Showing 56 items matching "copper ore"
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - AMY HUXTABLE COLLECTION: MINERAL COLLECTION
... copper, wave like form Malachite, copper carbonate, ore of copper... carbonate, ore of copper Chalcopyrite, copper iron sulfide, ore ...Fifty-three mineral samples collected by Amy Huxtable. Samples in two plastic partitioned boxes. Samples were originally housed in poor conditions in matchbox inserts and placed on cotton wool. Existing labels, hand printed on tan card: Cerussite, crystalline ore of silver lead Galena, ore of silver lead, fine grained Galena, ore of silver lead, coarse grained Native copper, wave like form Malachite, copper carbonate, ore of copper Chalcopyrite, copper iron sulfide, ore of copper lead Malachite, copper carbonate, ore of coppermining, sampling, mineral samples -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Chalcopyrite
... . Chalcopyrite is a copper iron sulphide mineral and a major ore... copper ore since it can be found in many localities and occurs ...This specimen originated from Mount Lyell on the west coast of Tasmania, where a large group of open cut and underground copper-silver-gold mines began operating in 1883. Between 1893-1994, the Mt Lyell Mining and Railway Company were responsible for operations. The Mt Lyell copper-gold mines produce some excellent crystallised specimens of chalcopyrite and other minerals. The deposits are generally considered to be of Cambrian volcanic origin, but there are indications of Devonian granitic influence on the ores, plus local remobilisation during Devonian deformation. Over 120 million tonnes of ore was produced from several workings, including the main Prince Lyell mine and the North Lyell mine, which was also of great importance. The Mount Lyell mines have a long history of human and environmental disasters, including the 1912 North Lyell fire that killed 42 miners, and two separate incidents in 2013 in which three people lost their lives. The environmental impacts from this complex of mines are extensive, with waste tailings and heavy metal contamination flowing directly into the King and Queen River catchments. In 1954, the eminent Australian historian, Geoffrey Blainey, published 'The Peaks of Lyell' which delves into the history of the 1912 North Mount Lyell Disaster.Chalcopyrite does not contain the most copper in its structure relative to other minerals, but it is the most important copper ore since it can be found in many localities and occurs in a variety of ore types. The brassy-yellow colours in Chalcopyrite mean it is often confused with pyrites and gold, leading to use of the term, "fool's gold." Chalcopyrite has been the primary ore of copper since smelting began five thousand years ago. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.This hand sized solid mineral specimen has shades of brass-yellow with spots of iridescent green-black tarnish. Chalcopyrite is a copper iron sulphide mineral and a major ore of copper common in sulphide veins and disseminated in igneous rocks. Chalcopyrite has a hardness of 3.5-4 on the Mohs Scale. It is a member of the tetragonal crystal system and has metallic lustre and opaque transparency.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geology, geological specimen, chalcopyrite, copper pyrites, copper mining, tasmanian geology, mount lyell, mount lyell mines, fools gold, mohs scale, crystals, minerals, historical geological collection, victorian geological survey, a.r.c selwyn, gold rush, van diemans land -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Azurite, Unknown
... by the weathering of copper sulphide ore deposits. Azurite is formed from... by the weathering of copper sulphide ore deposits. Azurite is formed from ...Azurite is a secondary copper mineral made by the weathering of copper sulphide ore deposits. Azurite is formed from copper, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. There are over 45 forms of azurite that are more well-known, however over 100 forms have been found. Azurite is also commonly found together with Malachite, and Azurite is often psuedomorphed to Malachite. This specimen was found at the Great Cobar Copper Mine in New South Wales, which was founded in 1870. At the time it was one of the largest mining operations in the world. It was the largest copper mine in Australia and housed the southern hemisphere’s tallest chimney stack. The international price of copper collapsed at the end of World War 1 which led to the closure of the Great Cobar Mine on March 16th 1919. A year later on March 10th 1920 an underground fire in the CSA (Cornish, Scottish, Australian) mine started and burned for 16 years. The closure of the mine and the fire left thousands jobless and many people left the area. These were factors in Cobar facing a long stretch of poverty, until a boom in the 1960s led to the reopening of the mine. The mine still operates today, obtained by Metals Acquisition Limited in June 2023. Azurite is considered an uncommon mineral. Named for its deep blue colour, azurite was historically used for pigment making and as a gemstone, despite its softness. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 as part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens. Many of the specimens in this collection were obtained as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria, which started in 1852. The Survey aimed to map the scientific makeup of the earth.A solid copper mineral with shades of darker blues almost covering it.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, cobar mines, great cobar copper mine, cobar mining, new south wales, azurite, azurite specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Chalcopyrite
... as the most important ore of copper for thousands of years... as the most important ore of copper for thousands of years ...This specimen was recovered from Mica Schist, Canada. Chalcopyrite is a copper iron sulfide mineral with a chemical composition of CuFeS2. Its name derives from the Greek words for copper (chalco-) and brass (pyrite). It can be found in shades of yellow, green and grey, and, when exposed to acid, it can change to purple, blue, violet and yellow tones. Weathering can cause loss of its metallic luster and its brass-yellow colour. Chalcopyrite forms under various conditions, with the most significant deposits being hydrothermal in their origin. It is known globally as the most important ore of copper for thousands of years, and is thus considered a very important mineral formation. Given its golden appearance, it is often confused for the mineral gold, earning it the popular reputation as 'fool's gold' or 'yellow copper'. However, it can be straightforwardly distinguished from gold; the latter is soft, with higher specific gravity and a yellow streak, whereas chalcopyrite is brittle, easily scratched by a nail, and has a greenish grey streak. Copper was the first metal that was used by people. It was discovered by the Neolithic man about 9,000 years ago and it gradually replaced stone as it was easier to be shaped. In Australia, search for copper began after the European settlement, leading to the discovery of substantial deposits, like the one at the Olympic Dam in South Australia, which is regarded as one of the largest copper deposits in the world. Chalcopyrite has been used for copper since smelting processes began approximately five thousand years ago. Although by no means rare, this the specimen of this mineral can be used to reflect a wider history of industrial uses of copper for a significant portion of human history. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized copper iron sulfide mineral of brass yellow, often with an iridescent tarnish, with greenish-black streak and submetallic luster. Chalcopyrite can be formed in several ways, including crystalizing from accessory minerals in igneous rocks, or from magma or within volcano sulfide deposits. Most commonly, chalcopyrite are found in hydrothermal conditions, where it forms in hydrothermal veins. As a member of the tetragonal crystal system, it often takes the shape of tetra-headed crystals, often with striations along the sides of the crystals. #18 Copper pyrites/(chalcopyrite) in/Laurentian Slate/(page 315 of inventory)/page missing from/descriptive catalogue/ Other label: 81 /fool's gold, chalcopyrite, mineral, rock, geology, geological, hydrothermal, neolithic, european settlement, olympic dam, south australia, stone, deposits, specific gravity, greenish grey streak, brittle, mineral gold, metallic luster, cufes2, greek words -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPainting - Artwork - Painting, 'School of Mines New Beginnings part a & b' by John Collier, 2008
... , iron ore, coal, copper, gold-silver, petroleum, heavy minerals... also has significant success with lead-zinc, iron ore, coal ...John COLLIER (1937- 2012) John Collier was born at Ballarat in 1937. He received a Diploma of Mining and a Diploma of Civil Engineering at the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB), later graduating from the University of Melbourne with a Bachelor of Engineering (Mining). Early in his career he received a Diploma of Accountancy from the Australian Society of Accountants. Collier believes his experience at SMB had a profound influence on his life, especially what he learnt in Geology, Engineering, Chemistry, etc., all of which he found beneficial to his later working life and he is proud of that association. Through his experience in the world-wide mining industry John Collier has made a major impact on the mining industry. He has been exploration leader for a large number of worldwide discoveries and farm-ins both major and minor. He has experience in every facet of the mining industry, and his record in identifying diamond opportunities include Australian (Argyle), Canada (Diabik), Zimbabwe, and the Brazil Pipe (Collier Falls). His success in diamond exploration may be unparalleled. John Collier also has significant success with lead-zinc, iron ore, coal, copper, gold-silver, petroleum, heavy minerals, nickel, uranium, industrial minerals, rare earths, and tin. In 2006 John Collier was made a Legend in Mining by the Australian Mining Industry. Over his last 10 years, he had become a passionate painter, holding several successful solo exhibitions. His naive style featured beautiful and unexpected colour combinations. Many of his most lauded paintings depicted mining scenes, harking back to his Ballarat days. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Two artworks by John Collier inspired by his alma mater, the Ballarat School of Mines. art, artwork, john collier, ballarat school of mines, alumni -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPainting - acrylic on canvas, Collier, John, 'Port Phillip Colonial GMC, Clunes' by John Collier, 2008
... , iron ore, coal, copper, gold-silver, petroleum, heavy minerals... also has significant success with lead-zinc, iron ore, coal ...John COLLIER (1937- 2012) John Collier was born at Ballarat in 1937. He received a Diploma of Mining and a Diploma of Civil Engineering at the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB), later graduating from the University of Melbourne with a Bachelor of Engineering (Mining). Early in his career he received a Diploma of Accountancy from the Australian Society of Accountants. Collier believes his experience at SMB had a profound influence on his life, especially what he learnt in Geology, Engineering, Chemistry, etc., all of which he found beneficial to his later working life and he is proud of that association. Through his experience in the world-wide mining industry John Collier has made a major impact on the mining industry. He has been exploration leader for a large number of worldwide discoveries and farm-ins both major and minor. He has experience in every facet of the mining industry, and his record in identifying diamond opportunities include Australian (Argyle), Canada (Diabik), Zimbabwe, and the Brazil Pipe (Collier Falls). His success in diamond exploration may be unparalleled. John Collier also has significant success with lead-zinc, iron ore, coal, copper, gold-silver, petroleum, heavy minerals, nickel, uranium, industrial minerals, rare earths, and tin. In 2006 John Collier was made a Legend in Mining by the Australian Mining Industry. Over his last 10 years, he had become a passionate painter, holding several successful solo exhibitions. His naive style featured beautiful and unexpected colour combinations. Many of his most lauded paintings depicted mining scenes, harking back to his Ballarat days. This work and subject matter was painted for the artist's alma mater, the Ballarat School of Mines (now Federation University Australia). This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Colourful acrylic on canvas painting depicting the Port Phillip Gold Mining Company, Clunes.art, artwork, john collier, port phillip cold mine, clunes, clunes, available, alumni, mining -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite, Unknown
... and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has... and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has ...Malachite is a green copper carbonate hydroxide mineral and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has been utilised as a gemstone and sculptural material in the past as its distinctive green color does not fade when exposed to light or after long periods of time. Malachite is formed at shallow depths in the ground, in the oxidizing zone above copper deposits. The material has also been used as a pigment for painting throughout history. This particular specimen was recovered from the Burra Burra Copper Mine in Burra, South Australia. Otherwise known as the 'Monster Mine', the Burra Burra Copper Mine was first established in 1848 upon the discovery of copper deposits in 1845. Within a few short years, people from around the world migrated to Burra to lay their claim in the copper economy. By April 1848 the mine was employing over 567 people and supporting a population of 1,500 in the local township. Up until 1860, the mine was the largest metals mine in Australia, producing approximately 50,000 tonnes of copper between 1845 to its closure in 1877. The Burra Burra Mine was also famous for a number of other specimens, including; crystalline azurite, cuprite, and botryoidal and malachite.Malachite is considered a rare gemstone in that the original deposits for the stones have been depleted leaving behind very few sources. In addition, the use of Malachite as gemstones and sculptural materials remains just as popular today as they were throughout history. It is quite common to cut the stone into beads for jewellery. The fact that Malachite has such a rich colour and one that does not fade with time or when exposed to light makes it particularly rare. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A solid hand-sized copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with shades of yellow, blue, and light green throughout.geological, geological specimen, burke museum, indigo shire, malachite, malachite specimen, burra burra mine, burra, south australia, australian mines, mines, monster mine -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Dolomite
Dolomite is a mineral, calcium magnesium carbonate, with the chemical formula CaMg(CO3)2. It is a principle component of various rock types sometimes also referred to as dolomite, including dolostone, dolomitic marble and dolomitic limestone (according to the composition of each type). Dolomite rock is found in sedimentary basins throughout the world, comprising approximately 2% of the Earth's crust. It is formed when lime mud or limestone encounters groundwater containing magnesium. Dolomite can contain elements such as lead, zinc and copper. Dolomite and limestone are used in various construction, landscaping and agricultural processes. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum in 1868 by Alfred Selwyn as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria. It was donated to the Museum in 1868. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole. Dolomite and limestone are mined at several locations in Victoria, including sites in the North-East of the state in Bindi and Limestone Creek. There are notable dolomite deposits in most Australian states. The dolomitised form of the mineral tends to come from older limestone deposits, formed during the palaeozoic era in marine settings, so this specimen may have come from a deposit located along a coastline in Victoria or another state. The specimen is significant as an example of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Hand-sized piece of pale pink dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate) with dark grey rim and hollowed centre. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, dolomite, mineralogy, geological survey, alfred selwyn, limestone, calcium magnesium carbonate -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite in Conglomerate, Unknown
... and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has... and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has ...Malachite is a green copper carbonate hydroxide mineral and was one of the first ores used to make copper metal. Malachite has been utilised as a gemstone and sculptural material in the past as its distinctive green color does not fade when exposed to light or after long periods of time. Malachite is formed at shallow depths in the ground, in the oxidizing zone above copper deposits. The material has also been used as a pigment for painting throughout history. Malachite is considered a rare gemstone in that the original deposits for the stones have been depleted leaving behind very few sources. In addition, the use of Malachite as gemstones and sculptural materials remains just as popular today as they were throughout history. It is quite common to cut the stone into beads for jewellery. The fact that Malachite has such a rich colour and one that does not fade with time or when exposed to light makes it particularly rare. Although there is no indication available of the locality from which the specimen was sourced, it is likely that the specimen was collected either in South Australia in the vicinity of the Burra Burra mines or in Victoria as part of programs of geological surveying undertaken in the Nineteenth and Twentieth centuries. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with quartz pebbles in red conglomorate matrix presenting shades of cream, brown and green.Existing label: Malachite / (green) in / conglomerate / (white quartz / pebbles / in red matrix /geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, geological, indigo shire, malachite, malachite specimen, australian mines, mines, geological survey, conglomorate, matrix -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Galena (lead sulphide), Unknown
Galena occurs in a range of deposit contexts, often in metalliferous veins, such as Broken Hill, Australia; Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, United States.; Clausthal Zellerfeld, Germany; and Cornwall, England. Large deposits also replace limestone, dolomite, or occasionally organic matter, or have a contact-metamorphic origin. Galena is additionally found in cavities, brecciated (fractured) zones in limestone and chert, and in coal beds. This specimen was recovered from Broken Hill NSW and is 60% lead with 8-12 oz/silver to the ton.Galena or 'lead glance' is a grey lead sulfide and the chief ore mineral of lead. It forms isometric crystals in which the ionic lattice is similar to sodium chloride. Galena is brittle and easily weathers to secondary lead minerals, with the upper part of mineral deposits often containing cerussite, anglesite, and pyromorphite. It usually contains silver, which is mined along with its lead content. Other commercially important minerals that form in close association with galena are antimony, copper, and zinc. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A small-sized solid specimen containing one mineral with a sparkly silver metallic lustre exterior and pastel-grey interior.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, galena, lead sulphide, alfred selwyn, broken hill -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCeramic Crucible, Morgan Fluxing Pot
A crucible is a vessel made of a refractory substance such as graphite or porcelain, used for melting and calcining materials at high temperatures. (http://www.thefreedictionary.com/crucible) Morgan Crucible was established in 1856. See http://ubshwiki.ballarat.edu.au/index.php/Morgan_Crucible_Co. A crucible is used to hold small amounts of chemicals during heating at high temperatures. The lid covers the bowl so nothing escapes, or to keep oxygen out of the reaction. (http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_a_crucible_and_how_is_it_used_in_a_laboratory)Two used narrow high shape crucibles with small spouts made by Morgan of England. They are heat-resistant containers used to melt ores, metals, and other materials. One has green (copper origin?) glaze like material on the base and sidecrucible, assaying, morgan -
 Federation University Historical Collection
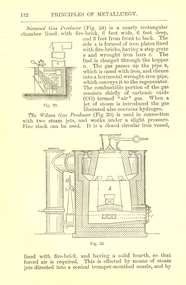
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Machinery for Metalliferous Mines, 1894, 1894
The 1st edition of this famous work, giving an excellent account of the machinery used in late 19th century metal mining in the UK and overseas is very rare. It covers a wide range of equipment - pumps, steam engines, drills, winding engines, stamps & concentration mills, aerial ropeways, tramways and early uses of electricity etc. Brown hard cloth covered book. xvi 564 pages with additional advertisements, with over 300 illustrations and drawings, some fold out. Chapters include Water as a motive power, Wind engines and ventilating machinery, Steam boilers/engines and oil engines, hoisting machinery, draining of Mines, pumping engines, rock drilling machinery, boring machinery, concentration machinery, sizing and classifications trommels, joggers and jigging, fine concentration, milling of gold ores, milling of silver ores, amalgamation plates and machinery, dry and roasting machinery, chlorination and cyandide processes for the extraction of gold, electricity as a motive power for mining, electric lighting and blasting, aerial wire ropeways, transport by rail and road. There a a number of lovely line illustrations in the book including: Poncelot's undershot waterwheel; Fromont furnace;Victor turbine; Pelton waterwheel; Root's positive blower;Cross section and front elevation of Lancashire boiler; Robey's Compound Mill Engine; Portable Winding Plant; Iron Pit Head Gear ; Loading Arrangement in an Incline Shaft; kibble; Worthington Pump; California Pump; Scram's Air Compressor; Rock drill Bits; Special Sharpening tools; Boring tools;Rotating Picking table; Ore Feeder; roller crusher; stamp battery; round buddle; slime table; vanner; amalgamating plant; belt elevator;roasting furnace;splicing wire rope; capel; tipping waggon;mining, cornish pump, linkenbach table, water wheel, ventilation, oil engine, california, america, water, steam boilers, steam engines, oil engines, pumpimg, rock drilling, boring, jiggers, milling, silver, gold, drying and roasting, chlorination, cyaniding, lead, zinc, copper, electricity, electric lighting, wire ropes, transport, wind engine, poppet head -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Principles of Metallurgy, 1901, 1901
... metallurgy brook hiorns pig iron steel silver acid stamp battery ores ...Maroon hard covered book of 388 pages. The book was written for the budding metallurgist, constituting an elementary treatise on the subject, dealing with principles rather than processes, the contents include: Intro., Definition, Properties, Principles, Alloys, Slags, Fuel, Iron, Steel, Silver-Gold-Platinum, Copper-Zinc, Lead-Tin, Nickel-Cobalt, Aluminium, Mercury, Antimony-Arsenic, Bismuth, Index.metallurgy, brook, hiorns, pig iron, steel, silver, acid, stamp battery, ores, zinc, copper, antimony -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Guide for Prospectors in Victoria, 1931, 1931
The handbook was intended for those with little experience who wanted to prospect of fossick.Grey soft covered book of 90 pages. Includes fold out map of a portion of Victoria showing auriferous areas and mineral localities. Also show Counties of Victoria and localities of minerals such as tin, antimony, copper, silver lead, Malybdenite, tungsten ores, manganese, platinum, osmiridium and iron. Chapter heading s include: working alluvial deposits, equipment, geology of Victoria, gold deposits, quartz reefs, indicators, economic minerals, assistance to prospectors, Miners' Right, mining bye-law, mining leases, forest regulations and glossary. Descriptions are given of a god dish, puddling tub, cradle, puddling machine, ground sluicing, boring, windlass, whim, hand dollying, sweeping, California pump, and wing dam.mining, baragwanath, gold, prospector, geology, quartz reefs, alluvial deposits, indicators, victorian goldfields, miners rights, mining leases, forest regulations, sluicing, sluice box, puddling machine, miner's cradle, whim, whip, california pump, gold nuggets, saddle reef, ballarat indicators, state batteries -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines Student's Magazine, Fourth Term, 1906, 1906
Table of contents: Editorial, Visit to the Cathcart Proprietary, Electric pumps, Random memories, Mining at and about Howell, N.S.W., Correspondence, Obituary, Routine assaying on a free milling W.A. gold ore, The deep leads and the old divide in the Ballarat district, The Lake Superior copper mine, The Melbourne trip, Hints on portraiture, Presentation fund, Electric power house, The Bun Club, Notes on copper smelting, Past students, Rowing notes, News and notes, Answers to correspondents, Editorial notices.Cream coloured booklet of 30 pagesballarat school of mines, students' magazine, obituary, alex saunders, a. e. c. kerr, j. a. reid, w. s. macartney, past students, f. m. lush, c. h. beaumont, o. e. jager, w. b. blythe, a. d. turner, j. w. hawthorne, p. a. pratt, l. lambert, donald clark, n. stuckey, s. b. vial, w. b. tucker, p. s. anderson, a. b. reid, r. j. robin, f. a. marriott, w. h. macready, c. mactaggart, g. s. hepburn, c. magennis, g. d. evans, alex fraser, g. govett, w. brokenshire, reg. williamson,, h. b. cooke, a. s. coyte, f. brinsden, r. vaughan, s. radcliff, harold irwin, f. t. fleetwood, max gaunt, j. t. marsh, w. b. blythe, a. d. turner, miss kerfupps,, din jurquot -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Exercise book, The Metallurgy of Gold and Ore Dressing, 1908
William Baragwanath studied at the Ballarat School of Mines, obtained a Geology certificate in 1911. He was born on 01 august 1878 at Ballarat. He joined the Victorian Department of Mines in 1897 and was Chief Mining Surveyor from 1924 to 1943. Baragwanath died at Prahran on 20 Septemeber 1966.Black covered exercise book containing handwritten notes by William Baragwanath on metallurgy of gold & orr dressing Headings include: Orr dressing Battery practice Physical properties Copper Gold Assaying ballarat school of mines, mining, william baragwanath, gold, copper -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, Vol. 8, No. 2., Second Term, 1905, 1905
Grey soft covered magazine on 18 pages. Contents include: Wet Lead Assay, Swedish Iron, Cambridge Life, Arizona Mining Camp (photograph) , Adelaide School of Mines, Blast Furnace, Cupellation and Parting.ballarat school of mines, ballarat school of mines students' magazine, david ham, swedish iron, blast furnace, refining, commercial wet lead-assay, daniel walker, woolfram ores, mounty lyell ore deposits, cambrisge university, arizona copper mining camp, g.j. dawbarn, arizona, new mexico, clifton, adelaide school of mines, j.a. haslam, biggest blast furnace in the world, o.e. jager, anaconda copper mining co., cupellation, j.m. baldwin, kerr grant, w.j. lakeland, e.m. weston, r. lamb, h.b. cooke, p. mathews, g.s. hart, john rahilly, martin h. bade, hugo eklund, cupulation -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, D.C. Davies et al, Metalliferous Minerals and Mining, 1892, 1892
Brown hard covered, illustrated book of 518 pages. It includes a bookplate of the Ballarat Ironworkers' and Polytechnical Association Library Rules. The book was bequethed to the Ironworkers' Association by the late James Oddie.mining, minerals, quartz, nova scotia, california, germany, ural mountains, gold deposits, virginia, new england, new brunswick, brazil, australia, new south wales, mount morgan, new zealand, africa, statistics, india, phillipines, aruba island, silver, russia, nevada, ruby hill, nevada, utah, emma mine, nevada, colarado, red mountain district, colorado, yankee girl mine, arizona, mexico, peru, bolivia, chili\copper, south africa, italy, austria, norway, swedan, france, cornwall, dolcoath mine, sandstone, parys mines of anglesea, carnarvonshire, cardiganshire, wicklow, ireland, mississippi valley, wisconsin, lake superior, wyoming, cuba, jamaica, venezuela, south australia, york peninsula, flinders ranges, japan, tin, banca, malaysia, bohemia, saxony, sweden, spain, cligga point, rin lodes of cornwall, andalusia, belgium, shropshire, isle of man, durham, westmoreland, limestone, flintshire, dengigshire, canada, lead, zinc, siberia, hungary, silesia, sardinia, algeria, ireland, new jersey, iron, lancashire, missouri, michigan, superstitions, equipment, cages, stopes, winzes, timbering, ventilation, fans, drilling, boring, dynamite, electricity, blasting, horse whims, water wheels, boilers, petterson's elephant ore stamp, stamper battery, jogs, linkenbach table, panning, cradle, quartz mining, hydraulic mining, alluvia; mining, altai mountains, north wales, neugluck mine, freiberg, christbescherung mine, drei prinzen lode, miask, woodville, virginia, gongo soco, brazil, sierra nevada, california, st john del rey mine, brazil, leydenberg gold field, south africa, banket reefs, transvaal, kongsberg, norway, santa rosa mine, peru, huelva, spain, dolcoath mine, cornwall, parys mine, anglesea, waterbury copper mine, lake superior, copiapo, chilli, altenberg, saxony, whea; uny, cornwall, wast wheel mine. redruth, cornwall, cligga point, cornwall, old hewas mine, cornwall, hartz, germany, snailbeach mine, shropshire, llangynog, north wales, van mine, mongomeryshire -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCeramic Crucible, Morgan Fluxing Pot
A crucible is a vessel made of a refractory substance such as graphite or porcelain, used for melting and calcining materials at high temperatures. (http://www.thefreedictionary.com/crucible) Morgan Crucible was established in 1856. See http://ubshwiki.ballarat.edu.au/index.php/Morgan_Crucible_Co. A crucible is used to hold small amounts of chemicals during heating at high temperatures. The lid covers the bowl so nothing escapes, or to keep oxygen out of the reaction. (http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_a_crucible_and_how_is_it_used_in_a_laboratory)Four used narrow high shape crucibles with small spouts made by Morgan of England. They are heat-resistant containers used to melt ores, metals, and other materials. One has green (copper origin?) glaze like material on the base and sideMorgan England stamped on side as well as letters indicating size.crucible, assaying, morgan, metallurgy -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: NOTE BOOK
Green, indexed, cloth bound note book containing fourteen pages of hand-written scientific experiments. Subjects include Iron, Standardization of KMn O4 solution, Ferrous Ammonium Sulphate, Sodium Oxalate?, Assay of Titaniferous? Iron ore, To make up Standard solution of Na2 S2 O? 5? For Copper, Standard Sol of (?H4)2 Mo O4) for Lead Assay, Sry Assay of Lead, Antimony, Resolution of ? Compounds, Clarks Modified Method Ores & Alloys, Method of reducing antimony solutions, Bromate Method, Standard Sol Pot Bromate, Standard, Assay, Oxides, Method suitable for alloys of Pb ? ?, Arsenic, Standard Iodine, Starch, Assay, Tungsten, Assay for Pyritic Scheelite, Illuminating Gas, Calcium, Permanganate method, Assay, ? O2, Iron, Ca O, Norman Solutions.sciences, instruments-general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection, scientific formulas, assay -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumTool - ROD
Used for crushing quartz in dolly potSOLID COPPER ROD USED FOR TOOLINGdolly pot, gold mining equipment, manual ore crusher, hand tool -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Amalgam bucket
Ore bearing rock brought out of the mine was crushed at the battery by heavy metal stampers and the fine material passed over copper pates coated with mercury. Gold particles would combine with the mercury forming an amalgam which was then scrapped off the copper plates and put into the amalgam bucket ready for retorting too extract the gold. The amalgam of mercury and gold was placed into the retort which was heated to evaporate the mercury. The mercury cooled as it ran down the pipe which was recovered to be reused leaving the gold behind. The gold would later be put into a crucible and heated to burn of impurities and the molten pure gold poured into an ingot.A heavy cast iron bucket 20 centimetres high, 16 centimetres in diameter at its base and 22 centimetres diameter at the top. It has a spout five centimetres wide protruding two centimetres. There is a handle which is a semi- circular shape 19 centimetre wide extending 14 centimetres above the bucket The inside of the bucket has an enamel coating. amalgam bucket, bendigo gold, gold retort -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - North-Eastern Gold Days, 1900
Bethanga was established as a result of the discovery of gold. Gold was first reported in the Bethanga area in 1852. Before 1876 gold mining in the Bethanga district occurred to the north of the town and was known as the 'Talgarno diggings'. Reports of alluvial gold date back to 1852. Early gold fields were worked at Ruby Creek, Gold Creek and Jarvis Creek. The opening of the Bethanga goldfields began with the discovery of a gold-bearing quartz reef on New Year’s Day 1876. The 'Gift' mine site is located southeast of Kurrajong Gap lookout to the west of Bethanga township. The Great Eastern Copper Smelting Works was opened in 1878. Due to the nature of the gold-bearing quartz reef, the gold was difficult to extract, and the discovery of copper led to a change in focus. It was not until the early 1890s that an efficient technique for extracting the gold from the ore was discovered, and once again gold became the focus, with copper as a by-product. Bethanga was removed from the official list of goldfields in 1912, however some mining activity has taken place since.This image reflects an important time in the development of Bethanga and Northeast Victoria.A large mounted and framed image of horse teams and their owners hauling a large boiler to the gold mine near Bethanga, Victoria. On label beneath image: "North-eastern "Gold Days"/ Combined teams hauling a boiler to Bethanga Mines, 1900. Teamsters - Mr. G. Pearce, W. Chapple, G, Bannon." Donated by Ron Saunders and Barbara Cadman"bethanga, gold mining northeast victoria, gold mining bethanga, bethanga history -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Model - MODEL of STAMPER
Gold bearing ore is pulverized by cast iron stampers (steam driven) and material then passes over a large copper plate covered in mercury causing the gold particles to combine with the mercury to form an amalgam which is scraped of and placed in a retort. The retort is heated causing the mercury to evaporate leaving the gold to be refined into ingots. The mercury is cooled as it leaves the retort and is reused. A second tray covered in what is called a blanket traps any fine gold that has passed the first plate. Finally the residue material goes over a vibrating table called a Wilfley Table which captures any iron pyrites which may contain about three percent gold. this is roasted and treated to recover any remaining gold at a special treatment plant.Wooden model of a five heads gold stamper battery. The gold stamper battery is a device for crushing ore. The parts of the battery are cams; dies; guides; kingposts; mortar box; shoes; stamps (or stampers); tappets. gold mining, mining equipment, gold stamper -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Student's Magazine, First Term, 1907, 1907
Table of contents: Editorial, Obituary, Professor A. Mica Smith, The choice of an economical heat engine, The direct estimation of Antimony, Electrical developments, R. B. Lamb, Easter geological camp, Sumitomo Bessi; The Great Copper Mine of Japan, Sporting notes, Professor Mica Smith's 25th Anniversary and students' second annual dinner, Correspondence, Modern treatment of gold ores, Answers to correspondents, News and notes, Past students, New students, Editorial notes.Orange coloured booklet of originally 26 pages, pages 3 to 14 are missing.ballarat school of mines, students' magazine, obituary, john heath ray, professor alfred mica smith, a. d. galloway, w. e. figgis, l. seward, a. c. stanger-leathes, h. r. murphy, c. dawson, g. h. davenport, j. m. sutherland, s. k. heron, f. treloar, t. s. hart, thomas hart, a. e. tandy, e. e. booth, figgis, pearce, p. a. pratt, past students, p. lewis, j. a. reid, r. d. nevett, j. mcfeeters, p. d. elliott, j. farrell, f. merton, w. b. tucker, j. peart, h. r. kofoed, w. h. macready, a. e. tandy, arthur elton tandy, lewis westcott, m. marks, latham watson, j. wallace, duncan mcdougal, e. e. booth, l. g. coulter, f. beaumont, g. w. evans, j. davidson, f. howell, a. e. ebbels, r. a. clinton, a. g. campbell, j. sides, m. j. roberts, r. ingram-moore, l. g. w. buchner, f. harvey, h. crabbe, colin c. corrie, h. manchester, glyn evans -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LITTLE 180 BATTERY - EXTRACT FROM BENDIGO ADVERTISER ON LITTLE 180 BATTERY
Handwritten extracts, with typed copies, from the Bendigo Advertiser Monday July 24th, 1933. First erected for 20 years. Mr. Cook performs Opening. Approx. 400 people attended the opening on Sat 22nd. Expected that when run in, the ore will be crushed for 2/6 per ton. Consists of 10 heads, 1000 lbs each. Boxes are of Homestake pattern with wooden horses of special timber and iron guides. Copper plate tables of ample area provided. Floors are of concrete and so graded that all washings - -. Expected later to expand to 30 head. A 114 H P Ruston-Hornsby crude oil engine is provided with a friction clutch to facilitate easy starting and will be capable of driving the battery when it is extended. Those who attended the opening were subsequently the guests of the Company at light refreshments. Copied 1/7/1970. Albert Richardson Collection gold mining, miners' safety cage, little 180 battery, mr cook, bendigo advertiser, 114 h p ruston-hornsby crude oil engine
