Showing 8 items
matching rural, themes: 'immigrants and emigrants'
-
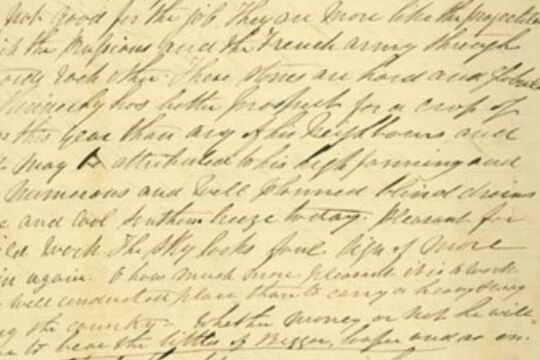
The Welsh Swagman
... rural life...Swagmen or swaggies have been a feature of the Australian rural environment since before Joseph Jenkins hitched his swag in the 1860s. As unemployed or itinerant workers, they moved around the country following available work. These images depict ...Joseph Jenkins was a Welsh itinerant labourer in late 1800s Victoria.
Exceptional for a labourer at the time, Jenkins had a high level of literacy and kept detailed daily diaries for over 25 years, resulting in one of the most comprehensive accounts of early Victorian working life.
Itinerant labourers of the 1800s, or 'swagmen', have become mythologised in Australian cultural memory, and so these diaries provide a wonderful source of information about the life of a 'swagman'. They also provide a record of the properties and districts Jenkins travelled to, particularly around the Castlemaine and Maldon area.
The diaries were only discovered 70 years after Jenkins' death, in an attic, and were in the possession of Jenkins’s descendants in Wales until recently, when they were acquired by the State Library of Victoria in 1997.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
... The Education Department had difficulty maintaining teaching numbers in rural communities. Teachers’ salaries were tied to attendance figures, so this might have deterred applicants, but above all else, the remoteness of these communities...Rural schools were a thorn in the side of the Education Department: expensive and hard to staff. One-teacher schools were the mainstay of government-funded education for children in the bush. Part-time schools and itinerant teachers were common... significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918). This online exhibition is based ...The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-

Drought Stories
... David Eltringham, Horsham Rural City Technical Services Manager, talks to John Francis about the impacts of ongoing drought in the Shire.... history of the current drought in Victoria. There were two aims to the project: to create a historic record of the experience, and to strengthen community capacity in rural and regional areas through telling and listening to local stories. Two types ...“The social impact it has is huge, but the footy club survives," says Charlie Gillingham, mixed farmer from Murrabit.
In this story the community talks about drought: its social impact, resilience, changes to farming practises, changing weather patterns and water trading.
The median annual rainfall of the Wimmera and northern plains of Victoria is 420mm. But this median does not convey the deluges that sometimes double the figure, or the dry spells that can halve it. Like semi-arid places elsewhere, the climate cycle of this region is variable.
Aboriginal people have had thousands of years to adapt to the fluctuations, whilst recent settlers are still learning.
The introduction of the Land Act of 1869 accompanied by the high rainfall La Niña years of the early 1870s brought selectors to northern Victoria and the Wimmera. A series of dry years in the 1880s initiated storage and channel projects to assist them to stay.
Irrigation was introduced in 1886 to settle the northern plains and was expanded under closer settlement legislation. The drought years from 1895 to 1902 came to be known as the Federation Drought. Water supplies dried up completely in the El Niño years of 1914 and 1915 and people took the opportunity to picnic in the empty bed of the River Murray.
Drought hit again during World War Two, and then in the period 1965-8. The drought of 1982-3 was short but devastating. Our most recent drought, lasting more than a decade, broke late in 2010 with extensive flooding.
Policy responses have changed over the years and with the recent onset of human induced climate change, continual adaptation will be required.
In 2009, the History Council of Victoria captured resident’s experiences in the project titled Drought Stories: a spoken and visual history of the current drought in Victoria. There were two aims to the project: to create a historic record of the experience, and to strengthen community capacity in rural and regional areas through telling and listening to local stories.
Two types of collections were produced: Drought Stories Local Collections, held by historical societies, and the Drought Stories Central Archive, a selection of interviews held by the State Library of Victoria.
The History Council of Victoria believes that the project material provides a rich resource to assist researchers understand Australian society at a crucial and revealing stage of adjustment to the Australian environment.
Legislation and other land records are held at the Public Record Office Victoria.
-

Language, A Key to Survival: Cantonese-English Phrasebooks in Australia
... , a tallyman is a person who keeps a tally of the quantity or weight of goods produced, shipped or received. This phrasebook was among the possessions of George Ah Ling (1884-1987), a market gardener, who lived for many years in Donald in rural Victoria... words/The Tallyman's Vocabulary, published in 1923 was among George's possessions when he died. George was a market gardener, who lived for many years in Donald in rural Victoria and was affectionately called 'Georgie'. He was born ...Most international travellers today are familiar with phrasebooks. These books provide a guide to pronunciation, useful vocabulary, but most importantly lists of useful phrases to help travellers negotiate their way around a country where they don't speak the language.
Anyone who has tried to communicate across the language divide without such a tool knows how valuable they are.
This web story explores how Chinese from the gold rush period onwards have used phrasebooks to help them find their way in Australia. You can compare examples of Cantonese-English phrasebooks from different eras; watch Museum volunteers Nick and David speak English using a gold-rush era phrasebook; learn a little about the lives of some of the people who owned these phrasebooks; and hear Mr Ng and Mr Leong discuss their experiences learning English in Australia and China in the early to mid-twentieth century.
This project is supported through funding from the Australian Government's Your Community Heritage Program.
-

Savoy Ladies Group
... It was a lonely experience for many of the Italian women who came to Myrtleford to raise families and farm tobacco. Often hailing from small and tightly-knit rural villages, it wasn’t unusual for women to have never travelled outside of their home town ...The Italian community of Myrtleford, in the picturesque Ovens Valley in alpine North Eastern Victoria, arrived mainly to work in the tobacco industry which once thrived in the area. The region now has a distinctive Italian-Australian culture with settled second, third and fourth generation Italian families.
Tobacco farming was a lonely experience for many of the Italian women who migrated to Myrtleford. Unlike their husbands, the women stayed largely on the farms and lacked social contact outside of their immediate circle. Once their children grew up and mechanisation changed the labour requirements on the farms, women were frequently on their own.
The Myrtleford Savoy Ladies Group was founded in 1983 by nuns concerned about the social isolation of women in the area. It has been a great success, forming a network of companionship amongst women of Italian heritage to this day.
Cultural Warning: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users of this website are warned that this story contains images of deceased persons and places that could cause sorrow.
-

Chinese Australian Families
... to their Chinese homes. Few saw the merit of having wives and children here. However, they were not without family in Australia. Chinese sojourners were not individual immigrants without family ties in Australia. Typically, rural villages in China were made up ...Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history
From the 1840s onwards, Chinese people have come to Australia inspired by dreams of happiness, longevity and prosperity - of 'jade and gold' in a new and strange land. For most of that time, Chinese people in Australia have been predominantly male. Most of them were temporary sojourners who came to earn money for their families back in the village - most did not intend to settle in Australia.
Despite the predominance of male sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms on their behalf amongst other Chinese families in Australia.
The majority of post-1905 Chinese brides of Chinese-Australian sons were never able to settle here. Some children were born in China or Hong Kong. Some were born in Australia. Families like this were split for decades, until immigration laws were relaxed.
In the nineteenth century, many of the Chinese men who wanted wives in Australia married or lived de facto with non-Chinese women. At least 500 European-Chinese partnerships are estimated to have occurred before 1900.
Despite repeated waves of racism and official discrimination from the 1840s to the 1970s, a sizeable number of families of Chinese background have put down roots in this country.
In 1973 the Whitlam government abolished racist provisions in immigration laws. Since then, the number of ethnic Chinese migrants has increased dramatically. They have come primarily as family groups - not as sojourners, but as permanent immigrants. They come not only from China and Hong Kong, but also from Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Indonesia, as well as from further afield. The Chinese are now a highly visible and generally accepted part of the Australian community of cultures.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay 'Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history' written by Paul Macgregor for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Rippon Lea Estate
... was constructed in the orchard according to designs suggested by the Department of Defence, and a rural property was purchased at Kyneton to provide for evacuation should the city be bombed. The staff at Rippon Lea was also heavily reduced. In the 1950s ..."Do you remember the garden in which you grew up, or the part the backyard played in your family life? Imagine if you had actually grown up in one of Australia's finest gardens.
Created in the English-landscape tradition which traces its roots back to Capability Brown and Humphry Repton, Rippon Lea is one of Australia's most important historic homes, exemplifying the lifestyle of wealthy families living in 19th and 20th century Australian cities. Although its architecture and that of its outbuildings is impressive, it is the mansion’s gardens, which are truly remarkable, both for their landscape qualities and because they have survived many threats and changes in the past 130 years.
Today, the amenities offered by a typical garden are still greatly valued: a safe place for children to play, somewhere to dry the washing, a plot for vegetables and a flower garden that adds colour and produces blooms for the home. Today as then, the scale differs but the experience of owning a garden - with its balance of utility and ornament - is essentially the same.
The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) now runs Rippon Lea as a museum, conserving the architecture and the landscape, and presenting the social history of the owners and their servants. Visitors to Rippon Lea enter a mansion preserved as the Jones family lived in it after their 1938 modernisation. In the pleasure garden the Sargood era is evoked by the staging of a range of performing arts events including opera, theatre, chamber music and outdoor activities."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Solid Joys and Lasting Treasure: families and gardens written by Richard Heathcote for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... and fibrous palm sheaths of the Chinese windmill palm (Trachycarpus fortunei). Although found throughout Asia and the tropics, the palm fibre cape has been specifically attributed to the rural areas of the Guangdong province in Southern China. Worn by both men ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
