Showing 65 items
matching measuring device
-
 Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.
Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.Scales, "Circa 1863"
... potter london measuring devices Date 25/1/1865.Various hallmarks ...This set of scales would have been used to check the acuracy of Weights and Measures.Where it was used is unknown, but it may have always been part of the Shire.The maker was J.D.Potter,Poultry,London Middlesex,U.K. One of several sets of scales of various sizes in collection of Learmonth And District Historical Society Inc.To measure precise weights,the instruments used were a set of precise balanced scales. Set on a wooden box,( which would have contained the weights).It is made of brass and has a brass beam balance,steel pointer with index and twin pans. Date 25/1/1865.Various hallmarks similar to "jewellers".tools, and, scales, weights, measures, potter london, measuring devices -
 Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.
Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.Scales, Circa 19th Century
... . tools.scales.measuring device. weights and measures nil Medium size set of scales ...These scales were possibly used by the former Shire of Ballarat to weigh letters and other small items.A means by which articles of the day were weighed.Medium size set of scales,Brass weighing pans on a beam balance with pointer.The base is wood with inserts to hold weights.niltools.scales.measuring device. weights and measures -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Spring Scale
... Scale. Has ring for hanging, spring and hook device..., spring and hook device for weighing. Measures in lbs. Instrument ...The first spring balance in Britain was made around 1770 by Richard Salter of Bilston, near Wolverhampton. He and his nephews John & George, founded the firm of George Salter & Co., still notable makers of scales and balances, who in 1838 patented the spring balance. They also applied the same spring balance principle to steam locomotive safety valves, replacing the earlier deadweight valves. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spring_scale Today, spring scales are very popular with recreational fishers. The ability to weigh things reasonably accurately with a small inexpensive apparatus allowed for the exact weight of items to be ascertained. However, it was not accurate enough to weigh small amounts in ounces or grams.Scale. Has ring for hanging, spring and hook device for weighing. Measures in lbs.Scale of pounds weight.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Stevenson Screen, Thomas Stevenson, ca. 1910
Stevenson screens were first introduced in Australia in the 1880s and were widely installed by 1910. The screens have been used to shelter and protect thermometers and other meteorological instruments from rain and direct heat while the holes and double-louvre walls allowed air to flow around them. Sometimes other meteorological instruments were included in the weather stations, so there were different Stevenson Screen sizes. This authentic, original Stevenson screen was previously owned by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology and was used for many years for weather readings at the Cape Otway Light Station in southwest Victoria. The Lighthouse Keepers recorded the readings for minimum and maximum temperatures at 9 a.m. every day from January 1865 until April 1994. The equipment was sheltered in a Stevenson Screen from 1902 until April 15 1994, when the mercury thermometer was replaced by a platinum resistance probe within an Automatic Weather Station (AWS). This Stevenson screen is one of the two screens that then became redundant. The other Stevenson screen was kept to display to visitors. Lightkeepers were no longer required at the Cape Otway Light station either, due to the automated system. The meteorological instruments donated with the screen were used for measuring temperature and humidity. They are mounted on a metal bracket that fits across the screw holes on the screen’s internal frame. The glass-covered Relative Humidity (RH) sensor was made by the renowned precision instrument maker, Rotronic AG of Switzerland, which was founded in 1965. The firm made its first electronic temperature and humidity instrument in 1967. Meteorological records have been collected in Australia from the 1800s. The records were collated, published and used as a basis for weather forecasts. Many sectors, such as maritime and agriculture industries, have relied on these figures for making important decisions. The quality and placement of the meteorological instruments used to measure temperature and humidity are of utmost importance for accuracy. In early colonial times, there were no national standards for meteorological instruments that would allow for accurate figures and comparisons. Once the Bureau of Meteorology was established (around 1908 to 1910) the department installed Stevenson screens throughout Australia, many at lighthouses and light stations, and the measuring instruments were standardised. The Stevenson Screen was named after its inventor, Scottish Civil Engineer Thomas Stevenson (1818-1887) who was also the father of Robert Louis Stevenson, author. Stevenson developed the small thermometer screen around 1867. It had double-louvred walls around the sides and a top of two asbestos sheets with an air space between them and was thickly painted with a white coating that reflected the sun’s rays. This design was modified in 1884 by Edward Mawley of the Royal Meteorological Society. Standards were set for the locations of the screens and instruments, including their distance above ground level and the direction the door faced.Stevenson screens played a significant part in providing a standardised shelter for all meteorological instruments used by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology from about 1910 until 1994. The readings from the instruments gave the meteorological statistics on which weather forecasts throughout Australia were based. This Stevenson screen was used locally at Cape Otway, along the Great Ocean Road in southwest Victoria, so contributed towards our local forecasts and weather warnings.Stevenson screen, original, from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology’s weather station at the Cape Otway Lighthouse. The screen is a white wooden cupboard with a slanted cover raised above the top. The top has ten drilled ventilation holes, and the sides and door are made of downward-slanting double louvres. Two brass hinges join the door to the lower edge of the screen and a metal fitting at the top edge allows for a padlock closure. The screen is supported on four short legs, each with a hole drilled from side to side for fitting to a frame. Inside the screen are two wooden frames fitted with hooks and screws. The floor has three boards; one across the back and one across the front at the same level, and a board wider than the space between these boards is fitted higher, overlapping them slightly. Inside the screen, a pair of electronic instruments with short electric cables is mounted on a metal bracket with drilled holes in it. One of the instruments is a Relative Humidity (RH) probe. It is 26 cm long and is a glass tube with a filter on one end and an electrical connection on the other. It has inscriptions on its label, showing that was made by Rotronic AG, Switzerland. The other instrument is a Resistance Temperature Device (RTD) thermometer. It is 22.5 cm long and has a narrow metal probe joined to a hexagonal metal fitting. A brass plate on the front of the screen has impressed inscriptions. The screen is Serial Number 01/C0032, Catalogue Number 235862.Stamped into brass plate "CAT. NO. / 253862 / SERIAL NO. 01/C0032" On instrument’s electrical fitting; “CD2” [within oval ‘+’ above S] “Serie693 op65 / 220/380V~16A” On instrument’s glass; “rotronic ag” “SWISS MADE” “CE / CH-8303 / Bassersdorf” Symbol for [BARCODE] “ART NO MP 101A_T4-W4W” “POWER 4.8.30VDC“ “OP. RANGE: 0-100%RH/-40+60° C” “OUT H 0-100% 0-1V” “OUT T -40+60°C -0.4..+0.6V” “SERIE NO 19522 009”flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, cotton region shelter, instrument shelter, thermometer shelter, thermoscreen, thermometer screen, measuring instruments, meteorological instrument, weather recording, weather station, lighthouse equipment, light station equipment, stevenson screen, marine instruments, mercury thermometer, platinum resistance probe, aws, automatic weather station, rotronic ag, swiss made, meteorological device, weather forecast, weather prediction, weather records, meteorological forecast, meteorological record, australian bureau of meteorology, bureau of meteorology, bureau, bom, relative humidity, rh, relative humidity probe, resistance temperature device, rtd, thermometer, temperature, humidity, cape otway, cape otway lighthouse, cape otway light station, rotronic, switzerland, swiss instrument, thomas stevenson, double-louvered walls, edward mawley, royal meteorological society, 01/c0032, serial number, cat. no. 235862, serial no. 01/c00323 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionLaptop Computer, Acer, Acernote 350 Laptop Computer, 10/10/1995
The Acer was one of the first notebook computers used in the Electrical Engineering Department of the School of Engineering at the Ballarat University College. It was purchased in 1995 at a cost of $1800. The Acer Note350 has a 3½ inch floppy drive and a hard drive with a capacity of 401 megabytes and a ram capacity of 64 kilobytes. The operating system is Windows 95. The computer was used most often in conjunction with a data acquisition device plugged into the parallel port. In 1996 the equipment was setup to measure the forces of acceleration on a cricket bat caused by impact with the ball. This debunked a long held misconception that Composition balls used in a cricket bowling machine caused more damage to a bat than normal leather balls. Grey Plastic laptop computer, with black AC Adapter. Model 350C Ext No 0P3 Serial No M0006862 DC rating 20v 1.7a computer, ballarat university college, laptop -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Scale, 1900-1930
The basic balance scale has been around for thousands of years and its accuracy has improved dramatically over the last several centuries, the principle behind this tool remains unchanged. Its parts include a fulcrum, a beam that balances on it, a pan at the end of the beam to hold the materials to be weighed, and a flat platform at the other for the counter-balancing weights. Balance scales that require equal weights on each side of the fulcrum have been used by everyone from apothecaries and assayers to jewellers and postal workers. Known as an unequal arm balance scale, this variety builds the counterweight into the device. Counter scales used in dry-goods stores and domestic kitchens often featured Japanned or (blackened) cast iron with bronze trims. Made by companies such as Howe and Fairbanks, the footed tin pans of these scales were often oblong, some encircled at one end so bulk items could be easily poured into a bag. Seamless pans were typically stamped from brass and given style names like Snuff (the smallest) and Birmingham (the largest). Some counter scales were designed for measuring spices, others for weighing slices of cake. In the 18th century, spring scales began to appear and would use the resistance of spring to calculate weights, which are read automatically on the scale’s face. The ease of use of spring scales over balance scales. These scales are significant as they identify one of the basic preparation items for the weighing of foodstuff in the family kitchen to prepare everyday meals. This item is significant as it gives a snapshot into domestic life within the average home in Australia around the turn of the twentieth century and is, therefore, an item with social relevance. Black cast iron, medium weighing scales, with a fulcrum which the beam that balances on, there is a scoop or large bowl at one end for the material to be weighted and a flat platform at the other end that holds the weights. Around the cast iron base is an embossed strip weight and bowl missing.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Dry Measurement Container, Late 18th to early 19th century (before the standardised measurement was introduced in England in 1824)
The peck has been in use since the early 14th century when it was introduced as a measure for flour. The term referred to varying quantities until the modern units of measurement were defined in the 19th century. Cities in England used to have official standard weights and measures for that city or area. These containers were marked with the city's name and emblem, merchant’s weights and measures would then be checked against this to make sure they weren't trying to cheat their customers. The item in the collection is a standard measure approved by Bristol City and used by that City’s grocers to measure dry goods such as peas, beans, sugar, flour, meal etc., and its metal banding ensures that the measure cannot be reduced in size to cheat customers. Additional Information: The British Imperial System evolved from the thousands of Roman, Celtic, Anglo-Saxon, and customary local units employed in the middle Ages. Traditional names such as pound, foot, and gallon were widely used, but the values so designated varied with time, place, trade, product specifications, and dozens of other requirements. Early royal standards were established to enforce uniformity took the name Winchester, after the ancient tenth century capital of Britain. King Henry VII reaffirmed the customary Winchester standards for capacity and length and distributed royal standards throughout the realm. This process was repeated about a century later in the reign of Queen Elizabeth I. In the 16th century, the rod (5.5 yards, or 16.5 feet) was defined (once again as a learning device and not as a standard) defined by the length of the left feet of 16 men lined up heel to toe as they emerged from the church. By the 17th century usage and legal statute had established the acre, rod, and furlong at their present values together with other historic units such as the peck. Establishment of the System: The Weights and Measures Act of 1824 and the Act of 1878 established the British Imperial System based on precise definitions of selected existing units. The 1824 act sanctioned a single imperial gallon to replace the wine, ale, and corn (wheat) gallons that were in general use. The new gallon was defined as equal in volume to 10 pounds avoirdupois of distilled water weighed at 62°F with the barometer at 30 inches, or 277.274 cubic inches (later corrected to 277.421 cubic inches). The two new basic standard units were the imperial standard yard and the troy pound, which was later restricted to weighing drugs, precious metals, and jewels. In 1963 an act of parliament abolished archaic measures as the rod and chaldron and a metric system was adopted. An early example of a dry measuring container giving a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures developed in England to evolve the British measurement system into the metric arrangement that most countries have adopted today including Australia. It has social significance as an item that was in everyday use by grocers and other merchants to measure dry goods in the late 18th to early 19th centuries and used specifically in the Bristol region of England as an officially recognised measurement.Wooden measurement container with iron banding and hand made rivets container is a Quarter Peck official measurement container. Inscriptions are impressed into the sides of the wooden body. The container has the official crown and emblem of the City of Bristol, indicating this item was the Bristol City standard quarter peck measurement.Impressed into the timber on the front, a crown emblem over "C B G / CITY OF BRISTOL / QUARTER", on one side "HALF" , another side "PECK". Handwritten in white chalk on the base is "1458"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, weights and measures, quarter peck, measurement container, dry grocery measure, bristol city measurement standard, city of bristol, british weights and measures, 18th and 19th centure standard measures -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: CORRESPONDENCE
Typed letter to R. J. Bartle, Esq., from D. O'Connor, Engineer and ?, Chief Engineer, of the National Roads and Motorists Association (N.S.W.) dated November 8, 1936. Letter mentions four tests done in a car over a stretch of ground to measure fuel consumption. Tests were done with and without the device installed in the fuel system. Paper has printed letterhead and the names of the President, Vice-Presidents, Hon Treasurer, Council and Secretary with the AAA and NRMA emblems on the left side of the page.sciences, instruments - general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection - correspondence, national roads & motorists' association (n.s.w.), n.r.m.a. house, australian automobile association, r j bartle esq, hon j c watson, hon g r w mcdonald, charles ludowici esq, alderman james mcmahon, j bryden brown esq, d m cooper esq, e h cowdery esq, c r davidson esq, hon j m dunningham mla, a m graham esq, a s lumby esq, rev father w nicol, dr harold norrie, dr f antill pockley, ald h l primrose mla, a e rudder esq, lt-col g c somerville cmg dso, major blair wark vc dso, g a l wilson mla, h i johnson fiis, d o'connor? -
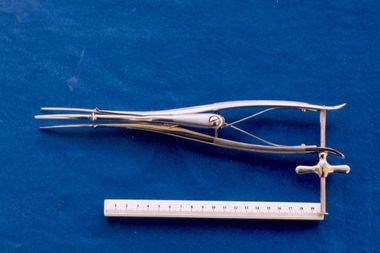 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sims-type uterine dilator used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
Used for probing a woman's uterus through the cervix, to measure the length and direction of the cervical canal and uterus. Dilators are primarily used to open and dilate the cervix to gain access to the uterine cavity but can also be used as sounds. This device was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Three bladed Sims uterine dilator, consisting of upper blade, lower blade, bridge, and wingnut. Blades are polished stainless steel with matte steel handles. Upper surface inscribed, (trademark) MADE IN GERMANY INOXIDABLE", "21"."21"box hill hospital -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Pelvimeter associated with Professor Bruce Mayes, W.M.Bailey & Co, c. 1950-1965
Item originally belonged to Professor Bruce Mayes, University of Sydney c1950-65. According to Professor Warren Jones the items had been in a back room of the medical facility and Professor Mayes gave it to Warren Jones, otherwise it may have been thrown out. Warren Jones took the device with him to Adelaide where he practiced from 1975.Pelvimeter. Device consisting of two thin measuring arms with external, circular measure at base of arms. The arms are curved at the distal (far) end so that the points of the arms face each other. Manufacturers stamp "W.M. Bailey & Co."obstetrics -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMeldometer, Joly
Joly Meldometer The Joly meldometer was created to determine the melting point of minerals. W.E. Wilson, an astronomer and author, stated in 1900 that the Joly meldometer consisted of a ‘a strip of platinum on which minute fragments of any mineral can be placed, while any alteration in its length can be determined by means of a micrometer screw which touches a lever connected with one end of the strip. The strip can be heated by an electric current, and is calibrated by observing the micrometer readings corresponding to the temperatures at which some substances of known melting-points melt’i . One reason why the Joly meldometer was seen as a successful addition to science was the small amount of any substance that it required for testing. Only a minute sample was needed for the instrument to work and so a tiny part could be taken from a delicate item without destroying itii . The instrument was originally manufactured by the Irish company Yeates & Son of Dublin. The Yeates family business was established in the early 1790’s and is thought to have operated until approximately 1922iii . Their business slogan was recorded as ‘Instrument makers to the University’, a slogan which proudly exhibited their relationship with Trinity College, Dublin. The company was located directly opposite Trinity College, the place where the Joly meldometer was created. Working in such close proximity must have assisted this business relationship. The inventor of this meldometer was Irishman John Joly. Joly was born in 1857 at the Church of Ireland Rectory, Hollywood House. His education led him to Trinity College Dublin where, by 1891, he had obtained a Bachelor of Engineering degree as well as a Doctorate of Science. The entirety of his working life appears to have taken place at Trinity College although he is known to have travelled in order to consult with other scientists such as the world renowned Sir Ernest Rutherford. The Joly meldometer was used for a variety of different purposes, with scientists often adapting the instrument to suit their own needs. For instance, the previously mentioned astronomer W.E. Wilson adapted the meldometer to assist him in measuring the radiation of the suniv . Joly used his device in an attempt to ascertain the age of the earth. In 1913, along with Sir Rutherford, Joly came to the conclusion that the earth was approximately 400 million years old. They did this by analysing the decay of radioactivity in minerals. According to our present knowledge of the earth this was a much more accurate date than the dates Joly had previously derived. He had first thought that the earth was 97 million years old due to the volume of sodium in the oceans. Joly’s second analysis of the topic had resulted in the age of 80 million years. This figure was based on the accumulation of sediment. Apart from designing his meldometer, Joly is also remembered for his work with colour photography. In 1894 Joly discovered a method for creating colour photographs from a single platev . He also studied the use of radiation as a treatment for cancer and persuaded the Royal Dublin Society to establish the Radium Institute to assist hospitals. In 1933 Joly passed away at the age of seventy-six. Jacqueline Eager Student Projects Placement, Cultural Collections 2005 iMollan, Charles, Irish National Inventory of Scientific Instruments, Samton Limited, 1995, p. 302. iiJoly, John, 'On the determination of the melting points of minerals, Part 1. Uses of the meldometer', Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy, Vol. 2., 1891. iiiInstitute for Learning Technologies, "Stephan Mitchell Yeates' http://www.ilt.columbia.edu/projects/bluetelephone/html/yeates.html, accessed on 04.10.2005 ivMollan, Charles, Irish National Inventory of Historic Scientific Instruments, op cit. vMollan, Charles, The Mind and the Hand: Instruments of Science 1685-1932, Samton Limited, Dublin, 1995, p. 34.The following from #2975 in UDE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN ENGINEERING list in the “Irish National Inventory of Historical Scientific Instruments” by Charles Mellon (P/C in file for Cat no 272. “....meldometer as an instrument ‘for the purpose of finding the melting-points of minerals, hence its name. As used by him (Joly), it consists of a strip of platinum,on which minute fragments of any mineral can be placed, while any alteration in its length can be determined by means of a micrometer screw which touches a lever connected with one end of the strip. The strip can be heated by an electric current, and is calibrated by observing the micrometer readings corresponding to the temperatures at which some substances of known melting-points melt’.” Ref. : J. Joly, Proc. Roy. Irish Acad. 3rd series vol 2 (1891),38-64. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMeldometer, Joly
The Joly meldometer was created to determine the melting point of minerals. W.E. Wilson, an astronomer and author, stated in 1900 that the Joly meldometer consisted of a ‘a strip of platinum on which minute fragments of any mineral can be placed, while any alteration in its length can be determined by means of a micrometer screw which touches a lever connected with one end of the strip. The strip can be heated by an electric current, and is calibrated by observing the micrometer readings corresponding to the temperatures at which some substances of known melting-points melt’i . One reason why the Joly meldometer was seen as a successful addition to science was the small amount of any substance that it required for testing. Only a minute sample was needed for the instrument to work and so a tiny part could be taken from a delicate item without destroying itii . The instrument was originally manufactured by the Irish company Yeates & Son of Dublin. The Yeates family business was established in the early 1790’s and is thought to have operated until approximately 1922iii . Their business slogan was recorded as ‘Instrument makers to the University’, a slogan which proudly exhibited their relationship with Trinity College, Dublin. The company was located directly opposite Trinity College, the place where the Joly meldometer was created. Working in such close proximity must have assisted this business relationship. The inventor of this meldometer was Irishman John Joly. Joly was born in 1857 at the Church of Ireland Rectory, Hollywood House. His education led him to Trinity College Dublin where, by 1891, he had obtained a Bachelor of Engineering degree as well as a Doctorate of Science. The entirety of his working life appears to have taken place at Trinity College although he is known to have travelled in order to consult with other scientists such as the world renowned Sir Ernest Rutherford. The Joly meldometer was used for a variety of different purposes, with scientists often adapting the instrument to suit their own needs. For instance, the previously mentioned astronomer W.E. Wilson adapted the meldometer to assist him in measuring the radiation of the suniv . Joly used his device in an attempt to ascertain the age of the earth. In 1913, along with Sir Rutherford, Joly came to the conclusion that the earth was approximately 400 million years old. They did this by analysing the decay of radioactivity in minerals. According to our present knowledge of the earth this was a much more accurate date than the dates Joly had previously derived. He had first thought that the earth was 97 million years old due to the volume of sodium in the oceans. Joly’s second analysis of the topic had resulted in the age of 80 million years. This figure was based on the accumulation of sediment. Apart from designing his meldometer, Joly is also remembered for his work with colour photography. In 1894 Joly discovered a method for creating colour photographs from a single platev . He also studied the use of radiation as a treatment for cancer and persuaded the Royal Dublin Society to establish the Radium Institute to assist hospitals. In 1933 Joly passed away at the age of seventy-six. -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Collin's-type pelvimeter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany , and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Metal pelvimeter. Consists of a device with two arms, which curve into rounded points at their ends. A semi-circular measuring gauge is attached to the end of the pelvimeter.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Mark-7 disposable uterine sound associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Searle Laboratories, 1984
Used to measure the depth/distance of the uterus. Uterine sounds are particularly useful for ensuring safe and accurate IUD placement.This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Disposable uterine sound in sterile sealed packaging. Label inside packaging reads 'Mark-7 brand of disposable uterine sound/ONE STERILE UNIT/NO. 154'. Label also includes manufacturer information, a sterile packaging warning, and a caution about sale of the item being restricted to physicians.intrauterine device -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumEquipment (item) - Graviscope for Lincoln (Australian) RAAF Ident No G6C/3972, Graviscope for Lincoln
Description White plastic doubled sided Graviscope stored in protective leather carry case. Case is fitted with pair of press studs, pocket in front for holding instructions and is stamped "Graviscope / for / Lincoln / (Australian) / Manufactured by / Melb > W & G < Aust / R.A.A.F / Ident. No G6C/3972". Plastic graviscope consists of a 277mm white disc, printed on both sides, overlaid on one side by a 224mm disc and the other side by a 175mm disc. All discs located by central screw, to which is attached a 160mm long x 25mm wide clear celluloid strip. History / Summary The graviscope is a computing device, which in aircraft was used for measuring the centre of gravity in an aircraft. This would vary depending on crew, bomb load, fuel and stores carried. It was used in the British designed but Australian manufactured, Government Aircraft Factory (GAF) Lincoln heavy bomber, which was operated by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) in the years following the Second World War. This aircraft was originally a derivative of the famous Avro Lancaster bomber. The Lincoln was used by both the RAAF and the Royal Air Force in operations against Malayan Communist terrorists during the Malayan Emergency, 1948-1960. This graviscope is of the type designed for and used by RAAF and RAF aircrew who operated this aircraft.Many by W and G Australia -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook (item) - GAF Collection - Graphical Symbols For Electrotechnical Documentation Part 108: Measuring Instruments, Lamps and Signalling Devices SAS 1102.108-1989
-
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Tactile tape measure, 200
... This tape measure is designed to indicate measurements by feel ...This tape measure is designed to indicate measurements by feel. The 150cm tape is marked by small eyelets at every cm, medium eyelets at 5 cm and two eyelets at every 10cm. 1 white measuring tape with black markings and numbers including tactile raised eyeletsassistive devices, recreation -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Royal National Institute for the Blind, Tactile yellow ruler
30 cm tactile yellow ruler with black marking every 5 centimeters with raised markings, has two different edges - straight and notched. The straight edge can be used for measuring and drawing, and the notched edge designed to help place pins when creating charts and graphs or using a compass. There are non-slip pads on the back of the ruler. 1 yellow ruler with black large print numbers and black measurement indicatorsRNIB LT21 (on back)assistive devices, royal national institute for the blind -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Rotary, Measuring tape
A retractable tape measure inside a cream disc. On the front of the tape measure is a round red sticker. In the middle of the sticker is a red button for retracting tape measure. Eyelets are placed at every number between 0 and 10, then at 10 centimeter intervals. 1 white measuring tape with red markings and numbers including tactile raised eyelets inside cream round containerRotary 1.5 Futuba Measureassistive devices, rotary -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture - Mace, 'University Mace' by Trefor Prest, 1995
The University's mace was carried in procession for the first time during the Graduation ceremonies in May 1996. The mace was presented to the University by former Chief Commissioner of the Ballarat City Council, Vern Robson, at a ceremony on 02 February, following a national competition for its design, sponsored by the Council. (The Flag, Issue 2, July 1996) Nineteen artists responded to the competition which called for a design that would embody a distinctive Australian image reflecting the heritage of the city and in relationship with gold, an Aboriginal element and the history of the University. The winning entry, dominated by a poppet head, was submitted by Central Victorian artist/sculptor Trefor Prest, a sessional lecturer in sculpture at the University.(The Flag, Issue 2, July 1996) The Herald Sun of 03 February 1996 reported 'the new mace shows importance elements of Ballarat's heritage as well as the university's focus on the future. The artist emphasises the egalitarian nature of Australia as embodied in Ballarat's famous slice of history - the Eureka uprising. ... The mace has a poppet head at the top of the shaft - an unusual element for a mace - but it represents Ballarat's mining history and the University's evolution from the Ballarat School of Mines. An opening egg at the top stands for the nurturing of development and learning. The mace's straight shaft is depicted as the tree of knowledge and, incorporating a bark canoe scar, Ballarat's Aboriginal heritage. At the end of the shaft is a surveying device, which represents precision and accuracy ads embodied in the university's academic pursuits.' Bob Morrell of the University organised the national competition to design the mace and said 'It is in keeping with the university's logo, 'proudly flying the flag', which incorporates the Southern Cross.' This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007. Trefor Prest lectured in Sculpture at the University of Ballarat from 1995-1996.The mace symbolises the office of the Chancellor. The design of the mace is the outcome of a national competition and represents the cultural diversity of Australia. The poppet head on the top of the mace refers to gold mining, which underpinned the development of Ballarat. The protruding spikes recall the Eureka Stockade. The 'egg' shape enfolds and nurtures the development of knowledge and learning. The shaft with the three 'branches' represents the Tree of Knowledge, and includes a bark canoe scar which recognises the integration of black and white Australian traditions. The lower part of the shaft culminates in a device suggestive of scientific or surveying and measuring technology. This represents precision and accuracy embodied in the academic pursuits of Federation University Australia.art, artwork, trefor prest, prest, mace, federation university, university, eureka stockade, aborigines, scarred tree, mining, university mace, ballarat -
 Diamond Valley Vietnam Veterans Sub-Branch
Diamond Valley Vietnam Veterans Sub-BranchEquipment - Trip Wire, c2015
Dept of Defence issued equipment: trip wire for a wide range of usages including preventative, precautionary measures against enemy.Trip wire was an effective and valuable resource used by Australian soldiers for their protection and an advanced warning of enemy presence whilst in the field.Small cardboard roll of trip wire, attached to beige paper label with red text.IMPORTANT/ run wire through finger and thumb to remove kinks before use.trip wire, explosive device, booby trap, vietnam war, diamond valley vietnam veterans sub branch, weapons -
 Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory LightstationContainer, Ventometer
The cylindrical cardboard container with lid formerly contained a ventometer, a small simple tool for measuring wind speed. It consisted of a clear tube containing a small diaphragm which had a hole in the bottom for wind to enter. Once the wind entered the tube it pushed up the diaphragm, indicating the rate of velocity. Ventometers were common devices that have since been replaced by more sophisticated measuring equipment, such as digital air speed meters. Further information on this particular example, including perhaps the name of the manufacturer, may survive on the container but this has not been recorded. The small simple tool for measuring wind speed pre-dates the electronic devices at Gabo Island.Tubed shaped cardboard container with lid to house instrument for measuring. (instrument is missing) Inscriptions and illustrations on exterior. -
 Parks Victoria - Gabo Island Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Gabo Island LightstationAnemometer
... This device was used to measure surface wind speed... This device was used to measure surface wind speed and direction ...This device was used to measure surface wind speed and direction. This anemometer was located on a concrete pad outside room 2.15 on a steel pole. The pole was considered unsafe and the anemometer was relocated to it's current position. When lowering the pole it fell over and was badly damaged. The Bureau of Meteorology donated it to the museum. It was then repaired and restored. The central pole on which it is mounted is galvanised iron pipe painted black. The anemometer, a portable device that manually measures wind speed, was a necessary instrument once common to all weather stations. The arms are attached to a vertical rod and as the wind blows, the cups rotate, making the rod spin. The stronger the wind blows, the faster the rod spins. The anemometer counts the number of rotations, or turns, which is used to calculate wind speed, surface wind and direction. They were designed to be durable to withstand the corrosive environment and strong winds expected at coastal sites such as those at Gabo Island. Anemometers existed in the nineteenth century and their design was improved by various experts including John Robinson in 1846, John Patterson in 1926, Brevoort and Joiner in 1935 and Derek Watson in 1991 who added wind direction measurement to its functions. This example was made for the Bureau of Meteorology by the Melbourne instrument company, Synchrotac, which became registered and incorporated on 26 July 1966. It is now displayed inside the building. A good example of its kind, the anemometer has first level contributory significance for its historic value and provenance to the lightstation.Anemometer and tripod stand. Three cupped brass discs on rotating arms fixed to turned brass cylinder shaped shaft. Beneath discs is a lead directional wind arrow attached to a rotating arm. A wooden three legged stand with central supporting pole of black painted hardwood and attached to a white painted marine ply circular base.Under wind cups: " SYNCHROTAC / MELB. / ser.no.70/372 / MADE IN AUSTRALIA." Above wind direction arrow: "C.OF.APT..../ SYNCHROTAC / MELB ? MADE IN AUSTRALIA / ser.no.70/372" -
 Parks Victoria - Gabo Island Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Gabo Island LightstationWind Speed Recorder, "Maximum Gust Register"
Used on Gabo Island to measure maximun gust over previous 3 hours or between weather observations. Information on the back of the device implies that it was battery powered and indicates that it was used in conjunction with a Synchrotac brand anemometer. Its particular function was to measure maximum wind speed over three hours between weather observations. Like the other weather recording instruments in the collection, it became redundant to the Bureau of Meteorology’s needs. It is a good example of its kind and has first level contributory significance for its historic value and provenance to the lightstation.Black metal box with grey metal front. Two chrome plated handles at front. Red plastic square, greenish coloured knob at front with inscriptions under them.On front,"MAXIMUM GUST REGISTER / KNOTS / READ" On back, "for use with a synchrotac anemometer / ANEMOMETER / RESET" On 2 black plastic discs at back, "BATTERY x 4 " -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Calculo - Every-Man's Ready Reckoner
A ready reckoner including a wide range of information to facilitate everyday calculations prior to the widespread use of electrical calculators and devices. Published post 1945, the booklet also includes a chronology of World War 11 as well as a list of household antidotes in cases of poisoning.A reference guide of 32 pages plus cardboard covers. The volume has wire spiral binding. It includes a perpetual calendar. Other pages include tables, charts, dates, mathematical information and useful information for farmers including weights and measures and animal gestation periods.A ready reckoner including a wide range of information to facilitate everyday calculations prior to the widespread use of electrical calculators and devices. Published post 1945, the booklet also includes a chronology of World War 11 as well as a list of household antidotes in cases of poisoning.ready reckoner, calendars -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Ventimeter, Wind anemometer in cardboard tube
Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many factors including temperature, relative humidity (RH), forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. But wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), as well as fire size, shape and direction. Wind speed can be measured using a variety of anemometers. This simple hand-held Venitimer was made by Elvometer in Sweeden, probably in the 1960s, and was designed for principally for mariners. Some models have a compass in the handle to measure wind direction. The small inlet hole on the side is faced towards the wind and air pressure lifts small plastic disk inside. The upper tube is tapered so that as wind speed increases more air escapes and stronger winds are needed to raise the disk. Wind speed in MPH is read from the side of the clear plastic tube. The waterproof container has instructions on use and conversion scales. Simple and robust device.Hand- held wind anemometer Instructions on use on containerbushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Actionmap measuring wheels
The map wheel is a simple, fast and accurate way to measure distances on maps, whether in straight lines or along curves. Hold the device from the tip and trace with the small wheel at the bottom along the line to be measured Measures distances in miles, kilometres or nautical miles depending on the scale on the side.Two metal map measuring wheel sMap scales on each side of wheelforests commission victoria (fcv), surveying, mapping -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - Aerotriangulation Production – Army Survey Regiment, Fortuna, Bendigo, c1970s to 1980s
This collection of 14 photos was most likely taken in the 1970s and 1980s in Air Survey Squadron. The PDP 11/70 minicomputer shown in photo .1P was the operating system introduced in 1977 as the mainframe system for the control of the APC4, aerial triangulation block adjustments, SORA OP Analytical Orthophoto control, APR Analytical Terrain Profile Recorder computation, graphics, and general computing. Technicians used the Wild A9 Stereocomparator shown in photo .2P to accurately measure between pass, tie, and survey control points on aerial photographs. The Zeiss D2 Planimat Stereoplotter shown in photos .3P to .4P was used for analytical orthophoto control. It was introduced in 1972-1973 The Zeiss (Jena) Stecometer analytic stereocomparator for air photography shown in photos .5P to .11P and .14P was introduced at Air Survey Squadron in 1963. Aerotriangulation production was expedited using computers for analytical photogrammetric processes. The technician accurately measured between pass, tie, and survey control points on aerial photographs. Wild PUG4 point transfer devices shown in photos .12P to .13P were introduced in c1968 superseding the PUG2 devices. PUG4 devices were used by technicians to stereoscopically view the photography containing the survey control points and the mapping aerial photography. The Control points were transferred from the control photography to the mapping diapositives of aerial photography by drilling their locations into the photographic emulsion.This is a set of 14 photographs of Air Survey Squadron personnel operating aerotriangulation equipment at the Army Survey Regiment at Fortuna, Bendigo, c1970s to 1980s. Photographs .1P to .13P were on 35mm colour slide film and scanned at 96 dpi. Photograph.14P was printed on photographic paper and was scanned at 300 dpi. They are part of the Army Survey Regiment’s Collection. .1) - Photo, colour, c1979, PDP-11 minicomputer. .2) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Unidentified technician operating a Wild A9 Stereocomparator. .3) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Zeiss D2 Planimat Stereoplotter. .4) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Zeiss D2 Planimat Stereoplotter, unidentified technicians. .5) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Zeiss D2 Planimat Stereoplotter, SGT Christopher Wardley. .6) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Zeiss D2 Planimat Stereoplotter. .7) to.9) - Photo, colour, c1970, Zeiss (Jena) Stecometer, unidentified technicians. .10) to.11) - Photo, colour, c1988, SPR Toni Wright operating a Zeiss (Jena) Stecometer. .12) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Wild PUG4 point transfer device, SPR John Shepard. .13) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Wild PUG4 point transfer device, SPR David Edwards. .13) - Photo, colour, c1970s, Wild PUG4 point transfer device, SPR David Edwards. .14) - Photo, colour, c1980, Zeiss (Jena) Stecometer, SGT Bruce Hammond.Some of the equipment is annotated on the frame of the 35mm slides.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, army survey regiment, army svy regt, fortuna, asr, aerotrig, photogrammetry -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaEquipment - Object, Soundscriber dictaphone, 1945-1960
The Sound Scriber Dictaphone allowed recordings to be imprinted into a soft disk that could then be replayed later. This was useful for blind stenographers who could transcribe the audio recording. The lid contains a speaker into which sounds are made, the front knob is allows for 'Talk' or 'Listen' and three other dials on the device allow for the tubes to be turned on/off, starting/stopping the turntable and the recording volume to be 'Dictation' or 'Conf". There are two measuring tapes placed near the recording head and the Listen head, which show the minutes in the recording. The large disk that is placed on this machine has been stopped at the 12 minute mark. At the rear of the device are two plugs, one of which is for electrical supply. This model of dicta phone remained popular until magnetic tapes.1 hinged leather case over a metal and wood machineSound Scriberaudio equipment, assistive devices -
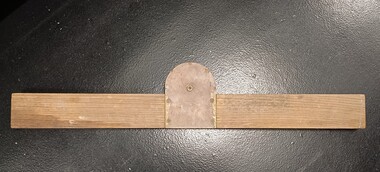 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Measuring aid, 1960-1980s
A wooden device that appears to have been used in a workshop. This device has a rotating pointer, hence it may have been used for balancing, measuring or alignment at the RVIB workshop.1 wooden board with metal attachmentassistive devices, royal victorian institute for the blind
