Showing 162 items matching "warrnambool pound"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Journal - Book, City Poundkeeper's Book, C 1950
... warrnambool pound... or if unclaimed , they were sold. The Warrnambool pound was situated... or if unclaimed , they were sold. The Warrnambool pound was situated ...This book records the impounding of animals which have been found wandering on local roads or trespassing on land. Many are farm animals and give the various breeds of animals from red Ayrshire cows to bay ponies, and nanny goats. Impounded animals were either claimed by their owners after payment of a fee or if unclaimed , they were sold. The Warrnambool pound was situated on Merrivale Drive.This book is a record of a practice which was necessary to remove stock which were wandering on local roads or trespassing on neighbours. It contains many local names and is of social interest. Rectangular book with hard cover Fawn cloth with red leather spine. Pages are lined in blue and red and pages are headed in black . It dates from 1957 to 1998 with one entry for 2004.Entries are hand written in blue and black. The entries give particulars of the animal impounded and where found with name of council officer and owner, if known, of the animal.various pieces of paper pasted inside front cover.There are many names included in this journal. Among the earlier entries are James P O'KeefeH C Bidmade, Keith Nixon, C Eccles, I Carmody,warrnambool, warrnambool pound -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, To the Pound Keeper at Warrnambool, C1967
... To the Pound Keeper at Warrnambool...warrnambool pound.... warrnambool warrnambool pound The top of each page reads ...This book records the impounding of animals which have been found wandering on local roads or trespassing on land. Many are farm animals and give the various breeds of animals from red Ayrshire cows to bay ponies, and nanny goats. Impounded animals were either claimed by their owners after payment of a fee or if unclaimed , they were sold to defray the costs. It operated from Merrivale Drive.Black cloth covered card cover . Rectangular in shape. The pages are written in black and blue giving details of cattle and animals which have wandered from farms. It dates from 1967 to 1980.The top of each page reads: To the Poundkeeper at Warrnambool impounded by ............. of ............................... the following cattle.. . The pages are signed by J P O'Keefe at the front of the book followed by K Nixon, C Eales, P Eccles,warrnambool, warrnambool pound -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote set, Bank of Australasia, 1899-1903
... . The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool ...This set of banknotes was issued by the Bank of Australasia's Head Office in Sydney, New South Wales. Two banknotes are dated before the Federation of Australia on 1st January 1901 and two are dated just two years after Federation. Each of the banknotes in this set has a rectangular piece cut from it. This indicates that the banknote was cancelled when the note was exchanged for Australian dollars after Decimal Currency was introduced on 14th February 1966. The Bank of Australasia was established under the Royal Charter of England. It first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool. It was established in 1854 and operated from leased buildings in Merri Street then Timor Street. The bank opened its own building on May 21, 1860, on the north-east corner of Timor and Kepler Streets. In that year, the Acting Superintendent of the Bank of Australasia in Sydney was David Charters McArthur. He went on to become the Superintendent 1867-1876. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970 the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. This set of banknotes has historical significance as it was issued by the Bank of Australasia. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool, established in 1854. The bank continued to operate until its merger in 1951 when it became the ANZ Bank, which is still in operation today. The Bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Warrnambool and throughout Australia. The banknotes also have a significant place in Australia’s history as two notes are just prior to the Federation of Australia and two notes just after.This banknote set of four notes comprises three (3) £1 one-pound notes and one (1) £5 five-pound note. The notes were published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales between 1899 and 1903. The denominations of the notes and their round pound-coin symbols are printed in green ink, and the remainder of the printing is in black ink. All notes have a black ink stamp impressed twice on each side. The stamp states that the notes are cancelled. There are handwritten initials in red ink on each note's obverse and text in pencil on their reverse. The reverse of the one-pound notes is unprinted but the five-pound note has a printed decorative border and images with an inscription and shield. The notes have a rectangular cut-out on the lower edge.Serial Numbers, Denominations and Dates: 5054.1 "ONE POUND" "Q50,806" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1903" 5054.2 "ONE POUND" "O50 551" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1903" 5054.3 "ONE POUND" "O24,385" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1899" 5054.4 "FIVE POUND" "A36,191" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "5th February 1900" Stamp "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA / CANCELLED" Handwritten in red [initials] Image on five pound note"(around border) "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA INCORPORATED BY ROYAL CHARTER" and (image on shield) [suspended sheep] in diagonal corners, and [sailing ships] in other diagonal corners, and four stars (or open flowers)" Text in pencil "L24"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, one pound note, bank of australasia, legal tender, £1, banknote, banknotes, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, five poind note, australian currency, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, one-pound note, five-pound note, £5, sydney, new south wales, pre-federation, post-federation, currency, set of banknotes -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote, Bank of Australasia, One-pound, 1st July 1903
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road This one-pound banknote is one of a set ...This one-pound banknote is one of a set of four banknotes issued by the Bank of Australasia's Head Office in Sydney, New South Wales. Two banknotes are dated before the Federation of Australia on 1st January 1901 and two are dated just two years after Federation. Each of the banknotes in this set has a rectangular piece cut from it. This indicates that the banknote was cancelled when the note was exchanged for Australian dollars after Decimal Currency was introduced on 14th February 1966. The Bank of Australasia was established under the Royal Charter of England. It first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool. It was established in 1854 and operated from leased buildings on Merri Street and then Timor Street. The bank opened its own building on May 21, 1860, on the northeast corner of Timor and Kepler Streets. In that year, the Acting Superintendent of the Bank of Australasia in Sydney was David Charters McArthur. He went on to become the Superintendent from 1867-to 1876. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970 the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. This set of banknotes has historical significance as it was used by the Bank of Australasia, the first bank in Warrnambool. The bank was established in 1854 and continued until its merger, when it became the ANZ Bank in 1951 and is still in operation today. The bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Warrnambool, Victoria, and Australia. The banknotes also have a significant place in Australia’s history as two notes are just prior to Federation and two notes just after Federation.One-pound note, one of a set of four (4) notes published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales. The obverse of the note is printed in black ink with the denomination and its round pound-coin symbol printed in green ink. There is no printing on the reverse. A black ink stamp is impressed twice on each side of the note, stating that the note is cancelled. Handwritten red ink text is on the note's obverse and pencil text on the reverse. A unique Serial number is printed twice on the obverse. The banknote has a rectangular cut-out notch on the lower edge. Printed: (Serial Number) "Q50,806" "ONE POUND" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1903" Stamped: "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA / CANCELLED" Handwritten in red pen: "undecipherable [initials]" Text in pencil "L24"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, one pound note, bank of australasia, legal tender, £1, banknote, banknotes, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, five poind note, australian currency, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, one-pound note, five-pound note, £5, sydney, new south wales, pre-federation, post-federation, currency, banknote set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote, Bank of Australasia, One-pound, 1st July 1903
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road One-pound note, one of a set of four (4 ...One-pound note, one of a set of four (4) notes published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales. The obverse of the note is printed in black ink with the denomination and its round pound-coin symbol printed in green ink. There is no printing on the reverse. A black ink stamp is impressed twice on each side of the note, stating that the note is cancelled. Handwritten red ink text is on the note's obverse and pencil text on the reverse. A unique Serial number is printed twice on the obverse. The banknote has a rectangular cut-out notch on the lower edge. The Bank of Australasia was established under the Royal Charter of England. It first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool. It was established in 1854 and operated from leased buildings in Merri Street then Timor Street. The bank opened its own building on May 21, 1860, on the north-east corner of Timor and Kepler Streets. In that year, the Acting Superintendent of the Bank of Australasia in Sydney was David Charters McArthur. He went on to become the Superintendent 1867-1876. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970 the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. This set of banknotes has historical significance as it was issued by the Bank of Australasia. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool, established in 1854. The bank continued to operate until its merger in 1951 when it became the ANZ Bank, which is still in operation today. The Bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Warrnambool and throughout Australia. The banknotes also have a significant place in Australia’s history as two notes are just prior to the Federation of Australia and two notes just after.One-pound note, one of a set of four (4) notes published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales. The obverse of the note is printed in black ink with the denomination and its round pound-coin symbol printed in green ink. There is no printing on the reverse. A black ink stamp is impressed twice on each side of the note, stating that the note is cancelled. Handwritten red ink text is on the note's obverse and pencil text on the reverse. A unique Serial number is printed twice on the obverse. The banknote has a rectangular cut-out notch on the lower edge.Printed (Serial Number) "O50 551" "ONE POUND" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1903" Stamp "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA / CANCELLED" Handwritten in red pen: "undecipherable [initials]" Text in pencil "L24"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, one pound note, bank of australasia, legal tender, £1, banknote, banknotes, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, five poind note, australian currency, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, one-pound note, five-pound note, £5, sydney, new south wales, pre-federation, post-federation, currency, set of banknotes, banknote set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote, Bank of Australasia, One-pound, 1st July 1899
... . The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool ...This set of banknotes was issued by the Bank of Australasia's Head Office in Sydney, New South Wales. Two banknotes are dated before the Federation of Australia on 1st January 1901 and two are dated just two years after Federation. Each of the banknotes in this set has a rectangular piece cut from it. This indicates that the banknote was cancelled when the note was exchanged for Australian dollars after Decimal Currency was introduced on 14th February 1966. The Bank of Australasia was established under the Royal Charter of England. It first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool. It was established in 1854 and operated from leased buildings in Merri Street then Timor Street. The bank opened its own building on May 21, 1860, on the north-east corner of Timor and Kepler Streets. In that year, the Acting Superintendent of the Bank of Australasia in Sydney was David Charters McArthur. He went on to become the Superintendent 1867-1876. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970 the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. This set of banknotes has historical significance as it was issued by the Bank of Australasia. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool, established in 1854. The bank continued to operate until its merger in 1951 when it became the ANZ Bank, which is still in operation today. The Bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Warrnambool and throughout Australia. The banknotes also have a significant place in Australia’s history as two notes are just prior to the Federation of Australia and two notes just after.One-pound note, one of a set of four (4) notes published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales. The obverse of the note is printed in black ink with the denomination and its round pound-coin symbol printed in green ink. There is no printing on the reverse. A black ink stamp is impressed twice on each side of the note, stating that the note is cancelled. Handwritten red ink text is on the note's obverse and pencil text on the reverse. A unique Serial number is printed twice on the obverse. The banknote has a rectangular cut-out notch on the lower edge.Printed: (Serial Number) "O24,385" "ONE POUND" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "1st July 1899" Stamp "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA / CANCELLED" Handwritten in red pen: "undecipherable [initials]" Text in pencil "L24"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, one pound note, bank of australasia, legal tender, £1, banknote, banknotes, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, five poind note, australian currency, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, one-pound note, five-pound note, £5, sydney, new south wales, pre-federation, post-federation, currency, banknote set -
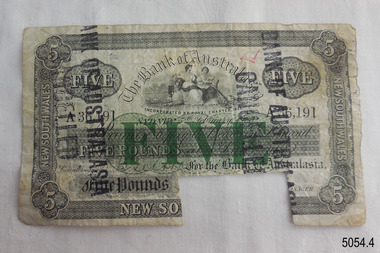 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote, Five-pound
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road This five-pound banknote is one of a set ...This five-pound banknote is one of a set of four banknotes issued by the Bank of Australasia's Head Office in Sydney, New South Wales. Two banknotes are dated before the Federation of Australia on 1st January 1901 and two are dated just two years after Federation. Each of the banknotes in this set has a rectangular piece cut from it. This indicates that the banknote was cancelled when the note was exchanged for Australian dollars after Decimal Currency was introduced on 14th February 1966. The Bank of Australasia was established under the Royal Charter of England. It first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. The Bank of Australasia was the first bank in Warrnambool. It was established in 1854 and operated from leased buildings in Merri Street then Timor Street. The bank opened its own building on May 21, 1860, on the north-east corner of Timor and Kepler Streets. In that year, the Acting Superintendent of the Bank of Australasia in Sydney was David Charters McArthur. He went on to become the Superintendent 1867-1876. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970 the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. This set of banknotes has historical significance as it was used by the Bank of Australasia, the first bank in Warrnambool. The bank was established in 1854 and continued until its merger, when it became the ANZ Bank in 1951 and is still in operation today. The bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Warrnambool, Victoria, and Australia. The banknotes also have a significant place in Australia’s history as two notes are just prior to Federation and two notes just after Federation.Five-pound banknote, one of a set of four banknotes published by The Bank of Australasia, Sydney, New South Wales. The obverse of the note is printed in black ink with the denomination and its round pound-coin symbols printed in green ink. The reverse has a decorative border and image with an inscription and shield. A black ink stamp was impressed twice on each side, stating that the note is cancelled. Handwritten red ink text is on the note's obverse and pencil text on the reverse. A unique Serial number is printed twice on the obverse. The banknote has a rectangular cut-out notch on the lower edge. Printed: (Serial Number) "A36,191" "FIVE POUND" "NEW SOUTH WALES" "5th February 1900" Stamp "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA / CANCELLED" Image: (around border) "BANK OF AUSTRALASIA INCORPORATED BY ROYAL CHARTER" and (image on shield) [suspended sheep] in diagonal corners, and [sailing ships] in other diagonal corners, and four stars (or open flowers)" Handwritten in red pen: "undecipherable [initials]" Text in pencil "L24"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, one pound note, bank of australasia, legal tender, £1, banknote, banknotes, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, five poind note, australian currency, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, one-pound note, five-pound note, £5, sydney, new south wales, pre-federation, post-federation, currency, banknote set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Leg Vice, Mid 19th Century
The blacksmith leg vise is also called the "solid box vise" and is one of the most important tools in the blacksmith's shop. It firmly holds hot iron while it is hammered, chiseled, or twisted. These are the only vises that are designed to take this kind of use day in and day out. A small 30-pound blacksmith's vise can survive pounding that would wreck a much heavier cast iron bench model. Three things make a blacksmith's vice special. One is that they are forgings, not cast iron or ductile iron. The second is the leg that provides support to the floor or from a sunken post. The last is the hinge, while not a perfect way to construct a vice the pin joint is durable and can take a considerable beating. If sheared it is easy to replace. These things all combine into a tool that can take decades of heavy use and abuse. Most in use is one to two hundred years old.Some of these vises were made by specialists such as Atwood of Stourbridge England, Steel City and Columbian in the U.S. and others were made in anvil manufacturing plants such as "Mousehole Forge" and "Peter Wright" in England and "Fisher-Norris" and others in North America. The design of these vises right down to the last chamfer seems to have been perfected in the 1600s and remained more or less the same until the 20th century. The bodies are forged wrought iron or mild steel and they have hard steel surfaces welded into the jaws. The jaws have little or very shallow serrations which are generally worn off.Around the turn of the 20th Century during the hey-day of the blacksmith shop in North America, these tools were considered so standard a commodity that they were sold without reference to the manufacturer. Very few were even marked with the maker's name. Size is best defined by weight as there is some variation in jaw size from manufacturer to manufacturer. They were sold by the pound and are still best judged by the pound.A vintage tool used in a Blacksmiths shop during the early 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century. Regarded as a significant into social history of the time.Leg Vice attached with screws to bench via a block of wood. Has large metal pole which practically reaches the floor. Also has a metal device to either tighten or slacken vice.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Jug, Between 1910 -1936
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995.An example of a brass measuring jug made specifically to maintain government standard liquid measurements that were sold to the public. The probability is that this artefact was made sometime between George V reign (1910-1936) and gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were checked by Government departments prior to decimalisation and how a standard for the various types of measurement was developed in Australian based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item used in Victoria as a legal standard measure to ensure that goods sold in Victoria were correct. Jug brass haystack form with a deep lip and pouring spout, small neck and broad base. It displays a curved pistol handle. Inscription at base of handle top of jug stamped 61 GVR SM. These marks signify that the measure complied with the Victorian Government capacity liquid standard measurement. Item made during the reign of George V (1910-1936 (GVR).Other marks indicate model number (61) & SM possible could be either small measure, the maker, or Standards Melbourne.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Galvanised Jug, 1930s
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995.An example of a galvanised measuring jug made specifically to maintain government standard liquid measurements that were sold to the public. The probability is that this artifact was made around the first quarter of the 20th century and gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used before decimalisation and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in Australian based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item used in Victoria as a legal standard measure to ensure that goods sold in Victoria were correct given the item is galvanised it was probability used for kerosene or petrol etc not for liquids used for human consumption. Jug conical shaped with rounded top coming to a very slight point wide handle at back. VIB.L.66 1/2 Gall capacity unsure of the markings 66 could mean the model number capacity is 1/2 an imperial gallon VIB.L markings not known possibly a company or Victorian Department that the jug was made for and no longer active.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGalvanised Jug
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. An example of a galvanised measuring jug made specifically to maintain government standard liquid measurements that were sold to the public. The probability is that this artifact was made around the first quarter of the 20th century and gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used before decimalisation and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in Australian based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item used in Victoria as a legal standard measure to ensure that goods sold in Victoria were correct given the item is galvanised it was probability used for kerosene or petrol etc not for liquids used for human consumption. Galvanised Iron jug with rounded top, Inscription on handle at back. 2 gallon GV.35flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Galvanised Jug
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995.An example of a galvanised measuring jug made specifically to maintain government standard liquid measurements that were sold to the public. The probability is that this artifact was made around the first quarter of the 20th century and gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used before decimalisation and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in Australian based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item used in Victoria as a legal standard measure to ensure that goods sold in Victoria were correct given the item is galvanised it was probability used for kerosene or petrol etc not for liquids used for human consumption. Jug galvanised conical shaped with rounded top, handle at back. 3 gallon GV.27flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Musical, Piano, Aucher Freres, circa 1880-1920
This piano was made by Aucher Freres of Paris, said to be famous for its pianos in the mid-late 1800s. Aucher Freres (Aucher Brothers) produced a model of piano that was built specifically for use on sailing vessels, the upright yacht-style piano. Pianos were amongst the domestic goods brought to Australia by many colonial immigrants. They were also imported by Australian distributors by the shipload and sought after by settlers. A piano was often found in a Missions to Seamen club room, where visiting seafarers would entertain or be entertained by music and song as part of their relaxation in port. A sarcastically written news article of January 2nd 1869 reported that the Secretary of the Loyal Liberals of Ballarat, Mr Henry Bell, was presented both with a “illuminated address” and a piano. The piano was made by Aucher Freres of Paris and was purchased for sixty guineas (which converts to around $7,500 Au in 2019). The gift was criticised for encouraging foreign industry rather than native Australian products, thus going against what the Loyal Liberals own protectionist policy. The writer goes on to state that several pianos made in the Colony compared very favourably at the International Exhibition with those manufactured by the English or French. He then says that “… the secretary … might learn a lesson from his piano ... the name Aucher Freres, Paris emblazoned on its front should be … a perpetual reminder of the hollowness of that protectionist imposture …” [Refer to Intercolonial News, Victoria, originally published in The Argus, was repeated in the Wallaroo Times and Mining Journal of South Australia 2-1-1869.] Aucher Freres pianos were still around in 1930. A second-hand model was advertised for sale as a good practice piano. The advertisement was placed by the Mount Gambier, SA, agents for Saver’s Pianos Ltd of Adelaide. The piano was described as “a sound little instrument of good tone and appearance”. The asking price in November 1930 was 32 pounds and ten shillings (which converts to about $2,500 Au in 2019). [Refer to Savery’s advertisement, Mt Gambier Border Watch 11-11-1930]This piano is significant for its connection with the time period of chapel and club room at Flagstaff Hill's St Nicholas Seamen's Church. It represents the form of entertainment enjoyed by seafarer's world wide, which is appropriate for a maritime village. The maker of the piano is famous for its quality pianos of the 19th and early 20th century.Piano, upright, polished wood. The wooden hinged keyboard cover lifts up to allow access to the keyboard. The piano also has two brass candlesticks. The top of the piano is hinged and lifts up to allow access to the piano mechanic's inside for tuning and maintenance. The inside flap has a music stand incorporated into it. It also has the usual two hard-soft pedals at the base. There are two brass decorated hooks at each end to allow for ease of movement when the position of the piano is changed. Maker's name inscribed inside keyboard lid in gold lettering. Made in Paris by Aucher Freres (Aucher Brothers)."AUCHER FRERES / Paris" (NOTE: the "C" is sometimes mistaken for a "G")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, piano, music, upright piano, paris, france, aucher freres -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeg Vice, c. early 1900s
This leg (post) vice once belonged to Goodall and Sons, who were blacksmiths in Terang. The leg vice is a common tool of the ‘smithies’ (blacksmiths). It is also an engineer's tool but in the early 1900s the smith was often the nearest approach to an engineer’s services for many miles around. The smith was called upon to do a variety of work. The leg vice is used to hold hot iron while the metal is pounded, heated and beaten again and again until it is the required shape. Henry Goodall (1870-1936) Henry Goodall was the proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The leg vice is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-1900s.Leg vice, also called a post vice. The large iron vice stands on a post on the floor and post brackets attach it firmly to a solid object such as a workbench. The sliding metal handle winds the screw spindle in and out to change the grip of the jaws that hold the workpiece. This leg vice once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmiths of Terang.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall, trade tools, blacksmith tools, leg vice, leg vise, pose vice, post vise, terang 1900s, warrnambool district 1900s -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, early 1900's
This photograph of the 10 crew of the SPECULANT would have been taken prior to Feb 10th 1911, when the ship was wrecked on the south coast of Victoria at a place called Cape Patton. The barquentine SPECULANT was a steel, three-masted sailing ship built in 1895 in Inverkeithing, Scotland, registered in Warrnambool, Victoria and wrecked at Cape Paton, Victoria, 10th February 1911. The SPECULANT had been involved in the timber trade between the United Kingdom and Russia, until sold to its Warrnambool owners and timber merchants Messrs. P.J. McGennan & Co. (Peter John McGennan) in 1902 for 3000 pounds and had her sailed to Warrnambool as her new port. Peter John McGennan was born in 1844 and worked as a builder and cooper in Holyhead, Anglesea, Wales. He immigrated to Australia in 1869 as a free settler and arrived in Warrnambool in 1871 and undertook management of a property in Grassmere for Mr. Palmer. Peter met his wife Emily in South Melbourne and they married in 1873. They had ten children including Harry who lived to 1965, and Andrew who lived until 1958. (The other children were their four brothers - John who was killed in the Dardenalles aged 35, Frederick who died aged 8, Peter who died aged 28, Frank who died aged 5 weeks - and four sisters - Beatrice who died age 89, Edith who died aged 49, Blanche who died aged 89 and Eveline who died aged 48.) In 1874 Peter starting a boating establishment on the Hopkins River. In 1875 he opened up a Coopers business in Kepler Street next to what was Bateman, Smith and Co., moving to Liebig Street, next to the Victoria Hotel, in 1877. In 1882 he then moved to Lava Street (which in later years was the site of Chandlers Hardware Store). He was associated with the establishment of the Butter Factory at Allansford. He started making Butter Boxes to his own design and cheese batts for the Butter Factory. In 1896 established a Box Factory in Davis Street Merrivale, employing 24 people at its peak, (it was burnt down in 1923); and in Pertobe Road from 1912 (now the Army Barracks building). Peter was a Borough Councillor for Albert Ward from 1885 to 1891, he commenced the Foreshore Trust (including the camping grounds along Pertobe Road), and he was an inaugural Director of the Woollen Mill in Harris Street, buying an extensive share-holding in 1908 from the share trader Edward Vidler. They lobbied the Town Hall to have a formal ‘Cutting’ for the waters of the Merri River to be redirected from its natural opening south of Dennington, to its existing opening near Viaduct Road, in order to have the scourings from the wool at the Woollen Mill discharged into the sea. He sold Butter Boxes around the state, and had to ship them to Melbourne by rail. Peter’s purchase of the SPECULANT in 1902 enabled him to back-load white pine from Kaipara, New Zealand to Warrnambool to make his butter boxes then, to gain profitability, buy and ship potatoes and other primary produce bound to Melbourne. (McGennan & Co. had also owned the LA BELLA, which had traded in timber as well, until she was tragically wrecked with the loss of seven lives, after missing the entrance channel to Warrnambool harbour in 1905. It appears that the SPECULANT was bought to replace the LA BELLA.) In 1911 the SPECULANT had been attempting to depart Warrnambool for almost the entire month of January to undergo docking and overhaul in Melbourne. A month of east and south-easterly winds had forced her to remain sheltered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool apart from one morning of northerlies, when an attempt was made to round Cape Otway; she had to return to shelter in Portland after failing to make any headway. With only 140 tons of sand ballast aboard, the ship would not have been easy to handle. Captain Jacobsen and his crew of nine, mainly Swedes, decided to make for Melbourne, leaving Portland Harbour on 5th February 1911. By the 9th they had reached Cape Otway, where they encountered a moonless night, constant heavy rain, and a heavy sea with a south-easterly wind blowing. After safely rounding Cape Otway the course was changed to east, then north-east to take the vessel to a point six miles off Cape Patton, following the orders of Captain Jacobsen, who told the crew to be very careful with the steering, as the wind and sea was running to leeward. The patent log (used to measure speed) had been out of order for the last four months as no-one in Warrnambool was able to fix it: it was intended to have it repaired in Melbourne. In the meantime the crew measured the vessel's speed by looking over the side and estimating wind strength. This compounded the difficulties of imprecise positioning, as the strong cross wind and sea were acting on the lightly laden vessel to steadily drive it towards the shore. At 3.30am on Friday 10 February 1911 Captain Jacobsen and the first mate were looking over the side of the vessel when they heard the sound of breakers and suddenly struck the rocks. The crew immediately knew they had no chance of getting the SPECULANT off, and attempted to rescue themselves by launching the lifeboat, which was instantly smashed to pieces. One of the crew then volunteered to take a line ashore, and the rest of the crew were all able to drag themselves to shore, some suffering hand lacerations from the rocks. Once ashore they began to walk along the coast towards Lorne, believing it was the nearest settlement. Realising their mistake as dawn broke they returned westwards to Cape Patton, and found a farm belonging to Mr C. Ramsden, who took them in and gave them a change of clothes and food. After resting for a day and returning to the wreck to salvage some of their personal possessions, at 10am on Saturday they set out for Apollo Bay, a voyage that took six hours, sometimes wading through flooded creeks up to their necks. The Age described the wreck as "listed to starboard. All the cabin is gutted and the ballast gone. There is a big rock right through the bottom of her, and there is not the slightest hope of getting her off". A Board of Marine inquiry found that Captain Jacobson was guilty of careless navigation by not taking steps to accurately verify the position of the vessel with respect to Cape Otway when the light was visible and by not setting a safe and proper course with respect to the wind and sea. It suspended his certificate for 6 months and ordered him to pay costs. The location of the wreck site was marked for a long time by two anchors on the shoreline, until in 1970 the larger of the two anchors was recovered by the Underwater Explorers' Club and mounted on the foreshore at Apollo Bay. The bell from the wreck was also donated to the Apollo Bay Surf Lifesaving Club but is recorded to have been stolen. Rusting remains of the wreck can still be found on the shoreline on the southern side of, and directly below Cape Patton. Parts of the SPECULANT site have been buried by rubble from construction and maintenance works to the Great Ocean Road, as well as by naturally occurring landslides. Peter J McGennan passed away in 1920. The Gates in the western wall of the Anglican Church in Henna Street/Koroit St are dedicated to him for his time of community work, which is matched with other prominent Warrnambool citizens; Fletcher Jones, John Younger, J.D.E (Tag) Walter, and Edward Vidler. After Peter J McGennan's death Harry, Andrew and Edith continued to operate the family business until July 11th 1923 when the company was wound up. (Andrew lived in Ryot Street Warrnambool, near Lava Street.) Harry McGennan (Peter and Emily’s son) owned the Criterion Hotel in Kepler Street Warrnambool (now demolished). His son Sid and wife Dot lived in 28 Howard Street (corner of Nelson Street) and Sid managed the Criterion until it was decided by the family to sell, and for he remained Manager for the new owners until he retired. Harry commenced the Foreshore Trust in Warrnambool around 1950. The McGennan Carpark in Pertobe Road is named after Harry and there are Memorial-Stone Gates in his memory. (The Gates were once the original entrance to the carpark but are now the exit.). Peter’s great-grandson, also called Andrew, is a Security Officer in Warrnambool. The Patent Log (also called a Taffrail log) from the SPECULANT, mentioned above, and a number of photographs, are now part of the Collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The SPECULANT is historically significant as the largest ship to have been registered in Warrnambool, and is believed to have been the largest barquentine to visit Melbourne. It is evidence of the final days of large commercial sailing vessels involved in the Victorian and New Zealand timber trade. The SPECULANT is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S626Photograph, black and white. of the 10 crew of the SPECULANT on board the ship holding two 'Speculant Warrnambool' lifebuoys. Taken early 1900's flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, warrnambool historical photograph, la bella, speculant, cumming and ellis, international timber trade, p. j. mcgennan and co. warrnambool, peter mcgennan, capt. james jacobsen, warrnambool maritime history, h. pengilley apollo bay -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePoster - Recreation, Warrnambool Hot Sea Water Baths, c. November 1908
The poster includes a cartoon by Arthur Jordan, with a conversation between an ailing man and a good man after baths visits. There are several reviews dating from 1906 to 1908 extolling the healing powers of the baths' waters. In February 1877 a Baths Company (1050 shares) was formed in the town of Warrnambool for the establishment of the baths at the south end of Gillies Street. The baths were filled with sea water from Lady Bay, originally pumped by a windmill situated near the current Surf Lifesaving Club and carried by iron pipes to the Public Baths; later the water was pumped by gas motor. Hot and cold fresh water baths were advertised. The gentlemen’s bath was 100 feet long and 50 feet wide, of graduating depth. A second bath, solely for ladies, was 60 feet long by 30 feet wide. Hot Sea-water Baths were also part of the institution, and were sought after for their ‘wonderful curative powers’, and ‘incomparable’ as a ‘tonic for the feeble’. In June 1881 the Hot Sea Baths were opened, and both hot and cold water baths were supplied at reasonable charges. Patrons came from near and far to receive the benefits. The manager of the Baths was J. Kirkpatrick. The Baths Company struggled for several years without success so in 1883 the baths were sold to the Borough Council for 1250 pounds. The original shareholders received nothing for their outlay; the overdraught was over the sale price. In May 1884 the Council announced that an estimated they has spent 1000 pounds in improving the baths since purchasing them and were now returning an income of 11 per cent. The poster promotes the healing powers of the hot sea water baths that were in use in Warrnambool in the late 19th century through to the early 20th century. The baths were a place for fitness, health and social activity, an example of the recreational activities during this period.Poster, black and white, mounted on card. It shows advertising Warrnambool Sea-water Baths and Hot Sea-water Baths. There are several references promoting the health benefits of baths, dating from 1906-1908. The cartoon was sketched by Arthur Jordan. The poster was printed by The Thompson Printing Co. Warrnambool. Handwritten inscription on the lower edge.Handwritten "10,000 mailed by post through Victoria"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, warrnambool salt baths, warrnambool therapudic baths, arthur jordan, baths company, sea water baths, hot sea water, swimming, healing powers, warrnambool baths, advertisement, thompson printing co. warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePoster - Recreation, Town of Warrnambool Swimming Baths, ca. May 1884
The poster advertises these Swimming Baths as “the most complete in the Southern Hemisphere”. In February 1877 a Baths Company (1050 shares) was formed in the town of Warrnambool for the establishment of the baths at the south end of Gillies Street. The baths were filled with sea water from Lady Bay, originally pumped by a windmill situated near the current Surf Lifesaving Club and carried by iron pipes to the Public Baths; later the water was pumped by a gas motor. Hot and cold fresh water baths were advertised. The gentlemen’s bath was 100 feet long and 50 feet wide, of graduating depth. A second bath, solely for ladies, was 60 feet long by 30 feet wide. Hot Sea water Baths were also part of the institution, and were sought after for their ‘wonderful curative powers’, and ‘incomparable’ as a ‘tonic for the feeble’. In June 1881 the Hot Sea Baths were opened, and both hot and cold water baths were supplied at reasonable charges. Patrons came from near and far to receive the benefits. The manager of the Baths was J. Kirkpatrick. The Baths Company struggled for several years without success, so in 1883 the baths were sold to the Borough Council for 1250 pounds. The original shareholders received nothing for their outlay; the overdraught was over the sale price. In May 1884 the Council announced that an estimated they has spent 1000 pounds in improving the baths since purchasing them and were now returning an income of 11 per cent. Historically significant to Warrnambool and the recreational facilities available in the 1880s to 1900s. The remains of the baths are still visible to the public today.Poster on heavy cream paper, landscape orientation, with coloured print. The poster advertises the Warrnambool Swimming Baths. It has several drawings such as Middle Island and the Merri River Mouth with vessels in the water, The inside of the Baths facility, the men's baths with the adjacent bathing rooms and figures in and out of the water, a cottage with figures in the garden, and fenced buildings with a windmill and aqueduct or pipes. The text describes the location and advantages, the opening times and various costs. It was printed in Ballarat by F.W. Niven & Co. Lithos."TOWN OF WARRNAMBOOL" "SWIMMING BATHS" "HOT SALT-WATER BATHS FOR LADIES AND GENTLEMEN" "HOURS FOR BATHING fROM 7 a.m. to 9 p. m. Closed on Sundays at 10 a.m." Single Bath 1s [1 shilling]; or 10s per Dozen Tickets" "HOURS FOR SWIMMING BATHS: Ladies and Gentlemen, from 6 a.m. to Sunset, Sundays 6 a.m. to 10 a.m." "Every information can be obtained from the Manager, J. Kirkpatrick" "HOT SEA-WATER BATHS ... strongly recommended by the Medical Faculty" "Hot and Cold Fresh Water Baths" "Showers etc." "LIST OF CHARGES ... Single Season Ticket, Single Monthly Ticket, Single Bath without towel ... with towel.. Tickets per dozen without towel, with towel..." "The Baths are situated at the end of Gillies Street, in the rear of the Post Office, and are of salt water pumped by gas motor continuously from the sea. The Swimming Bath is 100 feet long by 50 feet wide, of graduating depth; and a second bath for ladies' use solely, 60 feet long by 30 feet wide. The hot Sea-water Baths in connection with this institution have been extolled far and wide for their wonderfully curative powers in cases of rheumatism, sciatica, and nervous afflictions generally. As a tonic to an enfeebled system, they are incomparable, These Baths, the most complete in the Southern Hemisphere, have been recently re-erected and fitted with marble plunges, and everything provided for the comfort and convenience of invalids and visitors." "F.W. NIVEN & Co, LITHOS, BALLARAT"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, warrnambool swimming baths, hot sea water baths warrnambool, warrnambool baths company, f.w. niven & co, warrnambool therapudic baths, town of warrnambool, swimming baths, hot sea water baths, salt water baths, ladies' baths, gentlemen's baths, warrnambool town baths, j kirkpatrick -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Iron
Before the introduction of electricity, irons were heated by combustion, either in a fire or with some internal arrangement. An "electric flatiron" was invented by American Henry Seely White and patented on June 6, 1882. It weighed almost 15 pounds (6.8 kg) and took a long time to heat. The UK Electricity Association is reported to have said that an electric iron with a carbon arc appeared in France in 1880, but this is considered doubtful. Two of the oldest sorts of iron were either containers filled with a burning substance, or solid lumps of metal which could be heated directly. Metal pans filled with hot coals were used for smoothing fabrics in China in the 1st century BC. A later design consisted of an iron box which could be filled with hot coals, which had to be periodically aerated by attaching a bellows. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, there were many irons in use that were heated by fuels such as kerosene, ethanol, whale oil, natural gas, carbide gas (acetylene, as with carbide lamps), or even gasoline. Some houses were equipped with a system of pipes for distributing natural gas or carbide gas to different rooms in order to operate appliances such as irons, in addition to lights. Despite the risk of fire, liquid-fuel irons were sold in U.S. rural areas up through World War II. In Kerala in India, burning coconut shells were used instead of charcoal, as they have a similar heating capacity. This method is still in use as a backup device, since power outages are frequent. Other box irons had heated metal inserts instead of hot coals. From the 17th century, sadirons or sad irons (from Middle English "sad", meaning "solid", used in English through the 1800s[4]) began to be used. They were thick slabs of cast iron, triangular and with a handle, heated in a fire or on a stove. These were also called flat irons. A laundry worker would employ a cluster of solid irons that were heated from a single source: As the iron currently in use cooled down, it could be quickly replaced by a hot one. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clothes_ironThis iron is typical of the clothes iron used before electric irons superseded it.Salter iron no. 6, painted black but with rust showing through. Salter iron no. 6.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, iron, clothes, laundry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, early 1900's
This photograph of the SPECULANT was taken while she was in dock at the Warrnambool, Victoria, Breakwater in the early 1900's. Crew seem busy on her decks and others are watching from the breakwater. There are also 2 steamships in the photograph. The barquentine SPECULANT was a steel, three-masted sailing ship built in 1895 in Inverkeithing, Scotland, registered in Warrnambool, Victoria and wrecked at Cape Paton, Victoria, 10th February 1911. The SPECULANT had been involved in the timber trade between the United Kingdom and Russia, until sold to its Warrnambool owners and timber merchants Messrs. P.J. McGennan & Co. (Peter John McGennan) in 1902 for 3000 pounds and had her sailed to Warrnambool as her new port. Peter John McGennan was born in 1844 and worked as a builder and cooper in Holyhead, Anglesea, Wales. He immigrated to Australia in 1869 as a free settler and arrived in Warrnambool in 1871 and undertook management of a property in Grassmere for Mr. Palmer. Peter met his wife Emily in South Melbourne and they married in 1873. They had ten children including Harry who lived to 1965, and Andrew who lived until 1958. (The other children were their four brothers - John who was killed in the Dardenalles aged 35, Frederick who died aged 8, Peter who died aged 28, Frank who died aged 5 weeks - and four sisters - Beatrice who died age 89, Edith who died aged 49, Blanche who died aged 89 and Eveline who died aged 48.) In 1874 Peter starting a boating establishment on the Hopkins River. In 1875 he opened up a Coopers business in Kepler Street next to what was Bateman, Smith and Co., moving to Liebig Street, next to the Victoria Hotel, in 1877. In 1882 he then moved to Lava Street (which in later years was the site of Chandlers Hardware Store). He was associated with the establishment of the Butter Factory at Allansford. He started making Butter Boxes to his own design and cheese batts for the Butter Factory. In 1896 established a Box Factory in Davis Street Merrivale, employing 24 people at its peak, (it was burnt down in 1923); and in Pertobe Road from 1912 (now the Army Barracks building). Peter was a Borough Councillor for Albert Ward from 1885 to 1891, he commenced the Foreshore Trust (including the camping grounds along Pertobe Road), and he was an inaugural Director of the Woollen Mill in Harris Street, buying an extensive share-holding in 1908 from the share trader Edward Vidler. They lobbied the Town Hall to have a formal ‘Cutting’ for the waters of the Merri River to be redirected from its natural opening south of Dennington, to its existing opening near Viaduct Road, in order to have the scourings from the wool at the Woollen Mill discharged into the sea. He sold Butter Boxes around the state, and had to ship them to Melbourne by rail. Peter’s purchase of the SPECULANT in 1902 enabled him to back-load white pine from Kaipara, New Zealand to Warrnambool to make his butter boxes then, to gain profitability, buy and ship potatoes and other primary produce bound to Melbourne. (McGennan & Co. had also owned the LA BELLA, which had traded in timber as well, until she was tragically wrecked with the loss of seven lives, after missing the entrance channel to Warrnambool harbour in 1905. It appears that the SPECULANT was bought to replace the LA BELLA.) In 1911 the SPECULANT had been attempting to depart Warrnambool for almost the entire month of January to undergo docking and overhaul in Melbourne. A month of east and south-easterly winds had forced her to remain sheltered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool apart from one morning of northerlies, when an attempt was made to round Cape Otway; she had to return to shelter in Portland after failing to make any headway. With only 140 tons of sand ballast aboard, the ship would not have been easy to handle. Captain Jacobsen and his crew of nine, mainly Swedes, decided to make for Melbourne, leaving Portland Harbour on 5th February 1911. By the 9th they had reached Cape Otway, where they encountered a moonless night, constant heavy rain, and a heavy sea with a south-easterly wind blowing. After safely rounding Cape Otway the course was changed to east, then north-east to take the vessel to a point six miles off Cape Patton, following the orders of Captain Jacobsen, who told the crew to be very careful with the steering, as the wind and sea was running to leeward. The patent log (used to measure speed) had been out of order for the last four months as no-one in Warrnambool was able to fix it: it was intended to have it repaired in Melbourne. In the meantime the crew measured the vessel's speed by looking over the side and estimating wind strength. This compounded the difficulties of imprecise positioning, as the strong cross wind and sea were acting on the lightly laden vessel to steadily drive it towards the shore. At 3.30am on Friday 10 February 1911 Captain Jacobsen and the first mate were looking over the side of the vessel when they heard the sound of breakers and suddenly struck the rocks. The crew immediately knew they had no chance of getting the SPECULANT off, and attempted to rescue themselves by launching the lifeboat, which was instantly smashed to pieces. One of the crew then volunteered to take a line ashore, and the rest of the crew were all able to drag themselves to shore, some suffering hand lacerations from the rocks. Once ashore they began to walk along the coast towards Lorne, believing it was the nearest settlement. Realising their mistake as dawn broke they returned westwards to Cape Patton, and found a farm belonging to Mr C. Ramsden, who took them in and gave them a change of clothes and food. After resting for a day and returning to the wreck to salvage some of their personal possessions, at 10am on Saturday they set out for Apollo Bay, a voyage that took six hours, sometimes wading through flooded creeks up to their necks. The Age described the wreck as "listed to starboard. All the cabin is gutted and the ballast gone. There is a big rock right through the bottom of her, and there is not the slightest hope of getting her off". A Board of Marine inquiry found that Captain Jacobson was guilty of careless navigation by not taking steps to accurately verify the position of the vessel with respect to Cape Otway when the light was visible and by not setting a safe and proper course with respect to the wind and sea. It suspended his certificate for 6 months and ordered him to pay costs. The location of the wreck site was marked for a long time by two anchors on the shoreline, until in 1970 the larger of the two anchors was recovered by the Underwater Explorers' Club and mounted on the foreshore at Apollo Bay. The bell from the wreck was also donated to the Apollo Bay Surf Lifesaving Club but is recorded to have been stolen. Rusting remains of the wreck can still be found on the shoreline on the southern side of, and directly below Cape Patton. Parts of the SPECULANT site have been buried by rubble from construction and maintenance works to the Great Ocean Road, as well as by naturally occurring landslides. Peter J McGennan passed away in 1920. The Gates in the western wall of the Anglican Church in Henna Street/Koroit St are dedicated to him for his time of community work, which is matched with other prominent Warrnambool citizens; Fletcher Jones, John Younger, J.D.E (Tag) Walter, and Edward Vidler. After Peter J McGennan's death Harry, Andrew and Edith continued to operate the family business until July 11th 1923 when the company was wound up. (Andrew lived in Ryot Street Warrnambool, near Lava Street.) Harry McGennan (Peter and Emily’s son) owned the Criterion Hotel in Kepler Street Warrnambool (now demolished). His son Sid and wife Dot lived in 28 Howard Street (corner of Nelson Street) and Sid managed the Criterion until it was decided by the family to sell, and for he remained Manager for the new owners until he retired. Harry commenced the Foreshore Trust in Warrnambool around 1950. The McGennan Carpark in Pertobe Road is named after Harry and there are Memorial-Stone Gates in his memory. (The Gates were once the original entrance to the carpark but are now the exit.). Peter’s great-grandson, also called Andrew, is a Security Officer in Warrnambool. The Patent Log (also called a Taffrail log) from the SPECULANT, mentioned above, and a number of photographs, are now part of the Collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The SPECULANT is historically significant as the largest ship to have been registered in Warrnambool, and is believed to have been the largest barquentine to visit Melbourne. It is evidence of the final days of large commercial sailing vessels involved in the Victorian and New Zealand timber trade. The SPECULANT is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S626Photograph. black and white, of the three-masted barque SPECULANT in dock at the Warrnambool Breakwater in the early 1900's. A steam ship is docked behind her and another steamship is in Lady Bay on her left. There are people on the SPECULANT and others walking nearby. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, la bella, speculant, cumming and ellis, international timber trade, p. j. mcgennan and co. warrnambool, peter mcgennan, capt. james jacobsen, warrnambool maritime history, h. pengilley apollo bay -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGun Emplacement, 1890's
The Warrnambool Battery on Flagstaff Hill has embankments for 3 guns. Those on the left and right still have cannon in place but in the centre is an empty embankment, apart from this concrete ring with metal threaded studs. In 1898 a 5 inch breech loading gun (BL) was installed here. The gun had a hydro-pneumatic disappearing carriage (hence the sign on the concrete wall "5" BL HP").. This type of gun was faster to load and fire that the 80 pound RML’s installed on either side of it. Its arrival spelt the end of the 80 pound RML guns’ useful life, although they continued to be used for practice sessions. The 5 inch BL was the main defensive weapon of the Warrnambool Battery until the Battery was downgraded in importance. It was removed in 1904 and recalled to Melbourne in 1910. The gun emplacement ring is all that remains of the mounting for a 5 inch Armstrong rifled breech loading gun. HISTOR of the WARRNAMBOOL GUNS & CANNON In the years following the Crimean War (1854-1857J) there was a great concern in the Colony that Imperial Russia would attempt an invasion. Coastal defences in the colony of Victoria were greatly strengthened by the Government as a result. Warrnambool was originally protected by cannons at Cannon Hill, approximately 1 kilometer west of the Flagstaff Hill Fortifications. The cannons included two 1866 guns, both 80 Pound Rifled Muzzle Loaders (RML) purchased by Victoria’s Colonial Government. They were part of a shipment of 26 such guns sent from England in December 1866. They are registered as No. 23 (80cwt-2qr-0lbs) - Gun 1, and No.13 (81cwt-1qr-12lbs) - Gun 2. They were cast at the Royal Gun Factory, Woolwich Arsenal, in 1866 and have a 6.3 inch bore. Both barrels carry the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria, Insignia of the Royal Engineers, within the Garter and Motto surmounted by the Crown, with the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria within the Garter (letters in centre “VR”, motto “HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE”, "Shame be to him who thinks evil of it."). The guns were originally supplied with wooden carriages. (The Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, England, was established eleven years after the Restoration of King Charles II. It was the principal supplier of armaments to the British and Empire Governments. At the height of its operations during World War One the factory covered 1300 acres and employed very nearly 80,000 workers. Woolwich was the Headquarters of the Royal Artillery since the raising of that Regiment in 1716. The Arsenal was closed in the late 1960’s.) These two 80pdr cannons were transferred to the Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery Fortifications erected at Flagstaff Hill in 1887 as part of Victoria’s Coastal Defences. The original wooden carriages were subsequently replaced with the present iron garrison carriages in 1888. They are a “C” pivot. The ‘racers’ or curved track set into the floor of the gun emplacement (which enabled the guns to be traversed more quickly) are as specified for guns up to 10 inch, being of wrought iron 2.78 inches wide. A temporary third gun, now no longer on Flagstaff Hill’s site, was the 5 inch Rifled Breech Loading (BL) Armstrong gun mounted on an Elswick hydro pneumatic disappearing carriage and installed in this very concrete base or pad. The State of Victoria took over the ownership of the guns at the time of Australian Federation in 1901. In about 1901/1902 the Garrison Battery was converted to the Warrnambool Battery of the Australian Field Artillery (No 4 Field Battery). It was equipped with 4.7 inch naval guns mounted on field carriages. They were now a mobile unit but continued to use the Warrnambool Garrison area at Flagstaff Hill for practice. When the Fortifications were declared obsolete the two 80 Pounder RML were relocated to Cannon Hill in 1910. On the outbreak of World War One the 4.7 inch guns were recalled to Melbourne, and the Battery was disbanded. Most of the personnel probably re-enlisted in the local 4th Australian Light Horse Regiment. The two 80 Pounder RML were moved back to the Fortifications in 1973. They were both fully restored by Army First Year Apprentices at the Ordinance Factory in Bendigo in time for the centenary year of the fortifications in 1987. The guns are capable of firing 80 pound (32.3kg) armour piercing exploding shells 3.65kms out to sea. They were originally manned by volunteers before a paid Garrison was established. Now the Guns are again fired by volunteers on Special Event days. Since restoration the Gun Number 1 had been fired on a regular basis but Gun Number 2 hadn’t been fired since the mid 1990’s. In April 2015 Gun Number 2 was serviced in preparation for the firing of both cannons on the ANZAC Centenary commemorations on April 25th 2015. Other guns from the original Cannon Hill location were obsolete by the time the 1887 Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery was built. These guns are (1) a 32 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore (SB) cast in 1813 at the famous Carron Foundry, number 80837 and now located in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens. It is now mounted on a replica carriage due to the original carriage being in a fragile condition (the original carriage stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill). (2) a 68 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore cast in 1861 at the equally august Low Moor Foundry, number 10310 and now located on the lawn area at the entrance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. It is still mounted on its original wooden garrison carriage. Its wooden slide compressor mechanism is fragile and now kept in Flagstaff Hill’s storage. There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron and fifteen 68 Pounder SB made at Low Moor known to exist in the State of Victoria [references; Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village interpretation boards, information sheets and other documents; South Western Victoria Guns and Cannon report, May 2008, ref W/F/08] The Gun embankment is contained within the heritage listed Lady Bay Lighthouse Comples, on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1520. The gun emplacement base is evidence of the last defences installed on this stretch of coastline. The Warrnambool Garrison has been added to the Victorian Heritage Register H1250 “for its intact battery and guns, a strong reminder of Victoria’s wealth and determination to protect itself from the perceived threat of invasion in the 1880’s.” The City of Warrnambool is one of several custodians of a collection of artillery pieces of heritage significance at a state, national and international level. These pieces are directly related to the defence of south-west Victoria in the 19th century. The care and preservation come under the Heritage Act 1995. Gun emplacement; the remains of the mounting platform of a temporary third gun installed in 1898 in the centre of the battery. This consists of a circular concrete well or sump surrounded by two rings of mounting bolts, the inner of 10 and the outer of 20. The base once held a 5 inch Armstrong rifled breech loading gun with hydro-pneumatic disappearing. In the centre of the ring on the ground is a keyhole shaped space. The gun was removed in 1904. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, colonial defences, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, warrnambool volunteer corps, ordinance, armaments, cannon hill fortifications, flagstaff hill fortifications, 4th australian light horse regiment, garrison gun, 5 inch breech loading gun, emplacement for hydro-pneumatic disappearing carriage, gun emplacement -
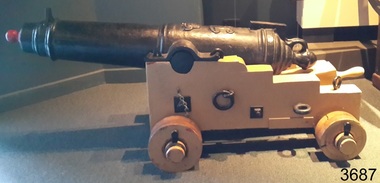 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Carronade, 1840
The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, but it also found a niche role on warships. It was produced by the Carron Iron Works and was at first sold as a complete system with the gun, mounting, and shot altogether. Carronades initially became popular on British merchant ships during the American Revolutionary War. A lightweight gun that needed only a small gun crew and was devastating at short range was well suited to defending merchant ships against French and American privateers. The invention of the cannon is variously attributed to Lieutenant General Robert Melville in 1759, or to Charles Gascoigne, manager of the Carron Company from 1769 to 1779. In its early years, the weapon was sometimes called a "mellvinade" or a "gasconade". The carronade can be seen as the culmination of a development of naval guns reducing the barrel length and thereby the gunpowder charge. The Carron Company was already selling a "new light-constructed" gun, two-thirds of the weight of the standard naval gun and charged with one-sixth of the weight of the ball in powder before it introduced the carronade, which further halved the gunpowder charge. The theory of its design was to use less powder and had other advantages that were advertised in the company's sales pamphlet of the time, state. The smaller gunpowder charge reduced the barrel heating in action, also reduced the recoil. The mounting, attached to the side of the ship on a pivot, took the recoil on a slider, without altering the alignment of the gun. The pamphlet advocated the use of woollen cartridges, which eliminated the need for wadding and worming, although they were more expensive. Carronades also simplified gunnery for comparatively untrained merchant seamen in both aiming and reloading that was part of the rationale for adopting the gun. Other advantages promoted by the company were. The replacement of trunnions by a bolt underneath, to connect the gun to the mounting, reduced the width of the carriage that enhanced the wide angle of fire. A merchant ship would almost always be running away from an enemy, so a wide-angle of fire was much more important than on a warship. A carronade weighed a quarter as much as a standard cannon and used a quarter to a third of the gunpowder charge. This reduced charge allowed Carronades to have a shorter length and much lighter weight than long guns. Increasing the size of the bore and ball reduces the required length of the barrel. The force acting on the ball is proportional to the square of the diameter, while the mass of the ball rises by the cube, so acceleration is slower; thus, the barrel can be shorter and therefore lighter. Long guns were also much heavier than Carronades because they were over-specified to be capable of being double-shotted, (to load cannons with twice the shot, for increased damage at the expense of range), whereas it was dangerous to do this in a carronade. A ship could carry more carronades, or carronades of a larger calibre, than long guns, and carronades could be mounted on the upper decks, where heavy long guns could cause the ship to be top-heavy and unstable. Carronades also required a smaller gun crew, which was very important for merchant ships, and they were faster to reload. The small bore carronade and carriage is part of a collection of nineteenth Century Flagstaff Hill Guns and Cannon, which is classified as being of significance and was made a few years after the beginning of Queen Victoria's reign in 1837 and fires a 6 lb pound cannon ball. This nineteenth century artillery piece is a rare and representative item of artillery of this era, used predominately on ships, both military and merchant. The artillery piece, individually and as part of the collection, is highly significant for its historical, scientific and aesthetic reasons at the state, national and world level. This carronade represents the methods of artillery technology, its advancement and its modifications to suit dangerous situations that sailors encountered from attacks from free booters (pirates, living from plunder) or others at the time. Carronade firing a 6 lb cast iron ball, with a smooth bore barrel 6.5 cm in dia the item is mounted on stepped wooden carriage with wooden wheels. Cannon barrel can have its elevation adjusted via a wooden wedge. Gun carriage has loops for locating and holding in position to a deck by ropes. Carriage is a replica made 1982Cast into the barrel is the royal emblem of Queen Victoria (VR "Victoria Regina") indicating the carronade was cast during Queen Victoria's reign / 1840 & 4-2-0 denoting the weight of the barrel. Right hand trunnion has a serial number “8708”. Also on top of the barrel is the British "Board of Ordinance" identifying mark a broad arrow indicating the carronade was in military use. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, colonial defences, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, warrnambool volunteer corps, ordinance, armaments, garrison gun, smooth bore cannon, carronade, black powder, 12 pounder, 1840, artillery, lieutenant general robert melville, charles gascoigne, carron company, mellvinade, gasconade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, 1813
This 1813 cannon is classified as a carronade, having been made by the Carron Ironworks foundry in Stirling, Scotland in 1813. It is a large calibre, short range, gun mainly used on ships. The carronade model of cannon was first used when introduced into the British Royal Navy in the American War of the Revolution (1775-1883). This cannon was originally a 28pdr, 48cwt, 8ft gun. The date ‘1837’ on the barrel probably indicates the date that the Board of Ordinance accepted the change in size to a 32pdr. It may originally have been a naval gun and the conversion undertaken when it was brought ashore. It is very probably one of the 15 guns that are known to have constituted the defences of Victoria in 1860. This group of 32pdrs was the shorter model of the 4800width and 8ft length cannon and as such are different from the 32pdrs found in NSW. It was originally located on Cannon Hill in Warrnambool when it was the site of the Warrnambool Battery Western Artillery, formed in 1866. It was obsolete by the time of the 1887 fortifications, and was moved from the Warrnambool Fortifications to the Botanic Gardens in 1910, when the Fortifications were declared obsolete. HISTORIC INFORMATION ABOUT THE CANNON IN THE WARRNAMBOOL AREA In the years following the Crimean War (1854-1857J) there was a great concern in the Colony that Imperial Russia would attempt an invasion. Coastal defences in the colony of Victoria were greatly strengthened by the Government as a result. Warrnambool was originally protected by cannons at Cannon Hill, approximately 1 kilometer west of the Flagstaff Hill Fortifications. The cannons included two 1866 guns, both 80 Pound Rifled Muzzle Loaders (RML) purchased by Victoria’s Colonial Government. They were part of a shipment of 26 such guns sent from England in December 1866. They are registered as No. 23 (80cwt-2qr-0lbs) - Gun 1, and No.13 (81cwt-1qr-12lbs) - Gun 2. They were cast at the Royal Gun Factory, Woolwich Arsenal, in 1866 and have a 6.3 inch bore. Both barrels carry the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria, Insignia of the Royal Engineers, within the Garter and Motto surmounted by the Crown, with the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria within the Garter (letters in centre “VR”, motto “HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE”, "Shame be to him who thinks evil of it."). The guns were originally supplied with wooden carriages. (The Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, England, was established eleven years after the Restoration of King Charles II. It was the principal supplier of armaments to the British and Empire Governments. At the height of its operations during World War One the factory covered 1300 acres and employed very nearly 80,000 workers. Woolwich was the Headquarters of the Royal Artillery since the raising of that Regiment in 1716. The Arsenal was closed in the late 1960’s.) The two 80pdr cannons were transferred to the Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery Fortifications erected at Flagstaff Hill in 1887 as part of Victoria’s Coastal Defences. The original wooden carriages were subsequently replaced with the present iron garrison carriages in 1888. They are a “C” pivot. The ‘racers’ or curved track set into the floor of the gun emplacement (which enabled the guns to be traversed more quickly) are as specified for guns up to 10 inch, being of wrought iron 2.78 inches wide. A temporary third gun, now no longer on Flagstaff Hill’s site, was a 5 inch Rifled Breech Loading (BL) Armstrong gun mounted on an Elswick hydro pneumatic disappearing carriage It was faster to load and fire than the 80 pound RMLs and its arrival spelt the end of the older 80 pound guns’ useful life, apart from being used for practice sessions. The 5 inch BL gun was the main defensive weapon of the Warrnambool Battery until the Battery was downgraded in importance and the gun was recalled to Melbourne in 1910. The gun emplacement still remains in place set between the 2 80pdr cannon. The State of Victoria took over the ownership of the guns at the time of Australian Federation in 1901. In about 1901/1902 the Garrison Battery was converted to the Warrnambool Battery of the Australian Field Artillery (No 4 Field Battery). It was equipped with 4.7 inch naval guns mounted on field carriages. They were now a mobile unit but continued to use the Warrnambool Garrison area at Flagstaff Hill for practice. When the Fortifications were declared obsolete the two 80 Pounder RML were relocated to Cannon Hill in 1910. On the outbreak of World War 1 the 4.7 inch guns were recalled to Melbourne, and the Battery was disbanded. Most of the personnel probably re-enlisted in the local 4th Australian Light Horse Regiment. The two 80 Pounder RML were moved back to the Fortifications in 1973. They were both fully restored by Army First Year Apprentices at the Ordinance Factory in Bendigo in time for the centenary year of the fortifications in 1987. The guns are capable of firing 80 pound (32.3kg) armour piercing exploding shells 3.65kms out to sea. They were original manned by volunteers before a paid Garrison was established. Now the Guns are again fired by volunteers on Special Event days. Since restoration the Gun Number 1 had been fired on a regular basis but Gun Number 2 hadn’t been fired since the mid 1990’s. In April 2015 Gun Number 2 was serviced in preparation for the firing of both cannons on the ANZAC Centenary commemorations on April 25th 2015. Other guns from the original Cannon Hill location were obsolete by the time the 1887 Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery was built. These guns are (1) a 32 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore (SB) cast in 1813 at the famous Carron Foundry, number 80837 and now located in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens. It is now mounted on a replica carriage due to the original carriage being in a fragile condition (the original carriage stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill). (2) a 68 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore cast in 1861 at the equally august Low Moor Foundry, number 10310 and now located on the lawn area at the entrance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. It is still mounted on its original wooden garrison carriage. Its wooden slide compressor mechanism is fragile and now kept in Flagstaff Hill’s storage. There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron and fifteen 68 Pounder SB made at Low Moor known to exist in the State of Victoria Plaque attached to the carriage “This replica carriage was constructed by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club in conjunction with the generosity of local businesses and the Warrnambool community. The original carriage (circa 1860) was removed for restoration and is now located at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The timber used for the replica carriage is Monterey Cypress, which was an early planting in the gardens. 2010 marked the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens.” (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008, item W/B/01; Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village datasheets and archives). There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron known to exist in the State of Victoria and this is one of them. On a world level, this cannon represents a high level of rarity. Further, as it has been modified (bored up) it is representative of the historical process of amending artillery in order to ensure a longer usefulness of each piece despite rapidly advancing artillery technology. The number of surviving carriages with traversing slides in this group in South Western Victoria is unique in Australia and probably in the World. Out of 10 such platforms surviving in Australia, the South Western Victorian group has half. Several survive around the world but probably not in such a large group. The wooden sliding compressor mechanism belonging to this cannon is extremely rare, and the only one in this South Western Victorian group of Guns and Cannons. As a whole, this cannon has undergone very little restoration or modification, giving it a high level of integrity. The City of Warrnambool is one of several custodians of a collection of artillery pieces of heritage significance at a state, national and international level. These pieces are directly related to the defence of south-west Victoria in the 19th century. The care and preservation come under the Heritage Act 1995. (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008).Cannon, or carronade, 32pdr with wheels. Muzzle loading smooth bore (SB) cannon. Cannon has original wooden Burmese Teak carriage and slide with wrought iron fittings and iron wheels. Manufactured by Carron in Scotland, in 1813. It has been converted from a 28pdr. There is a loop for a rope on the cascabel, which was part of the original casting. Re-bored in 1837. Marks include Serial Number, Royal Cypher of King George III, broad arrow of proofing, and numbers to represent the weight. NOTE: The cannon is displayed in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and is mounted on a replica wooden carriage; the original wooden carriage is now stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. This carriage has 4 wheels on swivel attachments and a central gear that allows the wheels to turn on rails. Pressed into left trunnion “80837 / CARRON / 1813”, cast on barrel“symbol (Royal Cypher of King George III”, “symbol (broad arrow of proofing)” and numbers “45-3-24 / 1837” . Cascable “CV” and marks with gradations from nought to three in quarters on each side, On the carriage the end of one of the main slide members carries the mark “W symbol (broad arrow) D” incised into the timber. Plaque attached to the carriage by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club, 2010, marking the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and the addition of the replica carriage. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, ordinance, armaments, cannon hill fortifications, victorian colonial government, carron ironwroks foundary, 32pdr smooth bore cannon, 28pdr smooth bore cannon, 1813 cannon, carronade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Victorian Statutes Vol 1 Collectors of Customs, 1866
Warrnambool's copy of Government Statutes for Victoria, dated 1866. One of a set of four volumes.The Victorian Statutes Vol 1 Collectors of Customs A-E, front cover has Collectors of Customs Warrnambool. Brown leather binding and corners, black canvas cover, red and black bands on spine. The Victorian Statutes in four volumes, Volume I. Published by Authority, 1866. Printed by John Ferres, Government Printer, Melbourne. (Price for the four volumes 3 pound 3 shillings. warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, government statutes for victoria 1866, warrnambool's copy of government statutes 1866 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Victorian Statutes Vol 3 Collectors of Customs P-W, 1866
Warrnambool's copy of Government Statutes for Victoria, dated 1866. One of a set of four volumes.The Victorian Statutes Vol 1 Collectors of Customs P-W, front cover has Collectors of Customs Warrnambool. Brown leather binding and corners, black canvas cover, red and black bands on spine. The Victorian Statutes in four volumes, Volume 3, Published by Authority, 1866. Printed by John Ferres, Government Printer, Melbourne. (Price for the four volumes 3 pound 3 shillings. )warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, government statutes for victoria 1866, warrnambool's copy of government statutes 1866 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hemmer Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Broad Hemmer Foot for a Wertheim sewing machine. Joseph Wertheim manufacturer, Germany, distributed by Hugo Wertheim William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Small Corder Foot, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Small corder foot for a Wertheim sewing machine. Joseph Wertheim manufacturer, Germany, distributed by Hugo Wertheim William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, small corder foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Seamer Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Seamer foot; feller single seamer for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Braider foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim.Wertheim braider; an accessory for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Sewing Machine Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Foot accessory, metal, for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Binder, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Adjustable binder for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion, binder
