Showing 608 items
matching victoria tower
-
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyFlyer (item) - Accommodation flyer, Tower Motel, Unknown
... . marysville victoria australia tower motel accommodation flyer 2009 ...An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities at the Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities at the Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, flyer, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyEphemera (item) - Business card, Tower Motel, Unknown
... the Tower Motel in Marysville. marysville victoria australia tower ...A business card from the Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.A business card from the Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, business card, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
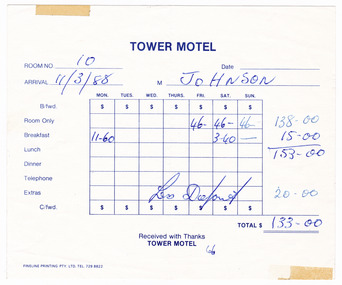 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyEphemera (item) - Receipt, Fineline Printing Pty. Ltd, TOWER MOTEL, Unknown
... victoria australia tower motel accommodation receipt 2009 black ...A receipt for payment for accommodation and breakfast at the Tower Motel in Marysville. The receipt dates from 11th March, 1988. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville to survive the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.A receipt for payment for accommodation and breakfast at the Tower Motel in Marysville. The receipt dates from 11th March, 1988.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, receipt, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPostcard (item) - Colour postcard, Nucolorvue Productions Pty. Ltd, TOWER MOTEL Marysville, Unknown
... A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville ...A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville. The postcard was published by Nucolorvue as a souvenir of Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville. The postcard was published by Nucolorvue as a souvenir of Marysville.A/ NU-COLOR-VUE/ OF/ AUSTRALIA PLACE/ STAMP/ HERE POST CARD Product of Australia RP66 NUCOLORVUE PRODUCTIONS PTY. LTD./ COPYRIGHT TOWER MOTEL/ Murchison St., Marysville, Vic./ Phone (059) 63 3225 New luxury Motel, 100 km north/ east of Melbourne in the heart of/ the big timber country - just a/ short drive from the magnificent/ floodlit Steavenson's Falls - the/ tallest in Victoria. Units equipped with all modern/ facilities, including colour T.V. and/ air conditioning.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, postcard, souvenir, nucolorvue productions pty. ltd., 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPostcard (item) - Colour postcard, Nucolorvue Productions Pty. Ltd, TOWER MOTEL Marysville, Unknown
... A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville ...A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville. The postcard was published by Nucolorvue as a souvenir of Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.A colour postcard from the Tower Motel in Marysville. The postcard was published by Nucolorvue as a souvenir of Marysville.A/ NU-COLOR-VUE/ OF/ AUSTRALIA PLACE/ STAMP/ HERE POST CARD Product of Australia RP66 NUCOLORVUE PRODUCTIONS PTY. LTD./ COPYRIGHT TOWER MOTEL/ Murchison St., Marysville, Vic./ Phone (059) 63 3225 New luxury Motel, 100 km north/ east of Melbourne in the heart of/ the big timber country - just a/ short drive from the magnificent/ floodlit Steavenson's Falls - the/ tallest in Victoria. Units equipped with all modern/ facilities, including colour T.V. and/ air conditioning.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, postcard, souvenir, nucolorvue productions pty. ltd., 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyFlyer (item) - Accommodation flyer, Tower Motel, Unknown
... . marysville victoria australia tower motel accommodation flyer 2009 ...An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at the Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at the Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, flyer, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyFlyer (item) - Accommodation flyer, Tower Motel, Unknown
... . marysville victoria australia tower motel accommodation flyer 2009 ...An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at the Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at the Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, flyer, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyFlyer (item) - Accommodation flyer, Tower Motel, Unknown
... . marysville victoria australia tower motel accommodation flyer 2009 ...An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at The Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at The Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, flyer, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyFlyer (item) - Accommodation flyer, Tower Motel, Unknown
... . marysville victoria australia tower motel accommodation flyer 2009 ...An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at The Tower Motel in Marysville. The Tower Motel was one of the few buildings in Marysville that survived the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires.An information flyer regarding the accommodation and facilities available at The Tower Motel in Marysville.marysville, victoria, australia, tower motel, accommodation, flyer, 2009 black saturday bushfires -
 Parks Victoria - Days Mill and Farm
Parks Victoria - Days Mill and FarmTextile - Assorted textile objects
... bag, "HAMEL / VICTORIA TOWER / PATENT SHOT / No 2".... / LONDON / No. 2". On other bag, "HAMEL / VICTORIA TOWER / PATENT ...Two cloth bags, one with a drawstring. Both bags have inscriptions. Also a portion of string fibres and a double headed brush - each brush head wound with wire.On bag with drawstring, the British coat of arms then , "WALKERS / PARK.R & CO / Patent Shot / LONDON / No. 2". On other bag, "HAMEL / VICTORIA TOWER / PATENT SHOT / No 2". -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPamphlet - digital photographs, Clare Gervasoni, Birregurra Water Tower, 2020, 2020
... Colour photograph of the Birregurra Water Tower, Victoria. ... of the Birregurra Water Tower, Victoria. Birregurra Water Tower, 2020 ...Colour photograph of the Birregurra Water Tower, Victoria. birregurra, birregurra water tower, railway -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Folder, Pelling, Nicholas and Anna
... The Hall Kangaroo Ground Victoria War Memorial Tower committee ...Nicholas Pelling, son of Charis Pelling, lived at Kangaroo Ground, and was active in local causes, including the Country Fire Authority, being awarded a National Medal in 1992. Contents Newspaper article: "CFA man 'someone who cared'". Diamond Valley Leader ,14 July 2004. Obituary of Nicholas Pelling.Newspaper clippings, A4 photocopies, etcnicholas pelling, charis pelling, woodlands kangaroo ground victoria, the hall kangaroo ground victoria, war memorial tower committee kangaroo ground, andrew ross museum kangaroo ground, plenty valley community radio, kangaroo ground telephone exchange, anna pelling, country fire authority, jeff newland, kerri newland, ron newland -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Kangaroo Ground. Dedication of Tower and Cottage by His Excellency the Governor of Victoria, Gen. Sir Dallas Brooks, K.C.B., C.M.G., D.S.O., K.St.J., 16 November 1951
... of victoria war memorial tower Digital image Kangaroo Ground ...Source: Shire of ElthamThis photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book,"Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as the 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.Digital imagesepp, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, kangaroo ground, sir dallas brooks, governor of victoria, war memorial tower -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour photograph, Tower Hill, 2016, 23/12/2015
... became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became...Panaramic view of Tower Hill, Victoria....Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia.... In 1892 Tower Hill became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961 ...Tower Hill is a volcanic formation believed to have erupted about 32,000 years ago. Its formation is known as a "nested maar" and it is the largest example of its type in Victoria. During formation, molten lava pushed its way up through the Earth’s crust and encountered a layer of water-bearing rock. Violent explosions followed creating a shallow crater which later filled with water to form the lake. Further eruptions occurred in the centre of this crater, creating the islands and cone shaped hills. In 1892 Tower Hill became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became a State Game Reserve under the then Fisheries and Wildlife Department and a major re-vegetation program began. (https://www.towerhill.org.au/index.php/about-reserve/history, accessed 23 December 2019)Panaramic view of Tower Hill, Victoria.tower hill, volcano, crater -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour photograph, Tower Hill, 2022, 24/12/2022
... became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became...Panaramic view of Tower Hill, Victoria....Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became ...Tower Hill is a volcanic formation believed to have erupted about 32,000 years ago. Its formation is known as a "nested maar" and it is the largest example of its type in Victoria. During formation, molten lava pushed its way up through the Earth’s crust and encountered a layer of water-bearing rock. Violent explosions followed creating a shallow crater which later filled with water to form the lake. Further eruptions occurred in the centre of this crater, creating the islands and cone shaped hills. In 1892 Tower Hill became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became a State Game Reserve under the then Fisheries and Wildlife Department and a major re-vegetation program began. (https://www.towerhill.org.au/index.php/about-reserve/history, accessed 23 December 2019)Panaramic view of Tower Hill, Victoria.tower hill, volcano, crater -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Water towers, 7/07/1996 12:00:00 AM
... throughout history. Photos of some of Victoria's storage towers... throughout history. Photos of some of Victoria's storage towers ...Article about how demand for water has been of importance throughout history.Article about how demand for water has been of importance throughout history. Photos of some of Victoria's storage towers including Mitcham.Article about how demand for water has been of importance throughout history. water supply, mitcham water tower -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Bird at Tower Hill, 2016, 31/12/2016
... Colour photorgaph of a bird at Tower Hill, Victoria...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... Hill, Victoria Bird at Tower Hill, 2016 Photograph - Colour ...Colour photorgaph of a bird at Tower Hill, Victoriatower hill -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Superb Fairy Wren at Tower Hill, 2016, 31/12/2016
... Superb Fairy Wren at Tower Hill, Victoria...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... at Tower Hill, Victoria Superb Fairy Wren at Tower Hill, 2016 ...Superb Fairy Wren at Tower Hill, Victoriatower hill, fairy wren, bird -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Koala at Tower Hill, 2013, 29/12/2013
... Colour photograph of a Koala in a tree at Tower Hill...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... of a Koala in a tree at Tower Hill, Victoria. Koala at Tower Hill ...Colour photograph of a Koala in a tree at Tower Hill, Victoria.koala, marsupial, tower hill -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Koala at Tower Hill, 2015, 25/12/2015
... Colour photograph of a Koala asleep in a tree at Tower Hill...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... Victoria. koala marsupial tower hill Colour photograph of a Koala ...Tower Hill is an extinc volcano in Western Victoria.Colour photograph of a Koala asleep in a tree at Tower Hill, Victoria.koala, marsupial, tower hill -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Volcanic Crater at Tower Hill, 2017, 2017
... became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became...Colour photographs of a lake in a volcanic crater at Tower...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia.... In 1892 Tower Hill became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961 ...Tower Hill is a volcanic formation believed to have erupted about 32,000 years ago. Its formation is known as a "nested maar" and it is the largest example of its type in Victoria. During formation, molten lava pushed its way up through the Earth’s crust and encountered a layer of water-bearing rock. Violent explosions followed creating a shallow crater which later filled with water to form the lake. Further eruptions occurred in the centre of this crater, creating the islands and cone shaped hills. In 1892 Tower Hill became Victoria’s first National Park. In 1961, Tower Hill became a State Game Reserve under the then Fisheries and Wildlife Department and a major re-vegetation program began. (https://www.towerhill.org.au/index.php/about-reserve/history, accessed 23 December 2019)Colour photographs of a lake in a volcanic crater at Tower Hill, Victoria. volcano, crater, lake, tower hill -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image, View at Tower Hill
... image of Tower Hill, Victoria...Tower Hill, Victoria, Australia... with a photographic image of Tower Hill, Victoria View at Tower Hill ...Photographic Image of a glass dish with a photographic image of Tower Hill, Victoriatower hill -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard - Main Street Bairnsdale, Bulmer, 1920 to 1930 c
... taken from the water tower Bairnsdale Victoria... from the water tower Bairnsdale Victoria Postcard Main Street ...Black and white postcard showing Main Street Bairnsdale taken from the water tower Bairnsdale VictoriaMain Street Reserves Bairnsdaletownships, roads and streets -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard - view of Bairnsdale Victoria, Bulmer, 1940 c
... from Wy Yung water tower and St Marys church tower Bairnsdale... church tower Bairnsdale Victoria view of Bairnsdale Victoria ...Black and white postcard showing general view of Bairnsdale from Wy Yung water tower and St Marys church tower Bairnsdale VictoriaA General view of Bairnsdale from Wy Yung Bulmer copyrightroads and streets, township -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Poster - Assorted posters
... the shipwreck of "Victoria Tower" near Torquay in 1869. 0424 - 2 posters... the shipwreck of "Victoria Tower" near Torquay in 1869. 0424 - 2 posters ...Assorted posters sent to the society. Contains: 0414 - Laminated poster promoting the history of Aboriginal station Coranderrk. 0415 - Poster commemorating the centenary of Federation. 0416 - Poster commemorating the centenary of Australian Federation. 0417 - Double-sided poster promoting the history of Federation in Australia in 1901. Highlights a snapshot of life in Australia in 1901. 0418 - Double-sided poster commemorating the centenary of Australian Federation. One side is a replica of a Federation poster in 1901, and the other side is a timeline of events leading to Federation in 1901. 0419 - Printed poster for the 'Fire Cycle' event held by the Dandenong Ranges Music Council, Inc. at Belgrave Heights Convention Centre on October 8th-9th 2005. Feature possum on a human's hand in front of a burnt landscape. 0422 - Poster of Station Pier. 0423 - Poster focusing on clay pipes from the shipwreck of "Victoria Tower" near Torquay in 1869. 0424 - 2 posters, one green and one blue, about the life of lyrebirds. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - ROY J MITCHELL COLLECTION: VIEW FROM LOOKOUT TOWER, QUEEN ELIZABETH OVAL, BENDIGO
... Colour photograph taken from lookout tower, Queen Elizabeth... on back :'January 1972, Bendigo, Victoria. From Lookout Tower ...Colour photograph taken from lookout tower, Queen Elizabeth Oval, Bendigo, looking southeast. Rifle Brigade Hotel on extreme RH side, carpark behind Art Gallery complex in centre of image. Written on back :'January 1972, Bendigo, Victoria. From Lookout Tower'Roy J Mitchellbendigo, streetscape, queen elizabeth oval -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard - Lookout tower Jemmy's Point, Valentine Series, 1940
... observation lookout at Jemmys Point, Lakes Entrance, Victoria, showing... lookout at Jemmys Point, Lakes Entrance, Victoria, showing ...Black and white small format postcard of the timber observation lookout at Jemmys Point, Lakes Entrance, Victoria, showing the timber tower with observation deck, signal light on steel tower nearby. Top of old standing lookout tree just visible.Jemmys Lookout Lakes Entrancehistoric sites, navigation -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Earthenware jar, Bailey & Co, circa 1878
... includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower... of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878 ...The handmade earthenware jar was one of a group of artefacts in the McCulloch Collection that were recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard. The jar could have been from the ship's cargo or personal effects. There are other jars in our collection that were recovered from the Loch Ard. The object is now one of the shipwreck artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s Mc Culloch Collection, which includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878). They were salvaged by a diver in the early 1970s from the southwest coast of Victoria. Advanced marine technology had enabled divers to explore the depths of the ocean and gather its treasures before protective legislation was introduced by the Government. The artefacts were donated to Queensland’s Department of Environment and Heritage Protection (EHP) by a passionate shipwreck lover and their locations were verified by Bruce McCulloch. In 2017 the Department repatriated them to Flagstaff Hill where they joined our vast collection of artefacts from Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast. The Loch Ard: - The three-masted, square-rigged iron ship Loch Ard belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. The ship was built in Glasgow in 1873. The Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. The Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo included straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that were intended for display in the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition, including the famous Loch Ard Peacock. On June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land but visibility was reduced by fog. As it lifted, the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came much closer than expected. The captain was unable to steer away and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck was loosened from the hull, the masts and rigging came down and knocked passengers and crew overboard, and even the lifeboat crashed into the side of the ship and capsized. Of the 54 people on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael. The well-packed Minton porcelain peacock also survived, safe inside its crate. Much of the cargo was washed up, smashed and broken, and some was salvaged. Other cargo is still with the wreck at the base of Mutton Bird Island, now protected by Government law. The artefact is an example of cargo or personal items on board a ship in 1878. It provides a reference point for classifying and dating similar items. This artefact is significant for its association with the sailing ship Loch Ard, one of the best-known, and one of the worst, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history. Container, round brown earthenware jar with a wide mouth, thick lip, a wide neck that tapers slightly inwards towards the shoulder, and a body that tapers slightly inward towards the base. The glazed surface is rough. The variegated colours of the clay also has small dark speckles. There are several chips and dents on the jar. The inscription is stamped into the lower edge. Made by Bailey & Co., England. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Inscription “Bailey [&] Co / ENGLAND” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, white star line, victorian heritage register, sailing ship loch ard, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, migrant ship 1878, cargo ship 1878, stoneware jar, domestic container, kitchenware, kitchen storage, bailey & co england, shipwreck artefact, wreck dive, mcculloch collection, bruce mcculloch, 1878, sailing ship, earthenware, stoneware, domestic jar -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Doll's Leg, circa 1878
... items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked... the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard ...This doll's leg was one of a set of artefacts recovered from the shipwreck of the Loch Ard that were donated together. The doll's leg could have been from the ship's cargo or personal effects. Dolls from this era were often made from fabric, which would have quickly deteriorated in the ocean. Ceramic limbs were joined to the body by tightening the fabric around the grooves on the limbs. There are other doll's limbs in our collection that were recovered from the Loch Ard The object is now one of the shipwreck artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s Mc Culloch Collection, which includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878). They were salvaged by a diver in the early 1970s from the southwest coast of Victoria. Advanced marine technology had enabled divers to explore the depths of the ocean and gather its treasures before protective legislation was introduced by the Government. The artefacts were donated to Queensland’s Department of Environment and Heritage Protection (EHP) by a passionate shipwreck lover and their locations were verified by Bruce McCulloch. In 2017 the Department repatriated them to Flagstaff Hill where they joined our vast collection of artefacts from Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast.The Loch Ard: - The three-masted, square-rigged iron ship Loch Ard belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. The ship was built in Glasgow in 1873. The Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. The Loch Ard: - The Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo included straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that were intended for display in the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition, including the famous Loch Ard Peacock. On June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land but visibility was reduced by fog. As it lifted, the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came much closer than expected. The captain was unable to steer away and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck was loosened from the hull, the masts and rigging came down and knocked passengers and crew overboard, and even the lifeboat crashed into the side of the ship and capsized. Of the 54 people on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael. The well-packed Minton porcelain peacock also survived, safe inside its crate. Much of the cargo was washed up, smashed and broken, and some was salvaged. Other cargo is still with the wreck at the base of Mutton Bird Island, now protected by Government law. The artefact is an example of cargo or personal items on board a ship in 1878. It provides a reference point for classifying and dating similar items. This artefact is significant for its association with the sailing ship Loch Ard, one of the best-known, and one of the worst, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history. Doll's leg, cream-coloured ceramic leg with two seams, a flat solid top and a glazed green ankle-length heeled boot. A shallow groove runs around the leg just below the top. An inscription is stamped into the leg below the groove. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Inscribed "2"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, wreck dive, mcculloch collection, bruce mcculloch, loch ard, 1878, loch line, victorian heritage register, sailing ship, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, migrant ship 1878, cargo ship 1878, doll's leg, ceramic doll leg, porcelain doll leg, doll's limb, 1870s doll, 1870's toy, ceramic limb from doll, children's toy, children's recreation, doll's leg with green boot -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lamp Fitting, circa 1878
... of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878... the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard ...This gas pipe fitting was one of a group of artefacts in the McCulloch Collection that were recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard and were donated together. The fitting could have been from the ship's cargo or a ship’s fitting. Lamps from this era were fuelled by gas. There are other gas lamp fittings in our collection that were recovered from the Loch Ard The object is now one of the shipwreck artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s Mc Culloch Collection, which includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878). They were salvaged by a diver in the early 1970s from the southwest coast of Victoria. Advanced marine technology had enabled divers to explore the depths of the ocean and gather its treasures before protective legislation was introduced by the Government. The artefacts were donated to Queensland’s Department of Environment and Heritage Protection (EHP) by a passionate shipwreck lover and their locations were verified by Bruce McCulloch. In 2017 the Department repatriated them to Flagstaff Hill where they joined our vast collection of artefacts from Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast. The Loch Ard: - The three-masted, square-rigged iron ship Loch Ard belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. The ship was built in Glasgow in 1873. The Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. The Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo included straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that were intended for display in the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition, including the famous Loch Ard Peacock. On June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land but visibility was reduced by fog. As it lifted, the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came much closer than expected. The captain was unable to steer away and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck was loosened from the hull, the masts and rigging came down and knocked passengers and crew overboard, and even the lifeboat crashed into the side of the ship and capsized. Of the 54 people on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael. The well-packed Minton porcelain peacock also survived, safe inside its crate. Much of the cargo was washed up, smashed and broken, and some was salvaged. Other cargo is still with the wreck at the base of Mutton Bird Island, now protected by Government law. The artefact is an example of cargo or personal items on board a ship in 1878. It provides a reference point for classifying and dating similar items. This artefact is significant for its association with the sailing ship Loch Ard, one of the best-known, and one of the worst, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history. Brass decorative gas lamp fitting. Two flat arms of different lengths are joined on either side of a fitting that has a fleur-de-lis-like design. The shorter arm has a J-shaped brass pipe fitted to it with a decorative threaded cube joint part way along, and ends with a triangular tap and knob. The longer arm is also J-shaped and ends with a feather design on it. There are remnants of green paint on the cube fittings and the knob. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, wreck dive, mcculloch collection, bruce mcculloch, loch ard, 1878, loch line, victorian heritage register, sailing ship, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, migrant ship 1878, cargo ship 1878, lamp fitting, gas lamp fitting, ship’s fitting, ship’s lamp, brass lamp fitting, lighting, domestic lighting, ship’s lighting
