Showing 26 items matching "news"
-

Burke and Wills: Have Camels Will Travel
... not be definitely promised it would answer my purpose as well if the claim be recognised as one which the authorities would as honorable men recommend to be paid if such calamity befall me or if no news of me had been received here for four years. I should ...Dromedary camels were introduced to Australia in 1840. The first significant shipment, however, was made to service the Burke and Wills expedition, which was the first exploring party to use camels, as well as horses, for transporting supplies.
In 1858, George Landells, who had worked as a horse trader in India, wrote to the Victorian Government explaining how the camel was ideally suited to the Australian landscape. He offered to travel to India and purchase camels on behalf of the Victorian government for use in exploration, and as the basis of a breeding stud. The government’s Board of Science and Zoological Gardens Committee agreed that the camel would be useful on the Australian continent, and Landells was authorised to borrow money from the Indian Government and make the purchase.
Landells traveled through India, Pakistan and Afghanistan to source the animals, engaging eight camel drivers to assist him on the journey from Karachi to Melbourne in December 1859, arriving mid-June 1860.
He was hailed for his travels through the ‘very unsettled’ lands by the English Scindian Newspaper, and similarly lauded in Melbourne where the ‘exotic’ animals caused a sensation, as did their handlers, identified variously as Indians, Sepoys, and Malays.
Partly in response to his fame, Landells was appointed second in command of the Burke and Wills expedition. He was also appointed officer in charge of the camels.
Landells recruited John Drakeford and John King, who had helped him bring the animals from Karachi to Melbourne, and four of the eight handlers: Samla (described by Becker as a Hindu), Dost Mahomet (or Botan), from Guznee; Esau Khan (or Hissand or Isaah), Belooch, who came from Mahadpoor in the Punjab, and another man from Kelat.
The expedition party departed Melbourne with 26 camels. As the expedition progressed, Landells and Burke disagreed over their treatment and Landells resigned in Menindee.
Four of the 26 camels were left at Menindee. Dost Mahomet stayed with 16 at the Coopers Creek depot. Burke and Wills took six animals with them on their trek to the Gulf and John King, travelled with them, to care for. Some of the animals strayed or were lost, others were abandoned. Burke, Wills, Charlie Gray and John King ate the last of them, as they struggled back from the Gulf of Carpentaria.
However the Burke and Wills Expedition was not the end of the story. Camels had proved their worth in negotiating the harsh and dry Australian interior and camels became an increasingly important form of transport in the Australian inland. Between 1870 and 1900, over 15,000 camels and 2000 cameleers were brought to Australia. The cameleers were commonly known as “Afghans” although small in number, they made a vital contribution to Australia’s exploration and development.
Feral camels now roam across outback Australia. In response, markets for live camels and camel meat have developed. It is more than likely that the descendents of Landells’ camels are among those that now roam the Australian continent.
-

William Barak
... Coranderrk was a successful hop farm in the early 1870s. This print was published in The Illustrated Australian News in May 1872. ...Diplomat, artist, story-teller and leader, Wurundjeri (Woiwurung) man William Barak worked all his life to protect the rights and culture of his people, and to bridge the gap between settlers and the land’s original custodians.
Barak was educated at the Yarra Mission School in Narrm (Melbourne), and was a tracker in the Native Police as his father had been, before becoming ngurungaeta (clan leader). Energetic, charismatic and mild mannered, he spent much of his life at Coranderrk Reserve - a self-sufficient Aboriginal farming community in Healesville.
Barak campaigned to protect Coranderrk, worked to improve cross-cultural understanding and created many unique artworks and artifacts, leaving a rich cultural legacy for future generations.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
Further information on William Barak can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-

Rippon Lea Estate
... in the 1960s. Having lost two court cases, she combined her efforts with the National Trust to successfully save the property for the people of Victoria. She received this news shortly before she died in 1972,aged seventy-eight. As Henry Bolte, Victorian ..."Do you remember the garden in which you grew up, or the part the backyard played in your family life? Imagine if you had actually grown up in one of Australia's finest gardens.
Created in the English-landscape tradition which traces its roots back to Capability Brown and Humphry Repton, Rippon Lea is one of Australia's most important historic homes, exemplifying the lifestyle of wealthy families living in 19th and 20th century Australian cities. Although its architecture and that of its outbuildings is impressive, it is the mansion’s gardens, which are truly remarkable, both for their landscape qualities and because they have survived many threats and changes in the past 130 years.
Today, the amenities offered by a typical garden are still greatly valued: a safe place for children to play, somewhere to dry the washing, a plot for vegetables and a flower garden that adds colour and produces blooms for the home. Today as then, the scale differs but the experience of owning a garden - with its balance of utility and ornament - is essentially the same.
The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) now runs Rippon Lea as a museum, conserving the architecture and the landscape, and presenting the social history of the owners and their servants. Visitors to Rippon Lea enter a mansion preserved as the Jones family lived in it after their 1938 modernisation. In the pleasure garden the Sargood era is evoked by the staging of a range of performing arts events including opera, theatre, chamber music and outdoor activities."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Solid Joys and Lasting Treasure: families and gardens written by Richard Heathcote for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Postcards: Stories from the Mornington Peninsula
... "The white wake of the paddle steamer, pink under the burning sun." Perth Daily News, 1920 ...Stories of a time in history when holidaying was a grand pastime, and when special and unique places in Victoria began to be appreciated, celebrated and shared in that iconic mode of communication: the picture postcard.
Inspired by postcards in their collections, eight historical societies developed themes to explore the history of the Mornington Peninsula.
This story is based on a touring exhibition which was initiated by the Mornington Peninsula Local History Network and the Mornington Peninsula Shire.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
... of three brothers who enlisted as soldiers. His brother Leslie was the only one to survive the war. We see them go forth from home in the prime of their manhood, and then the dreaded news arrives that never more will they return to those waiting ...The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... CHINESE RUSH TO GOLD News of the discovery of gold in Victoria in 1851 spread around the world, drawing fortune seekers and entrepreneurs from many nations. In China, news travelled quickly via the international shipping ports, most particularly ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
-
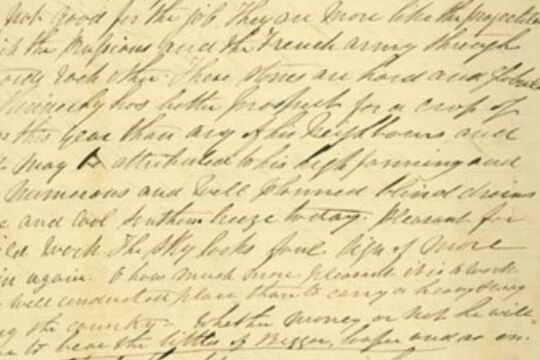
The Welsh Swagman
... This is a wood engraving published in The Illustrated Australian News. ...Joseph Jenkins was a Welsh itinerant labourer in late 1800s Victoria.
Exceptional for a labourer at the time, Jenkins had a high level of literacy and kept detailed daily diaries for over 25 years, resulting in one of the most comprehensive accounts of early Victorian working life.
Itinerant labourers of the 1800s, or 'swagmen', have become mythologised in Australian cultural memory, and so these diaries provide a wonderful source of information about the life of a 'swagman'. They also provide a record of the properties and districts Jenkins travelled to, particularly around the Castlemaine and Maldon area.
The diaries were only discovered 70 years after Jenkins' death, in an attic, and were in the possession of Jenkins’s descendants in Wales until recently, when they were acquired by the State Library of Victoria in 1997.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
... . This seemed good news: frogs had survived the bushfires and were breeding! However, back at the Museums Victoria DNA lab, the genetic data told a different story. Genetic fingerprint analysis showed effective frog populations were significantly reduced ...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-

The Ross Sea Party
... Page 25 "... personally I was prepared for almost any news whatever - in fact it seemed very likely that disaster had overtaken the whole party of six men. This is a very disjointed account of the history of Mackintosh party but naturally our ...As Shackleton’s ambitious 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition' of 1914 foundered, the Ross Sea party, responsible for laying down crucial supplies, continued unaware, making epic sledging journeys across Antarctica, to lay stores for an expedition that would never arrive.
In 1914 Ernest Shackleton advertised for men to join the Ross Sea Party which would lay supply deposits for his 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition'. Three Victorians were selected for the ten-man shore party: Andrew Keith Jack (a physicist), Richard Walter Richards (a physics teacher from Bendigo), and Irvine Owen Gaze (a friend of Jack’s).
The Ross Sea party commenced laying supplies in 1915 unaware that Shackleton’s boat Endurance had been frozen in ice and subsequently torn apart on the opposite side of the continent (leading to Shackleton’s remarkable crossing of South Georgia in order to save his men). Thinking that Shackleton’s life depended on them, the Ross Sea Party continued their treacherous work, with three of the men perishing in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis.
In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald Amundsen – an extraordinary achievement.
Jack, Gaze and others in the party took striking photographs during their stay. Jack later compiled the hand coloured glass lantern slides, which along with his diaries, are housed at the State Library of Victoria.
-

Against the Odds: The victory over conscription in World War One
In October 1916 and December 1917 two contentious referendums were held in Australia, asking whether the Commonwealth government should be given the power to conscript young men into military service and send them to war overseas.
These campaigns were momentous and their legacy long-lasting. This is the only time in history that citizens of a country have been asked their opinion about such a question, and the decisive 'No' vote that was returned remains the greatest success of the peace movement in Australia to date. Yet the campaigns split families, workplaces and organisations, and left an imprint on Australian politics that lasted for decades.
Many of the actors and events that were central to these campaigns were based in the northern Melbourne suburbs of Brunswick and Coburg. In many ways, these localities were a microcosm of the entire campaign. Against the Odds: The Victory Over Conscription in World War One tells the story of the anti-conscription movement in Australia during World War 1 through this lens.
