pen writers. The first patent for a “pocket-case for bottles”, a wooden case, was applied for in the US in 1891. Other materials such as steel, pewter and aluminum as well as Bakelite have also been used. The British Museum has an elaborately decorated bronze ink pot holder that is inlaid with turquoise. Today ink bottle cases are even available in fabric with loops to attach to a belt. Bakelite, the material used for this ink bottle case, is made from synthetic materials and is an early form of plastic, developed in 1907 and used extensively until the 1940’s. It is still in used today for specific applications but has been largely replaced by more modern forms of plastics. This ink bottle case carries the imprint of Mabie, Todd & Co. (Aust.) Pty. Ltd. This form of company name was used from 1938 to the mid 1950’s. The Swan ink bottle’s information says it was made by Mabie, Todd & Co. Ltd., London and Sydney, so dates the ink bottle from about 1908 until 1934. (Australian newspapers display advertisements dated 1908 until 1934 for Sydney wholesalers and agents for Mabie, Todd & Co. Ltd.) ABOUT PERSONAL FOUNTAIN PENS (FOUNT PENS) A 1917 newspaper advertisement recommends that the owner of a “Swan” doesn’t lend it to anyone else to use due to its qualities of it personalised to the owner. It reads “Don’t lend your “Swan” fountpen, recommend it, but don’t let other people use it. You see, a good pen doesn’t wear, but its “tamper” (or spring) works into the writer’s pressure and manner of holding. Another person with a dashing style of writing may strain it do that it will no longer feel just like your own.” This personalisation of nib pens may be the reason that legal documents in the past being acceptable only if they were signed using a ‘wet ink’ pen. Forgeries of signatures could be easily detected as the nib takes on the character of the pen’s owner. A ballpoint pen was not acceptable. This is a strong contrast to modern times when a digital signature is widely accepted. ABOUT MABIE TODD Pty Ltd. The American company Mabie Todd began by making pencil cases in New York in the 1860’s. The Bard Brothers, makers of Gold nibs, joined Mabie Todd and the company was established in the 1870’s as Mabie Todd and Bard. In 1878 the company filed a patent for the design of a fountain pen and in 1884 the first Swan fountain pen was released. In 1884 a Mabie Todd and Bard office and showroom was established in London. In 1906 the company’s name changed to Mabie Todd & Co, New York. The UK offices also used this new name and in 1907 the UK began producing their own Swan pens. Manufacturing was going so well in England that New York sold their rights to European and Colonial business to the new Mabie Todd & Company Ltd of England. By the end of the 1930’s all components for the pens were being made in the UK; the pens in the London factory, the gold nibs in Birmingham and the ink in Liverpool. Newspaper articles from 1934 stated that Mabie Todd were large buyers of Tasmanian iridium, which had been welded with gold and used since 1834 for the tips of nib and fountain pens. Fountain pen points were the largest market buyers for Tasmanian iridium, which was classed as “the best in the world”. Production growth continued up until WWII times, when the headquarters and main factory were destroyed. Mabie Todd & Company Ltd of England rebuilt out of the inner city and by 1946 pen production began again. The market for nib and fountain pens was diminishing by this time, with people beginning to use the new ballpoint ‘Biro’ pens. The Mabie Todd bought shares in Biro Pens and in 1952 became Biro Swan. They went on to make more ballpoint pens than any other manufacturer in Britain. The ink refills that Biro-Swan produced came in five different viscosity or thickness xhoices, depending on the season and location of where the pen would be used . Along with the ballpoint pens, Biro-Swan also introduced a range of Calligraph pens to attract those following the new trend for italic writing. In 1948 Mr. T. Burke, a director for Mabie Todd & Co. (Aust.) Pty Ltd., announced that there would be a £40,000 factory built in Sydney in 1949 for the manufacture of ink. The plant for the factory would be imported from overseas. Sadly the company struggled against competition and in 1956 Mabie Todd closed business and no more Swan pens were produced. The ink bottle and container was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The ink bottle case is significant for its association with writing methods commonly used during the colonisation of Australia until the mid-20th century. The protective Bakelite case demonstrates the value placed on caring for the user’s supply of ink and protecting other belongings of the user, enabling writers to easily carry and safely transport their ink without the concern of spilling it. The case’s design is a good example of the use of new technology. The properties of Bakelite have enabled its moulded design and make it waterproof and lightweight, easily cleaned, closely fitted to the shape of the ink bottle within and lid and base join together using a smooth screwing action. The maker’s marks have also been moulded into the Bakelite, therefore not distracting from the simple but elegant design. This ink bottle case also represents the period of early to mid-20th century when handwriting materials for writers using ink and nib pens were imported into Australia and developed for the Australian market and sold by wholesalers on behalf of overseas companies. Vintage brown Bakelite travelling ink bottle case (or holder, pot, well) containing glass ink bottle and original textured cardboard liner, made by Swan Ink, Mabie, Todd & Co. (Aust) Pty.. Ltd. The Bakelite container is shaped to fit snugly around the ink bottle. It still retains its original shiny finish, the lid screws on and off perfectly. The maker’s name is embossed on lid and base of the Bakelite container. The inkwell contains a glass Ink bottle with a tiny amount of dried up ink Swan triple filtered ink inside. The bottle is cylindrical with curved shoulders tapering to a neck of around 2cm. The white metal screw-on lid and the white and red paper label on the side of the bottle both have a printed description of the ink and maker. Circa 1934-1950’sBAKELITE INK CASE - embossed on either side of the lid “ “SWAN” INK / ”SWAN” INK “ - embossed into base, written in a circle “MABIE TODD & Co (Aust.) PTY. LTD.” GLASS BOTTLE – printed on lid “SWAN”/ [corporate logo combining letters ‘M, T, co’]/TRIPLE FILTERED/ INK.” - printed on label “SWAN” INK /FOR FOUNTAIN & / STEEL PENS / A BLUE BLACK INK OF/ THE FINEST QUALITY/ MADE IN ENGLAND/ MABIE. TODD & CO LTD …….. LONDON. SYDNEY/ Makers of “SWAN” Pens, Gold Pens & Ink“ - moulded into the base of the ink bottle and written around the bottom outside edge of the bottle are the words “THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS THE PROPERTY OF/ MABIE TODD/AUST”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, ink bottle holder, ink bottle case, ink bottle pot, travelling inkwell, portable inkwell, travelling ink pot, travelling ink bottle case, ink bottle, inkwell, ink well, swan ink, bakelite, dip pen ink, nib pen ink, fountain pen, fontpen, writing methods, stationery, mabie todd & co, swan fountain pens, biro-swan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Prior to 1878
This design of ink bottle was commonly referred to as a ‘penny ink well’ because it was very inexpensive to produce. It is also known as a dwarf ink bottle. Pen and ink has been in use for hand writing from about the seventh century up until the mid-20th century up until around the mid-19th century a quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used. In the 1850s the steel point pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. In the 1880s a successful portable fountain pen was designed, giving a smooth flowing ink and ease of use replacing the quill or dip pen. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from "Loch Ard" a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curle & Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen, and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead, and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Lochard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy that had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost families in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce, and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Lochard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Lochard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Lochard Gorge. Cargo and artefact's have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.This ink well is historically significant as it represents methods of hand written communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century, when fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefact's from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefact's from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collection's objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Stoneware penny Ink bottle ironstone salt-glazed, stoneware cylindrical shape with small mouth and squat neck, broad shoulders brown colour, . with light coloured encrustation spots.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, penny ink well, writing equipment, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, ink well, inkwell, ink bottle, dip pen, ink, hand writing, business, vintage, dwarf ink -
![Container - Inkwell, [Travelling Inkwell]](/media/collectors/4f729f5697f83e03086015b8/items/608a31574a74fac86fd4ac19/item-media/60911d3c291a287d6f365d78/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyContainer - Inkwell, [Travelling Inkwell]
Travelling inkwell, from the days before fountain pens and biros!Travelling inkwell, clear glass container with cork, in brass case with double hinged lidinkwells, ink bottles, writing equipment -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Writing Equipment, desk set, c1900
... equipment pens glass inkwells pederson-green carole cheltenham ...The family of Miss Carol Pedersen-Green migrated to Australia from Norway c1900 and probably brought this desk set with them. A desk set comprising a wooden base with 2 cut outs for 2 clear glass ink wells with silver hinged lids. A ledge on either side to hold pens. and 4 rubber stops under base to maintain stability 5 wooden pens with steel nibs writig equipment, pens, glass inkwells, pederson-green carole, cheltenham, moorabbin, bentleigh, early settlers -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybottle
An ink bottle was made of glass or ceramic and typically sat on a desk. The writer would dip the pen (or quill) into the bottle to put more ink on the pen. Because they sat on a desk, ink bottles were often decorative. We have mostly dispensed with ink bottles and quills. This item is an example of early stationery equipment commonly used.A cylindrical brown glazed ceramic ink bottle with a neck narrowing to a pouring lip and cork. Label is blue.Front bottom - Commercial.bottle ink-bottle ceramic domestic writing-equipment stoneware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Royal Doulton, Late 19th to early-20th century
The Royal Doulton company began as a partnership between John Doulton, Martha Jones, and John Watt was an English ceramic and home accessories manufacturer founded in 1815. Operating originally in Vauxhall, London, later moving to Lambeth, in 1882 it opened a factory in Burslem, Stoke-on-Trent, in the centre of English pottery. The business was specialised in making salt-glazed stoneware articles, including utilitarian or decorative bottles, jugs and jars, much of it intended for inns and pubs. The backbone of the business was a wide range of utilitarian wares, mostly stonewares, including storage jars, tankards and the like, and later extending to pipes for drains, lavatories and other bathroom ceramics. From 1853 to 1902 its wares were marked Doulton & Co., then from 1902, when a royal warrant was given, Royal Doulton. The company always made some more decorative items, initially still mostly stoneware, and from the 1860s the firm made considerable efforts to get a reputation for design, in which it was largely successful, as one of the first British makers of art pottery. Initially, this was done through artistic stoneware's made in Lambeth, but in 1882 the firm bought a Burslem factory, which was mainly intended for making bone China table wares and decorative items. An early utilitarian stoneware item made by a well-known company that specialised in making salt-glazed items that later earned a reputation for making stoneware art objects. This ink well is historically significant as it represents the method of hand written communication that was still common up until the mid-20th century, before fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience.Ceramic, salt-glazed, mid-brown ink bottle. It has a small round mouth, rounded lip that extends past neck, wide shoulders, straight sides, flat base. Handmade. The surface is matt. there are flecks of dark brown in the clay. The bottle has marks on the side.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, writing equipment, writing accessory, office equipment, stationery, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, inkwell, penny ink well, nib pen, dip pen, ink, hand writing, record keeping, household, business, vintage, blotting paper, ink bottle, dwarf ink, salt glazed -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBottle, Late 19th century
... bottle bank stationery equipment writing with pen and ink "82 ...This handmade ceramic bottle was made and used for pouring ink to fill ink wells. Businesses such as banks and post offices provided ink and dip pens for their customers' use, along with blotting paper to dry their writing.This bottle is significant for being both and example of handmade bottles and for its association with earlier methods of writing.Bottle, cream coloured, glazed ceramic bottle, cylindrical shape, with spout and flared lip moulded into mouth of bottle. Hand made. Bottle was used for pouring ink. Inscription stamped into base. "82 PRICE" (illegible) Label provided with donation is marked "SLATER AND PALMER works: MARSHGATE MILLS, STRATFORD ESSEX"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ink and pen writing, ink pouring bottle, bank stationery equipment, writing with pen and ink -
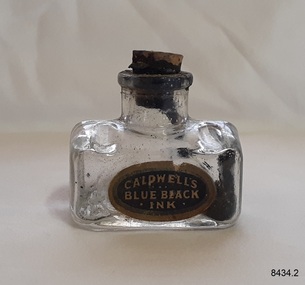 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Late 19th to early 20th centuries
This design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. The Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a three-piece mould, a method often used in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with the maker's name engraved into the mould section for the base. The glass blower would cut the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool and join a mouth onto the top, rolling the lip. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. This method of manufacture was more time-consuming and costly to produce than those made in a simple two-piece mould and 'cracked' off the blowpipe. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. This particular bottle is unusual as it has four sloping indents at the corners of the shoulder, most likely for resting a pen with its nib upwards and the handle resting on a flat surface. Most of the bottles made during this era had horizontal pen rests that were indented into both of the long sides of the shoulder. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. This only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This hand-blown bottle is significant for being the only bottle in our collection with the unusual sloping pen rests on its shoulder. It is also significant for being made in a less common three-piece mould. The method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle is of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. This ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Ink bottle; rectangular base, hand-blown clear glass bottle with its own cork. The bottle has side seams from the base to the mouth, an indented base and an applied lip. The corners of the shoulder sides have unusual diagonal grooves that slope down and outwards that may have been used as pen rests. Inside the bottle are remnants of dried blue-black ink. The glass has imperfections and some ripples on the surface. The bottle has an attached oval black label label with gold-brown printed text and border. The base has an embossed inscription. The bottles once contained Caldwell’s blend of blue black ink.Printed on label; “CALDWELL's BLUE BLACK INK” Embossed on the base "CALDWELLS"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture, three part mould, cauldwells, cauldwell's -
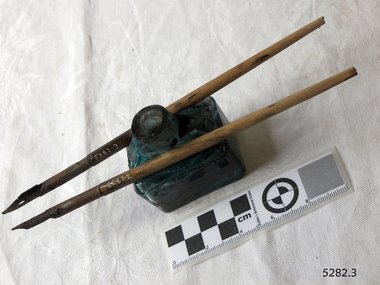 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle with pens, Early 20th century
This handmade, aqua glass ink bottle's design is sometimes called a ‘boat’ shape. The base was mouth-blown into a rectangular mould, evidenced by the lack of seams, the pontil, crease lies and the uneven thickness of the glass. The shoulder section was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould and then cut off from the blowpipe. The lip is sometimes referred to as a 'burst-lip, which was often filed to be smooth. This method of making bottles was often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The bottle would then be filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pens are a common item for that period. Pen and ink have been used for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used until the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy.The ink bottle is of interest, being made of aqua glass rather than the more common clear glass. This set of ink bottles and pens is significant because of the bottle's method of manufacture, which is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that has now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle and pens are historically significant as tools used for handwritten communication until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and mechanical typewriters became part of standard office equipment.Victorian 'Boat' ink bottle, small rectangular, aqua glass ink bottle with grooves along the long sides for pen rests. The base has a pontil, no seams, and the glass is uneven in thickness. The shoulder has two side seams and there is a ridge where it is joined onto the base; there are round indents on each of the shoulder, on the short sides, four in all. The mouth has rough edges. The neck leans to one side. The glass has impurities, crease lines and bubbles. There is dried ink in the bottle. Two pens with metal nibs are included with the ink bottle. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, copy ink, aqua glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle and Pen, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Early 20th century
This shaped ink bottle made by Caldwell's is called a 'boat ink bottle'. It was shaped especially to hold a nib pen when the pen was not in use. The design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. The Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This pen and ink bottle set is of significance as the bottle has its original cork and retains remnants of ink, which was made from a recipe that at the time was over 100 years old, according to Caldwell.. The handmade, mould blown method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle and its contents are of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. The pen and ink set is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Victorian boat ink bottle; small rectangular clear glass ink bottle with horizontal grooves made in the glass for resting and holding the pen. The set includes one pen and nib with the bottle and cork. The bottle is made by Caldwell's and contains its Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink brand."Caldwell's Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, flo-eesi, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, 19th to early-20th century
This design of ink bottle or ink well was commonly referred to as a ‘penny ink well’ because it was very inexpensive to produce. It is also known as a dwarf bottle. Pen and ink has been in use for hand writing from about the seventh century up until the mid-20th century. Up until around the mid-19th century a quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used. In the 1850s the steel point pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. In the 1880s a successful portable fountain pen was designed, giving a smooth flowing ink and ease of use. Ink wells, used with steel nib dip pens, were commonly used up until the mid-20th century. The pens only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib of the pen into an ink well for more ink. Hand writing with pen and ink left wet writing on the paper, so blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased, ready to use, or in the powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. After the invention of fountain pens, which had a reservoir of ink, and then ballpoint pens, which also had ink that flowed freely, the dip pen was slowly replaced. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy.This ink well is historically significant as it represents methods of hand written communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century, when fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience.Ink bottle or ink well, sometimes called a Penny Ink Well. Cylindrical body, salt-glazed, brown ceramic stoneware bottle, handmade. Stoneware bottle. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, writing equipment, writing accessory, office equipment, stationery, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, ink well, inkwell, ink bottle, penny ink well, nib pen, dip pen, ink, hand writing, record keeping, household, business, vintage, blotting paper, dwarf bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Late-19th to early-20th century
The design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. This handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy.This ink bottle still retains its original cork. The method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century, handcraft industry that is now largely replaced by mass production. The ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten personal and business communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Victorian 'boat' shaped ink bottle; small rectangular clear glass ink bottle with grooves in shoulders for holding pen. Bottle has side seams and a 'burst-lip'. The bottle retains its cork.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, stencil ink, copy ink -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Office Equipment, propelling pencil Eversharp, c1941
George Reed was a draftsman who lived in Bentleigh , City of Moorabbin in mid 20th C and used this pencil for his work. Eversharp is an American brand of writing implements founded by Charles Rood Keeran in 1913 and marketed by Keeran & Co., based in Chicago. Keeran commercialised Eversharp mechanical pencils (manufactured by two companies, Heath and Wahl) then expanding to fountain pens when the company was acquired by the Wahl Adding Machine Co. in 1916 and it was named "Wahl-Eversharp". In 1941 the company renamed itself, this time as Eversharp. The company continued until 1957 when it was acquired by Parker Pen, which continued to use the Eversharp brand for a time. In 1993 Parker was purchased by the Gillette Company, which already owned the 'Paper Mate' brand - the best-selling disposable ballpoint pen. In 2000 Gillette sold its writing instruments division to the company Newell Rubbermaid, USA, and In 2011 the Parker factory at Newhaven, East Sussex, England, was closed, and its production transferred to Nantes, France.An 'Eversharp' propelling pencil manufactured prior to to the development of the ball point penA gold plated propelling pencil c1941engraved : G. . Reed Made in Eversharpwriting implements, pencils, pens , propelling pencil, fountain pen, biro, ballpoint pen, keeran & company chicago, parker pen pty ltd, gillette pty ltd, eversharp, paper mate, bic pty ltd, -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Documents, condolence letter 1903, 1903
... equipment pen and ink clarke jane, clarke janet, mourning customs ...A Letter of condolence sent to Lily (Elizabeth Ann Jones) for the death of her Mother, Mary Ann Jones, who died on 18 January 1903, from her school friend Jane Clark. Following Queen Victoria’s example, it became customary for families to go through elaborate rituals to commemorate their dead. This included wearing mourning clothes, having a lavish (and expensive) funeral, curtailing social behaviour for a set period of time, and erecting an ornate monument on the grave. . Relatives and friends were expected to give handwritten Condolence Cards and Letters, preferably by hand when visiting the bereaved. The different periods of mourning dictated by society were expected to reflect the natural period of grief. In recent years some traditions have given way to less strict practices, though many customs and traditions continue to be followed. Condolence Cards and Letters are still expected for relatives and close friends. These can be individually composed and handwritten or purchased from a Greeting Card Manufacturer. The letter shows Tucker Road as being in East Brighton. Due to the confusion caused by so many 'Brightons' in the area of Henry Dendy's Special Survey of 1841 this area was renamed Bentleigh after Sir Thomas Bent. The Clark family and the Jones family were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireWhite paper with a black border used for a hand written condolence letter sent by Mrs Jane Clark in 1903 during the mourning period for the mother of her school-friend Lily, (Elizabeth Ann Jones).market gardners, pioneers, early settlers, mooorabbin, brighton, east brighton, bentleigh, correspondence, writing equipment, pen and ink, clarke jane, clarke janet, mourning customs, bereavement, condolence letters, -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Education kit - Vere Foster's New Copy-Book No 19, Bold Writing or Civil Service Series, c1890
... writing equipment pen and ink education Vere Foster Irish VERE ...This copy book was used by Maggie McKay in 1902 when in 6th Grade at Meeniyan State School (no 3165) and was learning to write in the approved manner. Vere Henry Louis Foster (1819-1900), an educationist, philanthropist, and humanist, who worked devotedly to improve the situation of the Irish poor, published a series of these copy books to improve writing skills, as better literacy and penmanship meant better chances of employment. The books were first published in 1865 and were sold for 1 penny, a fraction of what they cost to produce. In the first year alone one million Foster's Copy Books were sold. The series of books taught children the alphabet and writing. Copy books for older children taught basic business studies and book-keeping.The family of Maggie McKay were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireA school writing copy book with 14 pages divided so that the student copied the text on one half of the page. VERE FOSTERS NEW COPY BOOKS / BOLD WRITING / OR CIVIL SERVICE SERIES London BLACKIE & SON Glasgow and Dublin market gardners, pioneers, early settlers, mooorabbin, brighton, east brighton, bentleigh, correspondence, writing equipment, pen and ink, education, vere foster, irish -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Education kit - Wood shaft writing pens and nibs, Steel Nib Manufacturer, mid 20thC
A dip pen usually consists of a metal nib with capillary channels like those of fountain pen nibs, mounted in a handle or holder, often made of wood. Dip pens have no ink reservoir, so the user must recharge the ink from an ink bowl or bottle to continue drawing or writing. Dip pens emerged in the early 19th century, when they replaced quill pens and were generally used before the development of fountain pens in the later 19th centuryThe pioneer settlers in the Moorabbin Shire area valued education and established schools for their children in Cheltenham and East Brighton c1860's These wood shaft pens and steel nibs are typical of the type used up to the mid 20th Century in school classes.3 wood shaft writing dip pens with steel nibs schools, education, writing equipment, victoria melbourne, market gardeners, pioneer, settlers, cheltenham state school no. 84., bentleigh east state school no. 2083, st stephens c of e school tucker road east brighton, pen steel nibs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, 1890s to 1902
This design of ink bottle or ink well was commonly referred to as a ‘penny ink well’ because it was very inexpensive to produce. It is also known as a dwarf ink bottle. It was recovered from the wreck of the 1895-1902 ship Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance Collection. Pen and ink has been in use for hand writing from about the seventh century up until the mid-20th century. Up until around the mid-19th century a quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used. In the 1850s the steel point pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. In the 1880s a successful portable fountain pen was designed, giving a smooth flowing ink and ease of use. Ink wells, used with steel nib dip pens, were commonly used up until the mid-20th century. The pens only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib of the pen into an ink well for more ink. Hand writing with pen and ink left wet writing on the paper, so blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased, ready to use, or in the powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. After the invention of fountain pens, which had a reservoir of ink, and then ballpoint pens, which also had ink that flowed freely, the dip pen was slowly replaced. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of hand written communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century, when fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience. The Ink bottle also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Inverlochy in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. This Ink bottle is significant because of its historical connection to the barque Inverlochy, which is an example of a commercial international steel sailing barque and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S338. The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the kind of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history.Ink bottle or ink well; cylindrical shaped, salt-glazed, mid-brown ceramic bottle. It has a small round mouth, rounded lip that extend past the short neck, wide shoulders, straight sides, flat bottom. Handmade. Also called a Penny Ink Well.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, tramway cable, ingoldsby reef, point addis, anglesea, thompson’s creek, barwon heads, ink bottle, writing equipment, writing accessory, office equipment, stationery, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, ink well, inkwell, penny ink well, nib pen, dip pen, ink, hand writing, record keeping, household, business, vintage, blotting paper, dwarf ink
