Showing 63 items matching "washing equipment"
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Domestic object - Wooden & glass washboard, Laundry washboard, Unknown
... washboard. Example of domestic work equipment. Laundry Washing ...Small wooden & rippled glass domestic laundry washboard.Example of domestic work equipment.Serrated glass and wooden surround laundry washboard.Nillaundry, washing, domestic, pre-1950's -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Leisure object - Child's 'Washing Up' kit, C 1960's - 70's
Example of 'domestic equipment' for children.Approx .25 scale Wash Up Kit for child. Comprising X 2 drainers, mop and plastic spatula.Nilchildren's toys -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyWashing machine, 1900-1920 (Approximate)
Circular barrel on 4 legs with hand turning wheel, hinged lid - wooden dollie agitator inside. Internal corrugated base. Attachment for wringer. Handles either side of barrel. Cork bung for emptying. Metal bands round bowlOn wheel: "241X". On barrel: "Trade Mark / Banner Rotary / Made By / (illegible word) Washing Machine Co. / (illegible) Ohio, U.S.A.". On spindle covering: "163"laundry equipment, banner rotary -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncFunctional object, Corrugated Glass & Wood Wash Board, Twentieth century
A washboard is a tool designed for hand washing clothing. The traditional washboard was usually constructed with a rectangular wooden frame in which are mounted a series of ridges or corrugations for the clothing to be rubbed upon. In the 19th-century, the ridges were often of wood; by the 20th-century, ridges of metal were more common. Later examples substituted corrugated glass of plastic for the metal.A domestic glass and wood wash board designed for use with a wash tub. Annotation: "Donated by Mrs Grove (daughter of Dorothy ( Allan) Edwards-Flint".wash boards, laundry equipment -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment, Galvanised Iron Laundry Dipper, 20th Century
... dippers laundry equipment hand-washing Cylindrical galvanised iron ...A dipper was used to transfer clean water to the wash tubCylindrical galvanised iron laundry dipper with handle.laundry dippers, laundry equipment, hand-washing -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDomestic object, Galvanised Iron Wash Tub, 20th Century
... including washing infants. laundry equipment wash tubs galvanised ...Item of portable laundry equipment that might have multiple purposes including washing infants.Painted (exterior) galvanised iron oval wash tub. The portable tub has two handles and an overhanging rim.laundry equipment, wash tubs, galvanised iron household objects -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment, Wash Board, 20th Century
A washboard is a tool designed for hand washing clothing. The traditional washboard was usually constructed with a rectangular wooden frame in which are mounted a series of ridges or corrugations for the clothing to be rubbed upon. In the 19th-century, the ridges were often of wood; by the 20th-century, ridges of metal were more common. Later examples substituted corrugated glass of plastic for the metal.A domestic glass and wood wash board designed for use with a wash tub. laundry equipment, wash boards -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncEquipment, Wash Board, 20th Century
A washboard is a tool designed for hand washing clothing. The traditional washboard was usually constructed with a rectangular wooden frame in which are mounted a series of ridges or corrugations for the clothing to be rubbed upon. In the 19th-century, the ridges were often of wood; by the 20th-century, ridges of metal were more common. Later examples substituted corrugated glass of plastic for the metal.A domestic glass and wood wash board designed for use with a wash tub. laundry equipment, wash boards -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDomestic object - LAUNDRY MANGLE
... equipment LAUNDRY WASHING Trademark Wertheim Large green wrought ...Laundry equipmentLarge green wrought iron mangle with wooden rollers and metal pressure bar. Wheel to turn metal cogs to work rollers. Wooden shelf at base. Metal castors to maneuver into position.Trademark Wertheimlaundry, washing -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Shepherd’s Gold Book launching with Gold Pan and Gold Washing Cradle
Shepherd’s Gold Book Launched 1966 with gold mining equipment. Gold Pan and Gold Washing Cradle.stawell -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaEquipment - Object, Data Acquisition Ltd, Rain warning device
A battery operated device that is rectangular in shape with a sensor plate on top and an on/off switch on one end. At the other end is a round lid that screws off to allow a round 9 volt battery to be inserted. It was designed so that when placed outdoors would emit a noise at the first drop of rain, enabling vision impaired people to retrieve their washing from the line. 1 plastic box with metal plateRain warning device Made for the Royal National Institute for the Blind by Data Acquisition Ltd A price sticker reads: $49.assistive devices, royal national institute for the blind -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, Pamela Sandbrook, Laundry Bygones, 2004
This book illustrates the simple, rare but often extremely beautiful traditional laundry aids as well as machines which were used before and in the first quarter of the twentieth century.A small brown and blue covered book, Laundry Bygones, with the title in white lettering at the top of the front cover with the author Pamela Sambrook printed in blue underneath. The cover has a full sized photograph of the old fashioned laundry at Shugborough, Staffordshire Arts and Museum Service in England. The contents show the history of laundries from the past with information as well as black and white photographs. There is a List of Further Reading and Places to Visit at the back. Pp.32.non-fictionThis book illustrates the simple, rare but often extremely beautiful traditional laundry aids as well as machines which were used before and in the first quarter of the twentieth century. laundry aids, laundry equipment, laundry irons, laundry dollies, washboards, washing machines -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Fireplace Crane, Unknown
In the late 1800's and early 1900's kitchens were built separate from the main house for safety, as the open fire was used daily for all cooking, washing and heating of water. This very heavy strong fireplace crane could support several items such as cast iron kettles, pans and boilers which were hung on the hinged swing-arm, known as a “crane”. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. A black cast iron fireplace crane with a supporting pole bolted to the wall in the side of the brick open fireplace. It has a swinging handle with a rectangular hand grip at the end to move it over or away from the fire. The metal arm was swung out from the fireplace to access the hot water in a kettle relatively safely. There are holes in the bar for hanging hooks which kitchen cooking pots may be hung. Two small hooks are welded to the bar and there are two small removable hooks and two long ones. architectural elements, fireplaces, fireplace accessories, heating equipment, fireplace crane -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Cast Iron Kettle, Unknown
Heavy duty cast iron kettles were used as a domestic item to boil water safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier utensils had. The household depended on constant hot water availability for all cooking, washing and other household chores.A large vintage rusted black cast iron heavy kettle with no lid. It has a flat base and mushroom shaped handle welded onto the pot below the rim of the pot opening. It has a rim to position the teapot lid. The goose neck spout has a shaped pouring end. It was used as a domestic item to boil water safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier utensils had.kitchenware, kettles, kitchen equipment -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Wash Tub, early 1900's
These large tubs had multiple uses including washing clothes or bathing infants or children when water was not connected to the laundry or home in the early 1900's. The water was recycled by pouring it on the garden or fruit trees. It was used for containing crop harvesting too.A large vintage round galvanised iron tub tapering slightly to the flat base. It is seamed on both sides, made from two sheets of iron. It has two handles riveted on the sides and an overhanging rim at the top. It has been painted cream coloured on the inside. There is a wide steel band around the base which has been soldered on.laundry equipment, wash tubs, household objects -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Cast Iron Kettle, Unknown
Heavy duty cast iron kettles were used as a domestic item to boil water safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier utensils had. The household depended on constant hot water availability for all cooking, washing and other household chores.A large heavy black cast iron kettle with a curved handle, goose neck spout with a shaped pouring end and a removable lid with a small looped open knob. It has a flat base and mushroom shaped handle welded onto the pot below the rim of the pot opening. There is a shaped grip underneath at the top hold it steady. It was used as a domestic item to boil water safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier utensils had.On the base - 'England. First quality. No.3 6 pints. C. Clark and Co Ltd'kitchenware, kitchen equipment, kettles -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Cookie Press and Icing Set, Unknown
Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. This was the precursor to the current hand held machine for making forcer biscuits. The metal cylinder was filled with biscuit dough and the wooden piece pushed down inside the cylinder to force the dough through different shaped, detachable, apertures to produce various shaped biscuits. The wooden forcer is missing from this set. The tin base has a movable end for cleaning the wooden press. An incomplete rusted long tubular tin cookie or icing press with four pattern attachments. There is no handle or forcer. There are four original shaped profiles which can be interchanged tied together with brown string. The tube was to be filled with biscuit/pastry mixture and a wooden press was used to force the mixture out of it. biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Enamel Kettle, Unknown
This small kettle was from the home of Mrs Streizel and the family of Mrs Adamson. Kettles were used as a domestic item to boil water safely without the concern that the metal may contain lead or arsenic as earlier utensils had. The household depended on constant hot water availability for all cooking, washing and other household chores. These small kettles would have been used perhaps at the table to add water to the teapot instead of using the heavy large cast iron ones over the open fire or on the stove. This one is from the early 1900's.A small dark blue enamel hot water kettle with a black curved moveable handle riveted onto the top sides and a goose neck spout. It has a removable lid with a small knob. White enamel interior. kitchenware, kitchen equipment, kettles -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Biscuit Cutters, Unknown
Women in early settler days and 1900's managed the household and had to be self sufficient and were skilful cooks providing meals for their families. Normal daily life involved washing clothes, ironing, cooking meals and baking cakes, scones, bread, and pastries whilst caring for the children and making and mending the family's clothes. Nine round, one square vintage tin biscuit or pastry cutters: a set of five including a small, medium and large one with curved handles, plus two fluted and one plain cutter and one plain without handles.biscuit cutters, kitchenware, kitchen equipment, pastry cutters -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Menu, Bill of Fare ship Schomberg, circa 1855 - May 12 1856
A “Bill of Fare” is a menu or list of food offered for a meal. This Bill of Fare from the sailing ship Schomberg is handwritten in pen in hard-to-read script on the printed pages specifically for the Schomberg ship, of the Black Ball Line of Australian Packets. (‘Packets’ were vessels that had a regular trade run of cargo, passengers and mail; the sailing ship Schomberg was designed for long voyages between England and Australia.) These menus posed a puzzle as they have the handwritten dates of, May 10 and 12, 1856, by which time the Schomberg had sunk (she sunk on December 26, 1855). The donor of these pages of Bill of Fare is a stamp collector from Melbourne. He came across the menus in a package that he bought in 1980 at a stamp auction in Tasmania. He decided to give the menus to Flagstaff Hill this year during his annual family holiday in Warrnambool. A 1981 newspaper article about this donation included an interview with Flagstaff Hill’s curator Mr Peter Ronald, who said that the stationery of these menus is genuine. He went on to say that there would have been much stationery printed for use on the Schomberg although she sank on her maiden voyage. These menus could have been written at a dated late because the surplus Schomberg stationery could have been used for menus on other ships. We will probably never be sure of the answer but none-the-less the pages are still connected to the Schomberg. Below is what we believe the menu consists of although some of the writing is indecipherable - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (first menu) Roast Mutton Boiled Mutton? Ox Tail Mulligatawny? Or possibly Ox Tail Vegetables? Mutton Pies? ------------------------------- Vegetables Potatoes ---------------------------------- Dessert Fruit Puddings? Saturday May 10, 1856 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - AND - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (second menu) Boiled Mutton Roast Mutton? Roast Geese? Ox Tail?? Calves Head Broth? ------------------------------- Vegetables Potatoes ------------------------------- Dessert Tarts? Rice Pudding? ?...Maids?? Monday May 12, 1856 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Background of “SCHOMBERG” When SCHOMBERG was launched in July, 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line (one of three companies by that name), commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen, UK at a cost of £43,103. She was constructed with 3 skins: one planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her first class accommodation was luxurious: velvet pile carpets; large mirrors; rosewood; birds-eye maple; mahogany; soft furnishings of gold satin damask; an oak-lined library; and a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain James ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days at the launch, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway as well as a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. SCHOMBERG also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to Forbes regarding a card game as more important than his ship, SCHOMBERG eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the steamer SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled it. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 salvage efforts were abandoned after two men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck of the SCHOMBERG lies in almost 9 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated, the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen surrounding the wreck, by divers. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed in concretion), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. These Bills of Fare are significant due to their connection to Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg, which is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck S612. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The Schomberg collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The Schomberg collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Menu, or Bill of Fare, on cream coloured stationery from the sailing vessel “Schomberg”. Two rectangular pieces of paper, each bears the printed words “Black Ball Line of Australian Packets, Bill of Fare, Ship, Schomberg”, a printed symbol of the Black Ball line (a black ball on a red flag) and a decorative border. Both pages are handwritten, in similar but different sized writing, with a Bill of Fare and a date, Page (1) dated May 10th 1856 and (2) dated May 12th ’56, (Both dates are AFTER the Schomberg sank in December 26th 1855.) Both pages have three fold lines spaced across their width. To be used for the return voyage.Printed on the pages ““BLACK BALL LINE OF AUSTRALIAN PACKETS.” “Bill of Fare, / SHIP / “SCHOMBERG”.” Handwritten list of food, and on one page “Saturday May 10 1856” and on the other page “Monday May 12” warrnambool, peterborough, shipwrecked coast, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, flagstaff hill, sailing ship schomberg, shipwreck schomberg, black ball line of australian packets, bill of fare schomberg, menu schomberg 1856, food mid-1800’s, food on ships mid-1800’s, menu, may 10, 1856, may 12, 1856 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Padlock, c. 1855
This padlock has been salvaged from the wrecked sailing ship SCHOMBERG. It is not known whether the padlock was a part of the ship’s equipment or if it was among personal effects or cargo. At some point in time the padlock has been mounted and sealed in resin, perhaps for both display and preservation purposes. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When SCHOMBERG was launched in 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line, commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, (James Nicol Forbes) was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She carried 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking, 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The crew from the scouting party advised Forbes to wait until morning before trying to take the passengers to safety in the lifeboats because the rough seas could easily overturn the small vessels. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo that was still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864, after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water and the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets, menu and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. This brass padlock is registered as an artefact in the SCHOMBERG collection. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Hertage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural Brass Padlock lying in a wooden block and encased in resin. The wood encasing the padlock has seven man-made holes in it, perhaps used to hand as a display. There was a paper label with an inscription on the top and bottom of the wood immediately surrounding the padlock. the brass has tarnished. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in 1974.Marked on block - "Recovered 1974 'Schomberg'"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, padlock, schomberg shipwreck, brass padlock circa 1855, object salvaged from shipwreck, captain bully forbes, 19th century security hardware, sjouvenir, security, brass padlock -
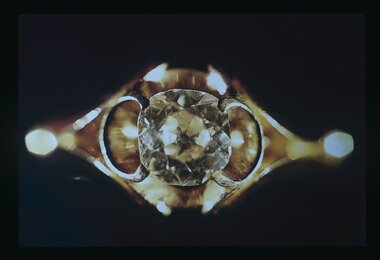 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Diamond ring, about 1855
In 1975, 120 years after the sailing ship Schomberg was wrecked, Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden) found an ornate communion set amongst the wreckage. The set comprised a jug, ciborium, lid, chalice and plate. The items, apart from the lid, were then displayed at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The lid had etchings that did not match the chalice and sat in storage for several years. Then in 1978, while the marine concretion inside the lid was being examined, a surface layer came loose and revealed a glint of gold that was assumed to be a piece of brass. The layers of concretion were carefully removed and a ring-like band emerged. Further treatment exposed a 'large faceted stone in an intricate gold setting. Weeks later a detailed examination estimated the value of the ring, known as the Schomberg Diamond, to be $7000. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, an oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signaled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in almost 9 meters of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. The actual lid in which the ring was found has not yet been completely identified and could belong to a coffee pot, sugar bowl or maybe a jug or something similar. Although all survived the wreck no-one came forward to claim the valuable diamond. The Schomberg Diamond is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village along with the rest of the communion set. Other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. One of the Schomberg bells is in the Warrnambool Library.The Schomberg Diamond is particularly significant in that it played a crucial part in having the legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter control over the salvaging of items from wreck sites. This ring is registered as Artefact S/105 in the Schomberg collection, the Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significant because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. A mid-Victorian gentleman's solitaire diamond dress ring with a Brazilian cut diamond (cushion cut), one and one-third carat set within an 18 carat yellow gold ring consisting of four claws within an open scroll setting and a divided scroll shank. Colour is classified as 'J', clarity SII. The setting is handmade. warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, ciborium, ring, schomberg-diamond, schomberg-ring, gentleman's ring, dress ring -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, Alexander Hall and Son, c. 1855
The Schomberg Cannon was recovered from the 1855 wreck of the SCHOMBERG in 1974 by Flagstaff Hill divers Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden. The wreck site was discovered in August 1973 by Stan McPhee and John Laidlaw. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When SCHOMBERG was launched in 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line, commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. The ship was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103. It was constructed with three skins: one planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Its first-class accommodation was simply luxurious; velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple, mahogany, soft furnishings of satin damask; an oak-lined library and a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the SCHOMBERG’s 34-year-old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. The ship departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and the cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune in those times. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and a photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells was in the old Warrnambool Library. The Schomberg cannon is currently on loan to the Port Campbell Visitor Information Centre.The SCHOMBERG collection is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Cannon; 6-POUNDER (6pdr) smooth bore cannon, mounted on a wooden frame. The cannon has a metal lug on each side. It is commonly known as the Schomberg cannon. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in 1974.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, cannon, the schomberg cannon, schomberg cannon, peterborough, 1855, sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail, 1855
The artefact is the lower portion of a rectangular shanked ‘planking nail’ with a straight-edged ‘flat point’. The distinctive ‘point’ of a planking/skirting nail was designed to be driven into timber across the grain in order to prevent the wood from splitting. This relic is from the shipwreck of the SCHOMBERG, which ran aground near Peterborough in 1855. It was retrieved in 1875 from a large section of the ship’s bow which had been carried by ocean currents to the western coast of New Zealand’s South Island. The nail is still fixed in a fragment of the original timber that it secured in the SCHOMBERG. The top portion, or ‘head’ of the nail, has corroded away but the pronounced rectangular shank and its flat point indicate its likely purpose and position on the vessel. Most fastenings used in sailing ship construction were either wooden treenails or copper bolts, which were relatively resistant to seawater corrosion. In addition, the preferred hull-frame timber of British Oak has a high content of gallic acid which rapidly corrodes unprotected iron work. The ferrous composition of this planking nail suggests it came from an internal and upper portion of the ship’s bow (protected from exposure to the sea or oak). According to an 1855 edition of the Aberdeen Journal, the five outer layers, or ‘skins’, of the SCHOMBERG’s pine hull were “combined by means of patent screw treenails”. However the “beams of her two upper decks” were of “malleable iron”, and “part of the forecastle” was “fitted for the accommodation of the crew”. It is therefore possible that iron nails of this description were used by the ship’s builders to secure floor and wall planks in enclosed areas of the crew’s quarters. (The same reasoning would apply to officer and passenger accommodation amidships and at the stern of the vessel, but it was the bow that floated to New.Zealand.) The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. This nail is a registered artefact from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG, Artefact Reg No S/35 and is significant because of its association with the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. The object is the bottom end of a slightly curved iron planking nail with remnant of timber still attached, recovered from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855). The shank of the nail is rectangular and it narrows to a flat (chisel like) ‘point’. The ‘head’ is missing although there is a quantity of dark red corrosion within the top of the surrounding wood, suggesting where it might have been. The artefact is from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855) and was retrieved from part of the ship’s bow which was carried by sea currents to the South Island of New Zealand. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, planking nail, rectangular ship’s nail, cast iron nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood encrustation, 1855
The object is a mass of small shipwreck debris that has been concreted together by sediment and marine growth. It was retrieved from the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG, which ran aground near the mouth of the Curdies River near Peterborough in 1855. The conglomerate of preserved wood impressions, rusted metal pieces, a small square of copper alloy, and black glass-like stones, presents too disjointed a collection to provide information on their purpose or function on the ship. The natural and gradual process of limestone accretion is a significant feature of the wreck-site, which was rediscovered by fishermen and skindivers in 1973. In his book “Exploring Shipwrecks of Western Victoria”, experienced diver and former director at Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald writes that the SCHOMBERG’s “triple layered wooden hull has disintegrated almost without trace…The turbulent shallow waters have promoted particularly heavy marine growth which tend to disguise the wreckage…the most prominent feature being a corroded mass of railway iron…Close inspection reveals small artefacts firmly embedded in the marine concretion which…is quite literally as hard as iron”. The huge oblong mass of concretion that now distinguishes the site covers the remains of this heavy cargo. A contemporary account of the SCHOMBERG’s fate (told by two of her passengers to the Melbourne Argus) alleges the ship “was overloaded, drawing over 25 feet when she left, and the cargo was chiefly iron and plant for the Geelong Railway”. The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. The shape and texture of this wood sample suggests a dense hardwood like Oak. The timber has been cut off at one end since its recovery from the sea, exposing a smooth and almost shiny surface. Seasoned English Oak has a similar light brown colour and tight grained finish. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. This object is listed on the Shipwreck Artefact Register, No S/49, and is significant because of its association with the ship SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. The object is an aggregate of limestone sediment that formed at the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG (1855). It is an irregularly shaped conglomerate of sand, shell-grit and marine worm casings from the ocean floor, but also incorporates an assortment of manufactured metal pieces and pipe fittings (corroded with red rust), a small rectangular piece of copper sheet, some ‘petrified’ wood remains (hardened and a soft brown colour), and pieces of black shiny stone (roughly cube shaped and possibly glass or porcelain remnants). There is an impression left in the stone of a joist or plank end but the original timber that the sediment formed around has since been dispersed by the sea.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwreck timber, alexander hall and son, shipwreck debris, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship Model, S.S. Schomberg, 1988
This model of the clipper ship SS Schomberg was researched and constructed to a scale of 1:64 by David Lumsden in 1988. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signaled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This item was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.This artifact is particularly significant in that along with other items salvaged from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Wooden model of the clipper ship SS Schomberg. The three masts are rigged with lines but have no sails. The model is mounted on pedestals on a timber board, exhibited in a glass case. The scale of this model is 1:64.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ship model, schomberg ship model, 1855, david lumsden, ship model maker, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood sample, 1855
The artefact is a piece of ship’s timber from the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG, a vessel which collided with the Peterborough reef on her maiden voyage in December 1855. This small wooden remnant of the disaster has been concreted on one side by the accrual of marine sediment while submerged. The build-up of sediment over the remains of the vessel is typical of the site as a whole. This artefact illustrates the reclaiming power of the ocean and the gradual disappearance of timber constructed vessels that have come to grief along this coastline (for example, the THISTLE in 1837, and the CHILDREN in 1838). The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. The shape and texture of this wood sample suggests a dense hardwood like Oak. The timber has been cut off at one end since its recovery from the sea, exposing a smooth and almost shiny surface. Seasoned English Oak has a similar light brown colour and tight grained finish. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. A piece of wood, concreted in sediment, from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855). The limestone accretion includes sand, shell grit and marine worm casings. The exposed surface of the wood is broken and worn smooth along the grain. One end of the timber has been cut or sawn off across the grain, presenting a smooth and shiny surface.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood segment, schomberg, shipwreck timber, alexander hall and son, limestone concretion, oak-framed hull -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Keg Spigot/Tap, Circa 1855
When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in almost 9 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This item was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.This artifact is particularly significant in that along with other items salvaged from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck. Brass keg spigot valve/tap, Schomberg Artifact Reg No S/94.Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, keg tap, brass keg tap -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Container
When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in almost 9metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This ceramic container was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.The ceramic container is particularly significant in that along with other items from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Stoneware Container with lid, white in colour,Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, container, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - MUG, 1969
The mug used for washing, shaving, cooking, making a brew. Refer Reg No's 3006 & 3007. Item issued to Peter Ball 3796117, refer Cat No 4704Stainless steel, kidney shaped mug with fold out handle.STOKES MELB 8465-50-242-7843 1969 [up arrow] Written: Peter BALLmilitary, cooking/personal hygiene
