Showing 15 items matching "rectifier"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionElectrical Equipment, AC/DC Power Supply Unit - Rectifier
What device converts AC to DC? rectifier A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification, since it "straightens" the direction of current. The unit was used at Ballarat School of Mines in the Maths, Science and Physics Departments.Grey metal unit with Dials on the front and vents at the back. Handle for carrying. Two switches for turning on and off. Yellow sticker - SMB - with number 116071. Engraved on back - S.M.B.. Maths / Science / Physics Sticker on cord indicating inspection of unit - 13/04/2005. Tag Number - 032735alternating current, direct current, ac, dc, rectifier, electrical, ballarat school of mines, science, maths, physics -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionObject, Synchronome Co. Ltd, Synchronome Frequency Checking Master Clock No. 2191, c1930
Information from Norman F. Dalton: Ballarat had a reticulated DC supply in the early part of last century and in 1905 had sufficient generating capacity to enable the trams to be changed from horse drawn to DC electricity. The use of electricity increased with the main power station located on Wendouree Parade, near Webster Street, under the ownership of The Electric Supply Company of Victoria. AC generating plant was installed in 1925 and conversion to AC proceeded. In 1934 the company was taken over by the State Electricity Commission Victoria (SECV) and more AC generation was installed and the changeover of customers was accelerated. This is around the time that the Synchronome Frequency Checking Mast Clock was installed at the Wendouree Parade Power Station. The SECV Annual Report of 1921 states: ::Section 11 of the act directed the COmmission to enquire into the question of securing the adoption of such standards of plant and equipment of a system, frequency and pressure for the generation and distribution of electricity as will admit of the efficient interconnection of undertakings throughout the State. In 1934 when the SECV took over the Ballarat operations the question of linking with the State grid had been a planned operation for some years but due to financial considerations had hindered it and in fact would continue to do so for a further 10 years. So while the need for close frequency control for interconnection was hardly an issue, the need to keep electric clocks correct was important, particularly as this item was a frequent sales point to cover the inconvenience and sometimes expense of converting from DC to AC. The clock is a very accurate pendulum clock with provision for varying effective length during operation for precise time regulation. There are two normal time dials and one is controlled by the pendulum and the other is operated by the system frequency. When the clock was in use it was installed by the MEter and Tests Laboratory and the time was checked daily by radio time signals. The two dials were repeated in the operators control panel in the Power Station. A maximum deviation between the two dials was set in the operating instructions (eg 5 seconds) and the operator would correct this when necessary by remote manual alteration of the turbine governor set point. The clock was used to drive and regulate a system of "slave" clocks which were used to display the time in various locations around the power station. A slave clock is a simple clock which is driven by a small electric motor, its accuracy is regulated by the master clock every 30 seconds to ensure that it and all the other slave clocks in the station are on exactly the right time; slave clocks were placed in various locations, from common rooms to workshops. A master clock could potentially run thousands of slave clocks at one plant. The clock also contains a rectifier. A rectifier is a device that is used to convert AC power to more stable DC current.Two clocks in a timber case. Both are electric, one is powered by the main pendulum mechanism, the other is a self contained electric clock. The main mechanism is of the gravity arm and roller type, which sends an impulse to the slave clocks every 30 seconds. The This Synchronome Frequency Checking Master Clock was used at the Ballarat Power Station. Below the main section of the case is a smaller cabinet containing a rectifier to provide consistent DC power for the clock. The rectifier was made by the Victorian company Hilco, which was located in Burwood. There is a high chance this is not the original rectifier from this clock as there appears to be brackets to hold a larger device in the space the rectifier occupies.Front below main clock face on front of case: "Patented Sychronome Brisbane" Lower left-hand clock face: "Frequency time" Lower right-hand clock face: "Standard Seconds" Synchronous electric clock mechanism on door (Frequency time clock): >200/250 V. 50~ >"Synchronomains" Made in England >Direction indicator for clock starting switch >"To start move lever in direction of arrow and release" >"Patent applied for" Mechanism for "standard seconds" clock: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "321" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Mechanism for "standard seconds" clock: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "321" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Mechanism for main clock face: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "8751" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Inside case, back panel, top enamel plate: >Seconds Battery + Pos. > Battery Common or - Neg. >1/2 min dials Inside case, back panel, bottom enamel plate: external seconds dial Inside case, right hand side, electrical knobs: two switches, both "A.C. mains" Pendulum rod, below suspension spring: Serial number (?) 0000005 Rectifier in bottom cabinet: >"Hilco Rectifier" >"A.C. Volts 230/240" >"Model 1060/S" >"A.C. Amperes" >"Serial No. 1060/S >"Phases 1" >"D.C. Volts 6" >"C.P.S. 50" >"D.C. Amperes 1" >"Made in Australia by Hilco Transformers McIntyre St., Burwood, Victoria." Bakelite electrical plug: makers mark Lower cabinet, RH side panel, pressed tin plate: "AC" (upside down) Brass speed adjustment, outer right RH side: "S" and "F" Ivory and wood pendulum beat ruler: >Ruler, with 0 in centre and numbers 1-5 in ascending order from centre on left and right. > "Synchronome Patent." Steel plate, back panel, inside case, right hand side: >N R A" (descending) >"2191" serial number/part number Face of main clock: "Synchronome Electric" synchronome frequency checking master clock, electricity, state electricity commission, wendouree parade power station, secv, clock, time, pendulum, electric supply company of victoria, norman f. dalton, ballarat power station, rectifier, slave clock -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumRectifier, McKenzie & Holland, 1925
This object was installed at the Victory Hall, Tatura, to change main power (AC 240 v), to DC (direct current 30 volts). This supply was required to run the hall's picture show.An electrical devise which changes AC power supply to DC supply.Makers name; title object; Ref. to voltage, amps. AC and DC.rectifier, victory hall tatura, electrical converters -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionElectrical Equipment, AC / DC Control Unit - Rectifier
The unit was used at Ballarat School of Mines in the Maths, Science and Physics Departments.Grey metal unit with Dials on the front and vents at the back. Handles for carrying. Two circuit breaker switches, two DC output sockets, two AC output socketsYellow sticker - SMB - with number 116069. Engraved on back - S.M.B.. Maths / Science / Physics Sticker on cord indicating inspection of unit - 13/04/2005. Tag Number - 032725alternating current, direct current, ac, dc, electrical, ballarat school of mines, science, maths, physics, ac/dc, scientific instrument -
 Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory LightstationBattery charger
The relatively large battery charger is in a metal cabinet that has dials and switches on the face. It was used by the PMG to charge radio telephone batteries between the 1960s and 1990s. Cape Schanck Lightstation also has a battery charger that is part of a set of items associated with the electric operation of the lighthouse Meets first level threshold.Battery charger encased in a large metal cabinet, with black dials, with white faces & switches on either side of the front of the cabinet. Makers label as bottom of cabinet. Some staining." Constant Potential Rectifier....." -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - STC Selenium Rectifiers Manual for the Manufacturer, Construction and Application of, 1938
STC Selenium Rectifiers Manual, 20 pages by R.F.Haren, ASTC (Elect. Eng.) Manager, selenium Rectifier Division. Standard Telephones and Cables Pty. Ltd. 252-274 Botany Road, Alexandria, Sydney NSW. Masse Batteries Pty Ltd. Sole Distributors in NSW and Victoria for the mining industry.history, bendigo, mining, stc -
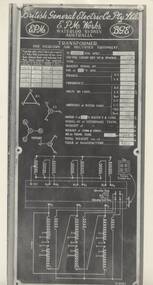 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), c1950
Black and White Photograph of a transformer face plate for a British General Electric transformer for use in Mercury Arc Rectifier Equipment, made 1950. Provides details of the transformer capacity, ratings and wiring diagram. Made at the EPM Works, Waterloo NSW.trams, tramways, transformer, mercury arc, substation, electrical equipment -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument, "Review of MTA Tram substation Network", 6/1989
A document dated June 1989 examines the then MTA tram substation network and its issues at the time, in particular the reliability of the aging rotary converters and mercury arc rectifiers. It also considers the need to upgrade the network, increase the power supply for B-class trams, and reduce voltage drop.Yields information about the status of the tram substation and electrical equipment in 1989Photocopy of a 38 page A4 document.tramways, substations, mta, the met, power supply, electrical engineering, rotary converters, mercury arc -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument, State Electricity Commission of Victoria, "Ballarat Tramway Inquiry - Overhead System", 10/1962
Report or document titled "Ballarat Tramway Inquiry - Overhead System", dated 18/10/1962 prepared by the SECV Distribution Engineer of the Ballarat Branch about the cost of refurbishing the Ballarat tramway electrical system including the status of the rectifiers at Ballarat A, steel poles, trolley wire, use of the DC system by customers in central Ballarat, and the cost of new recitifier systems.Yields information about the cost of refurbishing the Ballarat Electrical system for trams in 1962.Carbon copy on green paper with rounded and or cut corners, pinned with hand written notes. Second copy on foolscap sheet typed.Three hand written notes regarding distribution.tramways, state electricity commission of victoria, secv, electrical engineering, rotary converters, trolley wire, overhead, poles -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instument, Hewittic Rectifiers, X-Ray Tube, 1956
This item was acquired by the Ballarat School of Mines Electrical Engineering department for use in electric power laboratory as a source of D.C., and also for instructional purposes. This central mercury arc element was located in a cabinet with transparent side panels, and equipped with the required electric accessories, to be a self-contained stand-alone unit. Head of the Electrical Engineering Department at the time was John M. Sutherland.Mercury arc rectifier, 3-phase input. Constructed of blown glass, and complicated configuration: the central inverted truncated cone is provided with 3 large diameter "horns' and four smaller ones. Each horn has electrical connection to outside, some have side horns. Approximately half a cup of free mercury inside the glass complex. No. 33369scientific instrument, x-ray, x-ray tube, xray, john m. sutherland, electrical engineering, ballarat school of mines -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Cyclotron accelerator
Builit in 1950s and used till the mid 1970s within the Physics Department used in Melbourne. John Rouse and David Caro was involved in the construction.Black and white photo of cyclotron (nuclear physics accelerator): H.V. Power supplies & acceessories. Sticky typed labels on back from top and left to right: “4KV DRIVER POWER SUPPLY, 14KV RECTIFIER SET, 14KV CHOKE, OIL PUMP & HEAT EXCHANGER” Handwritten in pencil on top left hand corner: “6” -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumManual - Procedure, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Rectified Protection", Mid 1930's
Carbon typed copy of a technical procedure - 3 pages "Rectifier Protection" gives details on cell failures, surge voltage protection, bridge circuits, over current and provides four figures to illustrate the paper. Written D.B. Corbyn and N. L. Potter in a paper to the Institute of Electrical Engineers London. Not dated. Assumed mid 1930's. BTPS Number "216". "216" in ink on left hand bottom of first pagetrams, tramways, electrical engineering -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Project 3-75 - Replacement of Substation Equipment", 1975
Digital copy of a 9 page report by the MMTB, titled Project 3-75 - Replacement of Substation Equipment", proposing to replace the rotary converters installed between 1924 and 1930 with silicon rectifiers. Gives the locations, costs, schedule of replacement commencing 1975, in particular South Melbourne, Malvern and Young St Fitzroy. Gives a background to the system, a list of all the substations at the time, including date of installation, type, replacement of HV equipment, costs, reliability, maintenance costs, and benefit to cost ratio.Has the stamp of "Joint Ministry of transport and Tramways Library" and a "Plan & EPA Library barcode"trams, tramways, substation, transformer, power supply, electrical engineering, rotary converters -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Colour Photograph/s, 1993
Set of four Polaroid prints of a Mercury Arc rectified bulb. One photo has written on rear "Hewittic Rectifiers type 500/6". Image i4 has a person standing alongside. See Inscriptions. Craig Tooke, formally of Yarra Trams substations advised 12/8/2020 by email to Warren Doubleday. "An interesting photo. I don’t know who the person in the photo is. More than likely the bulb in from an industrial installation such as mine etc. and not tram or train. The reason is that only Melbourne trams has Hackbridge Hewittic rectifiers that were used for traction. There was three sets of bulbs installed at West Brunswick, Deepdene and Preston. West Brunswick is definitely still in existence and probably Deepdene is still in existence as the old substation was abandoned intact and just left intact. Preston of course has gone and was removed as part of the work done at PWS. Another clue is the number 500/6 which means it was from a 500 kW – 6 bulb unit. The traction units were all in multiples of 150 kW per bulb i.e. the tramway ones were 600 kW rated. The number "40246" is the bulb serial number. Each bulb manufactured had an individual serial number. Interesting the bulbs at Brisbane Tram Museum have the following serial numbers to the ones that were at Essendon tram sub. The bulbs at Essendon of course are now up at Brisbane as spares."On the envelop with the photographs is "Keith Wilkinson Ph Orbost 051 510050" and "For Bill Kingsley 4/10/93".trams, tramways, substation, electrical equipment, electrical engineering, mercury arc -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph, Peter Rufus, images of decommissioning mercury arc equipment or bulbs, 2005
Shows the removal and packing of the bulbs used in sub-stations to rectify or change the electrical power from AC to DC for tram use.Demonstrates the removal and packing of mercury arc rectifier bulbsSet of five digital images of decommissioning mercury arc equipment or bulbs at a sub station during 2005. trams, tramways, substation, mercury arc, yarra trams
