Showing 52 items matching "pinus"
-
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbournePhotograph - Photograph of Ripping 14-in. planks from Pinus insignis logs, Creswick Nursery and Plantations, Ripping 14-in. planks from Pinus insignis logs, Creswick Nursery and Plantations, 1928
... Ripping 14-in. planks from Pinus insignis logs, Creswick ...Mounted, copied and enlarged sepia image. This photograph is an enlarged copy of one of the photographs from the Creswick Nursery and Plantations, Pinus insignis. Album. These photographs were presented to the 1928 Empire Forestry Conference. Presented to the VSF Library by W.Horne, June 1970. The photograph shows John Johnstone and a 2nd unnamed person ripping planks.PhotographRipping 14-in, Planks from Pinus Insignis logs, Creswick Nursery and Plantations. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - 35mm Colour slides, Pinus radiata
... Pinus radiata ...1. 33 slides showing the height of Pinus radiata seedlings. 2. 7 labelled 'disorders of pinus radiata.' 7 'disorders of pinus radiata and eucalypts.'height, disorders, eucalypts, diseases, pinus radiata seedlings -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, 26. View of Pinus
... 26. View of Pinus ...Labelled, "View of Pinus."trees, mrs. jessep, alexander william jessep, principal, a.w. jessep -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesNewspaper - Newspaper Cutting, The Argus, Pinus insignis its Romantic History, 1928
... Pinus insignis its Romantic History ...Copy of transcription of article in "The Argus" 13 October, 1928 p. 6 by A.D. Hardy. Discussion of Monterey Pine and whether Pinus radiata and Pinus insignia are the same or different. Trees planted at Burnley in early years have been described as Pinus insignis.the argus, a.d. hardy, pine trees, pinus insignis, monterey pine, pinus radiata -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneAlbum - Photographs presented to: the Delegates to the 1928 Empire Forestry Conference, Creswick Nursery and Plantations - Pinus Insignis, 1928
... Creswick Nursery and Plantations - Pinus Insignis ...Creswick Nursery and Plantations, Pinus insignis. Photographs presented to the 1928 Empire Forestry Conference. Presented to the VSF Library by W.Horne, June 1970Five photographs in a Photograph album. Includes image of John Johnstone.Photographs presented to the delegates to the 1928 Empire Forestry Conference. Presented to the Library by Mr. W. Horne, june 1970. -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneEquipment, Forests Commission of NSW, A Card Key to Pinus Based on Needle Anatomy, 1966
... A Card Key to Pinus Based on Needle Anatomy ...Card sorting key for Pinus. Seried of punched cards. Cell structure diagrams on rear. Plant characteristics on face. Complete set with instruction booklet boxed in a red case. Produced by FC NSW, Joyce W. LanyonEquipmentJohn Mcdonald -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneArtwork, Pinus insignis logs ready for milling, Creswick Nursery and Plantations, 1928
... Pinus insignis logs ready for milling, Creswick Nursery and ...Metal framed photograph. Copied and enlarged sepia image.Photograph -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneManuscript, H.J. Semmens, Some factors influencing the regeneration of pinus raditia (D.DON) under canopy, 1967
... Some factors influencing the regeneration of pinus raditia ...Thesis submitted by Herbert James Semmens for the Diploma of Forestry.Document -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesDocument - Report, Forests Commission Victoria, A Study of the Flora and Fauna of Radiata Pine Pinus Radiata D. Don Plantations Near Myrtleford in North-Eastern Victoria III Third Progress Report Part C. Mammals, October 1977
... A Study of the Flora and Fauna of Radiata Pine Pinus ...forests, mammals, fauna, myrtleford, radiata pine, plantations, pinus radiata, forests commission victoria -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture, John Abery, 'Titanic' by John Abery, 2010
John ABERY Australian Artist and Sculptor John Abery works in a range of mediums including metal (bronze and steel), fiberglass, stone and wood.Laminated Pinus radiata and steelsculpture, john abery -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, C.J. Frazer Photo, Students and Staff 1927 or 1928, 1927-1930
Black and white photograph. Female students and Staff seated on benches and standing on the lawn under a Pinus canariensis in 1927 or 1928. 2 copies.On reverse, "From left to rt. Back Row..., Olive Matthews, Mary Stickland, Grace Campbell. See paper catalogue for list of names.olive matthews, mary stickland, grace campbell, group students and staff 1927-1928, pinus canariensis, canary island pine, publicity -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneSample
13 small bottles of pinus seedsSpecimen bottles -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, Principal's Residence, Unknown
Note by T.H. Kneen 8 April 1992, "Note: gable of Pavilion in background - 2 large Pinus radiata and at the right Prunus (sic) (Pinus) canariensis. The 2 P. Radiata did not survive until the Centenary. The bay windows were replaced in Mr. Jessep's (sic) McLennan's) time as Principal."Black and white photograph. Garden beds between Principal's Residence and Pavilion.garden beds, principal's residence, pavilion, a.w. jessep, bay windows, pinus radiata, pinus canariensis, mclennan -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Sepia print, A.E. Bennett, Entrance Gates, 1894-1990
Note by E.B. Littlejohn, "Is the roadway the original Swan Street? Entrance gates to Gardens in the distance. Roadway leading to the Pavilion hidden behind the trees. No elms showing along the roadway," and by T.H. Kneen, "The roadway appears to terminate at the gates outside the Curator's Residence, sweeping past the Pavilion on the right. I have seen a plan which showed an attractive avenue of trees (pine) from the western end of the property (where the Stockman's Cottage was later sited.)" 2 copies sepia photograph. Copy of sepia photograph of the roadway to the Entrance Gates and Curator's Cottage seen in the distance, with the Pavilion on the right, in, "Prize Essays," Alfred E. Bennett, c.1894, after p 116. Pinus radiata avenue on each side of the road.entrance gates, prize essays, alfred e. bennett, curator's residence, pavilion, stockman's cottage, pine tree avenue -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Letter/s, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIRO), Aug. 1935
Carbon copy of a letter to the Chief Engineer of the MMTB 16 August 1935 from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIRO) about the durability of various species of Eucalypti woods. Discusses service life, sleeper supply, pinus radiate sleepers in Adelaide, and further research work. Signed by Stanley A Clarke, Acting Chief Division of Forest Products.trams, tramways, mmtb, sleepers, trackwork, csiro -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, Administration Building, c. 1952
Note by T.H. Kneen 20 February 1991, "East facade, lawns and gardens in foreground. A very large Pinus radiata was removed from the approximate position of the staked tree in the middle foreground. It was removed by George Manley (43-57) and Andy Tylee (51-53) possibly in 1952."2 copies black and white photograph. Administration Building in the background with Emily Gibson beds in front. Willow at the edge of the ponds was replaced. Staked tree no longer there. Early 1950sgardens, trees, george manley, andy tylee, administration building, pinus radiata -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Stereoscopic Photograph, c1900
The gardens of Ovens District Hospital were laid out and planted by R H Jenkyns in 1874. Over 200 species of trees and shrubs were planted, including several large Himalayan Cedars (Cedrus deodora), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), rare Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris), Pencil Cedar (Juniperus virginiana), Bunya Bunya Pines (Araucaria bidwillii), a Purple-leaved Dutch Elm (Ulmus x hollandica 'Purpurascens'), American Ash (Fraxinus americana), Pinus radiata, and numerous Populus alba trees and suckers. The gardens were considered integral to the healing process, also including orchards and kitchen gardens. In the 1880s, tourists flocked to Beechworth as the area became recognised as a health resort and picturesque beauty spot. Although the hospital closed in 1940, and parts were subsequently demolished, the gardens remain and form part of the site's listing on the Victorian Heritage Register. This photograph is part of a collection of items held by the Burke Museum relating to Ovens District Hospital. At the time of being built, the Ovens District Hospital was the only hospital between Melbourne, Victoria, and Goulburn, New South Wales, treating patients from all of north-east Victoria, including Indigo Shire.Black and white stereoscopic photograph mounted on card.Reverse: 97-2292 / View up centre path of Hospital / A03177 / BMM3177 / Note: A03178 / View of the central path of the Ovens Hospital / (Church St) Beechworthovens hospital, hospital garden, gardens and parks, ovens district hospital -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Snow at the Wombat Hill Botanic Gardens, Daylesford, c2012-2016
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Digital imagesdaylesford, snow, weather, climate, winter, daylesford botanic gardens, botanic gardens, wombat hill, wombat hill botanic gardens, pinetum, trees, reservoir -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Postcard, Wombat Hill Gardens, Daylesford
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Black and white postcard of Wombat Hill Botanical Gardens, Daylesford.wombat hill botanical gardens, daylesford, gardener, wombat hill botanic gardens -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Wombat Hill Botanic Gardens 150 anniversary event Daylesford community event, 2013
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Digital imagesvictoria, 150, anniversary, botanic, gardens, wombat hill, botanic gardens, heritage, celebration, garden party, daylesford, people, crowd, community, john hawker, john madigan, stilt, trees, owls, wombat hill botanic gardens -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - digital photographs, Lisa Gervasoni, Wombat Hill, Daylesford, c2006-2016
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Colour photograph of Wombat Hill Botanical Gardens, Daylesford.heritage, daylesford, townscape, wombat hill, wombat hill botanical gardens, wombat hill botanic gardens -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Wombat Hill in the Fog, c2015
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Black and white photograph of a treed landscape covered with fog. The trees are in the Daylesford Botanical Gardens on Wombat Hill.wombat hill botanic gardens, wombat hill, daylesford, daylesford botanic gardens, fog, weather, arboretum -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Wombat Botanic Gardens, Daylesford, 2019, 23/04/2019
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )A tree in the Wombat Hill Gardens.wombat botanical gardens, daylesford botanical gardens, daylesford, trees, wombat hill botanic gardens -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Wombat Botanic Gardens, Daylesford, 2019, 23/04/2019
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, 2025)An avenue of trees in the Wombat Hill Gardens. wombat botanical gardens, daylesford botanical gardens, daylesford, trees -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Wombat Botanic Gardens, Daylesford, 2019, 23/04/2019
The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, 2025)A large tree in the Wombat Gardens. wombat botanical gardens, daylesford botanical gardens, daylesford, trees, lisa gervasoni, wombat botanic gardens -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Wombat Hill Botanic Gardens 150 anniversary event Daylesford organiser Gael Shannon, 2013
The Wombat Hill Botanic Gardens 150 anniversary event organiser was Gael Shannon. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of historic, scientific (botanic), and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant as a fine example of a regional botanic garden demonstrating the typical characteristics of a carriage drive, informal park layout, decorative structures and works such as the memorial tower, conservatory, rotunda, cascade and fernery, which contrasts with the open lawns planted with specimen trees, areas of intensive horticultural interest and close proximity to a township developed during the mid to late nineteenth century. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are historically significant for the design input by noted landscape designer William Sangster, and for the survival of his 1884 plan, which is a rare example of a plan from this prolific garden designer. The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of scientific (botanic) significance for the extensive conifer collection and cool climate plants. The Gardens contain an outstanding collection of conifers and other mature trees, many of which were donated by renowned botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. Significant trees include Pinus ponderosa (Western Yellow Pine), Pinus coulteri (Big Cone Pine), twoAbies nordmanniana (Caucasian Fir), Abies pinsapo, (Spanish Fir) and a Cedrus atlantica f. glauca(Blue Atlas Cedar), Pinus wallichiana (Bhutan Pine), Pinus pinaster (Maritime Pine), Sequoiadendron giganteum (Giant Redwood), (Monkey Puzzle) and Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse Chestnut), many the largest or finest examples in Victoria. Other outstanding trees include a Tilia cordata (Small-leaved European Linden), a row of Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican cypress), a Quercus robur (English Oak) planted in 1863, avenues of Dutch Elms and a rare Quercus leucotrichophora (Himalayan Oak). The Daylesford Botanic Gardens are of aesthetic significance as a rare example of a botanic garden spectacularly sited on an extinct volcanic cone which allows a panoramic view, aided by the 1938 Pioneers’ Memorial Tower, as well as vistas within and out of the gardens and from the township to the gardens. As the most prominent local landmark, the Garden’s vertical dominance in the landscape provides a dark contrast to the elms avenues, oaks and other deciduous species. (Heritage Victoria Register, )Four people photographed at the 150th anniversary event at the Wombat Botanic Gardens.victoria, 150, anniversary, botanic, gardens, wombat hill, botanic gardens, heritage, celebration, garden party, daylesford, people, crowd, community, organiser, tour, gael shannon, don henderson, wombat hill botanic gardens -
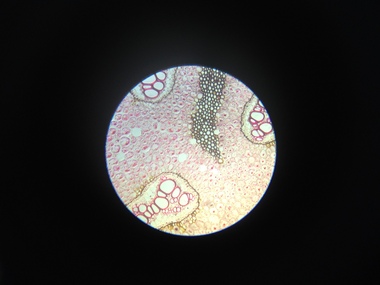 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Object, Norman H. Seward, Botanical Microscope Slides, c1950s
Botanical Microscope Slides in a cardboard box. .1) Zea Mais Annular vessels .2) Protoceus .3) Yeast .4) Eryol .5) Stomata .6) Lichen Physcia Thallus .7) Lichen Cladonia mascilenta .8) Californian Lichen .9) Rhizome Pteris Longitudinal Section .10) Brake fern Pteris Transverse and Longitudinal sections .11) Rhizome Pteris Transverse Section .12) Selaginella sp. - Macro & Micro-sporangia .13) Ovule Pinus Longitudinal section .14) Rachis Pteris Transverse Section .15) Stem Pine Transverse Section microscope, botanical microscope slides -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - 35mm Colour slides, Arboriculture Diseases and Disorders, 1965-1985
10 boxes of slides some labelled. 1. "Assorted Disorders" 1965-1984 some labelled Aug 84 M2. 2. "Nursery Diseases Yarram" Aug 84 M2. 3. "Disease Slides Pine" 78-89. 4. "Euc Diseases" 77-81.5. "Pinus radiata insects" 79-85. 6. "P. penetrans" 81-85, Sep 85 M11, Apr 83 M11. 7. "Phytophthera cinnamomi" 65-85. 8. "Phytophthera Talk" 75-82. 9. 10. Diseases various dates.diseases, plants, arboriculture, nursrey diseases, pine diseases, eucalyptus diseases, pinus insects, phytophthera cinnamomi -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Colour print, The Australian Garden Lover, "An Australian Horticultural School.", 1926
The 4 bottom photographs used as an illustration in, "Green Grows Our Garden," A.P. Winzenried p 52 and also used in the Centennial Display mounted on board. The espaliered fruit tree was located in the old nursery trained by George Russ. Top right orchard spraying. Bottom left View of Pavilion showing Luffmann's pond and a Pinus radiata planted in the 1860's. Bottom right A.W. Jessep (Principal) and E.E. Pescott (Lecturer). outside Principal's Residence. E.B. Littlejohn.See detailed description in paper catalogue and B91.404 for Journal Article.Colour photograph of part of the cover of , "The Australian Garden Lover," Vol. 2 No. 7 October, 1926, entitled, " 'An Australian Horticultural School.' Enterprise at Burnley, Vic." ella chalmers (née fry), green grows our garden, a.p. winzenried, centennial display, a.w. jessep, principal, e.e. pescott, lecturer, principal's residence, e.b. littlejohn, espaliered fruit tree, old nursery, george russ, orchard spraying, pavilion, pinus radiata, ponds., lily ponds, luffmann ponds -
 Mortlake and District Historical Society
Mortlake and District Historical SocietyLone Pine
This pine tree (Allepo Pine, Pinus halepensis) a native of the Gallipoli Peninisula (Gelibolu, Turkey), was grown from a cutting obtained from the War Memorial Canberra and planted in the Mortlake Botanic Gardens in 2002. It replaces the original which grew outside the Mortlake RSL Hall which blew down in a storm c.2000. That tree (Allepo brutius)came from 'the original on Gallipoli' and was planted to commemorate 'fallen comrades' in 'the Jubilee year 1965.' However, two soldiers first brought home pine cones direct from that fateful battlefield. . One was Sgt. Keith McDowell of the 24th Btn. His aunt, Mrs. Emma Gray of Grassmere (Vic.) planted the seeds c. 1928 and four seedlings resulted. One was planted in Wattle Park, Melbourne, one at the Shrine of Remembrance, one at the Soldier's Memorial Hall at The Sisters (c.15 km. south of Mortlake) and one at the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens. The First World War (or 'Great War') and in particular the battle for the Gallipoli Peninsula is of immense national significance. Lone Pine or Plateau 400 was the scene of a major offensive on August 6th 1915. All the trees on the ridge at this point were cut down but one, which was dominated by the 'Lone Pine'. In three days of fighting more than 2,000 Australians lost their lives and seven Victoria Crosses were won. Two Australian soldiers souvenired pine cones - one was brought back to Victoria (see above). Many young men from Mortlake and district volunteered to fight in the Great War and the presence of this tree in our Gardens reminds us all of the local as well as the national sacrifice.l pine tree Small plaque on railing western side. gallipoli, lone pine first world war great war mcdowell, keith
