Showing 45 items
matching aluminium alloys
-
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumManual - Procedure, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Extract from the 'Proceedings of the Electrical Association of New South Wales' session 1910 - 11", mid 1930's
... includes notes on cross falls of track, a table of aluminium copper... includes notes on cross falls of track, a table of aluminium copper ...Two copies of a Carbon typed copy of a technical procedure - 6 pages - "Extract from the 'Proceedings of the Electrical Association of New South Wales' session 1910 - 11" - giving advice on the location of Trolley Wire" giving the guide on how to locate trolley wire on curves and junctions, gives formulas, positioning at frogs, notes regarding various cars and trolley wire height includes notes on cross falls of track, a table of aluminium copper alloys - bending strength and failure modes. Consists of five pages with two blue print drawing. Each page has been scanned the blue print drawings reversed imaged as well. 4768.2 - blue print drawing showing references in the various formulas etc used. 4768.3 - ditto showing tracking for four wheeled and bogie cars and other diagrams for turnouts, frog locations and frog angles. BTPS Number "219". "226" in ink on left hand bottom of first pagetrams, tramways, overhead, trolley wire, points -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchSouvenir Ashtray
... Souvenir ashtray made from a metal alloy materaial..." Souvenir ashtray made from a metal alloy materaial (probably ...Souvenir ashtray made from a metal alloy materaial (probably Aluminium). The ashtray is in the form of a ships wheel and has a central circular insert which is stamped "MV DORSETSHIRE". Stamped with the inscription "MV DORSETSHIRE" -
 Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub BranchWeapon - Bayonet, SKS rifle spike with woven cord lanyard, Mid to late 20th century
Used by various oversea armed forces. Such as Chinese, Russan, Vietnamese.15 inch (30 cm) three sided fluted steel alloy pointed spike SKS rifle bayonet two colour (Aluminium and black mounting end). Missing the mounting fixure to attach the bayonet to the rifle. Dark green double woven cord Woven cord length (83 cm) attached by split ring. Woven loop at end of cord.sks, rifle, bayonet, lanyard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Saucepan
It is no secret that copper is currently experiencing a huge upsurge in popularity. This is mainly thanks to its beautiful colour featuring heavily in the ranges of countless homeware retailers. There is, however, far more to this lustrous metal than just its appearance. For example, it has a greater level of thermal conductivity than any other metal (except silver); roughly 60% higher than aluminium and 3000% higher than stainless steel. This means copper is capable of heating up very quickly when compared to other metals. Perhaps a less commonly known property of copper is it being inherently antimicrobial. A wide range of harmful microbes are unable to survive for more than a couple of hours when in contact with a surface made of copper or one of its alloys (brass and bronze). This has led to it often being used for frequently touched surfaces such as door knobs, push plates and taps. A seemingly perfect material for cooking, it is therefore no surprise that it has been used in kitchens for millennia. But exactly when did we learn to utilise copper and its valuable assets? Origins It is hard to pin down an exact date when copper cookware was first introduced. Pieces discovered in regions of the middle east were dated as far back as 9000BC, suggesting cooking with copper began during the Neolithic period (≈10000-2000BC). As civilisations became increasingly capable in metallurgical techniques, metals such as copper became more widely used. It would have been around this time that copper replaced stone as the material used for making tools and cooking vessels. The use of copper is also well documented in Ancient Egypt. Not only was it used to produce water and oil containers, but it was also used to in medical practices. The antimicrobial nature of copper was exploited long before the concept of microorganisms was fully understood. The Smith Papyrus, a medical text written between 2600 and 2200BC records the use of copper in sterilising wounds and drinking water. Tin Lining Although copper is essential to many processes within the human body, it can become toxic if consumed in excess. It was this knowledge that gave rise to lining cookware with tin, a technique used for hundreds of years to prevent copper leaching in to food. These tin linings would eventually wear out and during the 18th and 19th century, it was common for people to send pans away to be re-tinned. This practice is becoming increasingly rare, as are the craftsmen who perform it. Despite this, there are still manufactures producing tin-lined copper cookware who also offer a re-lining service. Perhaps the best known of these is Mauviel, a French manufacturer who have been making this type of cookware since 1830. Tin has now largely been replaced by stainless steel as an interior cooking surface. Not only is it more cost effective, but the high grade of stainless steel used in premium cookware (typically 18/10) is highly resistant to corrosion and more durable than tin.Copper saucepans are still used in many kitchens.Small copper saucepan with long handle and three ridges around the circumference. Extensive corrosion.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, copper, saucepans, kitchen equipment -
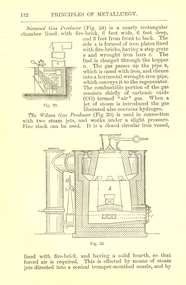 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Principles of Metallurgy, 1901, 1901
Maroon hard covered book of 388 pages. The book was written for the budding metallurgist, constituting an elementary treatise on the subject, dealing with principles rather than processes, the contents include: Intro., Definition, Properties, Principles, Alloys, Slags, Fuel, Iron, Steel, Silver-Gold-Platinum, Copper-Zinc, Lead-Tin, Nickel-Cobalt, Aluminium, Mercury, Antimony-Arsenic, Bismuth, Index.metallurgy, brook, hiorns, pig iron, steel, silver, acid, stamp battery, ores, zinc, copper, antimony -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instruments, Specific Gravity: Metal Cubes - boxed set of seven
... ; 4) Copper; 5) Aluminium; 6) ? a ferrous alloy; 7... aluminium ferrous alloy Number and metal of cubes: 1) Brass; 2) Lead ...Used in Physics Laboratory at Ballarat School of Mines for calculating/confirming relative density (or the specific gravity) of given metal samples. This would have been in Elementary physics experiments.A set of seven 2-cm cubes, individually numbered 1 - 7, in a hinged-lid storage box with black surface finish.Number and metal of cubes: 1) Brass; 2) Lead; 3) Steel; 4) Copper; 5) Aluminium; 6) ? a ferrous alloy; 7) ? a ferrous alloy.physics, laboratory, ballarat school of mines, relative density, specific gravity, metal, elementary physics, brass, lead, steel, copper, aluminium, ferrous alloy -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: LETTER
Letter from McPherson's Limited to Messrs Bendigo Electronic Co. of Australia, dated 15 November,1950. Letter is from John Byrt, Asst. Chemist for Attention Mr. Stevenson. Cover letter states they have enclosed copies of Report No. 17355 covering 'Dezincification of Brass Wire in 'Scalebuoy' Water'. Two pieces of wire were analized. In the discussion the brittleness had resulted from dezincification,which was known to be a common type of corrosion of that material. It was recommended that different wire be used. Four alloys were recommended: Cupro-nickel, Aluminium brass, Arsenical brass and Admiralty brass. Two copies of the report.sciences, instruments - general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection, mcpherson's limited, messrs bendigo electronic co of australia, mr stevenson, j byrt -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider - Sailplane, 1974
... sailplane design of aluminium alloy construction. australian gliding ...The Pilatus B4 is an all metal intermediate sailplane meeting Standard Class rules that was designed in 1966 by Ingo Herbst, Manfred Küppers and Rudolf Reinke. It did not immediately go into production. In 1972 Pilatus Aircraft of Switzerland acquired a licence to build the aircraft and began production. The PCII and PCIIA versions were semi-aerobatic. The PC11AF released in 1975 was rated as fully aerobatic. By 1980, when Pilatus sold the rights to manufacture of the aircraft to Nippi Aircraft of Japan, 322 of the Pilatus B4 had been produced. Nippi Aircraft built a further 13 and also one two seat version. The Pilatus B4 proved popular in Australia with 26 appearing on the Australian register. The Museum’s example is a basic semi-aerobatic type (Serial Number 092) that was built in 1974. It is registered as VH-GID on 8 July 1974 by H.G. Sutton of Mandura, Western Australia and flown out of the Narrogin Gliding Club in Western Australia until September 1986 when it was sold to the Albury – Corowa Gliding Club, New South Wales. In 1999 it was acquired by Michael Green and moved to Townsville, Queensland. The aircraft changed ownership again in 2004 and fell out of use for nearly 4 years. By then it had recorded 4377 hours in the air from 4304 flights. It returned to service briefly in January 2008 (5 flights totalling about 5 hours). It was donated to the Museum by David Millward of the Geelong Gliding Club, Victoria, on 10 April 2017. The aircraft is representative of a popular imported 1970s intermediate single seat sailplane design of aluminium alloy construction.Single seat sailplane of metal alloy constructionWhite colour scheme with yellow fuselage underside highlighted by blue stripe – “Pilatus B4” in black lettering on starboard side of cockpit – black anti-glare paint on the fuselage nose – Registration “GID” on the underside of port wing.australian gliding, glider, sailplane, pilatus b4, sutton, narrogin, albury, corowa, green, townsville, millward, geelong -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Rotol Aluminium Alloy Propellor Blades Repair Manual Publication Number 830 Series .01 Reference 5796
... Rotol Aluminium Alloy Propellor Blades Repair Manual... Moorabbin melbourne Loose Leaf Binder Manual Rotol Aluminium Alloy ... -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument - Test and Control Conditions for Spot Welded Aluminium and Aluminium Alloy Assemblies and Welding Machines
... Aluminium Alloy Assemblies and Welding Machines ... Welded Aluminium and Aluminium Alloy Assemblies and Welding ... -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - Handbook Of Service And Overhaul Instructions Model C532D Aluminium Alloy Electric Propellors Early Type (Three Blades) Curtiss
... Aluminium Alloy Electric Propellors Early Type (Three Blades... Aluminium Alloy Electric Propellors Early Type (Three Blades... And Overhaul Instructions Model C532D Aluminium Alloy Electric ...AN 03-20BK-1 A.P No.2110A -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - Aluminium in aircraft, circa 1930s, Aluminum in Aircraft
... aluminium alloy... Moorabbin melbourne Published 1930 aluminium alloy Study ...Study of understanding the characteristics of aluminium to get the best out of this material in aircraftSmall hardback book Study of understanding the characteristics of aluminium to get the best out of this material in aircraftaluminium alloy -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - (SP) Sizes and weights of Aluminium Alloy Bars Rods and Tubing
... (SP) Sizes and weights of Aluminium Alloy Bars Rods and... and weights of Aluminium Alloy Bars Rods and Tubing ...Possibly related to navigation -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Mangan Hedenbergite
... is a key component of certain widely used aluminium alloys ...This specimen was recovered from Broken Hill, NSW. It was given the name Mangan Hedenbergite in 1819 by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in honor of Mr. Anders Ludvig of Hedenberg who was the first to define hedenbergite as a mineral. Hedenbergite, belongs in the pyroxene group having a monoclinic crystal system. The mineral is extremely rarely found as a pure substance. Mangan Hedenbergite is a manganese bearing variety of Hedenbergite. Manganese is the world’s fourth most used mineral after iron, aluminium, and copper primarily because it has no satisfactory substitute in its major applications. Globally, the steel industry is the primary user of manganese metal, utilizing it as an alloy to enhance the strength and workability of steel and in the manufacture of tin cans. Manganese is a key component of certain widely used aluminium alloys and, in oxide form, dry cell batteries used in electric vehicles. These batteries are in high demand. Another potential use for manganese may as an additive to help coat and protect a car’s engine. Manganese is also used for non-metallurgical purposes such as plant fertilizers, animal feed, and colorants for bricks. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A hand-sized mineral specimen in shades of silver and blackmanganese, open cut mine, manganese ore processing, bell bay, tasmania, northern territory, steel industry, zinc-carbon batteries, alkaline batteries, tin cans -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - De Havilland propellers, The De Havilland Propeller Repair System
... with aluminium alloy blades, circa 1940s Very thin, booklet sized book ...Overview of methods for repairing DeHavilland propellers with aluminium alloy blades, circa 1940sVery thin, booklet sized book. Title unclear on front covernon-fictionOverview of methods for repairing DeHavilland propellers with aluminium alloy blades, circa 1940soutline of repair systems & methods
