Showing 177 items
matching engine equipment
-
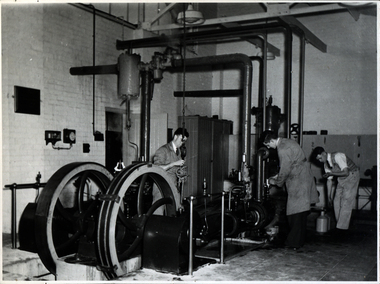 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and white photograph, Ballarat School of Mines Model Steam Engine
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.Black and white photograph of the Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine. On the brake is returned serviceman Norman WIlliam Ludbrook (Diploma Electrical Engineering, 1952). Far right is Roy E. Mawby (Diploma Electrical Engineering, 1950)steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, electrical engineering, laboratory, scientific instrument, norman ludbrook, norman william ludbrook, roay mawby, roy e. mawby -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Plaque Relating to the Thomas Bath Estate, c1990
Photograph of a metal plaque lThis original building and equipment of these workshops were presented by Thomas Bath Esq.thomas bath, workshops, steam engine -
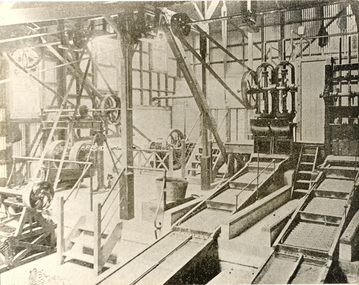 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White Image, Interior View of the Ballarat School of Mines Battery, c1901-1920
The Ballarat School of Mines Model Mine was used to give practical experience to students, as well as to conduct assays for companies and individuals for a fee. The fee assisted in keeping the Ballarat School of Mines afloat in its first years. The Battery, or model mine, included a Stamper Battery, Wilfrey Tables and various pieces of equipment students would encounter in their workplace. Steam engines were used to operate the large pulleys depicted in the photograph which in turn ran the equipment.Interior view of the Battery in the Ballarat school of Mines Model Mine. ballarat school of mines battery, model mine, stamper battery, steam, pulley, ballarat school of mines, battery house -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Standard measure, Mid to late 19th Century
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. J & M Ewan History: J&M Ewan was a Melbourne firm that began by selling retail furniture and wholesale ironmongery. They had substantial warehouses situated at the intersection of 81-83 Elizabeth and Little Collins Streets, the business was established by James M Ewan in 1852. Shortly afterwards he went into partnership with William Kerr Thomson and Samuel Renwick. When Ewan died in 1868 his partners carried on and expanded the business under his name J & M Ewan. The business was expanded to provide a retail shop, counting-house and private offices. Wholesale warehouses adjoined these premises at 4, 6 and 10 Little Collins Street, West. This company provided and sold a large and varied amount of imported goods into the colony that consisted of agriculture equipment, building materials, mining items as well as steam engines, tools of all types and marble fireplaces. They also supplied the Bronze measuring containers in the Flagstaff Hill collection and the probability is that these containers were obtained by the local Melbourne authority that monitored weights and measures in the mid to late 19th century. The company grew to employ over 150 people in Melbourne and opened offices at 27 Lombard St London as well as in New Zealand and Fiji. The company also serviced the Mauritius islands and the pacific area with their steamship the Suva and a brig the Shannon, the company ceased trading in 1993. Robert Bate History: Robert Brettell Bate (1782-1847) was born in Stourbridge, England, one of four sons of Overs Bate, a mercer (a dealer in textile fabrics, especially silks, velvet's, and other fine materials)and banker. Bate moved to London, and in 1813 was noticed for his scientific instrument making ability through the authority of the “Clockmakers Company”. Sometime in the year 1813 it was discovered that one Robert Brettell Bate, regarded as a foreigner in London had opened a premises in the Poultry selling area of London. He was a Mathematical Instrument maker selling sundials and other various instruments of the clock making. In 1824, Bate, in preparation for his work on standards and weights, leased larger premises at 20 and 21 Poultry, London, at a rental of four hundred pounds per annum. It was there that Bate produced quality metrological instruments, which afforded him the recognition as one of one of the finest and principal English metrological instrument-makers of the nineteenth century. English standards at this time were generally in a muddle, with local standards varying from shire to shire. On 17 June 1824, an Act of Parliament was passed making a universal range of weights, measures, and lengths for the United Kingdom, and Bate was given the job of crafting many of the metrological artifacts. He was under instruction from the renown physicist Henry Kater F.R.S. (1777-1835) to make standards and to have them deposited in the principal cities throughout the United Kingdom and colonies. Bate experimented with tin-copper alloys to find the best combination for these items and by October 1824, he had provided Kater with prototypes to test troy and avoirdupois pounds, and samples with which to divide the troy into grams. Bate also cast the standard for the bushel, and by February 1825, had provided all the standards required of him by the Exchequer, Guildhalls of Edinburgh, and Dublin. In 1824, he also made a troy pound standard weight for the United States, which was certified for its accuracy by Kater and deposited with the US Mint in 1827. Kater, in his address to the Royal Society of London, acknowledged Bate's outstanding experimentation and craftsmanship in producing standards of weights, measures, and lengths. An example of a dry Bronze measuring container made specifically for J & M Ewan by possibly the most important makers of measurement artefacts that gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in the Australian colonies based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item retailed by J & M Ewan and used in Victoria by the authorities who were given legal responsibility to ensure that wholesalers and retailers of dry goods sold in Victoria were correct. The container was a legal standard measure so was also used to test merchants containers to ensure that their distribution of dry goods to a customer was correct.Maker Possibly Robert Brettell Blake or De Grave, Short & Co Ltd both of LondonContainer bronze round shape for measuring dry quantities has brass handles & is a 'half-bushel' measurement"IMPERIAL STANDARD HALF BUSHEL" engraved around the top of the container. VICTORIA engraved under "J & M Ewan & Co London and Melbourne" engraved around the bottom of the container.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, standard measure, bronze, peck measurement, j & m ewan, victorian standard dry measurement, bronze container, victorian standards, melbourne observatory, robert brettell bate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Old Bus
Sir Charles Edward Kingsford Smith is a famous Australian, well known in civil aviation history for his courageous endeavours in flight. He broken many flight records for long distance and time travelled and he was also a war hero in World War 1. He has been referred to as being “known to millions of Australians as “Smithy” … he was one of Australia’s true twentieth-century legends”. In honour of his place amongst the world’s famous pioneers his image is featured on Australia’s $20 note, Sydney airport is named after him, there is a memorial to Kingsford Smith, Taylor and Ulm at the Anderson Park, also in Sydney and his plane “Southern Cross” is on view at Brisbane Airport. Kingsford Smith wrote ‘The Old Bus’ (1932) and he and Ulm were co-authors of ‘Story of 'Southern Cross' Trans-Pacific Flight’ (1928). His also wrote a book about his own life ‘My Flying Life’ which was published after his death in 1937. and the story of his life was filmed in Australia in 1946. A BRIEF HISTORY OF SIR CHARLES EDWARD KINGSFORD SMITH (1897 – 1935) … Kingsford Smith was born 9th February 1897 in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. His parents were William Charles Smith and Catherine Mary, nee Kingsford. His mother’s maiden name of “Kingsford” was added to the family name when they spent time in Canada from around 1903 to 1907, after which they returned to Sydney, Australia. In 1915 Kingsford Smith enlisted in Australian Imperial Force. He served in 4th Signal Troop, 2nd Division Signal Company at Gallipoli Peninsular as a ‘sapper’ or combat engineer and later in Egypt and in France as a dispatch rider. In 1916 Kingsford Smith was transferred to the Australian Flying Corps as a sergeant. He was discharged after training in England and commissioned as a second lieutenant in the Royal Flying Corps. He was appointed fling officer and soon joined the 23rd Squadron in France. He brought down four machines in his first month there and also did invaluable work attacking enemy targets. He was wounded and shot down and later awarded the Military Cross ‘for conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty’. He was promoted to lieutenant in 1918 and served as a Flying Instructor with the R.F.C. Kingsford Smith was not allowed to participate in the 1919 England to Australia air race because of assumed lack of navigational experience. He and his pilot friend Cyril Maddocks formed a business and flew joy-flights in both England and America. In America he did some stunt flying with a Flying Circus. Kingsford Smith returned to Australia in 1921 and found employment as a pilot. He soon realised the value of air transport in such a vast country. He formed a partnership with pilot Keith Anderson in 1924 and they purchased two Bristol Tourer biplanes. Their business broadened to include Charles Ulm and became the Interstate Flying services in Sydney. Together they performed important ‘demonstration’ flights including a flight around Australia in 10 days and 5 hours using very limited navigational equipment. Kingsford Smith immediately started to search for support to do a trans-Pacific flight. This support came from the New South Wales government, Sidney Myer and G. Allan Hancock, an American oil magnate. On 31st May 1928 Kingsford Smith, Charles Ulm and two American crewmen, Harry Lyan and Jim Warner, took off from Oakland, California and flew to Brisbane via Hawaii and Suva. This historic flight took 83 hours and 38 minutes. Their Fokker plane had three engines and was named the “Southern Cross”. This amazing achievement resulted in huge financial subscriptions. Kingsford Smith was awarded the Air Force Cross and appointed as honorary squadron leader, Royal Australian Air Force. Kingsford Smith flew his Southern Cross plane from Point Cook in Victoria to Perth nonstop. Then in September – October 1928, with Charles Ulm and an Australian crew, he piloted the Southern Cross from Sidney to Christchurch New Zealand. This flight showed that was possible for regular passenger and mail services across the Tasman Sea. Kingsford Smith flew his plane to England to an order for four aircraft, planning to use them for an inter-capital air service in Australia. Sadly on 1st April 1929 he was forced to land, having lost radio contact with the ground and having run into bad weather over north – west Australia. Keith Anderson and Robert Hitchcock both perished before the search party reached them. Once official enquiries were completed the flight to England continued in June and was completed in record time of 12 days and 18 hours. In January 1930 Kingsford Smith piloted the “Southern Cloud”, one of the new Avro Ten planes, on the first flight of his airline, the Australian National Airways, from Sydney to Melbourne. The “Southern Cross” was overhauled in Holland by the Fokker Aircraft Co. and in June 1930 Kingsford Smith achieved an east-west crossing of the Atlantic from Ireland to Newfoundland in 31.5 hours. Kingsford Smith returned to England and took delivery of an Avro Avian biplane that he named the “Southern Cross Junior” and flew solo from England to Darwin, Australia. This record breaking flight took less than 10 days. He beat four other planes that had left England before him and he was 5.5 days faster than Hinkler. Sadly Kingsford Smith’s “Southern Cloud” was lost during a flight from Sydney to Melbourne in 1931 with no surviving crew or passengers; in 1958 the wreckage was discovered in the Snowy Mountains. Later that year Kingsford Smith flew his “Southern Cloud” from Australia to Timor, collecting mail from a damaged Imperial Airways plane in Timor. Other flights followed. Kingsford Smith was knighted in 1932 for his services in Aviation. He returned to selling joy flights then established the Kingsford Smith Air Service, a flying training school in Sydney. In 1933 Kingsford Smith flew the amazing record flight in “Miss Southern Cross” – a Percival Gull - from London to Wyndham in Western Australia in just over ten days. The Australian Commonwealth then gave Kingsford Smith a large grant and he was also appointed as aviation consultant to Vacuum Oil Co. Another flying record was made when Kingsford Smith and Sir P.G. Taylor flow “Lady Southern Cross” from Brisbane to San Francisco in order to sell her there; the west-east-trans-Pacific flight made aviation history. They returned to Australia to make an attempt at the trans-Tasman flight but their attempt failed due to engine failure; they managed to get back to Sydney safely, minus most of their cargo. Kingsford Smith had his unsold “Lady Southern Cross” shipped back to England, from where he and J. T. Pethybridge in the “Lady Southern Cross” attempted another record breaking flight from England The Old Bus Author: Charles Kingsford Smith Publisher: Distibuted by Herald Feature Service Date; 1932Label on spine cover with typed text RA 629.1309 KIN flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, the old bus, charles kingsford smith -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSplint, c. 1910-1920
This is a pair of vintage DePuy wire mesh splints made to support a broken leg while the bone mended. The design was in use before and during WWI. It replaced the wooden splints previously used to reset bones in the late nineteenth to early 20th century. This new splint was invented by a traveling pharmaceutical salesman, Revra DePuy. He began manufacturing in his Warsaw, Indiana in 1895; the first commercial manufacture of orthopaedic equipment in the world . The company eventually became Johnson & Johnson. This pair of splints was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. These splints would have belonged to Dr Tom Ryan before being passed onto Dr. W.R. Angus. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The pair of splints was made by the world’s oldest orthopedic company, founded in 1895. The splint was a part of Dr. Tom Ryan’s equipment that was passed onto Dr W.R. Angus. It is part of the collection of historical medical equipment used in Western Victoria in the late 19th and early 20th century. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Splint, (pair of 2) from the W.R. Angus Collection. Stiff wire mesh with a hard metal border around the edges, shaped as a food and half leg, with printed paper labels attached to the top. Labels show manufacturer and instructions. Made for supporting Tibia and Fibula bones. Label attached to one split reads "DePuy Adjustable Wire / PATENTED / Tibia and Fibula Splint / No. 32 Medium Posterior / DePuy Manufacturing Co. / Warsaw, Indiana""DePuy Adjustable Wire / PATENTED / Tibia and Fibula Splint / No. 32 Medium Posterior / DePuy Manufacturing Co. / Warsaw, Indiana"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, medical text book, wire mesh splint, wire mesh cast, orthopaedic medical equipment, bone setting equipment, 1910’s medical equipment, medical artefact -
 Fire Services Museum of Victoria
Fire Services Museum of VictoriaBook - The Fire Brigade Handbook, The Fire Brigade Handbook by James Compton Merryweather
... Merryweather, of the Merryweather fire engine and equipment ...Personal copy of Captain James Kelly of the Prahran City Fire Brigade. Captain Kelly was killed at a fire in Melbourne in 1890. He was an advocate of brigade consoldiation and personal developmentHistoric: This book is a very early (1888) instruction manual and was the personal copy of Captain James Kelly of the Prahran City Fire Brigade. Published in England by James Compton Merryweather, of the Merryweather fire engine and equipment manufacturing company. It is the only known copy in MelbourneThe Fire Brigade Handbook by James Compton Merryweatherfire-brigade-organization capt-james-kelly prahran-city-fire-brigade merryweather fire-brigade-training fire-brigade-equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Stretcher, 1965 to 1999
A Neil Robinson stretcher is a lightweight carrying device modelled on Japanese bamboo litters, the Neil Robertson rescue stretcher was developed in the early 1900s by John Neil Robertson. Used for lifting an injured person vertically. The stretcher is made from stout canvas reinforced with bamboo slats. The stretcher is designed for removing an injured person from spaces wherein access, doors or hatches are too small to permit the use of regular stretchers. Spaces such as ship engine room spaces, cargo holds, pump rooms, boiler rooms etc. are a few examples of such compact spaces.An item designed to transport injured personnel from tight places, either at sea or on land.A rescue stretcher made from white canvas reinforced with bamboo slats and adjustable canvas straps. The canvas straps are secured with metal buckles and there is a metal ring attached to lengths of ropes at both ends. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, stretcher, neil robertson, neil robertson rescue stretcher, rescue equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chest of Drawers, British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, 1905-1927
This early 20th-century chest of drawers is unique. It was made from recycled timber kerosene boxes and metal tins. The case was made in South Australia between 1905 and 1927 by the British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, which was the first business to import bulk petroleum products into Australia. Before this, ships carried crates of kerosene as cargo. Items salvaged from the 1880 wreck of the vessel Eric the Red included kerosene boxes. Kerosene replaced plant and animal-based fuel, such as whale oil, for lighting in homes and for the lamps in lighthouses and on marine vessels. It was also used for cooking and heating and as engine fuel. The last kerosene-fueled lighthouse lamp was transferred to solar power in 1985. The chest of drawers is one-of-a-kind. The original uses for the components of the chest of drawers, the wooden box and metal tins were for containing and transporting kerosene. Kerosene was used from the late 19th century for fuel in lamps, heating, and cooling. Previously whale oil was used for the lamps in lighthouses. The company providing the kerosene was the first to import it into Australia in bulk quantities. The set of drawers is one of the many ways that inventive Australians were able to repurpose materials.Chest of drawers; wooden frame and rails, metal drawers with vertical metal handles. The frame has been constructed from the wooden panels of a vintage oil and kerosene box. The three drawers have been created from empty kerosene cans that were cut in half from top to bottom, some with the round opening closed over. Inscriptions from the original box and cams are stencilled on the top and base of the frame and impressed or painted on the metal cans. The frame has provision for a further drawer. The wooden case and metal tins were made in Australia.Top and base of frame; "THE BRITISH IMPERIAL OIL CO. LTD." "OIL ENGINE KEROSENE" "CASE ANDTINS AUSTRALIAN MADE" On tin; "POWIRIN" "BIOCO LTD" Logo [cross} with inscription on horizontal bar "CROSS" Impressed in timber drawer dividers (indecipherable text) Side of drawer, painted in orange on black; "TY -, REG U S - TIDE - "flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, antique, domestic equipment, chest of drawers, tool box, furniture, storage, recycled tin, recycled box, kerosene, fossil fuel, lighthouse lamp fuel, british imperial oil company ltd. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Machinery for Metalliferous Mines, 1894, 1894
... and overseas is very rare. It covers a wide range of equipment - pumps ...The 1st edition of this famous work, giving an excellent account of the machinery used in late 19th century metal mining in the UK and overseas is very rare. It covers a wide range of equipment - pumps, steam engines, drills, winding engines, stamps & concentration mills, aerial ropeways, tramways and early uses of electricity etc. Brown hard cloth covered book. xvi 564 pages with additional advertisements, with over 300 illustrations and drawings, some fold out. Chapters include Water as a motive power, Wind engines and ventilating machinery, Steam boilers/engines and oil engines, hoisting machinery, draining of Mines, pumping engines, rock drilling machinery, boring machinery, concentration machinery, sizing and classifications trommels, joggers and jigging, fine concentration, milling of gold ores, milling of silver ores, amalgamation plates and machinery, dry and roasting machinery, chlorination and cyandide processes for the extraction of gold, electricity as a motive power for mining, electric lighting and blasting, aerial wire ropeways, transport by rail and road. There a a number of lovely line illustrations in the book including: Poncelot's undershot waterwheel; Fromont furnace;Victor turbine; Pelton waterwheel; Root's positive blower;Cross section and front elevation of Lancashire boiler; Robey's Compound Mill Engine; Portable Winding Plant; Iron Pit Head Gear ; Loading Arrangement in an Incline Shaft; kibble; Worthington Pump; California Pump; Scram's Air Compressor; Rock drill Bits; Special Sharpening tools; Boring tools;Rotating Picking table; Ore Feeder; roller crusher; stamp battery; round buddle; slime table; vanner; amalgamating plant; belt elevator;roasting furnace;splicing wire rope; capel; tipping waggon;mining, cornish pump, linkenbach table, water wheel, ventilation, oil engine, california, america, water, steam boilers, steam engines, oil engines, pumpimg, rock drilling, boring, jiggers, milling, silver, gold, drying and roasting, chlorination, cyaniding, lead, zinc, copper, electricity, electric lighting, wire ropes, transport, wind engine, poppet head -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment - Model, 'Model Steam Engine' by Frederick Mitchell, 1886, c1892
Frederick Mitchell was born c1874 at Staffordshire Flat, Redcastle, near Heathcote. His father was an engineer from Cornwall, and had a quartz crushing battery at Staffordshire Flat from 1870 to at least the 1890s. Around 1886 Frederick Mitchell was an 18 year old "Engineer and Instrument Maker". He was awarded an 'Honorary Mention' at the Australian Juvenile Exhibition 1890-1. It was donated to the Ballarat School of Mines Museum in 1892. In the early 1960s the model was transferred to the Heat Engines Laboratory. All Heat Engines laboratory was moved from the Ballarat School of Mines to the Mt Helen Campus on October 1869. The model was accommodated in the thermodynamics laboratory. It was shown working during open days. The Ballarat School of Mines Calendar for 1893, page 66 refers to this item. There is correspondence between Frederick Mitchell's grandson, F.W. Mitchell; E.J. Barker, Director of the Ballarat College of Advanced Education; and Graham Beanland, Ballarat School of Mines.A working model of a vertical oscillating twin cylinder steam engine with fly wheel, mounted on a wood base board and covered in glass. Usually stored under a wood-framed glass cover. steam, model, engine, frederick mitchell, flywheel, ballarat school of mines museum -
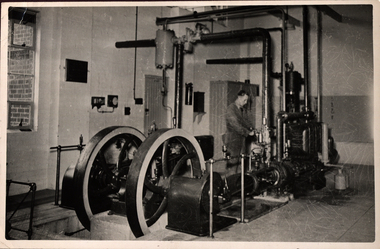 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Black and white, Ballarat School of Mines Model Steam Engine
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.Black and white photograph of the Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine installed at the Ballarat School of MInes. steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, thomas bath, experimental steam engine -
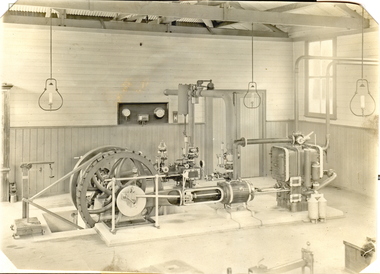 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Ballarat School of Mines Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine, c1902
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only. Black and white photograph of an experimental steam engine which was produced for the Ballarat School of Mines. It was designed for experimental purposes, such as testing of efficiency, etc. The laboratory which housed the steam engine was lit with gas lighting. davey paxman experimental steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, steam, thomas bath, thermodynamics -
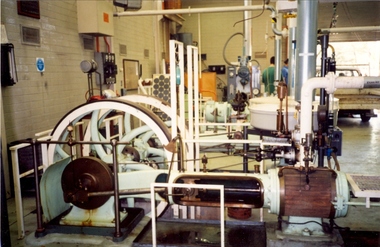 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour photograph, Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine in the Mount Helen Workshop, c1994
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased by the Ballarat School of Mines as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath.The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.davey paxman experimental steam engine, model steam engine, steam, thermodynamics laboratory, thomas bath, bequest -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Equipment from the Carlton and United Brewery, Ballarat, 2007, 2007
When the Ballarat Brewery was demolished the Ammonia Compressor was moved to near the Brew Tower, Armstrong Street.Three photographs of the 140 ton Ammonia Compresor used at the Ballarat Brewery. The compressor was possibly moved to Ballarat from Carlton, and was used from c1930. It was built by Werner of Richmond.Label associated with the compressor "The School of Mines and Industries Ballarat Limited 140 ton Ammonia Compressor, c1930 Built by Werner of Richmond, Melbourne, this compressor was removed from the Carlton and United Breweries Richmond factory and installed in Ballarat in 1959 in order to upgrade the refrigeration plant. Refurbished by members of the former Ballarat Brewery Engine Room it serves as a reminder of the establishment of the brewery on this site by Tulloch and McLaren in 1862."ballarat brewery, ballarat brewing company, brew tower, brew, carlton and united breweries, werner, brewing, tulloch and mclaren, brewery, ballarat school of mines -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Standard measure, Mid to late 19th Century
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. J & M Ewan History: J&M Ewan was a Melbourne firm that began by selling retail furniture and wholesale ironmongery. They had substantial warehouses situated at the intersection of 81-83 Elizabeth and Little Collins Streets, the business was established by James M Ewan in 1852. Shortly afterwards he went into partnership with William Kerr Thomson and Samuel Renwick. When Ewan died in 1868 his partners carried on and expanded the business under his name J & M Ewan. The business was expanded to provide a retail shop, counting-house and private offices. Wholesale warehouses adjoined these premises at 4, 6 and 10 Little Collins Street, West. This company provided and sold a large and varied amount of imported goods into the colony that consisted of agriculture equipment, building materials, mining items as well as steam engines, tools of all types and marble fireplaces. They also supplied the Bronze measuring containers in the Flagstaff Hill collection and the probability is that these containers were obtained by the local Melbourne authority that monitored weights and measures in the mid to late 19th century. The company grew to employ over 150 people in Melbourne and opened offices at 27 Lombard St London as well as in New Zealand and Fiji. The company also serviced the Mauritius islands and the pacific area with their steamship the Suva and a brig the Shannon. Robert Bate History: Robert Brettell Bate (1782-1847) was born in Stourbridge, England, one of four sons of Overs Bate, a mercer (a dealer in textile fabrics, especially silks, velvet's, and other fine materials)and banker. Bate moved to London, and in 1813 was noticed for his scientific instrument making ability through the authority of the “Clockmakers Company”. Sometime in the year 1813 it was discovered that one Robert Brettell Bate, regarded as a foreigner in London had opened a premises in the Poultry selling area of London. He was a Mathematical Instrument maker selling sundials and other various instruments of the clock making. In 1824, Bate, in preparation for his work on standards and weights, leased larger premises at 20 and 21 Poultry, London, at a rental of four hundred pounds per annum. It was there that Bate produced quality metrological instruments, which afforded him the recognition as one of one of the finest and principal English metrological instrument-makers of the nineteenth century. English standards at this time were generally in a muddle, with local standards varying from shire to shire. On 17 June 1824, an Act of Parliament was passed making a universal range of weights, measures, and lengths for the United Kingdom, and Bate was given the job of crafting many of the metrological artifacts. He was under instruction from the renown physicist Henry Kater F.R.S. (1777-1835) to make standards and to have them deposited in the principal cities throughout the United Kingdom and colonies. Bate experimented with tin-copper alloys to find the best combination for these items and by October 1824, he had provided Kater with prototypes to test troy and avoirdupois pounds, and samples with which to divide the troy into grams. Bate also cast the standard for the bushel, and by February 1825, had provided all the standards required of him by the Exchequer, Guildhalls of Edinburgh, and Dublin. In 1824, he also made a troy pound standard weight for the United States, which was certified for its accuracy by Kater and deposited with the US Mint in 1827. Kater, in his address to the Royal Society of London, acknowledged Bate's outstanding experimentation and craftsmanship in producing standards of weights, measures, and lengths. An example of a dry Bronze measuring container made specifically for J & M Ewan by possibly the most important makers of measurement artifacts that gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in the Australian colonies based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item retailed by J & M Ewan and used in Victoria by the authorities who were given legal responsibility to ensure that wholesalers and retailers of dry goods sold in Victoria were correct. The container was a legal standard measure so was also used to test merchants containers to ensure that their distribution of dry goods to a customer was correct. Bronze round container with brass two handles used as a legal standard for measuring dry quantities & is a 'peck' measurement. "IMPERIAL STANDARD PECK" engraved around top of container with " VICTORIA" engraved under.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, standard measure, bronze, peck measurement, j & m ewan, victorian standard dry measurement, bronze container, victorian standards, melbourne observatory, robert bettell bate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Standard measure, Mid to Late 19th Century
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. J & M Ewan History: J&M Ewan was a Melbourne firm that began by selling retail furniture and wholesale ironmongery. They had substantial warehouses situated at the intersection of 81-83 Elizabeth and Little Collins Streets, the business was established by James M Ewan in 1852. Shortly afterwards he went into partnership with William Kerr Thomson and Samuel Renwick. When Ewan died in 1868 his partners carried on and expanded the business under his name J & M Ewan. The business was expanded to provide a retail shop, counting-house and private offices. Wholesale warehouses adjoined these premises at 4, 6 and 10 Little Collins Street, West. This company provided and sold a large and varied amount of imported goods into the colony that consisted of agriculture equipment, building materials, mining items as well as steam engines, tools of all types and marble fireplaces. They also supplied the Bronze measuring containers in the Flagstaff Hill collection and the probability is that these containers were obtained by the local Melbourne authority that monitored weights and measures in the mid to late 19th century. The company grew to employ over 150 people in Melbourne and opened offices at 27 Lombard St London as well as in New Zealand and Fiji. The company also serviced the Mauritius islands and the pacific area with their steamship the Suva and a brig the Shannon. Robert Bate History: Robert Brettell Bate (1782-1847) was born in Stourbridge, England, one of four sons of Overs Bate, a mercer (a dealer in textile fabrics, especially silks, velvet's, and other fine materials)and banker. Bate moved to London, and in 1813 was noticed for his scientific instrument making ability through the authority of the “Clockmakers Company”. Sometime in the year 1813 it was discovered that one Robert Brettell Bate, regarded as a foreigner in London had opened a premises in the Poultry selling area of London. He was a Mathematical Instrument maker selling sundials and other various instruments of the clock making. In 1824, Bate, in preparation for his work on standards and weights, leased larger premises at 20 and 21 Poultry, London, at a rental of four hundred pounds per annum. It was there that Bate produced quality metrological instruments, which afforded him the recognition as one of one of the finest and principal English metrological instrument-makers of the nineteenth century. English standards at this time were generally in a muddle, with local standards varying from shire to shire. On 17 June 1824, an Act of Parliament was passed making a universal range of weights, measures, and lengths for the United Kingdom, and Bate was given the job of crafting many of the metrological artifacts. He was under instruction from the renown physicist Henry Kater F.R.S. (1777-1835) to make standards and to have them deposited in the principal cities throughout the United Kingdom and colonies. Bate experimented with tin-copper alloys to find the best combination for these items and by October 1824, he had provided Kater with prototypes to test troy and avoirdupois pounds, and samples with which to divide the troy into grams. Bate also cast the standard for the bushel, and by February 1825, had provided all the standards required of him by the Exchequer, Guildhalls of Edinburgh, and Dublin. In 1824, he also made a troy pound standard weight for the United States, which was certified for its accuracy by Kater and deposited with the US Mint in 1827. Kater, in his address to the Royal Society of London, acknowledged Bate's outstanding experimentation and craftsmanship in producing standards of weights, measures, and lengths. An example of a dry Bronze measuring container made specifically for J & M Ewan by possibly the most important makers of measurement artefacts that gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in the Australian colonies based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item retailed by J & M Ewan and used in Victoria by the authorities who were given legal responsibility to ensure that wholesalers and retailers of dry goods sold in Victoria were correct. The container was a legal standard measure so was also used to test merchants containers to ensure that their distribution of dry goods to a customer was correct.Maker Possibly Robert Brettell Blake or De Grave, Short & Co Ltd both of LondonContainer brass round for measuring quantities- Has brass handles & is a 'Bushel' measurement. 'Imperial Standard Bushel Victoria' engraved around container. Container bronze round shape for measuring dry quantities has brass handles & is a 'Bushel' measurement"IMPERIAL STANDARD BUSHEL" engraved around the top of the container. VICTORIA engraved under "J & M Ewan & Co London and Melbourne" engraved around the bottom of the container.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, standard measure, bushel, bushel measurement, j & m ewan, dry measurement, victorian measurement standard, bronze container, melbourne observatory, robert brettell bate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Boiler, ca 1880
This little steam boiler has been beautifully built. It could have been used to drive an engine in a small workshop, a boat or launch, or even farming equipment. It is an example of the steam technology and mechanisation of the 19th century. William Cook introduced steam heating in England in the 18th century. Steam combined with pressure was used for powering transport, such as steam engines for trains, and manufacturing, such as steam engines driving manufacturing machines. Steam boilers are still used today as an energy-efficient means of power.This steam boiler would have been suitable to drive a small engine, possibly that of a small boat. Coal was added to the firebox for fuel to heat water in the boiler. It is an example of the power used to drive machinery and equipment in the mid-to-late 19th century. Steam boilers like this one have played a part in the evolution of steam power. Steam engine boiler; vertical cylindrical coal-fired boiler with a black firebox at its base and a dome top. The cylinder's sides and top have brass fittings, inlet and outlet taps. A round opening near the base is covered by an adjustable metal plate that controls the boiler's temperature. The front door of the firebox has two hinges at the base and when the side clips are opened. A shiny brass collar tops the tall chimney. Oak wood planks around the sides of the boiler, and held in place by brass bands with nut and screw fixtures. The boiler stands on a metal and wood frame with a looped handle at the back. An inscription has been noted. Circa 1880. "1948 D/430" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, boiler, steam engine, steam boiler, coal fired boiler, vertical boiler, boat boiler, power source, steam driven, engine boiler, steam machine, firebox, steam engine boiler -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionJournal, The Mechanical World and Steam Users' Journal, 04/12/1884
the magazine describes some of the earlier equipment used in mining8 pages of the journal, some edges are torn, pages are discoloured, contains images of mining machinerymining, mining equipment, weston-capon friction clutch, steam engine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Bedspread, early 20th century
This crocheted bedspread was used by Dr. and Mrs. Angus in their home in "Birchwood" Warrnambool. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the "W.R. Angus Collection" that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments, and material once belonging to Dr. Edward Ryan and Dr. Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr. Angus's belongings. The Collection's history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr. Angus, up until 1969. WR Angus Collection: Doctor William Roy Angus qualified as a doctor from Adelaide University in 1923. Dr. Angus was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 until he died in 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at the University of Adelaide and was a Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period house surgeon to Sir Henry Simpson Newland. Dr. Angus was also briefly an Assistant to Dr. Riddell of Kapunda SA, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was a physician, surgeon, and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr. Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr. Tom Ryan's absence. Dr. Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and it was decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK. in 1927 He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship's Surgeon on the Australian Commonwealth Line's T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr. Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat and had one son Graham born in 1932, and two daughters (Helen and Bernice, both were born at Mira, Nhill SA Dr. Angus was a 'flying doctor' for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928. The Organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr. Angus was stationed. He was locum there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp taking up the position of 'flying doctor' in response to a call from Dr. John Flynn; the Organisation later became known as the Flying Doctor Service. Between 1928-1932 he was a surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia but in1933 he returned to Nhill where he'd previously worked as a Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr. Les Middleton the current owners of what was once Dr. Tom Ryan's practice. When Dr. Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital's Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner's plate from his Nhill surgery states "Hours Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10 am, 2-4 pm, 7-8 pm. Sundays by appointment". This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr. Edward Ryan and Dr. Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr. Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill, Dr. Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr. Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased "Birchwood," the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr. John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station.) The Angus family were able to afford gardeners, cooks, and maids with their home becoming a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr. Angus had his silkworm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr. Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940's when the government no longer required the service of a medical officer he then became Warrnambools last serving Port Medical Officer. Dr. Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital from 1939 to 1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII from 1942 to 1945, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., he completed his service just before the end of the war as he suffered a heart attack. It was during his convalescence he carved an intricate and 'most artistic' chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was an Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr. Angus was elected member of Spain's Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this accolade, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne. In his personal life, Dr. Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along 'for the ride' and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr. Angus' patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she'd seen as an eye witness from the late 1880s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950's Dr. Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret's book, Shipwrecks, and More Shipwrecks. Dr. Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys' Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council, and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death on 28th March 1970, his family requested his practitioner's plate, medical instruments, and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the "W. R. Angus Collection". The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for the social and medical achievement's that Dr. William Roy Angus had accomplished in his lifetime and the collection of equipment that he and his predecessors had used to treat patients give an insight into the working lives of early colonial medical practices in rural Australia. This collection of medical artefacts is on display located at Flagstaff Hill Village and the Port Medical Officers building where Doctor Angus had practice as the last Port Medical Officer for Warrnambool.Crocheted double bedspread, from the W.R. Angus Collection. White cotton, hand crocheted 30 squares joined as patchwork then a border crocheted around edge. Each square is 41cm square.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, hand crafted manchester, crocheted bedspread, patchwork bedspread, household linen, early 20th century bedspread, dr. w r angus -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Black & White, Mr F. Guumes 1884-1950 & Hand made Harness outfit c1947, c1947
Mr Francis Guumes1884-1950, was born in the Cheltenham district and later bought land in Heatherton Rd, Heatherton, where he and his two sons developed a market garden. Mr Guumes , a self taught leather worker, made every piece of this harness. He entered this outfit in the Royal Melbourne Show c1947 and was awarded 1st Prize in his section. ( H. Stanley 2005)Early settlers in Moorabbin Shire had to be resourceful and self sufficient as they developed market gardens and farms. The community learned to make, repair and invent tools and equipment that was needed on their properties. Black & White photograph, enlarged, showing Mr Francis Guumes, with the rig and leather work that he entered and won 1st prize in the Royal Melbourne Show c 1947guumes francis, royal melbourne show 1947, leatherwork, saddles, harness, draught horses, horse drawn carts, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, , chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Dorade Ventilator, 1930s
A dorade is a type of ventilator that allows air to move in and out of a vessel's cabin or engine room but baffles or screens within the box it is fitted to prevent the rain and seawater from getting inside. A Dorade was first seen in use on the "Dorade", an ocean racing yacht designed by Olin James Stephenson II and built in 1929. Since then there have been modifications to the original design. The yacht, Dorade, could have been named after the Mediterranian dorade fish.An early piece of marine equipment from the 1930s that still is in use today on smaller vessels to improve below-deck ventilation.Dorade vent cowl; a cast brass ventilator. A' J' shaped hollow brass cylinder with a wide open mouth twisted to the side. The inside is painted. A Dorade vent is normally fitted into a chamber box but this was not included.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ventilator, dorade, vent, cowl, ship fittings, maritime equipment, ventilator box, dorade vent, collector box, cowl vent, olin james stephenson ii -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchEngine Room Telegraph
... Belgrave RSL Sub Branch 1 Mast Gully Road Upwey melbourne Equipment ...Display Modelequipment, ran -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BLACK AND WHITE PHOTOGRAPH OF THE BIG DEBORAH MINE
black and white photograph of the Big Deborah mine, showing infrastructure, chimney, large steel tank. Note the absence of cables from top of the poppet to the engine room.mining, surface equipment, big deborah mine. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CALEB THOMAS - CROSS SECTIONS 10/10/84
Handwritten notes cross sections mentioning mine, engine location, height of legs and for two the height of the landing brace. Mines mentioned are: South Catherine, Ellenborough, Belmont & Saxby, York & Durham, (Snobs Hill) Old Williams and Acadia Catherine.mining, equipment -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - NELL GWYNNE REEF'S MINE
Black and white photograph. Nell Gwynne Reefs; Mine winding engine. Walker and Coy. Dwellings in background. Machinery, winding drums, steel platform, lever, etc. Plant growing up between. Inscriptions: on back - in ballpoint pen 'Nell Gwynne Reef's Mine, winding engine, Walker & Co'.mining, surface equipment, nell gwynne, bendigo, mines and mining, mines, place, gold, surface equipment -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - WINDING ENGINE AT MONUMENT HILL MINE
Black and white photograph of a winding engine (Roberts & Son) at Monument Hill Mine. Winding gear, large drum with wire cable wound on, sitting on concrete base. Inscriptions: on back - lined paper, glued in centre 'Monument Hill Mine, Winding Engine, Roberts and Sons'.place, mining site, rope winding drum, mines and mining, equipment, mining equipment, bendigo, mines, mining, surface equipment -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALBERT RICHARDSON COLLECTION: HERCULES MINE REPORT 1936
a. four page handwritten report on the Hercules Mine, half yearly reports 1936. Extract: Reef worked below the 1620 feet level has been opened up at 1,840 feet. Profit has been earned but values are now unprofitable. At the Stanfield shaft, erection of plan was completed and shaft sunk to 344 feet. X cuts put out at 230 and 310 feet. Angus Mackay Chairman. b. Summary of sale of mine from Bendigo Advertiser 19.6.1950, handwritten by Albert Richardson, re the sale of the mining equipment at the Hercules Mine. ' Winding engines sold for £200 Compressor £425 and the oregon poppet legs for £41. The three main buildings went for £435 , the office and store room for £80, and die room for £12 Most spirited bidding was for 5 tons of firewood which finally went for £12Albert Richardsonbendigo, mining, hercules mine -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALBERT RICHARDSON COLLECTION: WATTLE GULLY GOLD MINE, CHEWTON
One page document. On top of page 'Wattle Gully Mine, Chewton, Mining and Equipment' Document details the main shaft, concentrating plant, drainage water, compressed air and ventilation. Machinery mentioned: Ingersoll -Rand compressor; Ruston-Hornby diesel engine and Jaques jaw crusher.bendigo, mining, wattle gully gold mine chewton -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALBERT RICHARDSON COLLECTION: REPORT ON INSPECTION OF DEBORAH MINES
Two page document ( carbon copy ) detailing report on inspection, mining machinery 17 November, 1971. Report states ' Met Mr. R. Barker, first to Nth Deborah met Frank Vincent at this mine. Inspected Great Southern engine. Other mines mentioned are South Deborah, Deborah Extended. Second page details tyhe mining machinery made and used in Bendigo such as R. Roberts' Winding Engine and Poppet legs at the Central Deborah Mine. Also a Thompson (Castlemaine) air compressor at this mine. Document signed by Albert Richardson 19.11.1971.bendigo, mining, mining equipment
