Showing 21 items matching "traveller block"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Breeches Buoy and Traveller Block, 1860s to 1950s
... Breeches Buoy and Traveller Block...traveller block...The breeches buoy and traveller block are part of the beach... for attaching it to the traveller block. Wooden traveller block has... Warrnambool great-ocean-road The breeches buoy and traveller block ...The breeches buoy and traveller block are part of the beach rescue apparatus used by lifesaving crew overseas and in Australia in the 1860s to 1960s. The breeches buoy (or chair bucket or petticoat breeches) were invented by Lieutenant Kisbee by the 1850s. It looks like a pair of canvas shorts with a cork lifebuoy ring attached around the top. The set-up works similar way to a zip wire and allows for two-way travel. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The first use of a lifesaving rocket rescue system is often credited to Captain Manby and his invention of a life mortar, first used in 1808 to fire a line onto a ship to rescue lives. Henry Trengrouse’s invention of 1820 was the first to use a sky rocket’s power to throw a line, and his invention included a chair for carrying the shipwrecked victims to shore. In 1832 John Dennett invented a rocket specifically for shore to ship rescue. It had an iron case and an 8 foot pole attached and could shoot the line as far as 250 yards (about 230 metres). From the 1860s the rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. Colonel Boxer, who had invented an early line-thrower, designed a rocket in 1865 with a range from 300 to 470 yards. It was the first two-stage rocket, with two rockets placed one in front of the other in a tube that carried the rescue line. The hemp line was faked, or coiled, in a particular way in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired, and the angle of firing the rocket was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol around 1920, which used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. Victoria’s Government adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain, which used Colonel Boxer’s rocket apparatus rescue method. The British Board of Trade published instructions in 1850 for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line attached, then firing it across the stranded vessel. A tally board was then sent out with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the continuous whip line and attach the whip block to a mast or sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a heavier hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser is then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rocket system could also be used from one ship to another. This item is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Breeches buoy and traveller lock; white canvas breeches (shorts) with lifebuoy ring attached to its waistband, with ropes for attaching it to the traveller block. Wooden traveller block has double brass inline sheaves and brass rollers on each cheek of the block, and each shell is scored for the strop. The thimble attached to the strop has a wooden slat for quick release of the breeches buoy. The ropes comprise of two equal lengths of rope that have been bunched together to form two loops, then bound together just below the loops, while the four hanging ends are looped around the lifebuoy, equally spaced, with each end finished in an eye-splice. The apparatus is suspended by the loops at the top and attached to the traveller block, which has a quick release device.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, irish hand barrow, government of victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Traveller pulley block, 1860s
... Traveller pulley block...traveller block... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended...Wood and brass pulley block or 'traveller', used... was attached to a traveller block such as this one. The assembly ...The life saving breeches buoy was attached to a traveller block such as this one. The assembly was sent from shore to ship and back to transport the stranded people and goods safely to shore. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them.This traveller block is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost. Wood and brass pulley block or 'traveller', used in conjunction with the Breeches Buoy. The block has double brass inline sheaves and brass rollers on each cheek of the pulley. Each shell is scored for the strop. The thimble on the strop has a wooden slat attached for quick release of the Breeches Buoy. A portion of rope is connected.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, petticoat breeches, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, life jacket, traveller, traveller block, running block, block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, faking board, italian hemp, quadrant, protractor, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, welsh hand barrow, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, government of victoria, harbour master, l.s.r.c., lsrc -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket set, John Dennett, ca. 1860s
... traveller block.... It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended... a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line ...This rescue line-throwing rocket set was made for the Dennett rocket system, which was used by the Rocket Rescue crews in South West Victoria from around the 1860s to the 1890s. John Dennett - John Dennett was from Carisbrooke, in the Ilse of Wight, UK. In 1826 he invented, patented and demonstrated an improved method of rocket powered, line firing rescue equipment for saving lives. The rockets had a longer range than the mortars being used, they were lighter, needed less preparation time, only needed one line for repeated shots, and fewer people were needed to move the equipment. Very favourable reports of Dennett’s rockets were received by those in charge of His Majesty’s Naval and Military services. In 1832, Dennett’s rocket-thrown line was sent out to the wreck of the ‘Bainbridge’, and was responsible for nineteen survivors coming ashore in two boatloads, along the fired line. Dennett’s rocket received national fame, and a one-year contract to supply rockets to the Coastguards. He became known as ‘Rocket Man’ and his rockets were used in rescues at least until 1890, when his son Horatio was running the business. A rocket weighing 23 lb would have a range of about 250 yards (228 metres), on average. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The first use of a lifesaving rocket rescue system is often credited to Captain Manby and his invention of a life mortar, first used in 1808 to fire a line onto a ship to rescue lives. Henry Trengrouse’s invention of 1820 was the first to use a sky rocket’s power to throw a line, and his invention included a chair for carrying the shipwrecked victims to shore. In 1832 John Dennett invented a rocket specifically for shore to ship rescue. It had an iron case and an 8 foot pole attached and could shoot the line as far as 250 yards (about 230 metres). From the 1860s the rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. Colonel Boxer, who had invented an early line-thrower, designed a rocket in 1865 with a range from 300 to 470 yards. It was the first two-stage rocket, with two rockets placed one in front of the other in a tube that carried the rescue line. The hemp line was faked, or coiled, in a particular way in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired, and the angle of firing the rocket was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol around 1920, which used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. Victoria’s Government adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain, which used Colonel Boxer’s rocket apparatus rescue method. The British Board of Trade published instructions in 1850 for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line attached, then firing it across the stranded vessel. A tally board was then sent out with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the continuous whip line and attach the whip block to a mast or sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a heavier hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser is then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rocket system could also be used from one ship to another.The Dennett rocket set is quite rare - there are not many examples in existence and little information is available. This Dennett's rocket set is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.A Dennett rocket set in six parts; the rocket head, three shafts (poles) and two rocket-head toting boxes. The rocket head, mounted on one of the shafts, is a long, red painted, iron tube with rounded ends and a protruding fitting around each end. The wooden rocket shafts are octagonal, with a metal sheath at the ends, carved elongated slots towards each end, and a scribed channel above the black foot. The rocket head toting boxes are thick timber, covered in fabric and painted black. They have a hinged wooden lid that slants downwards from back to front, and a metal closure. Small deliberate holes, in groups of four, on the box’s sides, indicate missing attachments, likely to have been handles. Impressed one a shaft "8"flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, irish hand barrow, rocket head toting box, explosives, rocket shaft, rocket pole -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket Launcher, John Dennett, 1860s
... traveller block... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...This rocket launching machine is used in conjunction with the Dennett Rocket Set. Both are part of the rocket rescue equipment that launches the line-throwing rescue rockets. A light line is threaded through the carved holes in the 8 foot long shaft and attached to the scribed channel at the base of the shaft. The rocket head is fitted to the shaft and inserted into the machine. The machine is set at an angle determined by the person in charge of the rescue crew, and the legs and base of the machine are adjusted accordingly with the use of the quadrant, or protractor, and plumb-bob on the side of the machine. The rocket is then ignited and fired across the vessel in distress. John Dennett - John Dennett was from Carisbrooke, in the Ilse of Wight, UK. In 1826 he invented, patented and demonstrated an improved method of rocket powered, line firing rescue equipment for saving lives. The rockets had a longer range than the mortars being used, they were lighter, needed less preparation time, only needed one line for repeated shots, and fewer people were needed to move the equipment. Very favourable reports of Dennett’s rockets were received by those in charge of His Majesty’s Naval and Military services. In 1832, Dennett’s rocket-thrown line was sent out to the wreck of the ‘Bainbridge’, and was responsible for nineteen survivors coming ashore in two boatloads, along the fired line. Dennett’s rocket received national fame, and a one-year contract to supply rockets to the Coastguards. He became known as ‘Rocket Man’ and his rockets were used in rescues at least until 1890, when his son Horatio was running the business. A rocket weighing 23 lb would have a range of about 250 yards (228 metres), on average. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket launcher machine is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket launcher, named a Rocket Machine, and storage box. Launcher has a long open metal channel with a spike at the base, and narrow, rectangular device, which is the line-firing rocket machine, at the top, all painted blue. Two hinged wooden legs are attached where the channel and machine meet. The side of the machine has an oval cut-out window and an attached quadrant, or protractor, with a plumb-bob on it. The quadrant has angles marked in degrees. The long protective box has white stencilled letters along the side. Its lid has three hinges and is fastened with two metal latches.On box “ROCKET MACHINE” On quadrant “10” “20” “30” “40”flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, protractor, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set -
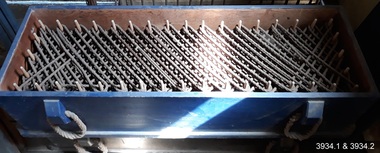 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Line faking box, Government of Victoria, 1860s
... traveller block... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue ...The rocket line faking box with lid has a frame inside with a specifically designed perimeter of faking pegs. The rocket shot line has been faked, or skilful wound, around these pegs to prevent it from tangling. The line is stored in the box, ready for attaching to the line throwing rocket. Some line faking boxes have a false base that is removed before firing the line-throwing pistol, leaving the line to feed out from the box when the rocket is fired. After the line is attached to the rocket the box tilted slightly and faced towards the wreck to allow it to be freely dispatched. The equipment often includes more that one faking box to make allowance for possible errors, broken lines or the need for a heavier line. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket line faking box is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket line faking box with loose fitting lid, painted blue on the outside. Rectangular box has two rope handles within wooden rope holders fixed onto each long side and one at each end. The box has a hook and ring at the base each end for releasing the top from the inserted faking frame. The line faking frame is inside the box. It has seventeen wooden pegs along each long side of the frame and three pegs along each short side. A continuous length of rocket line has been faked around the pegs in a specific pattern.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, beach rescue set, traveller, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, italian hemp, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set, rocket line faking box, faking frame -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Line faking box, Government of Victoria, 1860s
... traveller block... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue ...The rocket line faking box has a frame inside with a specifically designed perimeter of faking pegs. The rocket shot line has been faked, or skilful wound, around these pegs to prevent it from tangling. The line is stored in the box, ready for attaching to the line throwing rocket. Some line faking boxes have a false base that is removed before firing the line-throwing pistol, leaving the line to feed out from the box when the rocket is fired. After the line is attached to the rocket the box tilted slightly and faced towards the wreck to allow it to be freely dispatched. The equipment often includes more that one faking box to make allowance for possible errors, broken lines or the need for a heavier line. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket line faking box is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket line faking box with loose fitting lid, painted black on the outside. Rectangular box has two rope handles within wooden rope holders fixed onto each long side and one at each end. The box has a hook and ring at the base each end for releasing the top from the inserted faking frame. The line faking frame is inside the box. It has seventeen wooden pegs along each long side of the frame and three pegs along each short side. A continuous length of rocket line has been faked around the pegs in a specific pattern.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, beach rescue set, traveller, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, italian hemp, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set, rocket line faking box, faking frame -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Sand anchor, Mid-19th to mid-20th Century
... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block ...The rocket rescue crews used a sand anchor at a beach rescue site to weigh down the rescue apparatus. The crew would connect the steel cables to the connecting cable and then join heavy ropes or chains to the connecting cable. They would then bury the anchor in a trench about three-quarters of a metre deep, keeping the connecting cable’s end free. The length of heavy rope or chain was attached to a pulley block onto the heavy hawser line. The block and a crotch pole were used to keep the hawser line high and taught, keeping the survivors above the sea as they were hauled to shore on a line or in a breeches buoy. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s, the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This sand anchor is part of the rocket rescue equipment and is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.The sand anchor comprises a plank with steel cables and a connecting cable. The rectangular wooden bevelled-edged plank with two pairs of square metal plates bolted through it. Each metal plate has an eyelet and the two steel cable lengths are permanently attached by their eyelets to the plates. The eyelets at each end of the cable lengths are reinforced with rope work and one length also has a ‘U’ bolt shackle connection. The steel connecting cable also has reinforced eyelets at both ends. The plank has a black stencilled inscription on the upper surface. Stencilled in black paint "ANCHOR" "BACKER"flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket equipment, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, whip line, endless whip, harbour board, sand anchor, rocket set, anchor backer, rescue anchor, beach anchor, backer, anchor, steel cable, wire cable, connecting cable -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Sand peg set, Mid-19th to mid-20th Century
... buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block ...This set of Victorian era wooden sand pegs was part of the equipment used by the Rocket Rescue Crew when attending a shipwreck. The broad pegs were designed to give a strong grip on soft sand and soil. The pegs could be used with the sand anchor as well as to give a stronger hold on the tripod holding the hawser. The same design is still available today and is used by the Army and by campers. The rocket rescue crews used a sand anchor at a beach rescue site to weigh down the rescue apparatus. The crew would connect the shackle to the other cable on the anchor and to the loose steel cable to form a triangle with the cable lengths. They would then bury the anchor in about a 0.75-meter trench, keeping the free end of the cable above the surface. This end of the cable was then connected to a block that was attached to the heavy hawser line. The block and a crotch pole were used to keep the hawser line high and taught as the survivors were hauled to shore on a line or in a breeches buoy. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s, the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This set of sand pegs would have been used with sand anchor that is part of the rocket rescue equipment . It is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Peg or spike; set of twelve wooden pegs, painted red. Pages have a long, thick square shank with bevelled side edges, flat top with broad hook on one side of the top and a point at the other end. A small hole goes from one side to the other side near the centre of the shank, on the face without the hook. flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket equipment, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, whip line, endless whip, harbour board, sand anchor, rocket set, anchor backer, beach anchor, backer, steel cable, wire cable, sand peg, wooden tent peg, army peg, military peg -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Water Canteen and Ladle, mid-to-late 19th century
... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block ...The horizontal water canteen has been carefully designed to fit snugly on the hip when worn with the straps diagonally across the body. The ladle allows quick and easy scooping of the contents to refresh the lifeboat and rocket launching crew, and the survivors of the disaster Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. This water canteen is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Water canteen and ladle; blue painted oval metal cylinder with a removable round threaded lid. Two adjustable leather shoulder straps are attached to the canteen through metal rings on the sides of the lid. A blue-painted copper ladle with a fixed, 45-degree angled handle is attached to the canteen with a length of string. The water canteen is designed to be carried horizontally.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, survival canteen, rescue canteen, dipper, cup, canteen and dipper, canteen and ladle, water canteen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Beach cart cover, Government of Victoria, 1860s
... , breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol..., cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing ...The load of heavy beach apparatus life saving equipment was held in place on the beach cart by the hand worked rope net cover. It would be stored in the Rocket House packed and ready to use for practice or rescue. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. This cover was used with the beach cart. The cart is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rectangular rope cover, hand worked for the purpose of covering the beach cart. The cover is made from heavy rope in a pattern that looks similar to crochet. A loop has been worked into each corner.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, beach rescue, rescue equipment, rocket rescue equipment, marine technology, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, stranded vessel, rocket rescue apparatus, beach apparatus, life jacket, rocket shed, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, beach cart, hand barrow, welsh hand barrow, harbour board, government of victoria, harbour master, l.s.r.c., lsrc, rocket house -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Hand Barrow, 1860s
... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...This hand barrow, sometimes called a Welsh hand barrow, was used to transport a load of marine rescue equipment from the beach cart to the rescue site, particularly over hilly, uneven or rough terrain. Hand barrows were in common use in the 19th century. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This hand barrow is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Hand barrow; a transporting device carried between two people walking one in front of the other. A wooden ladder-like frame with two handles at each end, blue painted body with unpainted handles. Seven equal-length slats are joined at equal distance between two parallel poles, and two longer slats are attached diagonally between the first and last slats as a brace. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, hand barrow, manual transport, welsh hand barrow -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Canvas Bag, mid-to-late 19th century
... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block... and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block ...This drawstring canvas bag is amongst the Rocket Rescue equipment. It could have been used to carry equipment, clothing or provisions between the crew on the shore and the victims of a shipwreck or other rescue need. It could be worn on the shoulder or as a backpack or winched out to a vessel on the block and pulley system. The strong canvas could be weatherproof and waterproof to a large extent, provided the drawstring was pulled tight. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in a wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. This canvas bag is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Canvas bag; thick beige canvas bag, cylindrical with a round base. The top has a thin rope in a drawstring closure. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, survival kit, rescue kit, canvas bag, storage bag, carry bag, equipment bag, drawerstring bag -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket Key, John Dennett, c. 1860s
... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...This rocket launcher key was used with the Dennett's Rocket Launcher system to remove the end cap of the Dennett's Rocket to expose the propellant to be fused . Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This rocket launcher key is a necessary part of the equipment for the the rocket launcher, which is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Key, part of the Rocket Rescue equipment. T shaped metal key, round handle across the top and hexagonal shaped shaft and square end. Used to remove the end cap of the Dennett's Rocket to expose the propellant to be fused . Donation from Ports and Harbour.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket house, rocket shed, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, john dennett, rocket key, rocket launcher key, life saving -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Beach cart and cover, Government of Victoria, 1860s
... , cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing... and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand ...The beach cart was hand drawn by a team of six people; two in front, one on each side and two behind. The wide iron tyres on the the wheels helped prevent the cart from sinking into the sand. The load of heavy beach apparatus equipment was held in place by the hand worked rope net cover. It would be stored in the Rocket House packed and ready to use for practice or rescue. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. This cart and cover set is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Beach cart; a blue and white painted, wooden cart with two, red coloured metal wheels. The wheels have twelve spokes and wide iron tyres. The cart has a long draw bar with T- handles at the end. It was pulled by two people, usually steered by another two and pushed by a further two. It was supplied by the Government of Victoria. There is an inscription on the front end panel. The cart has a removable hand worked rope cover. Stencilled in white paint “G of V” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, beach rescue, rescue equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket equipment, marine technology, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, shore to ship, stranded vessel, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, life jacket, rocket house, rocket shed, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, beach cart, hand barrow, welsh hand barrow, harbour board, government of victoria, harbour master, l.s.r.c., lsrc -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Beach Cart, Government of Victoria, 1860s
... and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand... buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach ...The beach cart was hand drawn by a team of six people; two in front, one on each side and two behind. The wide iron tyres on the the wheels helped prevent the cart from sinking into the sand. The load of heavy beach apparatus equipment was held in place by a separate hand worked rope net cover. It would be stored in the Rocket House packed and ready to use for practice or rescue. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. This cart and its matching cover is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Beach cart; a blue and white painted, wooden cart with two, red coloured metal wheels. The wheels have twelve spokes and wide iron tyres. The cart has a long draw bar with T- handles at the end. It was pulled by two people, usually steered by another two and pushed by a further two. It was supplied by the Government of Victoria. There is an inscription on the front end panel.Stencilled in white paint “G of V” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, beach rescue, rescue equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket equipment, marine technology, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, shore to ship, stranded vessel, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, life jacket, rocket house, rocket shed, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, beach cart, harbour board, government of victoria, harbour master, l.s.r.c., lsrc, rope cover, rope net -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Case, Early 20th century
... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...This small case is lined with a metal insert and shows remnants of a carry strap. It could have been used for storing and carrying fuses or cartridges for the life saving Rocket Launcher machine. The protective metal insert would help keep the contents dry or cool and protect from flame. It is part of the collection of rescue equipment in the Rocket House used by the life saving rescue crew. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This small leather carrying case is significant for its connection with the rocket rescue equipment, local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Leather case, brown with contrasting stitching, protective metal insert divided into two compartments. Rectangular shape. Roller buckle on front with remnants of the matching strap. Also remnants of a leather strap on the side, possibly a shoulder strap.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, line throwing cartridge, l.s.r.c., lsrc, leather case, cartridge case, fuse case, ammunition case -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageUniform - Arm Bands, c. 1860s
... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...Members of the Life Saving Rescue Crew would wear scarlet arm bands such as these as part of their uniform, with each member having a different number. The crew would work as a team to haul in the victims of the shipwreck. The leader of the crew would call out one or several member's numbers to give them a break during the rescue, while other members took their place. All members would then be relieved at some time during the rescue. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This set of scarlet arm bands is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Arm bands; three scarlet flannel arm bands with black cotton backing and a metal buckle on one end. White cotton embroidery forms letters and numbers, with each arm band having a different number. Part of the uniform of the Life Saving and Rescue Crew.Embroidered on front "L.S. 1 R.C." "L.S. 8 R.C." "L.S. 13 R.C." flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, arm band, armband, scarlet arm band, l.s.r.c., lsrc, red arm band -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Tally Board, 1860s
... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended... and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended ...The boards each have instructions adhered to each side, printed in four languages (English, French, Dutch and German). At the beginning of a shore-to-ship rescue the instructions are sent to the distressed vessel after the first rocket line was received by them. The stranded people on the vessel follow the instructions to assist the life saving rescue crew in saving their lives. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest themThis pair of tally board is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Tally boards, two, rectangular wooden boards, both with a hole drilled into one short end. Instructions are glued onto the boards. They were printed in light letters onto dark canvas in four languages (English, French, Dutch and German). Text (English) "MAKE THIS HAWSER FAST ABOUT 2 FEET ABOVE THE TAIL BLOCK. CAST OFF WHIP FROM HAWSER. SEE ALL CLEAR AND THAT THE ROPE IN THE BLOCK RUNS FREE, AND SHOW SIGNAL TO THE SHORE."flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, beach apparatus, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, tally board, rescue instructions -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySafe Coolgardie, circa early 1900s
The harsh summer temperatures and the isolated rural environment(of the 1890's) provided the inventor of the "Coolgardie safe" (Arthur Patrick McCormick) with an idea to cool perishable foods by using water soaked "hessian" cloth to provide the "coolant" for the evaporation process to cool the inside temperature of the "safe". Items such as meat,cream/milk/butter and cool "drinks" are a few perishables that need cool environments , especially in isolated "ice free" locations. Cities during this time period had large "ice works" which delivered block ice to all areas that required a form of refrigeration. These ice blocks where held in early refrigerators to keep perishables cool to cold. This "Coolardie" safe was the next best thing for isolated rural households and travellers/campers/stockmen to provide a cooler environment for foodstuff affected by heat. Ice filled "esky" coolers and ice boxes are a modern day off shoot to the original Coogardie safe however they still rely on ice or frozen coolant bricks for cooling.This "Coogardie" safe is very significant to the Kiewa Valley and the Bogong High Plains because it represents not only the initiative thinking of the early settlers and communities but also the "primitive" solution to an everyday (1800s to 1930s) problem (before gas and electric run refrigerators) of keeping "perishables" at a low temperature and thereby prolonging their "shelf" life. This was before electricity and gas was available to the inhabitants of the Kiewa Valley and Bogong High Plains. Another cooling method for food was to have "water tight" containers dipped into the very cold streams running from the "cooler" alpine mountains and the Bogong High Plains. This however could not be carried out in all situations eg. fast flowing currents and locations away from streams. This "Coolgardie safe" is made from a medium grade steel enclosure and its appearance is of a perforated box with a wire handle and one side (long side) being a hinged "door" with a clasp securing "lock". There are air holes grouped into a small "boxed" pattern. Each "box" is divided by a crossed pattern, dividing the "holed" sections(4) into a diamond configuration of 49 small holes each. There are four sides (long) which have the perforations except for the base which does not. The base has an indentation with a loose "catch" tray to catch water spills. When in use the "box" is covered with a water "soaked" cloth. The wet cloth is used as "coolant" ie. fibers in the cloth hold the water droplets seep out evaporating the area and thereby (in mass) cooling the air inside the container.domestic refrigeration cabinets, coolgardie "safe", insect and vermin proof food containers, electric and gas free cold storage containers -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LUCKY ENVELOPE INSERT: BENDIGO TRAVELLERS' CHARITY CLUB, 1963
Lucky Envelope insert - Bendigo Travellers' Charity Club, Easter Effort 1963. Proceeds of 50,000 Lucky envelopes going 60% to Nurses Wing No 2 Block, Bendigo Base Hospital and 40% to air-conditioning Mens Ward, Bendigo Benevolent Home. ''We are sorry you have not won a prize but we thank you for your very generous support''. Support ads printed on front and back - Coca Cola; Cohn's; Gillies.bendigo, clubs, bendigo travellers charity club, bendigo benevolent home, coca cola, gillies, cohn's, bendigo traveller's charity club, bendigo base hospital. -
 City of Melbourne Libraries
City of Melbourne LibrariesPhotograph, Commercial Travellers' Association, Victoria, Board Room
Description: Seven seated and fifteen standing men dressed in suits around a long table in a panelled room hung with formal portraits of men. A trophy sits on the long table amongst loose paper sheets. Research by project volunteer, Fiona Collyer: The Commercial Travellers’ Association of Victoria (CTA) was formed at a meeting of 40 commercial travellers held at the Duke of Rothesay Hotel, 24 Elizabeth Street on 1 December 1880. Their charter was to advocate for better working conditions for commercial travelling salesmen, including improved accommodation at discounted rates and travel concession fares. At first by locomotive, horse and buggy, steamers and horseback, later also by motor car and motorcycle, “The Man on the Road” went into the back-blocks of the country to extend the interests of commerce to the stores and households of Australian regional towns and isolated settlements. Affiliated organisations existed in all states and New Zealand and in 1895 they integrated to form the United Commercial Travellers’ Association of Australasia (UCTAA). By the turn of the 20th century, the Victorian branch of the CTA had 421 Association Members and 520 Club members. The CTA continued to hold meetings in leased rooms in hotels and offices until 1898 when they commissioned purpose-built premises at 190-192 Flinders Street (extant, now the Macstore, next to former Metropolitan Gas Company Buildings). Designed by leading architectural firm of brothers H.W. & F.B.Tompkins (Dimmey’s Model Store, Swan Street, London Stores, Herald and Weekly Times, Myer building, Diamond House, Centreway Arcade, Manton’s Store) in the Queen Anne Revival style at the cost of £20,000, the four storey building had a facade of red Northcote bricks and an entrance of Pyrmont stone. It was very modern for the time, featuring elevators, offices, bars, kitchen, dining, card and billiard rooms and 31 bedrooms with shared bathrooms for the footsore travellers. However, despite adding two storeys in 1901, and another storey and a basement in 1905, they soon outgrew their premises, and in 1912 the CTA commissioned a new building at 328 Flinders Street. At this time, buildings in Melbourne were constrained by the city height limit of 132 feet (40 metres)- the maximum height of firefighting ladders. The new CTA building was the tallest building in Melbourne until 1932 when regulations changed allowing the Manchester Unity Building to be built. The new CTA headquarters was the epitome of comfort and luxury with cutting edge facilities to ease the fatigued salesman and prepare him for another stint on the road. General Secretary, James Davies travelled to Britain and America to acquire the very best and latest innovations. After visiting the new premises, Punch magazine 11 June 1914 reported “furnishings, appliances, and labour-saving conveniences which were more than up to date- they were up to-morrow.” The Edwardian Baroque style building was again designed by architects H.W. & F.B. Tompkins at the cost of £100,000 and built by contractors F.E. Shillabeer and Sons (Nicholas Building, Kellow-Falkiner Pty Ltd car showroom). The nine storey plus basement building is of steel frame construction with concrete floors. The ground floor facade is of grey granite and above that it is faced with cream glazed bricks chosen to combat discolouration from the pollution emitted by Flinders Street Station trains across the road. The facade is decorated with mascarons, gum leaf trim and balconies with classical style balustrade. The club was entered through revolving doors into a two storey high, circular, domed lobby with white columns, American oak panelled walls and intricate mosaic flooring. The ceiling is festooned with plaster gum leaf and gum nut detail, a theme that is repeated throughout the building. The basement kitchen had modern, labour saving appliances that would be the envy of any Edwardian housewife, including an electric toaster, a potato peeling machine, heated dumb waiter, dishwashing machine and electric refrigeration and cooking. It serviced the commodious second floor dining room which seated 200 people and the cafe/breakfast room, 80 people. Members were permitted to entertain their lady friends there for afternoon tea between the hours of 3 and 5 pm every day, except Sunday. The members’ facilities included a barbershop, clothes pressing machine, boot cleaning chair, pipe and cigar stall with electric humidor, public telephones, lockers and safe deposit. The building was serviced with five elevators, a built in vacuum cleaning plant, hot water radiators and linen and postal chutes. The first floor was devoted to business and relaxing, containing the Board, Writing, Reading and four Business Rooms. The board room had Queensland maple panelling with huge blackwood tables topped with blue morocco and golden tortoise-shell trim and cane bottomed chairs. Large framed photographs of past presidents since 1884 lined the walls. The Reading Room ran the whole width of the building. Arthur Streeton’s painting “Between the Lights, Princes Bridge 1888” and Frederick McCubbin’s “Looking North from Mount Macedon” were hung there, as well as paintings by renowned Australian artists Hans Heysen, Walter Withers, John Mather, Jan Hendrik Scheltema. The Argus 30 May 1914 quipped “Around the walls hang evidences that the commercial traveller's soul has not been killed in his pursuit of commerce”. The blackwood panelled room was furnished with Queen Anne style tables and chairs and green leather armchairs with inviting rocker foot rests allowing weary travellers to relax after traversing the railways and dusty roads of Victoria while planning their next sales trip. “The Australasia Traveller” Volume 10, Number 2, April 1914 page 35 noted “An attendant will be constantly employed on this floor to take care of the stationary supply, to tidy up newspapers, and generally study the convenience of members.” The third floor was for amusements with billiards, a bar and four rooms for playing cards, dominoes and chess. The huge billiard room had seven Alcock billiard tables including a table in a partitioned match-room for tournaments, exhibitions and matches. The walls were lined with members’ cues and for spectators, comfortable lounges with marble topped tables and electric bell pushes for drinks service. There were 150 bedrooms over five floors, each with their own telephone and wash basin and five suites with a private sitting room attached. There were four bathrooms per bedroom floor and capacious, well-lighted shaving rooms. Top rate club tariff for bed and breakfast - 6 shillings, if called for a country train leaving Melbourne before 8am - 4 shillings, suite and breakfast- 9 shillings, sixpence. “The Australasia Traveller” Volume 10, Number 2, April 1914 page 35 reported “All “early calls” will be made from the Club Office to Bedrooms by means of the Telephone, so that instead of waking everybody else up on the corridor, only the member concerned will know that it is his unpleasant duty to get up.” The new CTA premises was widely regarded as the finest club in the Southern Hemisphere. The CTA also built the adjacent six storey Commerce House with 52 sample rooms for travellers to display their wares with the remainder rented to retail businesses and a post and telegraph office. After the CTA moved into their new, larger premises in 1914, neighbouring department store Ball & Welch expanded into the former CTA. The CTA saw themselves in a nation building role and were an influential lobby group to the Government. They advocated for inter city trunk telephone lines, standard gauge railway lines between NSW and Victoria, improved roads and highways, the Murray River water scheme and maintaining the White Australia Policy. They were very active in fund raising for the war efforts. The CTA offered its members support in other ways with benevolent funds for widows and orphans, mortuary, accident, sickness and an annuities fund for members over 65 years. There were scholarships for members’ children and home purchase scheme to assist with home ownership. A secondary membership scheme provided access to non commercial travellers (men only) to its exclusive club premises. They also organised social events and activities such as billiard tourneys, golf tournaments, dances and an annual “Smoke Social” which was a social event where men gathered for a formal dinner, community singing, lectures, speeches and of course, to smoke! Daylesford born James Davies OBE, (1865-1931) worked at the CTA for 50 years, starting as an office boy and working his way up to General Secretary and editor of the monthly trade journal for UCTAA members, “The Traveller” (1890-1905, later “The Australasian Traveller” 1905-1924 and then “The Australian Traveller” 1925-1976) and the annual colour supplement magazine “Australia To-Day” (1904-1973). “The Australasia Traveller” featured commentary on the issues of the day like wars, tariffs and trade, articles on new products and hotel recommendations and their rates and lots of advertising, especially alcohol, tobacco and accommodation in regional hotels. There were regular columns, each illustrated with a line drawing and these included “Our Immigration Record” a state by state summary of arrivals of “desirable immigrants” to Australia, while bemoaning the declining (white) birth rate. The column followed the arrival of British boys sent to Australia as agricultural apprentices to work on rural properties which were short of labour. Between 1913-1928, 1750 “Barwell Boys”, some as young as 14 years of age arrived in South Australia to work. NSW had a similar program known as the Dreadnaught Boys Scheme where 5595 boys immigrated between 1911-1939. The boys were considered of “good British stock”. There was a “Home Page For The Ladies” showcasing the latest fashions in women’s clothing, millinery and hairstyles and tips and trends in home furnishings.“Children’s Corner for Dear Little Folks” which featured puzzles, jokes and stories and members could send in photographs of their children. “Road Echoes” devoted to “The Man On The Road” and his doings. “Face Massage, Smiling is the Best Face Massage”, the humour page full of jokes and funny stories. “Railway Rumbles” news of innovations, timetables, tickets and grumbles about lavatories, food and drinking water on trains and at railway stations. And in case we forget that members had a home away from their CTA home, gardening tips with “The C.T. as Gardener” column. The annual magazine “Australia To-Day” was a vehicle to promote Australia here and overseas as a modern, prosperous country with abundant opportunities and pleasant climate. It sought to showcase its manufacturing, agriculture and tourism and encourage British immigration to Australia. The magazine featured articles about recently arrived migrants at work, quirky native flora and fauna, beach culture, recreation and the Australian way of life in the settler nation. Many of the articles were written by politicians of the day, including Robert Menzies. The UCTAA commissioned original artwork for the front covers and feature articles of “Australia To-day” from leading Australian artists. These included Norman Lindsay, Frederick McCubbin, Napier Waller, Lionel Lindsay, Hans Heysen, C Dudley Wood, Louis McCubbin, Penleigh Boyd, Louis Buvelot, Christian Waller and Ellis Rowan and her Australian wildflowers. Some of the photographs in “Australia To-Day” were provided by state and federal government departments as well as manufacturers, newspapers and mining companies. Amongst the credited photographers was Helmut Newton who later earned world acclaim as a fashion photographer, and architectural and industrial photographer Wolfgang Sievers (unfortunately their photographs remain in copyright and aren’t available online). Also featured was Richard C. Strangman, a professional photographer from Canberra, William Howieson of Melbourne, who has 22 photographs in the collection of NGV, Tasmanian wilderness photographer Frederick Smithies, Athol Shmith, portrait photographer and educator from Melbourne, Gordon de Lisle, a Melbourne commercial, industrial, aerial and society portrait photographer. (One of Gordon’s assignments was as the stills photographer for the 1959 movie “On The Beach” filmed in Melbourne). Photographs taken by acclaimed Antarctic and official war photographer Captain Frank Hurley OBE for Adelaide’s Centenary were also featured. The Australian Government was keenly aware of the influence and quality of the UCTAA publications. On 1 June 1914 The Age reported that to advertise Australia in Great Britain and elsewhere, the Department of External Affairs purchased 6500 copies of “Australia To-Day” magazine for £515 to distribute free to “places where they are most likely to come under the notice of a desirable class of immigrants.” In 1950, the office of Prime Minister Robert Menzies ordered 2550 copies of that year’s issue of “Australia To-Day” for the Department of Commerce and Information to distribute. The CTA donated their archives to University of Melbourne Archives which includes original artworks and photos used in “Australia To-Day” (Melbourne University has digitised 1114 photos) and sundry items including trophies, ashtrays, commemorative souvenirs, menus, a rare “Safechek” sovereign changer, a bust of James Davies and even a CTA embossed wash bowl and chamber pot. After the death of General Secretary James Davies in 1931, the CTA held the annual “James Davies Memorial Cup” golf tournament at various Melbourne golf courses, the winner receiving a splendid silver cup. “Table Talk” magazine photographs from 29 June 1933 depict the travellers beautifully (and I would say correctly) attired in tweedy plus fours, Fair Isle knitwear, flat caps and of course fringed brogues. I have been unable to ascertain whether the trophy in our photo is for golf or another CTA social activity. The CTA Victoria membership peaked in 1951 with 4,672 Aassociation members and 3,693 Club members. In 1959, Hollywood came to Melbourne when film stars Gregory Peck, Ava Gardner, Anthony Perkins and Fred Astaire descended to film ‘On the Beach,’ directed by Stanley Kramer. The film is based on the bestselling Neville Shute novel about the aftermath of World War Three, a nuclear war that has obliterated most of the Northern Hemisphere. Radioactive dust is heading toward Australia and everyone is preparing for death. Scenes with Anthony Perkins were filmed in the CTA billiards room as the exclusive Pastoral Club. Anthony Perkins’ character, Lieutenant Commander Peter Holmes of RAN tells Gregory Peck’s character, Commander Dwight Lionel, that The Pastoral Club is…"A mahogany and polished brass sort of place-some people claim it was the stuffiest club in the Commonwealth” before assuring him that despite shortages, the club is likely to have some Scotch left. In a scene at the Pastoral Club two, old (probably red faced) codgers discuss the challenge of drinking all of the 400 bottles of Gould Campbell vintage port in the club wine cellar before they succumb to radiation sickness in five months time. The NGV has 12 photographs in their collection of wardrobe stills of Ava Gardner modelling costumes designed by the Fontana Sisters of Rome for “On The Beach”, taken by Italian photographer G.B.Poletto. During the filming, Gregory Peck and his family stayed at “Kurneh” 206 Domain Road, South Yarra, the former home of three times Grand Slam winner Norman Brookes. Through the decades, Australian society was changing and in order to stay relevant, the CTA had to change too. In 1971, two women were elected for club membership, although they were only granted limited access to the club’s facilities and in 1972, women were invited for the first time to participate in the previously men only annual “Smoke Social”. In 1975, dwindling membership forced the closure of The Commercial Travellers’ Association building and in 1977, the building was sold, with the CTA ceasing to operate in 2014. It was the end of the road for the “Knights of the Road”. In 1992, the CTA building at 328 Flinders Street was placed on the Victorian Heritage Register in recognition of its architectural and cultural significance. The building has been meticulously restored with many of the original fittings, decorative plasterwork, mosaic flooring, stained glass windows, columns, chandeliers and the panelling made from Australian timbers retained. After renovations the building became first the Euro Asia Hotel, then the Duxton Hotel and in 2005 The Rendezvous Hotel, Melbourne. In tribute to the history of the building and the film “On The Beach”, the Rendezvous Hotel has the Ms Ava Bar, Perkins room, Mr Tompkins restaurant, Commerce Room and the Davies Room.Photographer notations on slide: commerce, clubs and associations, queen anne style architecture, federation/edwardian style architecture, railways, card games, department stores, agriculture, tourism
