Showing 300 items matching "steel manufacture"
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - Aircraft manufacture, steel construction, The Steel Construction of Aeroplanes
... Aircraft manufacture, steel construction...Aircraft Manufacture, Steel Construction...Aircraft Manufacture, Steel Construction Oveview of hte use ...Oveview of hte use of steel in aircraft construction, circa World War 1Oveview of hte use of steel in aircraft construction, circa World War 1 -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Barbers' Equipment, hair clippers 'BURMAN", c1950
... and ball, steering gears, steel manufacture, birmingham... and ball, steering gears, steel manufacture, birmingham england ...Hair clippers are specialized implements used to cut human head hair. They work on the same principle as scissors, but are distinct from scissors and razors. :Hair clippers comprise a pair of sharpened comb-like blades in close contact one above the other which slide sideways relative to each other, a mechanism which may be manual or electrical to make the blades oscillate from side to side, and a handle. The clipper is moved so that hair is positioned between the teeth of the comb, and cut with a scissor action when one blade slides sideways relative to the other. Friction between the blades needs to be as low as possible, which is attained by choice of material and finish, and frequent lubrication. Hair clippers are operated by a pair of handles that are alternately squeezed together and released. Barbers used them to cut hair close and fast. The hair was picked up in locks and the head was rapidly depilated. Mid 20thC such haircuts became popular among boys, and young men in the military and in prisons. Burman & Sons Ltd, of Ryland Road, Birmingham, West Midlands, manufactured Burman-Douglas steering gear. Their recirculating worm and ball design of steering gear was fitted to pre-war vehicles such as the Ford Eight and the Ford Prefect, the Bedford CA, plus heavy trucks and off-road vehicles - both pre and post-war. In its day, Burman-Douglas steering-gear was regarded as.... a "quality" feature of a car chassis specification, but the worm and ball design was eventually surpassed by the cheaper rack and pinion design that dominates today. The company also manufactured motorcycle gearboxes, horse clippers and barbers’ clippers. 1871 Company founded. 1897 Private company. 1930s Gearbox for Ariel Square-four motorcycle. (Exhibit at Birmingham Thinktank museum) 1933 Burman and Sons Limited, manufacturers of horse and barbers' clippers, sheep shearers, motor cycle gear boxes and steering gears, Ryland road, Edgebaston 1953 S. F. Burman, M.B.E., Managing Director, Burman and Sons, Ltd 1955 Acquired by Vono Industrial Products. 1961 Manufacturers of motor and motorcycle accessories. 1,500 employees. 1968 Supplied rack and pinion steering units to Ford 1978 Adwest Group acquired Burman and Sons, the steering gear part of Duport. 1986 Major reduction in staffing at Burman due to fall in demand for its products and delivery problems. A set of hand held barbers’ hair clippers with an adjustable screw, from Burman and Sons Ltd of Birmingham, England. Chrome plated, in good condition, c1950. On left arm ; BURMAN On right arm ; MADE IN ENGLANDbarbers, hairdressing, hair clippers, grooming, horse clippers, cars, motor cycles, gear boxes, rack and pinion , worm and ball, steering gears, steel manufacture, birmingham england, burman and sons ltd, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond, cheltenham, market gardeners, -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Barbers’ Equipment, hair clippers steel, c1950
... clippers, steel manufacture, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond..., steel manufacture, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond, cheltenham ...Hair clippers are specialized implements used to cut human head hair. They work on the same principle as scissors, but are distinct from scissors and razors. :Hair clippers comprise a pair of sharpened comb-like blades in close contact one above the other which slide sideways relative to each other, a mechanism which may be manual or electrical to make the blades oscillate from side to side, and a handle. The clipper is moved so that hair is positioned between the teeth of the comb, and cut with a scissor action when one blade slides sideways relative to the other. Friction between the blades needs to be as low as possible, which is attained by choice of material and finish, and frequent lubrication. Hair clippers are operated by a pair of handles that are alternately squeezed together and released. Barbers used them to cut hair close and fast. The hair was picked up in locks and the head was rapidly depilated. Mid 20thC such haircuts became popular among boys, and young men in the military and in prisons. A set of hand held barbers’ hair clippers with an adjustable screw. Chrome plated, in good condition, c1950 barbers, hairdressing, hair clippers, grooming, horse clippers, steel manufacture, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond, cheltenham, market gardeners, -
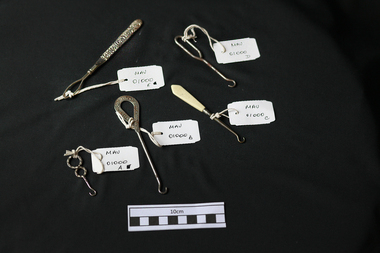 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Craftwork, 5 assorted crochet hooks, c1900
... steel manufacture... pioneers moorabbin bentleigh cheltenham steel manufacture 5 ...The women of the pioneer families were very skilled at dressmaking , needlework and lace making. The early settlers had to be self reliant and made and repaired their own clothes, haberdashery and furnishings These tools were used to make crochet work doilies, antimacassars, and add decorative work to lingerie, collars, cuffs, baby clothes, bonnets and bibs.5 assorted steel crochet work hookscraftwork, crochetwork, needlework, early settlers, pioneers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, steel manufacture -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomCabin Trunk, Wolverhampton Japanning Works, abt 1900
... CLOSE ANNEALED STEEL. MANUFACTURED AT WOLVERHAMPTON JAPANNING... CLOSE ANNEALED STEEL. MANUFACTURED AT WOLVERHAMPTON JAPANNING ...Black painted steel cabin trunk.On maker's label inside lid: "GUARANTEED BEST COLD ROLLED CLOSE ANNEALED STEEL. MANUFACTURED AT WOLVERHAMPTON JAPANNING WORKS" Displays a Registered Trade Mark in form of a piece of cord in shape of a slip knot. In white stencil paint applied to end: "BOURCHIER MELBOURNE"world war 1, bourchier, 4th light horse, cabin trunk -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDomestic object - Electric Toaster, Hecla Electrics Pty Ltd, c1940s
... A small chrome steel toaster manufactured by Hecla... domestic appliance used throughout Australia. It was manufactured ...Hecla produced a wide range of appliances for domestic use, beginning with heaters and later branching out to a wider range of kitchen appliances Hecla was established by Clarence William Marriott, a young Melbourne metal worker. He began manufacturing Australia's first carbon filament electric radiators in 1899. He originally worked for his father James Marriott who commenced business in Melbourne as an art metal worker in 1872 and was, in 1907, appointed as the official art metal worker to the Victorian Government producing items including the ornate iron gates and gas lamp standards outside Melbourne's Parliament House. With the invention of nickel chromium wire after 1900, C.W. Marriott began making more efficient heating elements using this new material in 1916. After being influenced by the eruption of Mount Hekla in Iceland, on 19 December 1918, Clarence registered the brand name "HECLA" with an erupting volcano as its logo. The company Hecla Electrics Pty Ltd was officially registered in 1922. In 1928 the company adopted the advertising slogan, 'By Hecla, it's Good'. The Hecla range rapidly expanded to include electric heaters and radiators, electric foot warmers, electric kettles, ceramic & metal electric jugs, immersion hot water elements, electric fans, electric coffee percolators, electric toasters, electric grillers and stoves, electric irons and electric frypans, clocks and curling wands. Electric blankets were introduced shortly after WWII.In 1930, a controlling interest in Hecla Electrics Pty Ltd was acquired by General Electric Corporation. Clarence William Marriott died in June 1967 in Melbourne, Victoria.This item is representative of a common domestic appliance used throughout Australia. It was manufactured by a pioneering Australian company.A small chrome steel toaster manufactured by Hecla Australia. It has a door on either side which flips down to insert or remove a slice of bread on each side, Each door has two black Bakelite knobs. The electric element is placed down the centre of the cavity. A detachable electric cord is included.240 Volts, 600 Watts. Cat. No. T4 Submitted to Electrical Approval Board Ref Application A1/AD01 SECV 240 Volt 600 Watt MANFED. IN AUSTRALIA SOLID BRASSelectrical appliances, hecla corporation australia, clarence william marriott, domestic appliances -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Leisure object - Toys, child's sewing machine, Circa 1940
... is cast, with a wooden handle. Some workings are made of steel..., with a wooden handle. Some workings are made of steel. The manufacture ...The family of Mrs Nancy Maggs were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireCirca 1940/1950. Child's small tin-plate toy sewing machine. The body of the sewing machine is painted black with red and gold floral decoration - some loss of paintwork. The flywheel is cast, with a wooden handle. Some workings are made of steel. The manufacture is such that the machine could actually be used for sewing small articles. toys, sewing machines, early settlers, pioneers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, ormond, market gardeners, maggs nancy, maggs geoff, f -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBedpan
... Enamel and porcelain pre dates stainless steel which... and porcelain pre dates stainless steel which was first manufactured ...Enamel and porcelain pre dates stainless steel which was first manufactured in 1913. This hospital equipment was available in the 1950s when the Tawonga District General Hospital was built specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme.Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment.White enamel bedpan pear shaped with the front (narrow) edge having no overlap. From the front an overlap gradually increase to the sides and back which form a narrow bench (for sitting on). The edges are rounded and black.3 small dints on bench. Sticker with UKV 270 stuck on base.hospital equipment, enamel bedpan, tawonga district hospital -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchHelmet, Adrian M26
... helmet used during WW11. Painted matte black and manufactured... helmet used during WW11. Painted matte black and manufactured ...An example of the standard issue French infantry battle helmet used during WW11. Painted matte black and manufactured from steel, complete with a brown leather chinstrap, inner liner missing. It has a dent on the righthand side of the crown.B3 stamped on the inside of the crown.helmet, french, ww1 -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumLancet Horse Flem
... and Roebuck and is seen in the 1902 catalogue. Made of brass and steel.... Made of brass and steel and manufactured by Joseph Rodgers ...This item was the property of Mr Robert Cornall of Kardella. He was one of the first selectors in the area and the name of his property "Fleetwood" which he took possession of in 1882. He grew potatoes as his main income and was the first farmer to use fertiliser to increase his crops quantity. He died in 1924 and is buried in the Korumburra cemetery. This item is engraved with his name and name of his property. The lancet was sold by Sears and Roebuck and is seen in the 1902 catalogue. Made of brass and steel and manufactured by Joseph Rodgers and sons. The item is called a lancet but is also known as Horse Flem and was used for bleeding horses to remove bad blood. This object is of historic and scientific importance as it was used by a local potato farmer, Robert Cornall of Kardella as a bleeding tool for his horses. When purchased this item would not have been engraved. This item is engraved with the name Robert Cornell 1886 and reverse Fleetwood Gippsland Korumburra. Fleetwood was the name of his property which he settled in 1882.Bleeding of horses during this period was a way of removing bad blood.lancet -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumScales, Weighing
... unknown material 00222.5 : Steel fulcrum rod - Possibly... : Steel fulcrum rod - Possibly manufactured by Aldo Gios. Scales ...Metal suspension scales. Very rusted. 00222.1 : Metal arm - brass 00222.2 : Forked handle - brass. 00222.3 : Larger dish - of unknown material, has a broken piece 00222.4 : Smaller dish - 0f unknown material 00222.5 : Steel fulcrum rod - Possibly manufactured by Aldo Gios.weighing scales, goldfields, chinese, buckland valley -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Uniform - GERMAN MILITARY ARMY HELMET
... The World War II German steel combat helmet...The World War II German steel combat helmet ...The World War II German steel combat helmet was manufactured in 3 different variations. The first model which appeared in 1935 (M35) was a sophisticated craftwork and the M40 was an improved version. The last model, the M42 was simplified to make it faster and easier to manufacture larger numbers of helmets to compensate the huge losses of helmets during the last years of the war. The number refers to the year eg. M40 = 19407296. German Military Army Helmet. Damaged. Cracked and holed in the crown. No webbing or straps. -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTool - Metal Files, c. 1920
... of the building for 34 years. Files are ‘Cup Brand’ – ‘Best refined steel... of the building for 34 years. Files are ‘Cup Brand’ – ‘Best refined steel ...Selection of metal files used for cutting wool bale stencils with an accompanying box. Not all files belong to this box as some are too long to fit within. Used in Denny’s Lascelles Bow Truss building by Maurice Dalton who was the foreman of the building for 34 years. Files are ‘Cup Brand’ – ‘Best refined steel files’ and were manufactured by the no longer trading Moss & Gamble Brothers LTD at the Franklin works in Sheffield, England.12 steel files of varying length, thickness and shape. The longest and thickets are in a flat half circle with some files being fully flat, others complete cylinders, one is a complete square and others are in the shape of a triangle. Cardboard box is brown with black inscription on lid of box.stencils, denny’s lascelles bow truss building -
 Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub BranchEquipment - Binoculars, WW1 Binoculars, World War 1 era
... World War 1 era black coloured brass and steel 5x50 field... black coloured brass and steel 5x50 field binoculars ...World War eraWorld war 1 eraWorld War 1 era black coloured brass and steel 5x50 field binoculars, manufactured by Jagdglas Voigtlander in Germany. The front lens has an extendable metal shade cover. The binoculars body and extendable shade covers have a leather-look embossed pattern. Three brass pieces hold the two sides of the binoculars together and mounts the circular plastic turnbuckle that allows the binoculars to be adjusted. The two rear eye pieces are black plastic.Jagdglas Voigtlander 5x The left barrel of the binoculars has the markings 6 W and the broad arrow.binoculars, world war 1, germany, 5x50, military -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Luke Group, 1959
... made badges and manufactured items for the Armed Forces during... Manufacturing - stainless steel products and hospital equipment, Luke ...K.G. Luke had a foundry in Queen's Parade, Melbourne which made badges and manufactured items for the Armed Forces during the First World War. He bought 40 acres of cherry orchard in Mitcham in 1952 from a Miss Cook, then went to England and attracted finance from Singer Brass Founders. The company became Luke and Singer. The three factories on site were Luke Manufacturing - stainless steel products and hospital equipment, Luke and Singer - a non-ferrous foundry producing components for industry such as nuts and cutlery, and Concentric Engineering - machinery components. Later the manufacture of refrigeration and air conditioning was added at the rear of the complex. A small aerial photograph and 2 A4 photocopies of the K.G.Luke Group of companies in 1959. The factory site is divided into three groups with Whitehorse Road situated at the bottom of the photo and Cook Road Mitcham to the left. Notes at ND6245luke manufacturing, k.g.luke group, luke and singer, concentric engineering, wheatland, vic, manufacturing industry, foundries, engineering industries -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Auger, Robert Sorby, First half of the 20th Century
... , they also diversified into the manufacture of crucible steel..., they also diversified into the manufacture of crucible steel ...A scotch eye auger is perfect for quickly making holes in dry or wet wood for making chairs, stools, and any number of woodworking projects. The scotch eye serves as a peg gauge and whatever peg you make to go into the hole should fit into the augers eye. Robert Sorby & Sons: The forbearer's of Robert Sorby had been cutlers in the Sheffield region of England, dating from the mid 17th century. Robert Sorby and Sons were registered in Sheffield in 1828 as a manufacturer of edge tools, saws, scythes and hay knives. In addition to manufacturing tools, they also diversified into the manufacture of crucible steel for tool manufacture. From circa 1860-1967, the Sorby factory in Sheffield was known as the “Kangaroo Works”. The Kangaroo Brand of tools was made by Robert Sorby & Sons. During the 19th century, they had a large trade in Australasia. By the early 20th century, they were manufacturing carving tools, planes and plane irons, circular saws, wood saws, butchers saws and cleavers, garden tools, pruning knives, coopers’ knives, bricklayers tools and joiners tools. In 1923 Robert Sorby & Sons was bought by Sheffield company Hattersley and Davidson. They are today one of the few remaining British tool manufacturers.The company has a long tradition of making edged tools for various uses and exporting them to Australia, however the subject item was probably made from the early 20th century up until 1967 when the company stopped exporting to Australia.Scotch Eye Auger, Double Twist with Lead Screw, square shaft, socket set at right angleRob Sorbey Sheffield stamped on shaft with Kangaroo trade markflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ring auger, carpenders tools, hole drilling, rob sorby & sons -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional Object - Cap Badge, Stokes & Sons Melbourne, "17 Conductor", 1905?
... a manufactured and steel plate, nickel plated to indicate the staff... number "17" Made from a manufactured and steel plate, nickel ...Cap or arm Badge for the Electric Supply Co. of Victoria (ESCo) "Conductor" with conductor staff number "17" Made from a manufactured and steel plate, nickel plated to indicate the staff number position held by the wearer as part of their uniform. Letters and number stamped, with horizontal lines. At each side of the badge are vertical holes through which light leather straps have been fixed with button holes to enable securing the badge on an arm. Leather straps black on one side and tan on the other. On the rear, silver soldered on are two loops at each end of the badge to enable badge to be sewn or fitted with clips onto the cap or the uniform. Badge appears in some photos of ESCo staff in the 1900's. On the back of the back of the badge in letters is the name of the manufacturer - "Stokes & Sons". Stored within tissue paper, within a heavy cardboard, Kodak Photo paper box.tramways, trams, cap badge, hat badge, uniforms, badges, esco -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Education, Pen Nibs ' R. Esternbrook Co. Ltd, 20thC
... in the United States to manufacture Steel Pens. In 1856 R.Esterbrook... in the United States to manufacture Steel Pens. In 1856 R.Esterbrook ...Dip pens emerged in the early 19th century, when they replaced quill pens. They were generally used prior to the development of fountain pens in the later 19th century, and are now mainly used in illustration, calligraphy, and comics. A nib pen usually consists of a metal nib with capillary channels like those of fountain pen nibs, mounted on a handle or holder, often made of wood. Other materials can be used for the holder, including bone, metal and plastic. Generally speaking, dip pens have no ink reservoir; therefore the user has to recharge the ink from an ink bowl or bottle in order to continue drawing or writing. Birmingham, England was home to many of the first dip pen manufacturers. John Mitchell pioneered mass production of steel pens in 1822; prior to that the quill pen had been the most common form of writing instrument. His brother William Mitchell later set up his own pen making business in St Paul's square. The Mitchell family is credited as being the first manufacturers to use machines to cut pen nibs, which greatly sped up the process. Germany 1842 began at the factory of Heintze & Blanckertz in Berlin By 1860 there were about 100 companies making steel nibs in Birmingham, but 12 large firms dominated the trade. Dip pens are rarely used now for regular writing, most commonly having been replaced by fountain pens, rollerball pens, or ballpoint pens. However, dip pens are still appreciated by artists, as they can make great differences between thick and thin lines, and generally write more smoothly than other types of pens. Dip pens are also preferred by calligraphers for fine writing. Richard Esterbrook was a Cornish Quaker from England who saw an opportunity in the United States to manufacture Steel Pens. In 1856 R.Esterbrook traveled to the US to set up shop as 'The Steel Pen Manufacturing Company' where Richard made these steel pens by hand using special tools and machines (mostly that Richard had to invent). In 1858 he was able to establish himself as the sole pen manufacturer in the USA and he changed the company name to 'The Esterbrook Steel Pen Mfg. Co.' The company settled down in Camden, New Jersey. Quality was a key factor in his success. His steel pens were versatile, long lasting, and came in many different styles to fit the varied writing styles of the public. Sadly, Richard Esterbrook didn't see the 'empire' his company was to become as he passed away in Atlanta on October 12th 1895 . in 1896 they started an Esterbrook branch in England to join the ranks of the other main pen manufactures in Birmingham . In 1912 the company had gotten so large that they erected a 5 story building, just to continue manufacturing pens. By 1920 the fountain pen was fast becoming more popular amongst people who were tired of 'dipping.' To meet this demand the company manufactured its first fountain pen. In 1930 the company sought less expensive means of manufacturing pens because gold and 'jewel' tips were too expensive and in this same year they began selling fountain pens in England . The Esterbrook Company began using the metal Iridium which they called 'Durachrome.' To meet the fountain pen demand the company reformed as 'The Esterbrook Hazel Pens Ltd.' In 1940 war had come to strike a blow at the Esterbrook company. On November 19th 1940 their England location was hit by an incendiary bomb destroying half of the location! To make matters worse, when putting out the fire using a human water bucket chain, someone accidentally grabbed a bucket of paraffin and set the place further ablaze. Oddly enough, the company was able to rebuild the structure during the war. However, the government had placed a stipulation that 50% of its capacity was to be used for government related purposes. In 1947 the company bought out John Mitchell and the American branch had already acquired Hazel Pen Co. The company re-formed again as 'The Esterbrook Pen Company.' This is the last company name the dip pen nibs were manufactured under. A box of Steel dipping nibs for writing pensOn Box; Photo of man / R. Esternbrook Co. / PENS / PROBATEsteel nibs, writing pens, education, schools, writing, caligraphy, artists, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, dip pens, inkwells, fountain pens, mitchell john, birmingham england, esternbrook richard, maple barbara -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePen Nibs, 1920's
... in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen... in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen ...The two cards of nibs are retail display cards of the dip pen nibs that William Mitchell Calligraphy produced, dating back to around the 1920’s, which was the time of the Great Exhibition in the UK. At that time dip pens with steel nibs were the main writing instruments. British Pens Ltd. had recently formed as a company and its subsidiaries included the the company William Mitchell, which is why British Pens Ltd. is named on the cards as well. One card (1) has the Round Hand nib, which is widely used today for calligraphy scripts. The other card (2) has the Script nib that has round upturned points for monocline or unshaded lettering that is also used for calligraphy. The nibs also have a detachable reservoir. The pen nibs are shaped to fit into a slot in the base of a wooden or Bakelite pen holder. The hole at the front of the nib is for collecting ink from a well, which is then stored in a reservoir at the back of the nib. The nibsare stamped with their nib size and Pedigree (what type of nib it is) and maker’s details. William Mitchell Calligraphy still makes these nibs today with a slightly difference finish. (ref: Sales and Marketing Director of William Mitchell Calligraphy in 2016). HISTORY of the Ink Pen Quills and ink were common writing tools until the early 19th century when the pen trade began mass producing steel nibs and pens. The steel nibs each have a hole in the middle that acts like a well for the ink. When the nib is dipped into the ink well the writer needs to ensure that it is dipped to only just past that well. India Ink was one of the most popular inks used with the nib pens, notable for its satin-like smooth flow. This ink is composed of a particularly fine carbon mixed with water; it can also be obtained as a dry stick that is then crushed and mixed with water as required. The Jewellery Quarter of Birmingham had the largest concentration of independent jewellers in Europe. Birmingham became the centre of the world’s pen trade for many years -, during the 1800’s over 100 factories, employing 1000s of skilled workers, manufactured the ‘Birmingham Pen’. ABOUT WILLIAM MITCHELL CALLIGRAPHY LTD.* (*The following text is quoted from the William Mitchell Calligraphy website) British based William Mitchell Calligraphy has been designing and manufacturing exceptional pens for almost 200 years. The William Mitchell heritage in making pen nibs began whilst working with his brother John Mitchell in the early 1820s. William Mitchell established his own business in 1825 to become one of the leading nib manufacturers and famous for lettering pens. Almost 100 years later William Mitchell merged with Hinks, Wells & Co, another pen manufacturer, to form British Pens, employing around 1000 people in the Bearwood Road area of Birmingham. During the early 1960s British Pens acquired the pen business of other pen manufacturers Perry & Co and John Mitchell, once again reuniting the two brothers. Joseph Gillott, who were famous for their artist drawing and mapping nibs, amalgamated with British pens in 1969. William Mitchell and Joseph Gillott established in Birmingham during the early part of the nineteenth century and [their products] are still proudly made here. British Pens were subsequently purchased by its current owner Byron Head, the owner of William Mitchell (Sinkers) in 1982, and was subsequently renamed William Mitchell (calligraphy) Ltd. Established in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen nib manufacturing. The company was particularly strong in the American market, prompting Elihu Burrit, the American consul, to write “In ten thousand school houses across the American continent between two oceans, a million children are as familiarly acquainted with Joseph Gillott as with Noah Webster” (The compiler of the famous American dictionary). The company consequently received visits from many notable Americans, including president Ulysses S Grant. The early 19th century invention and mass production of pen nibs such these in our collection had a large impact on education and literacy because the nibs could be produced in great numbers and affordable prices.Pen nibs; 2 cards of steel dip pen nibs from the 1920’s. The steel nibs are attached to cards by 2 rows of entwined cotton cord. Reverse sides of cards have some hand written marks. Manufacturer; William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. Card issued by British Pens Ltd. Nibs have shaped ends, a hole in the centre with a well on the underside, and the tops are shaped approximately quarter circle. Inscriptions are pressed into each nib. The script pens have detachable reservoirs made of a metal different to the nib. (Card 1) Round Hand Pens, 11 nibs remain from card of 12. Printed on card “Round Hand Pens for Beautiful Writing, Twelve degrees of point, Square points. William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. This card is issued by British Pens Ltd. MADE IN ENGLAND” Also printed on top left of card is a pen drawing of a person writing at a desk, background of decorative 3-paned window in brick wall. (Card 2) Script Pens; 11 nibs remain from card of 12. “Script pens fitted with detachable reservoir. William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. This card is issued by British Pens Ltd. MADE IN ENGLAND” Also printed on top right of card is a pen drawing of a person writing at a desk, background of decorative 3-paned window in brick wall. On Card 1, - each nib is stamped with its size, and “Wm MITCHELLS / PEDIGREE / ROUND HAND / ENGLAND” - hand written on front bottom of card in ball point pen “Lettering 5 times size of nib” - hand drawn on back of card in red and blue ball point pen are scribbled lines On Card 2 - each nib is stamped with its size, and “WILLIAM / MITCHELLS / SCRIPT PEN / ENGLAND” - a black circle corresponding to the nib is printed on the card above each nib. - hand written on back of card in black felt tip pen are numerals - hand drawn on back, 4 parallel lines in red ball point pen with the numbers “10” between 2 of the lines flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, william mitchell calligraphy ltd, british pens ltd., pen nib, writing implement, dip pen, round hand nib, script nib, birmingham manufacturer, communication in writing, mass produced pen nibs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNibs & box, late 19th to early 20th century
... in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen... in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen ...Box of dip pen nibs made by William Mitchell Calligraphy dating back to late 19th or early 20th century when dip pens with steel nibs were the main writing instruments. The pen nibs are shaped to fit into a slot in the base of a wooden or Bakelite pen holder. The hole at the front of the nib is for collecting ink from a well, which is then stored in a reservoir at the back of the nib. The nibs are stamped with their nib size and Pedigree (what type of nib it is) and maker’s details. William Mitchell Calligraphy still makes these nibs today with a slightly difference finish. (ref: Sales and Marketing Director of William Mitchell Calligraphy in 2016). HISTORY of the Ink Pen Quills and ink were common writing tools until the early 19th century when the pen trade began mass producing steel nibs and pens. The steel nibs each have a hole in the middle that acts like a well for the ink. When the nib is dipped into the ink well the writer needs to ensure that it is dipped to only just past that well. India Ink was one of the most popular inks used with the nib pens, notable for its satin-like smooth flow. This ink is composed of a particularly fine carbon mixed with water; it can also be obtained as a dry stick that is then crushed and mixed with water as required. The Jewellery Quarter of Birmingham had the largest concentration of independent jewellers in Europe. Birmingham became the centre of the world’s pen trade for many years -, during the 1800’s over 100 factories, employing 1000s of skilled workers, manufactured the ‘Birmingham Pen’. ABOUT WILLIAM MITCHELL CALLIGRAPHY LTD.* (*The following text is quoted from the William Mitchell Calligraphy website) British based William Mitchell Calligraphy has been designing and manufacturing exceptional pens for almost 200 years. The William Mitchell heritage in making pen nibs began whilst working with his brother John Mitchell in the early 1820s. William Mitchell established his own business in 1825 to become one of the leading nib manufacturers and famous for lettering pens. Almost 100 years later William Mitchell merged with Hinks, Wells & Co, another pen manufacturer, to form British Pens, employing around 1000 people in the Bearwood Road area of Birmingham. During the early 1960s British Pens acquired the pen business of other pen manufacturers Perry & Co and John Mitchell, once again reuniting the two brothers. Joseph Gillott, who were famous for their artist drawing and mapping nibs, amalgamated with British pens in 1969. William Mitchell and Joseph Gillott established in Birmingham during the early part of the nineteenth century and [their products] are still proudly made here. British Pens were subsequently purchased by its current owner Byron Head, the owner of William Mitchell (Sinkers) in 1982, and was subsequently renamed William Mitchell (calligraphy) Ltd. Established in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen nib manufacturing. The company was particularly strong in the American market, prompting Elihu Burrit, the American consul, to write “In ten thousand school houses across the American continent between two oceans, a million children are as familiarly acquainted with Joseph Gillott as with Noah Webster” (The compiler of the famous American dictionary). The company consequently received visits from many notable Americans, including president Ulysses S Grant. Email on file, from Mike Chappell, Sales and Marketing Manager, William Mitchell Calligraphy, “20161122 - William Mitchell re pen nibs” How to use a dip pen to create modern calligraphy, https://thepostmansknock.com/how-to-use-a-dip-pen-to-create-modern-calligraphy/ India Ink, Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/India_ink birmingham Pen Trade, Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birmingham_pen_trade The Pen Museum, http://penmuseum.org.uk/ The early 19th century invention and later mass production of pen nibs such these in our collection had a large impact on education and literacy because the nibs could be produced in great numbers and affordable prices.Box of patent Mitchell nibs containing 48 "Pedigree" nibs. Box depicts picture of William Mitchell on lid, and picture of nib pen on lid and side. Made in Birmingham, England. Nib “0505 Wm MITCHELLS PEDIGREE ENGLAND” Box “PEDIGREE / MAINFOLD SLIP”, “WILLIAM MITCHELL / BIRM - - - - - - LOND” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, william mitchell calligraphy ltd, pen nib, writing implement, writing accessories, dip pen, birmingham manufacturer, communication in writing, mass produced pen nibs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSteel Sample, ca. 1876
... bending of steel in a press or through rollers is the typical... bending of steel in a press or through rollers is the typical ...The sample of steel from which the S.S. Julia Percy’s boiler was made has been tested, according to the attached label. The test involved heating the steel to blood red temperature (or dark red colour) then dipping it into water and bending it when it was cold. A “very severe test for quality” was written on the ticket by T.H. Osborne. (Mr Thomas Hamilton Osborne was the secretary for the Western Steam Navigation Co, established in Warrnambool in 1886. The company’s office was on the corner of Timor and Liebig Streets in Warrnambool and its north-western wall is now part of the current Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery. ) Cold bending of steel in a press or through rollers is the typical method of curving steel for construction. The steel needs to be manufactured in such a way that it is strong enough yet still flexible enough not to crack when bent or rolled. The boiler on the Julia Percy could have been a Scotch Boiler, a design introduced in the 1870’s and still being used today. This design was more robust that previous boilers, generating higher working steam pressures. The design incorporate greater ability to roll iron plates, leading to greater strength, thicker plating and fewer riveted joints. They were originally made of iron then later incorporated steel sections until they were entirely constructed of steel. Many examples of this type of boiler can be found on wreck sites. Shipping was the cheapest and most practical means of carrying produce and goods during the period 1840-1890. Regular domestic steamer services commenced in the Warrnambool district in the late 1850’s and by 1870 the passenger trade was booming. Produce was loaded from the jetty into ‘lighters’ (small boats), which took it to the ships at anchorage in the bay. Passengers were taken to the ship’s side then climbed aboard up ladders or gangways. The coming of the railway in October 1889 meant the gradual decline and end of the steam shipping era. Originally the ship was known as the SS Julia Percy and was later renamed as the Leeuwin. She was an iron passenger-cargo steam ship built in Glasgow by Thomas Wingate for the Warrnambool Steam Packet Company, which commissioned the ship for the steamship trade in Victoria’s western district. She was first registered in Warrnambool, Victoria in 1876. At one point in time the Julia Percy would sail from Warrnambool to Melbourne every Friday and return from Melbourne to Warrnambool every Tuesday. The cost of a return ticket for a Saloon Fare was £1.0.0. She would sail “if practical and weather permitting”. The Julia Percy changed hands several times. Her next owner was the Western Steam Navigaiton Co of Melbourne (1887). It was the manager of this company, Mr. T.H. Osborne, who tagged ths steel sample above. Melbourne Steamship Co became the next owners (1890), followed by William Howard Smith and Sons (1901) for use in Queensland coastal trades, then she was bought by George Turnbull in 1903 and used for local mail contract in Western Australia. She was sold to the Melbourne Steamship Company Ltd. (1906) and re-named the Leeuwi but continued in her Western Australian coastal run. She was converted into a coal hulk in Melbourne in 1910 as a result of damaged caused when she was driven against the jetty at Dongara during a gale. The ship was eventually dismantled and scuttled in Bass Strait on 28 December 1934. The steel sample is significant for its association with the wreck of the Leeuwin (Julia Percy), which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. It is historically significant for being a rare artefact that has potential to interpret aspects of western Victoria’s 19th century steamship trade and Victorian cultural history, including the testing and manufacturing process associated with steam power. Leeuwin is listed on the Victorian heritage Register as being historically significant ‘as one of only four wrecks of steamships in Victorian waters associated with the western district of Victoria’s coastal steamship trade. Her registered number is VHR S413. A sample of the steel from which the boiler of the "SS Julia Percy" (later named Leeuwin) was made. The piece of steel is a ‘C’ shape with the ends almost meeting. A luggage ticket is tied onto the steel and has an inscription on it. The steel is rusty.Ticket with typed information “Steel of which the Boiler of the “Julia Percy” (Warrnambool Steam Navigation Co) was made. TEST: Made Blood hot or Dark Red then dipped into water and bent cold. A very severe test for quality T.H. Osborne. Below these words is the hand written inscription in black “FM 151 / 9.75” julia percy, leeuwin, steel, boiler, steam ship, metal testing, western steam navigation co., flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, t.h. osborne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Working Plane, Mathieson and Son, 1880-1900
... class and were also engaged in the manufacture of steel, file... class and were also engaged in the manufacture of steel, file ...A Mathieson & Son History: In 1792 John Manners had set up a workshop making woodworking planes at 14 Saracens Lane Glasgow. He also had employed an apprentice Alexander Mathieson (1773-1851). But in the following year at Saracen's Lane, the 1841 census describes Alexander Mathieson as a master plane-maker now at 38 Saracen Lane with his son Thomas Adam working with him as a journeyman plane-maker. Presumably, Alexander must have taken over the premises and business of John Manners. Now that the business had Thomas Adam Mathieson working with his father it gradually grew and became more diversified, and it is recorded at the time by the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory that by 1847-1848 Alexander Mathieson was a “plane, brace, bit, auger & edge tool maker.” In 1849 the firm of James & William Stewart at 65 Nicolson Street, Edinburgh was taken over and Thomas was put in charge of the business, trading under the name Thomas A. Mathieson & Co. as plane and edge-tool makers. Thomas's company went on to acquire the Edinburgh edge-tool makers “Charles & Hugh McPherson” and took over their premises in Gilmore Street. In the Edinburgh directory of 1856/7, the business is recorded as being Alexander Mathieson & Son, plane and edge-tool makers at 48 Nicolson Street and Paul's Work, Gilmore Street Edinburgh. The 1851 census Alexander is recorded as working as a tool and plane-maker employing eight men. Later that year Alexander died and his son Thomas took over the business. Under the heading of an edge-tool maker in the 1852/3 Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory the firm is now listed as Alexander Mathieson & Son, with further entries as "turning-lathe and vice manufacturers". By the early 1850s, the business had moved to 24 Saracen Lane. The directory for 1857/8 records that the firm had moved again only a few years later to East Campbell Street, off the Gallowgate area, and that through further diversification was also manufacturing coopers' and tinmen's tools. The ten-yearly censuses report the firm's growth in 1861 stating that Thomas was a tool manufacturer employing 95 men and 30 boys; in 1871 he had 200 men working for him and in 1881 300 men. By 1899 the firm had been incorporated as Alexander Mathieson & Sons Ltd, even though only Alexander's son Thomas appears ever to have joined the firm so the company was still in his fathers' name. In September 1868 Thomas Mathieson put a notice in the newspapers of the Sheffield & Rotherham Independent and the Sheffield Daily Telegraph stating that his firm had used the trade-mark of a crescent and star "for some time" and that "using or imitating the Mark would be proceeded against for infringement". The firm had acquired its interest in the crescent-and-star mark from the heirs of Charles Pickslay, the Sheffield cutler who had registered it with the Cutlers' Company in 1833 and had died in 1852. The year 1868 seems also to be the one in which the name Saracen Tool Works was first adopted; not only does it figure at the foot of the notice in the Sheffield press, it also makes its first appearance in the firm's entry in the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory in the 1868/9 edition. As Thomas Mathieson's business grew, so too did his involvement in local public life and philanthropy. One of the representatives of the third ward on the town council of Glasgow, he became a river bailie in 1868, a magistrate in 1870 and a preceptor of Hutcheson's Hospital in 1878. He had a passion for books and was an "ardent Ruskinian". He served on the committee handling the bequest for the setting up of the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. When he died at Coulter Maynes near Biggar in 1899, he left an estate worth £142,764. Company's later years: Both Thomas's sons, James Harper and Thomas Ogilvie were involved in the continuing life of the firm. James followed in his father's footsteps in becoming a local public figure. He was appointed Deputy Lieutenant of the County of the City of Glasgow and was made a deacon of the Incorporation of the Hammermen of Glasgow in 1919. His brother Thomas Ogilvie was recorded as tool manufacturer and employer in the 1911 census. Thomas Ogilvie's son Thomas Alastair Sutherland Ogilvie Mathieson was born in 1908 took a rather different approach to engineering, however, by becoming a racing driver. In 1947 he wed the French film actress Mila Parély. The firm had won many awards at world fairs for their goods. At the Great Exhibition, London, 1851. Prize medal for joiners' tools in the class of Cutlery & Edge Tools, Great London Exposition, 1862. Prize medal honoris causa. International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1880. Gold medal International Exhibition of Industry, Science and Art, Edinburgh, 1886. Prize medal James Howarth & Sons History: James Howarth and Sons, of Broomspring Works, Bath-street Sheffield were among leading manufacturers of edge tools and joiners tools. The business was commenced in 1835, by James Howarth who was joined by his sons in 1863. Howarth manufacture light and heavy edge tools of all kinds, including a variety of joiners’ tools, hammers, skates, augers. The firm soon was extended and began exporting their products to the USA, Canada, Australia, China, and many other overseas destinations as well as to the home market. They were exhibitors at the London Exhibitions of 1851 and 1862, and Paris in 1855, receiving awards. Howarth was primarily operating from Sheffield. J Howarth & Sons produce goods of a very high class and were also engaged in the manufacture of steel, file, saw, and similar trades. Upon the death of James Howarth, the firm was managed by his four sons James, Samuel, Edwin, and John Howarth. The firm was discontinued in 1913, and its trademark was acquired by Robert Sorby and Sons in 1922.A significant tool made in the late 19th century by a known makers and sought after by collectors of vintage wood working tools.Smoothing Plane Coffin type. 2" stamped on one end and Tertius Keen & Co (plane maker.) Blade has James Howarth Warranted Cast Steel Sheffield (maker of blade only.)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Cassiterite
This specimen is Cassiterite in Quartz. Cassiterite is a tin oxide metal that forms in thin crystals which can have a beautiful lustre. Quartz is made of silicon dioxide, also known as silica, and is one of the most common minerals on earth. Cassiterite has been a fundamental source of tin ore for humans throughout history, including today. Tin is an important metal that has a wide variety of human uses in different areas, from dying fabric, to making mirrors, and their most well-known use ‘tin’ cans. Tin cans are primarily made of steel and are coated with tin in order to take advantage of tin’s property of being non-corroding. This is a massive step in the history of food preservation. Tinned food first reached Australia in 1815 with early settlers, and it began to be manufactured here in the 1840s. It was incredibly popular, and was a highly exported product, which would be a contributing factor to the ‘tin mining boom’ of the early 1880s. This specimen was collected at Jingellic, New South Wales, in about 1852. Although the Goldfields of the 1800s are much more well-known, tin mines existed alongside the gold mines which began in the mid 19th century and extended almost one hundred years, to the mid 20th century. Specimens like this would have been used as evidence to justify tin mining operations in the region as an investment. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. The Geological Survey of Victoria was headed by British geologist, Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn (1824-1902), who was responsible for issuing over 60 geological maps during his 17 years as director. These maps were all hand-drawn and coloured and became the benchmark for accuracy for geological mapping. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A fist-sized solid geological specimen made on one half of tin oxide, which is dark grey, and on the other side of silica, which is brown and cream.burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Leg Vice, Mid 19th Century
The blacksmith leg vise is also called the "solid box vise" and is one of the most important tools in the blacksmith's shop. It firmly holds hot iron while it is hammered, chiseled, or twisted. These are the only vises that are designed to take this kind of use day in and day out. A small 30-pound blacksmith's vise can survive pounding that would wreck a much heavier cast iron bench model. Three things make a blacksmith's vice special. One is that they are forgings, not cast iron or ductile iron. The second is the leg that provides support to the floor or from a sunken post. The last is the hinge, while not a perfect way to construct a vice the pin joint is durable and can take a considerable beating. If sheared it is easy to replace. These things all combine into a tool that can take decades of heavy use and abuse. Most in use is one to two hundred years old.Some of these vises were made by specialists such as Atwood of Stourbridge England, Steel City and Columbian in the U.S. and others were made in anvil manufacturing plants such as "Mousehole Forge" and "Peter Wright" in England and "Fisher-Norris" and others in North America. The design of these vises right down to the last chamfer seems to have been perfected in the 1600s and remained more or less the same until the 20th century. The bodies are forged wrought iron or mild steel and they have hard steel surfaces welded into the jaws. The jaws have little or very shallow serrations which are generally worn off.Around the turn of the 20th Century during the hey-day of the blacksmith shop in North America, these tools were considered so standard a commodity that they were sold without reference to the manufacturer. Very few were even marked with the maker's name. Size is best defined by weight as there is some variation in jaw size from manufacturer to manufacturer. They were sold by the pound and are still best judged by the pound.A vintage tool used in a Blacksmiths shop during the early 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century. Regarded as a significant into social history of the time.Leg Vice attached with screws to bench via a block of wood. Has large metal pole which practically reaches the floor. Also has a metal device to either tighten or slacken vice.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDrill Press, early to mid-20th century
This post drill press has been made by Melbourne business, Dawn Manufacturing Company. It can be operated manually or by a pulley driven flywheel, with the aid of an engine connected to a power supply. In the late 1800s early 1900s a drill press like this would have been driven by steam from a boiler, the main power source for manufacturer’s power at that time. Dawn’s Golden Anniversary 1917-1967 Catalogue describes this model 611 drill as … “Ruggedly constructed with accurately reamed bearings. The coupling between the main spindle and feed screw engages the full circumference of the spindle, and embraces a ball-bearing thrust race. The pillar, as in all “Dawn Drilling Machines” is a solid bright steel bar, in place of the usual light tubing. Adjustable automatic feed.” And “F. & l. Pulleys extra, if required”. DAWN MANUFACTURING CO. The Dawn Manufacturing Co. was founded in Coburg, Melbourne, in 1917 by the four Blake brothers, who were all engineers. After World War I Dawn was supplying drills Australia wide and the company was growing at a healthy rate. During the depression they remained busy, with employees working 60-80 hour weeks. Dawn was contracted to supply vices and clamps to the Australian Defence Department and munitions factory during the World War II. - 1959 the company was taken over by G.N. Raymond Group. - 1967 the Dawn Manufacturing Co. had distributors in Australia and overseas, including USA, Canada, New Zealand, Asia and the Middle East. - 1973 the Siddons Ramset Limited acquired Dawn. - December 1991, Dawn became a unit of the United States owned Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. - November 1998 Dawn became 100 per cent Australian owned. The drill is a typical tool of a blacksmith, cart wright, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-20th century.Post type drill press machine with gear driven flywheel. Drill press is attached to a post and is fitted with a pulley belt and will run at a speed of maxim 200 r.p.m. The machine can also be manually operated. It has an aperture in the centre, a chuck, for the drill bit and has two metal handles at the centre, on the right hand side. Gear ratio 2:1 main drive, 6" diam, 3:1 reduction gear. Made by Dawn of Melbourne, Australia. Model No. 611, Code No. 9157"DAWN MFG COY”, “MELB. AUSTRALIA", " 611"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, blacksmiths, blacksmith’s drill, blacksmith tools, dawn drill model no. 611, dawn drill code no. 9157, dawn manufacturing coy melbourne, dawn manufacturing coy coburg, dawn post drill, drilling machine, drill with gear driven flywheel, forging tool, metal working tool, post drill, steam powered drill, trade tool, warrnambool district 1900s -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVice, 1800s
A wheelwright’s spoke vice was used to hold the wheel hub firmly while the spokes were hammered into the wheel hub, then the spokes would be joined to the wooden wheel felloe before finally the metal flat tyre, or later the rubber tyre, would be attached to the felloe. A wheelwright’s spoke vice would have been very necessary for blacksmiths circa 1800s-1920s as it would have been used in the manufacture and repair of carts, wagons, coaches and other horse-drawn vehicles. This wheelwright’s spoke vice was once used by Harry Goodall of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. corner of McKinnon and High Streets, Terang. Victoria. Henry Goodall & Sons Henry Goodall (1870-1936) was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The wheelwright’s spoke vice is significant as it demonstrates how blacksmiths or wheelwrights could make new metal rims for wagon wheels for carts, wagons, stage coaches and carriages over a 135 years ago. The machine is a part of our social history as it demonstrates part of the process of making wagon wheels, which played an important part in aiding the continuation of daily transport needs that people had at the time, such as farming, personal transport and commercial activities. The tool is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. Vice; wheelwright’s wheel spoke vice. Manufactured in 1800s. This was once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmith's of Terang. Victoria.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, machinery, wagon wheel, steel rim wheels, henry goodall (1870-1936), terang, wheelwright tool, blacksmith trade, blacksmithing equipment and supplies, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, wheel hub, wheel spoke, wheel felloe, wheel tyre, wheel tire -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood moulding Plane, Auburn Tool Company, 1870 to 1893
Moulding Plane: A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. Auburn Tool Company: The Auburn Tool Company is known to exist from 1864 to 1893. George Casey reorganized the firm of Casey, Clark and Company as a joint-stock company in 1864, under the company name of Auburn Tool Company. The 1865 New York State Census noted the firm as a manufacturer of the plane, plane irons, and skates. The production that year was listed as 30,000 pairs of skates and 35,000 planes along with 25,000 dozen plane irons. The plane irons carried the trademark "Thistle". Both skates and plane irons were made from welded wrought iron and cast steel. The Auburn Tool Company was among the five leading plane manufacturing firms existing in the mid to late 19th century USA. Others were: H. Chapin's Son; Greenfield Tool Company; and Sandusky Tool Company. Auburn Tool Company, with these others, was also a founding member of the Plane Makers Association, organized around 1858 to fix prices. Most of the companies tools were manufactured by prisoners and in 1866 the firm was outbid for prison labour by J M Easterly and Co. After losing the contract with the prison authority they constructed a new building and continued in the plane manufacturing business with private labour. The 1870 US Census reported the firm had 21 machines, driven by water power, employing 66 males, producing annual products valued at us$70, 000. After A. Howland and Company was dissolved in 1874, the Auburn Tool Company again resumed using contract labour at the State Prison until 1877. The Auburn Tool Company merged with the Ohio Tool Company of Columbus, Ohio, on Nov 14, 1893. Although plane manufacturing was continued at Auburn until after 1907, after this merger the firm went under the name of the Ohio Tool Company. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used to make such a unique item. It also gives an insight into how many manufacturing companies bid for the rights to use prison labour to make their products at this time in our history. Decorative wood Moulding, plane Round type Auburn New York. Owner A Neudt Size 14 flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Butter Churn, Malleys Ltd, 1930-1950
This is a steel, bench-mounted, hand-operated (60 rpm) butter churn for making small amounts of butter from cream in the home. It was made by the Sydney firm of Malleys Ltd from the 1930s until the 1950s and came in 3 and 5 quart sizes. Malleys Ltd was established in about 1890 by Francis Malley (1863-1932). This firm was located in the Sydney suburb of Alexandria, in McEvoy Street. They manufactured items for use in the dairy industry, as well as for hardware related to building and plumbing. Many of the Malley dairy products were sold under the "Sunrise" name. Malley retired in 1912. In 1931 there were branches at Parramatta, Hurstville & North Sydney. Butter churns were machines used to produce butter by the violent agitation of separated cream. Depending on the design of the churn, the agitation would be variously achieved by a repetitive thrashing, centrifugal motion or internal paddles. Churns were typically constructed from wood, glass and cast-iron; with tin or steel commonly used for some fixtures. The subject item gives an insight into domestic life where butter was made in the home.Heavy red cast iron base, with a long handle, wooden grip, connected to a shaft along the base, thence, to a cog wheel, and gear, to a second shaft and paddle in a metal basin. Basin has lid, and hole in base with a screw cap to allow the draining of the butter milk. Designed to be placed on a bench, with the handle over the edge. Malleys is written in raised letters on the base, and on the handle, '60 rev. pr. min.'warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, malleys, butter churn, domestic object, dairy machine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Suppository Mould
Before factory production became commonplace in medicine, dispensing was considered an art and pill and suppository machines such as these were a vital component of any chemist’s collection. This mould dates back to the days when the local chemist or apothecary bought, sold, and manufactured all his own drugs and medicines to everybody who lived within the local community. In Victorian times, there was no such thing as off-the-shelf medicine. Every tablet, pill, suppository, ointment, potion, lotion, tincture and syrup to treat anything from a sore throat to fever, headaches or constipation, was made laboriously by hand, by the chemist. Some medicines are formulated to be used in the body cavities: the suppository (for the rectum), the pessary (for the vagina) and the bougie (for the urethra or nose). History Suppositories, pessaries and bougies have been prescribed for the last 2000 years but their popularity as a medicinal form increased from around 1840 - suppositories for constipation, haemorrhoids and later as an alternative method of drug administration, pessaries for vaginal infections and bougies for infections of the urethra, prostate, bladder or nose. Manufacture The basic method of manufacture was the same for each preparation, the shape differed. Suppositories were "bullet" or "torpedo" shaped, pessaries "bullet" shaped but larger and bougieslong and thin, tapering slightly. A base was required that would melt at body temperature. Various oils and fats have been utilised but, until the advent of modern manufactured waxes, the substances of choice were theobroma oil (cocoa butter) and a glycerin-gelatin mixture. The base was heated in a spouted pan over a water-bath until just melted. The medicament was rubbed into a little of the base (usually on a tile using a spatula) and then stirred into the rest. The melted mass was then poured into the relevant mould. Moulds were normally in two parts, made from stainless steel or brass (silver or electroplated to give a smooth surface). To facilitate removal the moulds were treated with a lubricant such as oil or soap solution. To overcome the difficulty of pouring into the long, thin bougie mould, it was usual to make a larger quantity of base, to partially unscrew the mould, fill with base and then screw the two halves of the mould together thus forcing out the excess. When cool, any excess base was scraped from the top of the mould, the mould opened and the preparations removed, packed and labelled with the doctor's instructions. https://www.rpharms.com/Portals/0/MuseumLearningResources/05%20Suppositories%20Pessaries%20and%20Bougies.pdf?ver=2020-02-06-154131-397The collection of medical instruments and other equipment in the Port Medical Office is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century.Proctological mould for making suppositories.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, suppositories, medicine, health -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Suppository Mould
Before factory production became commonplace in medicine, dispensing was considered an art and pill and suppository machines such as these were a vital component of any chemist’s collection. This mould dates back to the days when the local chemist or apothecary bought, sold, and manufactured all his own drugs and medicines to everybody who lived within the local community. In Victorian times, there was no such thing as off-the-shelf medicine. Every tablet, pill, suppository, ointment, potion, lotion, tincture and syrup to treat anything from a sore throat to fever, headaches or constipation, was made laboriously by hand, by the chemist. Some medicines are formulated to be used in the body cavities: the suppository (for the rectum), the pessary (for the vagina) and the bougie (for the urethra or nose). History Suppositories, pessaries and bougies have been prescribed for the last 2000 years but their popularity as a medicinal form increased from around 1840 - suppositories for constipation, haemorrhoids and later as an alternative method of drug administration, pessaries for vaginal infections and bougies for infections of the urethra, prostate, bladder or nose. Manufacture The basic method of manufacture was the same for each preparation, the shape differed. Suppositories were "bullet" or "torpedo" shaped, pessaries "bullet" shaped but larger and bougieslong and thin, tapering slightly. A base was required that would melt at body temperature. Various oils and fats have been utilised but, until the advent of modern manufactured waxes, the substances of choice were theobroma oil (cocoa butter) and a glycerin-gelatin mixture. The base was heated in a spouted pan over a water-bath until just melted. The medicament was rubbed into a little of the base (usually on a tile using a spatula) and then stirred into the rest. The melted mass was then poured into the relevant mould. Moulds were normally in two parts, made from stainless steel or brass (silver or electroplated to give a smooth surface). To facilitate removal the moulds were treated with a lubricant such as oil or soap solution. To overcome the difficulty of pouring into the long, thin bougie mould, it was usual to make a larger quantity of base, to partially unscrew the mould, fill with base and then screw the two halves of the mould together thus forcing out the excess. When cool, any excess base was scraped from the top of the mould, the mould opened and the preparations removed, packed and labelled with the doctor's instructions. https://www.rpharms.com/Portals/0/MuseumLearningResources/05%20Suppositories%20Pessaries%20and%20Bougies.pdf?ver=2020-02-06-154131-397The collection of medical instruments and other equipment in the Port Medical Office is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century.Proctological mould for making suppositories.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, suppositories, medicine, health
