Showing 35 items matching "wiradjuri"
-
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, A New Wiradjuri Dictionary, 2010
An English to Wiradjuri and Wiradjuri to English dictionary.Colour photographs, word listswiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Stan Grant et al, Learning Wiradjuri : book 3 : extending language structures &? vocabulary, 2006
Text in Wiradjuri and English.Colour photographs, word listswiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant et al, Wiradjuri Language songs. Book 2, 2004
Includes information on the sound patterns of the Wiradjuri language. Melody line only, with text of songs in Wiradjuri. Includes English translations of the songs. See also companion volume Wiradjuri language songs for children of all ages /? Stan Grant (snr) and John Rudder.B&w illustrations, b&w photographs, sheet music, word lists, CD-ROMwiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant, Wiradjuri Language : some useful words and phrases
Word lists, colour illustrations, CD-ROMwiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant, Wiradjuri Language : some useful words and phrases vol. 2, 2011
word lists, colour illustrations, CD-ROMwiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant et al, Learning Wiradjuri : book 2 : about actions, 2001
B&w illustrations, b&w photographs, word lists, CD-ROM (contains place and direction; about actions)wiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant et al, Wiradjuri language songs for children of all ages, 2001
B&w illustrations, b&w photographs, sheet music, word lists, CD-ROMwiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBooklet with CDROM, Stan Grant et al, Learning Wiradjuri : book 1 : place and direction, 2006
Colour photographs, b&w illustrations, games, word lists, CD-ROM (contains place and direction; about actions)wiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Introducing Wiradjuri sentences, 2000
B&w illustrations, b&w photographs, word listswiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Stan Grant et al, Wiradjuri language : how it works : a grammar in everyday English, 2001
B&w illustrations, b&w photographs, word listswiradjuri -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesAudio CD, Songs recorded at Swan Hill and Finley, 1962
Wiradjuri war chant and songs sung by Hilton Walsh at Swan Hill; Madi Madi songs sung by Mary Moore; war chant and other songs sung by Tom Lyons at Finley.CD, recording noteswiradjuri, madhi madhi, oral histories -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Sue Wesson et al, Aboriginal flora and fauna names of Victoria : as extracted from early surveyors' reports, 2001
The Flora and Fauna Names Project is an initiative of the Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages and the Victorian Biodiversity Strategy. The researcher has examined material from the archives of the Department of Natural Resources and Environment (NRE), the State Library of Victoria, the Victorian Public Records Office and the Australian Archives Office. This first stage of the project focussed on the NRE archives, in particular the field notebooks of the earliest surveyors and their maps although other NRE resources, libraries and public records were accessed. A total of 3028 words were found of which a significant proportion have previously been unknown to linguists. It appears that the place names and word lists in early surveyors notebooks, the 1858 surveyors responses to the Surveyor General and an extensive Wiradjuri wordlist by James Baylis have not yet been widely used or published. Fifteen percent of these 3028 words describe flora and fauna and six percent describe habitat. Of particular interest is the evidence provided by these lists of the existence of fauna in the mid nineteenth century in regions where it is now extinct. For example, magpie geese, eastern quolls, bustards and pademelons were assigned names in the Jardwadjali language area of the upper Glenelg and Wimmera Rivers. The outcomes of this project may help to assist in ascertaining the distribution of flora and fauna assets in Victoria.maps, b&w photographs, colour photographs, illustrations, word listswiradjuri, jardwadjali, glenelg river, wimmera river -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncSign, Wagana, 1920s
In the 1920s and 30s, rowing on the Yarra was a very popular weekend pastime. Each of the early boats was individually named in gold letters on its varnished wooden backboard. This is all that remains of one of the Thames pulling boats from Burns' Boatshed at Studley Park which was destroyed by a falling tree in a storm. Their entire fleet of rowing boats has now been replaced by fiberglass boats.Varnished wooden backplate of a rowing boat. The shaped sign is embossed with the name 'Wagana" in gold lettering, outlined and shaded in black paint. Gilt scroll work surrounds the name. The ends of the backplate shows the holes where the plate was once attached to the seat of the boat. The name Wagana means 'to dance' in Wiradjuri language."Wagana"burns' boatshed, thames pulling boats, yarra river -- kew (vic.), boathouses - river yarra -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Trish Albert, Keeping language alive, 2008
Maps, colour photographs, colour illustrations, sheet music, gamesguugu yimithirr, wiradjuri, torres strait creole -
 Darebin Art Collection
Darebin Art CollectionPhotograph, Karla Dickens, Looking at You VI, 2017
"Karla Dickens was born in Sydney in 1967. She is a Wiradjuri woman and an award-winning contemporary artist whose work draws on her Indigenous heritage, sexuality and experiences as a single mother on welfare. She has more than twenty years of artmaking practice, first graduating with a Diploma of Fine Arts in 1993, then a Bachelor of Fine Arts in 2000, both from the National Art School, Sydney." -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Vicki Couzens, tyama-teeyt yookapa : interviews from the Meeting Point Project, 2014
This book is a collection of stories, reflections and hopes abuot Language revival in Australian Aboriginal communities, extracted from a series of interviews carried out during 2009-2010.B&w photographslanguage revival, interviews, indigenous language victoria, indigenous language nsw, parkes, gumbaynggirr, wiradjuri -
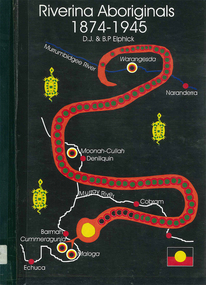 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Riverina Aboriginals : 1874-1945, 1996
Lists of residents of the Warangesda 1880-1925, Maloga 1874-1888, Cummeragunja 1889-1953 (Stn) 1883 - present (Res) Moonah Cullah 1910-1952(Stn) 1896-1962(Res) Aboriginal Stations and other Rivereina Aboriginals 1874-1954maps, b&w photographs, registry listingsyorta yorta, wemba wemba, wiradjuri, warangesda, maloga, cummeragunja, moonah cullah -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, J Hobson, Re-awakening languages : theory and practice in the revitalisation of Australia's Indigenous Languages, 2010
Language policy and planning, Language in communities, Language centres and programs, Language in education, Literacy and oracy, Language and technology, Language documentationScreen shots, b&w photographs, b&w diagramslinguistics, sociolinguistics, kaurna, wiradjuri, ngapartji ngapartji, dharug, dhurga, language and technology -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesCeramic - Photograph - Colour, Ceramics Decorated by Bill Onus, c1955
William (Bill) ONUS (15 November 1906-1968) Born Cummeragunja Aboriginal Reserve, Murray River, New South Wales Clan: Wiradjuri William Townsend (Bill) Onus was a shearer, actor and activist who revived the Australian Aboriginese League in Melbourne in 1946. He retired from politics in to start the Aboriginal Enterprises workship in Belgrave with his brother Eric. They produced boomerangs, woomeras, fabrics and greeting cards imprinted with Aboriginal motifs. He ran the business from his small factory and shop at Belgrave in the Dandenong Ranges. To promote his wares Bill Onus toured widely in Victoria and beyond as a travelling showman, giving demonstrations of boomerang-throwing, which he advocated as a national sport. (ADB) Bill Onus adopted similar imagery to that which appeared in mass-produced indigenised design; however, he used such works to draw attention to his political work with the ‘Committee for Aboriginal Citizen Rights’ and the ‘Australian Aborigines League.’ William McLintock (Lin) Onus is the son of Bill Onus. Ceramic form decorated with Aboriginal design by Bill Onus.aboriginal, bill onus, aboriginal enterprise novelties, ceramics -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, 'Wirrin' by Bill Onus
William (Bill) ONUS (15 November 1906-1968) Born Cummeragunja Aboriginal Reserve, Murray River, New South Wales Clan: Wiradjuri William Townsend (Bill) Onus was a shearer, actor and activist who revived the Australian Aboriginese League in Melbourne in 1946. He retired from politics in to start the Aboriginal Enterprises workship in Belgrave with his brother Eric. They produced boomerangs, woomeras, fabrics and greeting cards imprinted with Aboriginal motifs. He ran the business from his small factory and shop at Belgrave in the Dandenong Ranges. To promote his wares Bill Onus toured widely in Victoria and beyond as a travelling showman, giving demonstrations of boomerang-throwing, which he advocated as a national sport. (ADB) Bill Onus adopted similar imagery to that which appeared in mass-produced indigenised design; however, he used such works to draw attention to his political work with the ‘Committee for Aboriginal Citizen Rights’ and the ‘Australian Aborigines League.’ William McLintock (Lin) Onus is the son of Bill Onus. Wooden plate decorated with Aboriginal design by Bill Onus.Stamped on back "Made in Australia Bill Onus"aboriginal, bill onus, aboriginal enterprise novelties, ceramics -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Boomerang, Probably by Bill Onus, c1960s, 1960s
William (Bill) ONUS (15 November 1906-1968) Born Cummeragunja Aboriginal Reserve, Murray River, New South Wales Clan: Wiradjuri William Townsend (Bill) Onus was a shearer, actor and activist who revived the Australian Aboriginese League in Melbourne in 1946. He retired from politics in to start the Aboriginal Enterprises workship in Belgrave with his brother Eric. They produced boomerangs, woomeras, fabrics and greeting cards imprinted with Aboriginal motifs. He ran the business from his small factory and shop at Belgrave in the Dandenong Ranges. To promote his wares Bill Onus toured widely in Victoria and beyond as a travelling showman, giving demonstrations of boomerang-throwing, which he advocated as a national sport. (ADB) Bill Onus adopted similar imagery to that which appeared in mass-produced indigenised design; however, he used such works to draw attention to his political work with the ‘Committee for Aboriginal Citizen Rights’ and the ‘Australian Aborigines League.’ William McLintock (Lin) Onus is the son of Bill Onus. Painted boomerang thought to be decorated by Bill Onus.boomerang, aboriginal, bill onus, aboriginal enterprise novelties -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, A W Howitt, The native tribes of South-East Australia : part 1, 2003
Alfred William Howitt 1830-1908 was a pioneer anthropologist. ?The Native Tribes of South-East Australia? is not only a great classic anthropological work, it contains an enormous wealth of material of interest to anyone interested in Australian history, particularly the people of Koorie descent. His work has been presented here in total as originally produced.maps, b&w illustrations, b&w photographs, tablesdieri, wonkanguru, yuin, wonkamala, kulin, kurnai, wiradjuri, kamilaroi, wotjobaluk, wurrunjerri, wimbaio, yaurorka, urabunna, yantruwunta -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, A W Howitt, The native tribes of South-East Australia : part 2, 2003
Alfred William Howitt 1830-1908 was a pioneer anthropologist. ?The Native Tribes of South-East Australia? is not only a great classic anthropological work, it contains an enormous wealth of material of interest to anyone interested in Australian history, particularly the people of Koorie descent. His work has been presented here in total as originally produced.musical notations, b&w illustrations, b&w photographsdieri, wonkanguru, yuin, wonkamala, kulin, kurnai, wiradjuri, kamilaroi, wotjobaluk, wurrunjerri, wimbaio, yaurorka, urabunna, yantruwunta -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Native names
Journal of handwritten notes from various 19th-century suveyors? sources. The sources are numbered and indicated in contents. Includes definitions of most placenames, but most languages not identified. * Marked ?Hem 164.?wiradjuri, portland, smythesdale, redcastle, ballan, bairnsdale, swan hill, terricks, echuca, mansfield, dunolly, bontherambo, beechworth, james j baylis -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap, Aboriginal Language Areas in Victoria: A Reconstruction
A4 sized map of Victoria showing Aboriginal Langauge Areas. Black, white and red writing aboriginal, aboriginal language, victoria, djadja wurrung, woi wurrung, watha wurrung, gadubanud, girai wurrung, dhauwurd wurrung, djab wurrung, wiradjuri, tatungalung, wadiwadi, dadidadi, yuyu -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Isobel White, The opal that turned into fire : and other stories from the Wangkumara, 1994
These stories are written versions of legends handed down through the oral tradition of Aboriginal storytellers from the Riverina of New South Wales and Victoria, coastal regions and other parts of Australia.Colour photographs, illustrations, mapswongaibon, kamilaroi, kirrea, dharawal, ualarai, gandangara, darkinjung, dhurga, ngemba, bandjalang, wiradjuri, muruwari, riverina, lake eyre, murray river -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, The Macquarie Library, Macquarie Aboriginal naming book : an Australian guide to naming your home or boat, 1996
An English-Aboriginal word list for the purpose of naming houses or possessions - information is derived from ?Macquarie Aboriginal Words? and includes source languages for words.word listsbundjalung, datiwuy, diyari, eastern arrernte, gooniyandi, kaurna, meryam mir, murrinh-patha, ngiyampaa, nyungar, paakantyi, torres strait creole, wemba wemba, wik-mungkan, wiradjuri, yindjibarndi -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Gang Gang Cockatoo (male), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Gang-gang Cockatoo can be found throughout much of south-eastern Australia. They reside in mountainous forests and open woodlands, often in small groups or larger flocks at sources of food and water. They eat mainly seeds from native trees and shrubs along with wattles, eucalypts and hawthorns. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is also known to incorporate berries, nuts, fruits and insects to their diet. The sound made by this type of Cockatoo is often described as a rasping screech which resembles the sound of a rusty hinge being moved.This type of call is made when the bird is in flight. These birds also fond of attention and can pick their own feathers if they are bored. The name "gang gang" derives from a New South Wales Aboriginal language, either the Ngunnawal or Wiradjuri. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The male Gang Gang Cockatoo is standing stylised on a wooden perch. The Cockatoo has a dark slate-grey coloured body with a scarlet red/orange coloured head with a wispy crest. This specimen stands with its wings positioned to its sides and has round glass bead eyes. The bill has a hooked shape and is horn-coloured. The legs and feet of this specimen are dark grey.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, cockatoo, gang-gang cockatoo, cockie -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Gang Gang Cockatoo (female), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Gang-gang Cockatoo can be found throughout much of south-eastern Australia. They reside in mountainous forests and open woodlands, often in small groups or larger flocks at sources of food and water. They eat mainly seeds from native trees and shrubs along with wattles, eucalypts and hawthorns. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is also known to incorporate berries, nuts, fruits and insects to their diet. The sound made by this type of Cockatoo is often described as a rasping screech which resembles the sound of a rusty hinge being moved.This type of call is made when the bird is in flight. These birds also fond of attention and can pick their own feathers if they are bored. The name "gang gang" derives from a New South Wales Aboriginal language, either the Ngunnawal or Wiradjuri. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Gang-gang Cockatoo has a grey head and crest with brown glass eyes. The beak is hooked and a pale bone colour. The neck and torso of the cockatoo is patterned with orange and black stripes. The feathers of the underparts and back are slate-grey with an edging of pink and yellow. The female cockatoo has more yellow in their feathers than the males which gives them a further barred appearance. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, australaisian shovelor, shovelor, cockatoo, gang-gang cockatoo, cockie -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Aboriginal Community Elders Service et al, Aboriginal elders' voices : stories of the "tide of history" : Victorian Indigenous elders' life stories &? oral histories, 2003
This book is a collection of Victorian Indigenous Elders' life stories and oral histories. The Elders share their stories in an attempt to ensure that both sides of Australia's history are finally heard. These stories tell of cultural resistance on missions, of defying assimilation laws, of forever moving around to save children from the welfare. They document the development of both fringe and urban communities and work in the Aboriginal rights movement. They clarify the ways in which these experiences have affected the individual authors along with the indigenous population in general. Also included in the book is a brief history and analysis of the legislation, policies, attitudes and strategies that have affected the lives of the authors and their families since colonisation. This aspect provides an historical perspective, encouraging a deeper understanding of the Elders' stories. Reconciliation can only eventuate with an understanding gained from hearing and including the voices of Indigenous Australians. Contents: The writing team Indigenous elders: keepers of knowledge; custodians of land and culture Aboriginal lands Missions and reserves Growing up running from the welfare /? Aunty Olive Jackson Respecting our Elders /? Aunty Lola James If your mother didn't tell you, then your grandmother did! /? Uncles Les Stewart Don't dwell on trouble /? Aunty Audrey Critch There are my people /? Aunty Gwen Nelson We were all cousins, more or less /? Aunty Iris Lovett-Gardiner Aboriginality is about culture, not colour /? Aunty Dianne Phillips Take up the opportunities we struggled to make /? Aunty Frances Gallagher Home /? Aunty Eileen Alberts We were supposed to forget our Aboriginality /? Aunty Gwen Garoni Not enough heart to say sorry? /? Uncle Brian Kennewell-Taylor Learning from indigenous elders: Keeping the traditions, keeping the culture strong; Since time immemorial; Invasion: the tide ran red; The flood of legislation; Stolen children; Cultural resistance: holding on to children traditions and land; Organised resistance: a movement is born; The 1950s: community resistance to race laws; The price of assimilation; The Aboriginal rights movement; After the flood: self-determination; Turning the tide Bibliography Appendix. Cultural custodianship: developing an indigenous methodology.maps, colour illustrations, b&w photographswiradjuri, victorian indigenous elders, oral histories, yorta yorta, dja dja wurrung, language maps, victorian missions and reserves, lake condah, framlingham, coranderrk, ramahyuck, lake tyers, wahgunyah, cummeragunja, moonahcullah, balranald, ebenezer, maloga, acheron
