Showing 8 items
matching traditional%20dance, themes: 'gold rush','land and ecology'
-
 Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library Victoria
Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library VictoriaKoorie Art and Artefacts
... traditional dance..... Over his lifetime William Barak created a series of unique paintings, drawings and artefacts, recording the traditional ways of his culture and passing this knowledge down through the generations. Most of his paintings were completed at Coranderrk...William Barak was a leader of the Wurundjeri, one of the groups of the East Kulin nation, the traditional owners of the lands now occupied by Federation Square.... of short films Uncle Wally Cooper, Aunty Linda Turner and Aunty Connie Hart practice a range of traditional techniques and skills. These short documentaries show the strength of Koorie culture today and the connection with past traditions experienced ...Koorie makers of art and artefacts draw upon rich and ancient cultural traditions. There are 38 Aboriginal Language Groups in Victoria, each with unique traditions and stories. These unique traditions include the use of geometric line or free flowing curving lines in designs.
This selection of artworks and objects has been chosen from artworks made across the range of pre-contact, mission era and contemporary times and reflects the richness and diverse voices of Koorie Communities. It showcases prehistoric stone tools, works by 19th century artists William Barak and Tommy McRae right through to artworks made in the last few years by leading and emerging Aboriginal artists in Victoria.
The majority of the items here have been selected from the extensive and significant collections at the Koorie Heritage Trust in Melbourne. The Trust’s collections are unique as they concentrate solely on the Aboriginal culture of south-eastern Australia (primarily Victoria). Over 100,000 items are held in trust for current and future generations of Koorie people and provide a tangible link, connecting Community to the past.
Within the vibrant Koorie Community, artists choose their own ways of expressing identity, cultural knowledge and inspiration. In a number of short films Uncle Wally Cooper, Aunty Linda Turner and Aunty Connie Hart practice a range of traditional techniques and skills. These short documentaries show the strength of Koorie culture today and the connection with past traditions experienced by contemporary Koorie artists.
Taungurung artist Mick Harding draws upon knowledge from his Country about deberer, the bogong moth: "The long zigzag lines represent the wind currents that deberer fly on and the gentle wavy lines inside deberer demonstrate their ability to use those winds to fly hundreds of kilometres to our country every year."
Koorie artists today also draw inspiration from the complex and changing society we are all part of. Commenting on his artwork End of Innocence, Wiradjuri/Ngarigo artist Peter Waples-Crowe explains: "I went on a trip to Asia early in the year and as I wandered around Thailand and Hong Kong I started to think about Aboriginality in a global perspective. This series of works are a response to feeling overwhelmed by globalisation, consumerism and celebrity."
Koorie culture is strong, alive and continues to grow.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... In this extended audio interview Rick Nelson, Jaara descendant, is interviewed by Lucinda Horrocks on the banks of the Bet Bet Creek, in Eddington, Victoria, part of the traditional land of the Dja Dja Wurrung language peoples. Rick talks about how... to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-
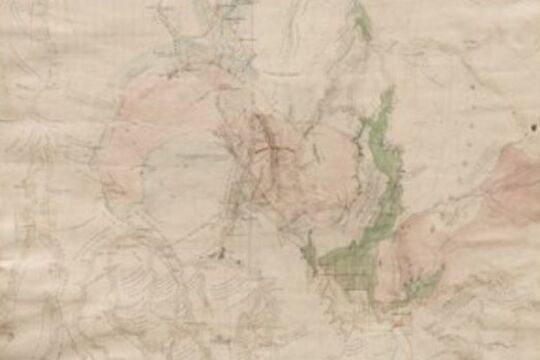
Mapping Great Change
... and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land. ...This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
-

But That's Another Story
... of Australian traditional music and dance continues with the Nariel Creek Folk Festival. A history of engine power: Watch out... refurbishing engines can become an addiction. The gem of this collection of over 150 engines is an 1866 Ransom Sims engine, one ...This innovative collaboration between community museums and local artists captures the unique living memories and rich cultural heritage of communities along the Murray River between Wodonga and Corryong.
Seven short films were created as part of the project:
Nox-All Rabbits: How do you deal with a plague of rabbits? With Nox-All. Rabbiting was a way of life in Victoria, especially during the plague of 1932. Rabbits were a source of food and income (the felt from their pelts used in Akubra hats), and thought by some to be "better than chickens".
Jim Simpson's knitted war trophy: During World War II Jim Simpson's aircraft was shot down over Germany and he became a prisoner of war at Stalag IVB. Jim's ingenuity helped to keep prisoners warm, and ultimately resulted in an extraordinary memorial.
Old time music in the blood: Nariel Creek residents have music in the blood, so much so that they've been told their accordion style is special, using all four fingers at once. The Nariel old time style of Australian traditional music and dance continues with the Nariel Creek Folk Festival.
A history of engine power: Watch out... refurbishing engines can become an addiction. The gem of this collection of over 150 engines is an 1866 Ransom Sims engine, one of only 5 in the world, which has been lovingly restored.
The Saleyards Made Wodonga: Cattle were one of the biggest industries in Wodonga, and the saleyards a focal point town, not least because plum pudding was served in the luncheon room all year round.
The Icon of Wodonga: You need more than a trickle of water to fight a fire. The Wodonga water tower was welcomed as it brought the 'luxury' of water to town, and when it was decommissioned the community rallied to prevent its demolition.
The Saw Doctor's Wagon: The 'Sharpening King' and his family travelled throughout eastern Australia sharpening knives in their 'road urchin'. A circus-like wagon, the urchin was first pulled by horses, then a Chevron truck, and finally, by a David Brown tractor.
Participating museums: Granya Pioneer Museum, Man From Snowy River Museum, Tallangatta & District Heritage Group, Wodonga Historical Society.
Supported by: the Commonwealth Government’s Regional Arts Fund, Regional Arts Victoria, National Museum of Australia, City of Wodonga, Shire of Towong, Museums Australia (Vic) and Arts Victoria. Auspice organisation: Murray Arts
-

Goldfields Stories: Dai gum san, big gold mountain
... Fan banners were eye-catching emblems associated with the Eight Immortals of Chinese mythology. Pairs of fan banners have traditionally stood on rods flanking altars in Chinese temples and feature in ceremonies and processions. In the following ...It may come as a surprise to some that the oldest Imperial Dragon in the world, Loong, is to be found in Bendigo, Victoria.
In 1851 gold was found in the Bendigo region. News reached China and by 1853 Chinese miners started to arrive at Dai Gum San (Big Gold Mountain). By 1855 there were up to 4000 Chinese in the Bendigo goldfields, about one fifth of the population.
By the 1860s, Bendigo was becoming a wealthy and established town, and in 1869 The Bendigo Easter Fair and Procession was initiated to raise funds for the Bendigo Benevolent Asylum and Hospital. By 1871, the Chinese, keen to support the wider community, joined the procession, providing music, theatre and acrobatic displays. Their position as the main attraction at the Fair was confirmed by 1879.
All of the costumes, flags and musical instruments were imported from China, with no expense spared. For the 1882 Fair, 100 cases of processional regalia were imported. In 1892 a further 200 cases arrived, along with Loong, the Imperial five-clawed dragon, who made his first appearance that year.
The traditions established in the 1860s by the Bendigo Chinese community continue to this day. As well as providing the main attraction in the Bendigo Easter Festival, ceremonies such as the Awakening of the Dragon are conducted. These traditions reflect uniquely preserved traditions, many of which were lost or discontinued in mainland China. They also reflect traditions, such as the main celebration taking place at Easter rather than Chinese New Year, that trace the history of the Chinese in Victoria.
The remarkable collection of 19th Century processional regalia that has been preserved by the Chinese community in Bendigo is held in the Golden Dragon Museum. It is not only a collection of world significance but, importantly, it contextualises and preserves the living heritage of both Victoria and China.
-

Language, A Key to Survival: Cantonese-English Phrasebooks in Australia
... are traditionally termed) spoken. In modern China over 200 languages have been documented. These languages can be categorised into seven groups: Gan, Hakka, Mandarin, Min, Wu, Xiang and Yue. There are numerous languages and dialects within each of these groups, all ...Most international travellers today are familiar with phrasebooks. These books provide a guide to pronunciation, useful vocabulary, but most importantly lists of useful phrases to help travellers negotiate their way around a country where they don't speak the language.
Anyone who has tried to communicate across the language divide without such a tool knows how valuable they are.
This web story explores how Chinese from the gold rush period onwards have used phrasebooks to help them find their way in Australia. You can compare examples of Cantonese-English phrasebooks from different eras; watch Museum volunteers Nick and David speak English using a gold-rush era phrasebook; learn a little about the lives of some of the people who owned these phrasebooks; and hear Mr Ng and Mr Leong discuss their experiences learning English in Australia and China in the early to mid-twentieth century.
This project is supported through funding from the Australian Government's Your Community Heritage Program.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
... and protection of threatened species. A popular bushwalking, camping and rock climbing destination, it is particularly significant to the Djab Wurrung and Jardwadjali, the Traditional Owners of the area. Curation notes by: Lucinda Horrocks, Wind & Sky ...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... to and from the gold fields of Ballarat, circa 1854. In it, Aboriginal and Chinese people mingle with others on the broad flats of Ballarat East. Ballarat was the traditional country of the Wadawurrung speaking peoples of the Kulin nation. Gold was discovered ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
