Showing 380 items matching " dial"
-
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind annual report 1940, 1940
From its beginning, the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind grew in size and its number of employees and benefactors. These bound volumes of annual reports contain the information sent to subscribers of the Institute and outline the notable events and difficulties facing the blind and the RVIB. In this report praise for both the school and the work of the Insitute by external agencies is mentioned, the program of allowing children to handle exhibits courtesy of the Museum of Victoria, Hugh Jeffrey has just attained his degree as a Bachelor of Music (only the second to do so), honours also to Arthur McKay and other pupils who received Honours passes at university, over 1000 piano tunings were carried out this year by RVIB trained specialists, the Institute classes in cooking and hand and machine sewing have proven useful to single and married women of Melbourne, the Institute supports two cricket teams as well as other physical culture, and providing advisc to the Post Master General concerning telephone dials.1 volume bound with illustrations.royal victorian institute for the blind, annual reports -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumFunctional object - HEATER METERS, ONE SHILLING, Landis & GYRS.A, Pre 1970
.1) This one was used in the Writing room which later became a Meeting room then finally the RSL Building & History room. it was attached to the LH side of the Fire Place and ran an old Electric Heater on the Hearth. It was used up to about 2005. .2) This one was in the Old Kitchen built on the side of the Soldiers Memorial Institute in the mid 1960's This one ran the Electric stoves used by the Womens Auxiliary of the Bendigo RSL and to make the Rum & Coffee for the ANZAC Day Dawn service. The kitchen was removed as part of the Renovations in 2016 - 18..1) Heater meter, metal construction black coating, top face has a glass section with a "usage meter" saying "coins paid, unused", metal plate under with details re numbers, maker, coins per hour, on right side slot for "Shillings only" with knob, removeable lockable tray at bottom for coin storage and removing. .2)Same style as .1) but a different glass face style metering, it has 11 circular dials with one hand, these show "Coins paid, coins unused", this one shows the round meter going around when in use. The only differance between to two shapes is at the top re fixing to a wall..1) On plate, "Remote Control Switch - for alternating switch No 26 204 020 - Type Wik 36.1 - Adjustable 1-6 coins per hour, Adjusted for 1 coin per hour" On stickers, "insert 10 cents - Turn knob to right". .2) On glass section, "230/240 revs per KWH - 1200 - Serial No 8338380 - 5 - 50". On label stuck on, "10 c equals 1/2 hour"brsl, smirsl, shilling -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BENNETTS ARCADE: BENDIGO, 1955
Black and white photograph of Bennett's Arcade. Clock face up high at rear with policeman's face on dial., Taubmans paint sign under. Baskets, garbage bins, lawn mowers, enammelled cast iron pots. Various other hardware. Adult male in sports coats, jumper, shirt and tie holding hand of small girl in dark coat with beret, lace up shoes. Female in background with hat, overcoat. Female figure in foreground dressed in long coat with flower on collar, scarf, hat. Small boy in double breasted coat, cap and lace-up shoes. Patterned, tiled floor. C. Bennetts Arcade in ink on rear of photo.A. Doneyplace, arcade, bendigo -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Incubator, neonatal, Australia/ tVictor Watson/Limited/ New Zealand”, late 1950s- early 1960s
This item was purchased at Leski's, Melbourne, Medical collection auction, 8 May 2013. The incubator was part of a rare collection of medical, dental and pharmaceutical objects belonging to a tourism business, Kryal Castle, near Ballarat, Victoria from 1974. At some point,apparently, an officer manager discarded the museum records, so the provenance of the neonatal incubator, and many other items in the Leski auction, has been lost.Neonatal incubator, "Glenleigh", made and used, late 1950s- early 1960s. The four side laminated panels as well as bottom panel are possibly made of asbestos fibreboard,. Each panel is sealed with polished aluminium strips, and has a metal handrail.The incubator is mounted on four castors made by "Shepherd USA'. On the front panel is a bakerlite dial and a bakerlite switch. The item is incomplete: the cover, probably glass, is missing. Inside the unit is an old calico infant's mattress.There are two name plates on the front panel; “Australia/ Victor Watson/Limited/ New Zealand” and "Glenleigh/ Baby Incubator/ Aeronautical & Industrial Lighting Co/ 677-9 North Road Carnegie”. Australia/ Victor Watson/Limited/ New Zealand” "Glenleigh/ Baby Incubator/ Aeronautical & Industrial Lighting Co/ 677-9 North Road Carnegie”. Castors::"Shepherd USA' -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1975
The Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister has sterilized an autoclave pack for use by the RDNS Sisters when attending their patients in their homes who are requiring specific treatments for e.g. catheterization. This photograph is taken in the sterilizing room at a RDNS Centre. The Sister is wearing the RDNS Summer uniform of a short sleeve white blouse under a royal blue V neck tunic style frock with the RDNS logo on its upper left.Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) supplied sterilized equipment, such as ready set up catheter trays and dressing trays, as well as dressing packs for their Sisters to take to the home when attending to specific patient care. Patients bought their own future dressings, if these had not been given to them when discharged from Hospital. Following their day in the community the Sisters returned to the RDNS Centre and washed and set up the trays again ready for re-sterilization. Black and white photograph showing a Royal District Nursing Service, (RDNS), Sister who has blonde short hair; is wearing a short sleeved white blouse and dark tunic style frock, standing in the Autoclave room in an RDNS centre. She is emptying the Autoclave chamber after sterilizing a wrapped, 'gown and towel', which is written on the wrapping. Her right arm is extended with her hand on the metal wire basket which has a protective floral cloth covering the edge of the basket. The photograph shows a tall vertical Autoclave, which is made of metal. To the left above the chamber is a dark rectangular section with several switches, and to right of it are three white faced dials. royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns equipment, sterilizing -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, The Association for the Blind, Blind Members' Council meeting minutes 10/8/1976 to 1/10/1982, 1976-1981
These meetings were held at the Kooyong office and the minutes include Present, Chair, Apologies, Minutes, Matter arising from minutes, Correspondence, Life governors, Election of members, Nominations, Reports from Regional Blind Members groups. Some highlights were: 1/8/1979 Mr Maxwell reported from an article in Sound Magazine which stated that if the present circulation of 2,600 copies of the Large Print Age was not increased it may have to be discontinued. 5/3/1980 a letter of thanks was sent to Sister Toni Cocks for her effort in arranging for Telecom to produce the raised large print telephone dials at no charge to the visually impaired. 2/3/1982 The Secretary reported that the ANZ Bank cheque templates will be launched Australia wide on March 16 and will be on display at the Kooyong Family Fair. 2/7/1982 The Secretary reported that the National Bank has produced a cheque template and that Westpac is proposing to do the same 4/51982 includes a draft copy of AFB philosophies. Minute book for Blind Members Councilassociation for the blind, blind members council -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Clover, The Holborn Surgical Instrument Company, 1877
Dr. Joseph Clover (1825-1882), an English physician, first described his Portable Regulating Ether Inhaler on Jan. 20, 1877. Clover was an especially sought after anesthesiologist and early pioneer in the specialty. This was the best-known of many inhalers that Clover designed. The dome-shaped reservoir was turned to points on a control dial to gradually increase or decrease the percentage of the air that passed over the ether. Several inventors based new inhalers on this, while the original continued to be manufactured as late as the beginning of WWII. Clover, to spare the patient the unpleasantness of induction with his "closed" inhaler (1877), suggested the "mitigated-ether" technique. The inhaler was fitted with a bypass tap for the reception of N2O. The bag was filled with the gas and anaesthesia was inducted a combination of N2O and asphyxiation. Ether was then admitted gradually by rotation of the bowl of the inhaler. When the patient had been duly "weaned over" to ether, the mask was lifted, the N2O allowed to escape, the bag refilled with exhaled air, and normal anaesthesia "a la Clover's inhaler" was continued.Metal domed chamber with a bulb attachment for rebreather bag, including a tap mechanism. Remnants of the paper rebreather bag are attached to the bulb. At the other end is a yellow facemask made of plastic (probably celluloid). The manufacturer's logo has been moulded into the dome of the chamber.Manufacturer's logo: THE HOLBORN / SURGICAL INSTRUMENT CO. LTD. / LONDON •Blue sticker with white writing: O.2.4.joseph clover, mitigated-ether, nitrous oxide, n2o, closed method -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Ticket punch - Bell Punch - MT&OCo No. D406, Railway Register Manufacturing Company, 1885c
Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. Bell Punch No. D406. A heavy nickel or chrome plated steel ticket or fare strip canceling / registering mechanism used on Melbourne cable trams. When a fare was sold, the bell would ring advising the passenger that their fare have registered. "An ingenious device resembling in principle the ticket punch of a railway porter. It is carried by the conductor who wears pinned to his coat a 'trip-slip'. He punches this once for every fare received; the action is simultaneously registered on a dial inside the punch and bell rings to appraise the passenger of the fact. The punch is provided with a patent lock, the secret of which is known only at headquarters and effective system of check is thus secured." (" A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System" - page 54). Used by the MT&O and MMTB until 1922/23 when replaced by the check ticket system. Manufactured by the Railway Register Manufacturing Company. Has "MT&O Co. ..." stamped on one side along with patent dates.Demonstrates the equipment used by the Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. to register fares and provide an accounting method.Nickel or chrome plated steel ticket punch, used by the Melbourne Tramway and Omnibus Co. stamped "MT&OCo" and "D406", c1885.ticket punch, tramways, trams, bell punch, tickets, fares, cable trams, railway register manufacturing company -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumFunctional object - Yarn Spinner and Accessories, John Nesbitt, 19th Century
Nino Corda was a Geelong based textile designer who worked at various textile mills between 1957 & 2003. He travelled the world in search of the latest fashions and techniques and developed timeless designs that were much loved by Australians. These items are on rotational display at the National Wool Museum’s ‘In the Factory’ exhibition. For many years, Nino also worked as part of the Honorary Staff of the National Wool Museum. His passion for the world of textiles provided energy and knowledge to the visitors and staff of the museum. Although Nino has now retired from his honorary position and has hung up his Australian Tartan vest, these items will continue to serve the community in sharing the stories of Australian Textile design.Custom made wooden hinged box with a hook latch. Brass yarn spinner, attached to a mahogany wood plinth base, which spins fibre into cord/yarn/thread. It has dials to set the rate that it spins. Metal plaque with black inlaid enamel lettering. Small cork inlay. Brass rod with hinge and wingnut, and ball at end. Ball at end has an adjustment mechanism. Rod also has an adjustable circular collar. Pair of curved tweezers. Circular magnifying glass on long thin handle. Glass has two concave lenses. Weaving sample in shades of blue, green and brown. Twill weave. Alternate pattern samples separated by red thread.Brass plaque on base of spinner: 42 MARKET St / John Nesbitt / REGd TRADE MARK / LIMd / MANCHESTER Underside of wooden plinth: 4976apparatus, textile, testing, spinning, nino corda, magnifyer, tools, brass, mahogany, tweezers, yarn, spinner, design, john nesbitt, manchester, england, 19th century, engineering, manufacturing -
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchBinoculars
These binoculars appear to have been made for use by service personnel, carrying a broad arrow symbol on the barrel. The inscriptions "MG" may indicate the manufacturer or initials of the owner. The service number 48582 may indicate that the pair was owned by Lionel James O'Dempsey, a Victorian who served as a Lance Sergeant with the 3 Light Anti Aircraft Regiment during the Second World War.Brass binoculars with cotton cord acting as strap, fastened via a knot on one side of a small loop cast into the side of the barrel. Two cone shaped barrels with circular convex glass disc on each wide end. Each barrel joined together via a joint platform approximately halfway and 9/10ths of the way up the binoculars. Binoculars can change shape by barrels swivelling on a central pin. Binoculars also zoom in and out (i.e. barrel reduces and expands) due to grooved dial in centre of pin. One eye piece missing on left side, right side intact but able to be unscrewed. Barrels are tinted green from copper corrosion and retractable barrel sections have black colouring in parts.Inscribed on centre platform between eye pieces "M G", in the direction of the wearer. On top of adjustable barrels: "[broad arrow] (right side)", "Mk VSP-/48582"second world war, worl war two, world war ii, binoculars, looking glass, surveillance -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTransformer Lamp System, late 1950's
This transformer lamp system, which has a dial to transform 240 volts to a minimum of 32 volts was used by electrical technicians to inspect internal parts of the large generators (even in small confined spaces). The reason for the reduction of the 240 volts to the 32 volts was for the safety of the inspector. The SEC Victoria Hydro Scheme's electrical generators are powered by the hydro force of "stored" water at a higher altitude. The establishment of both the NSW and Victorian Hydro schemes was achieved from the mid 1900's to the 1960's. At this the point in time the need for additional power sources to quench both an industrial and domestic demand for electricity was purely an economic and not and environmental (carbon reduction) factor. This hydro scheme was instigated by "the Government of the day" as a bold move and was the major force of the World War II refugee and "technical" workforce inclusion of skilled and unskilled migration into the Australian environment. Although this mass "invasion" of workers with families was thought of in some circles as intrusive, the expansion of population post war years and its integration into the Australian rural sector, produced the multi- lingual multi-cultural diversity of later years.This transformer lamp is very significant to the Kiewa Valley as it was introduced as a very small part of the explosion of human resources into the valley. This influx of population transformed the region from that of a basically quiet rural region to one which evolved into both industrial and larger residential community. This evolution in the valley created a change, not only in the "physical" landscape but also the socio-economic expansion which permitted other "tourist" based industries into the valley. This is also a specific electronic item which was manufactured in Melbourne and not sourced from Europe or Asia. This demonstrates the fast evolution of Australian technology to a high standard compatible to that of the rest of the world.This heavy hand held electrical transformer (transforms 240 volts to 32 Volts) an has one leather handle on the top with three small (gauze filtered) air holes. It also has two 2 pin directional cable distribution (clipsal) in/out points 10amps / 240 volts. There is one glassed in volts/ac meter and one variable switch (180 to 150 voltage in settings of 10 volt increments.There are two vents (one on each of the smaller sides). There is also one three pin electrical lead coming out from the top.On one side is a manufacturer's plaque with "ELECTRONIC A & R EQUIPMENT MELBOURNE" and underneath "TYPE 1719, PRI V. 180 250" underneath "V.A. 1250" underneath "CYC 50" underneath "SEC V. 115" underneath "SEC A. 10 . 8". The label on topside "CAUTION SET SWITCH TO 250 v BEFORE CONNECTING TO MAINS THEN, WITH EQUIPMENT OPERATING, SET METER TO RED LINE.kiewa hydro electricity scheme, victorian state electricity commission, transformers -
 Harcourt Valley Heritage & Tourist Centre
Harcourt Valley Heritage & Tourist Centremanuel telephone exchange
A manual telephone exchange, manufactured by British Ericson, History Originally in use at Cohuna. When Cohuna was converted to automatic dialing this exchange was relocated to Harcourt, to become the third and last in a bank of three exchanges. At this time Harcourt exchange was expanded to 260 lines. It was connected to the district central exchange at Castlemaine. Operated by mains power with battery back-up. Harcourt exchange was operated by Betty McLean, Miss Mitchell, Josie Hogarth, Mr. & Mrs. Heighway, Bill & Valerie Milford, Irene Bolitho and others. Decommissioned approx. 1970. Incoming calls prompted the fall of a shutter. The operator made the connection by plugging the line into the number requested. While responding to calls the operator needed her hands free to jot down the billing particulars or to write out each telegram. Nearby stood pigeonholes with various items of stationary. Many telegrams were received each day, particularly advising fruit growers on interstate markets. Most telegrams were phoned through by the operator. This exchange was restored in 2004 - 2005 by Trevor Grant.. Many people relate to this exchange. It is a survivor of the pre-electronic era when ‘telephonist’ was a common occupation. A vital element in the communications between households and between district orchardists and their suppliers and clients.A manual telephone exchange, manufactured by British Ericson complete with operator hands-free headset/earphones and speaker mouthpiece. Wooden case with one hundred shutters and sockets. Accommodates twelve lines with extension leads with associated switches. Operated by mains power with battery back-up. Decommissioned approx. 1970. Incoming calls prompted the fall of a shutter. The operator made the connection by plugging the line into the number requested. This exchange was restored in 2004 - 2005 by Trevor Grant. -
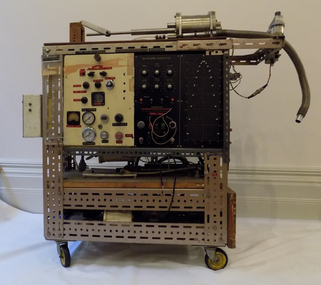 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Waveform Ventilator, 1970
Professor Arthur Barrington (Barry) Baker was the first Australian anaesthetist to gain a DPhil in anaesthesia. He completed his DPhil at Oxford University at the Nuffield Department of Anesthesia in 1971, titled, Physiological Responses to Artificial Ventilation. The Waveform Ventilator is the machine developed to illustrate his DPhil. The waveform ventilator was used in several scientific studies on 'the effects of varying inspiratory flow waveforms and time in intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV)', published in the 'British Journal of Anaesthesia'. Professor Arthur Barrington Baker had an extensive career in research and clinical practice including holding the position as the Nuffield Professor of Anaesthetics at Sydney university (1992 - 2005) and also as the Dean of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) (1987-1990).The variable waveform ventilator is of national significance, due to its association with Professor Arthur Barrington Baker (Prof. Baker) the first Australian academic anaesthetist, and the representation of historical social themes and research and design, in anaesthesia. Historic significance – It is a rare type of ventilator in good condition and well provenanced. It is a tangible record of the beginning of the long established and distinguished career of Prof. Baker, the first anaesthetist in Australia to gain a DPhil. Prof Baker has a strong involvement in the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) organisation. The object is a product of Prof Baker’s Doctorate of Philosophy (DPhil) on respiratory physiology and is associated with the prestigious Oxford University and the well-known Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics. It also represents the social theme of migration to England from Australia in the 1960s and 1970s to access and experience academic and artistic opportunities limited in Australia at the time. Scientific Value – The object is of scientific value as it offers major potential for education and interpretation in anaesthesia. Although ventilators are common equipment, this specific design and construct prototype is one of a kind, designed and used specifically for research purposes. A rectangular shaped object on a trolley with four wheels. The top half of the object consists of two panels, one of cream coloured painted wood, the other black plastic, both containing several dials of different shapes and sizes. The wood surface also contains several gauges and a safety pressure clear plastic box. The plastic surface also contains a pin board. The bottom half of the object consists of two shelves. The whole object's perimeter is lined with perforated metals. The top wooden surface has several metal pieces of equipment and a long tube. The rear of the object contains numerous types of tubing and wire, a gas cylinder and two leather straps with buckles. The bottom half of one side of the objects has 3 electrical power outlets.Waveform Generator, Drs Colliss N Cowie, Dr Baker Dr Murray Willson, Dr Babbington, Safety Pressure, Error POS F/B, Position, Feedback, Set Balance, Reset, Full Stroke, Velocity, Converter Current, line Pressure, Low Pressure, Bias Pressure, Start, Stop, Stop, Reset Press, Max Press, W/G Output, A/CRO B/2.baker, arthur barrington, baker, barry, professor, academic anaesthetist, oxford university, nuffield department of anaesthesia -
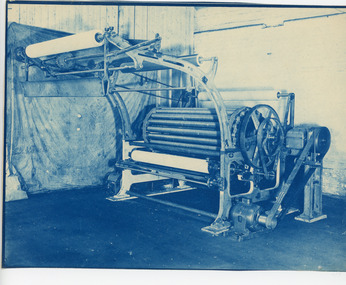 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPhotograph, Q-VEE Machine, 29/06/1937
Photographs were most likely used for promotional purposes. The Q-VEE machine is a scouring machine. When fabric is removed from the loom it is often stiff, rough or uneven. Scouring removes the oils and dirt picked up from manufacture, leaving the fabric soft and fluffy. The photographed machine was made by J. Stone & Co, a British marine and railway engineering company based in Deptford in south east London.Four black and white, blue tinged photos of a Scouring Machine from different angles. Black writing on the rear, typed with a typewriter and stamped with the company stamp.8051.1 - rear - "Q-VEE" Machine. Tomlinsons (Roshdale) Limited. SOHO Works Rochdale. 29.6.37 849 8051.2 - rear - "Q-VEE" Machine. Tomlinsons (Roshdale) Limited. SOHO Works Rochdale. 29.6.37 856 8051.3 - rear - "Q-VEE" Machine. Tomlinsons (Roshdale) Limited. SOHO Works Rochdale. 29.6.37 851 8051.4 - front on machine - FIY Chain Gear J.Stone & Co Ltd London rear - P.I.V. Dial Control Tomlinsons (Roshdale) Limited. SOHO Works Rochdale. 29.6.37 853textile machinery, wool manufacture, wool, scouring -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchEquipment - Mortar Sight
Large green coloured metal case with canvas carry strap containing 3 INCH Mortar Sight MK2 Outside: Case No 2 MK 2 C.M. 1019. A. Distinctive Products Pty Ltd When replacing sight in case SET Sight Lensatic to Horizontal & Zero, Dial Plate to Zero, Drum to Max. Range INSIDE: Contents of case Sight 3" Mortar Mk. 2 or Sight S.B 4.2 Mortar MK. 3 and Screwdriver No 7 Director Mk 2/L. (W/O cord, disc or eye) Thimbles, Luminous, Mk. 1. X 3 Bubble, spirit, cased, no.10 MK.1mortar sight, mk2 -
 Plutarch Project
Plutarch ProjectMachine - Shortwave Radio Antenna, Active Antenna, circa late 1980's
This antenna was used between 1989 and 1990 to help receive the daily news service in the Greek language directly from Athens, Greece. At the time, news from Greece for the Greek people in Australia were arriving in Melbourne a week late, on newspapers from Athens sent through air-mail. These newspapers were displayed at Salapatas and Carras newsagents at Lonsdale street in Melbourne. One thing that was a problem for this service was that the news came at least 7 days late. Using the Shortwave Antenna we could get the latest news from Athens on shortwave radio directly and within an hour these news were recorded on a cassette tape and taken to the Tricom Group P.L. offices in Melbourne (1155 Malvern Road, Malvern 3144). The tape was loaded onto a system which allowed people to call a local phone number and listen to the latest news with a cost of a local call, or a little bit more. As this was prior to the Internet being established around the globe, it was the fastest news service directly from Greece, in the Greek language. It was used for a span of about 12 months, until Tricom closed down their dial-in services, sometime in 1990. The service was captured and loaded onto the system by Iakovos Garivaldis, then an employee of the Tricom Group which was a subsidiary of Southern Cross TV.The Primary significance of this object is of its historical value, social and informative value for the first generation of Greeks in Victoria"World Tuner AT4 SW" antenna with a 920mm fully extended aerial, a tuned circuit and two transistors to prevent loading of the antenna and boost signal output. It is made of plastic, black in colour with the aerial being made of steel. The signals picked up by the antenna are fed via a 15pF ceramic capacitor to a tuned circuit consisting of either VC1a or VC1b and either L1, L2, L3 or L4. The slider switch S1 selects the band to be tuned. The band range is normally from 3 to 30MHz. When S1 is in position A, L1 and VC1a are selected and the antenna can be tuned from 3-9MHz. Similarly positions B, C, and D select higher frequencies up to 30MHz. It was purchased by Iakovos Garivaldis for this use for $119.WORLD TUNER AT4 SW "Amplituned" Shortwave Antennaantenna, radio, short-wave, language, greek -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Speedy Moisture Meter, Thomas Ashworth and Co, c 1950
The most common technique to measure fuel moisture content in Victorian forests until recently was the Speedy Moisture Meter - which is essentially a pressure cylinder. Originally developed in England during the 1920s for measuring moisture in wheat and other grains it was adapted for Australian forest fuels in the 1950s. Fuel was first ground using a Spong domestic food mincer, often attached to the bullbar of a vehicle, and a small measured (using the beam balance) sample placed into the Speedy together with a measured amount of calcium carbide and then sealed. The chemical reaction between the moisture in the fuel and the calcium carbide created acetylene gas; the pressure of which was read on the external dial which gave the read-out as the moisture content (percentage of net weight) of the sample. There were important techniques with preparing the minced samples, using the chemical and the subsequent cleaning of the Speedy to give reliable readings, but it was quick, inexpensive, robust, portable and practical in the field - it gave readings which were reproducible to within +/- 0.5% moisture content. It was used routinely before igniting a fuel reduction burn or measuring fuel moisture differentials on slash burns. In about 1996, Karen Chatto and Kevin Tolhurst from the Department’s Creswick Research Station developed the Wiltronics Fuel Moisture meter which measured electrical resistance.First reliable tool for measuring bushfire fuel moisture content in the fieldSpeedy Moisture Meter in wooden boxmanufacture's marks and instructions on usebushfire, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Ship Log
The ship's log part, called a fish, is likely to be from a mechanical taffrail log system. It was recovered from the wreck site of the barque, the 1840-1852 Grange. There are no marks on the fish to identify its maker or model. It is part of the John Chance Collection. This ‘fish’ is part of an early to mid-1800s ship's log. It would likely have been part of a taffrail log connected to a rotor (also called propeller, spinner) by a strong line, and the other end connected by a line to a dial mounted on the taffrail, or stern rail, at the stern of the vessel. As the propeller rotated through the water it would spin the log, which in turn would cause a number to register on the dial, showing the current speed in knots; one knot equals one nautical mile per hour. TAFFRAIL LOGS A taffrail log is a nautical instrument used for measuring the speed of a vessel, providing vital navigational information to be calculated, such as location and direction. A log has been used to measure the speed of a vessel since the 1500s. A simple piece of wood was tied to a long line and thrown into sea at the back of the vessel. The rope was knotted all along at equal distances apart. On a given signal the log line was pulled back into the vessels, the knots counted until the log came up, then the figures were calculated by a navigator In 1802 the first successful mechanical log available for general use was invented by Edward Massey. It had a rotor 'V' section connected to a recording mechanism. The water’s movement rotated the rotor, which intern sent the movement to the recorder. There are examples of this invention available to see in some of the maritime museums. Thomas Walker, nephew of Edward Massey, improved on Massey’s design, and Walker and his son took out a patent on the A1 Harpoon Log. In 1861. Both Massey and Walker continued to improve the designs of the taffrail log. New designs were still being introduced, even up to the 1950s. THE GRANGE, 1840-1858- The wooden barque ’Grange’ was a three-masted ship built in Scotland in 1840 for international and coastal trade. On March 22, 1858, the Grange set sail from Melbourne under Captain A. Alexander, carrying a cargo of ballast. The barque had left the Heads of Phillip Bay and was heading west along the Victorian coast towards Cape Otway. The ship struck Little Haley’s Reef at Apollo Bay due to a navigational error and was stuck on the rocks. The crew left the ship carrying whatever they could onto the beach. Eventually, the remains of the hull, sails and fittings were salvaged before the wreck of the Grange broke up about a month later. About 110 years later, in 1968, the wreck of the Grange was found by divers from the Underwater Explorers Club of Victoria. They were amazed to find a unique, six to nine pound carronade (type of small cannon) and a cannonball on the site. There have been no other similar carronades recorded. In that same year the anchor of the Grange was recovered by diver John Chance and Mal Brown. The ship’s log is significant historically as an example of hardware used when building wooden ships in the early to mid-19th century. The ship’s log is historically significant as an example of the work and trade of blacksmith. The ship’s log also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Grange in the 1968. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The ship’s log is historically significant for its association with the 1840s wooden barque, the Grange. The Grange is an historical example of a Scottish built vessel used for international and coastal trader of both cargo and passengers in the mid-19th century. The Grange is an example of an early ship, designed with a wooden hull. It is significant as a ship still available to divers along the south coast of Victoria, for research and education purposes. The Grange is an example of a mid-19th century vessel that carried a weapon of defence onboard. Ship log fitting, called a fish; part of a brass navigational instrument, likely to be from a taffrail log. The metal is a tan colour and has rough surface with a sheen, and discolouration in places. Its basic shape is a hollow cylinder with ends tapering to a smaller size. In the centre there are opposing openings cut out, showing a rough texture inside. One end on the cylinder is closed with a ring and shank installed, fixed by an embedded screw through the end of the cylinder. There are no inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, west coast trader, apollo bay, mid-19th century shipwreck, the grange, scottish barque, little henty reef, captain a alexander, underwater explorers club of victoria, vhr 5297, coastal trader, wooden shipwreck, john chance, wooden ship, taffrail log, marine instrument, marine technology, navigation, nautical instrument, mechanical log, nautical navigation, navigation equipment, scientific instrument, ship log, ship log register, ship speed, taff rail log, patent log, towed log, taffrail log fish, edward massey, thomas walker -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Ticket punch, Railway Register Manufacturing Company?, Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. Bell Punch, MID 1880S
Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. Bell Punch No. D382. A heavy nickel plated steel ticket or fare strip cancelling / registering mechanism used on Melbourne cable trams. When a fare was sold, the bell would ring advising the passenger that their fare have registered. "An ingenious device resembling in principle the ticket punch of a railway porter. It is carried by the conductor who wears pinned to his coat a 'trip-slip'. He punches this once for every fare received; the action is simultaneously registered on a dial inside the punch and bell rings to appraise the passenger of the fact. The punch is provided with a patent lock, the secret of which is known only at headquarters and effective system of check is thus secured." (" A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System" - page 54). Used by the MT&O and MMTB until 1922/23 when replaced by the check ticket system. Manufactured by the Railway Register Manufacturing Company. Lock code IDMA. Has "MT&O Co. ..." stamped on one side along with patent dates.Has "D 382" punched above ticket entry slot (both sides), "335" on handle, "MT&O Co." stamped on numbering registering face.trams, tramways, ticket punch, bell punch, tickets, fares, cable trams -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCompass, 1940's
Henry Browne and Son Ltd, of Barking, made aviation and nautical compasses, clocks and dials. The company made compasses for aircraft notably, Spitfires, Tiger moths and Concord. Henry Browne was born in Lewis, Sussex in 1842 and died in Barking in 1935. His company was a well respected English instrument maker that had been making and selling fine quality compasses, ship's clocks, inclinometers, sextants, and chandlery items for over 140 years. It started in a factory in Brightlingsea, Essex and moved to Barking in 1929. The Trade Mark brand Sestrel was used on all their equipment. Their “Dead Beat“ compass design is well dampened serving to reduce oscillations. It is reported that this design compass was fitted to many Allied ships during WW II. The company went through a boom period in the 1970s but collapsed in the 1980s due to the popularity of cheaper plastic compasses over tradition brass ones. Over more recent years, there has been a consolidation of British instrument makers and the firm of Henry Browne & Son has changed hands a number of times. At last count, it became part of Lillie & Gillie of London in 1985 when John Lilley & Gillie Ltd acquires the assets of Henry Browne & Sons (Sestrel) Ltd, a major competitor for what may be the second time. The model name of Sestral came about via the following.Take first two letters of the word Sensitive then the firs two letter of steady and the firs three letters of reliable hence the trade name of "Sestral". Item relates to the second world war used in many ships of the time merchant and military, It reminds us of a time in our social and world history when most of the world was in conflict.Henry Browne and Sons “Dead Beat“ compass design is well dampened serving to reduce oscillations and was an innervation that many makes of compass of the time din't have as a result the "Sestrel" design was fitted to many Allied ships during WW II.A liquid-filled Sestrel compass, with a brass housing and gimbal ring, wired for an internal low voltage light to illuminate the compass card. Inscriptions printed on face and impressed in metal around outer rim TRADE MARK", "Sestrel Dead-Beat", "No 1724 N", "Barking & London" HENRY BROWNE & SON", additional inscription "AFT No 1724 N". flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, compass, marine compass, henry browne & son barking london, sestrel dead-beat marine compass, navigation instrument, sestrel dead-beat marine compass -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, colour, c.2000
The photograph was taken in a Shopping centre and shows an RDNS Sister about to check the blood pressure of a lady..Over many years the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), was involved with carrying out health screening checks at many Shopping centres, and other venues, when requested.A coloured photograph taken in a Shopping centre, showing a Royal district Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister, who is wearing glasses and has short blonde straight hair, standing on the left hand side of a seated elderly lady. The RDNS Sister, is wearing RDNS dark blue slacks and a jumper over a white blouse, with the collar and cuffs seen. She is looking down at a blood pressure machine and holding the dial with her right hand. A stethoscope is hanging down from around her neck. The elderly lady has a blood pressure cuff around her right arm. She has grey curly hair and is wearing a blue and pink patterned jacket over a navy blue frock. She is facing the camera and looking serious. To the Sister's left are some open cardboard boxes, one with a white balloon on a stick from it, and further to the left part of a table covered with a red tablecloth can be seen. A shoe shop can be seen in the rear, as well as a vertical dark banner with the word 'Police' running down it in white letters.royal district nursing service, rdns, health screening checks -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumGas Detector
1990 -24/04: To "Salvageman Ltd" at Douglas (IOM)One gas detector housed inside a black leather carry case, with a carry strap, and a pocket at back of carry case.1993 circa.on detector: "OMA-3/ON/OFF/ TYPE OMA-3/ KOMYO Paper card inserted in case, written with pen: "1) Turn on/off switch "ON"/ 2) Battery Check:/ Hold down smaller/ Button. Needle must be / within lower red scale/ 3 Zero Calibration Scale/ Press Larger Dial and Turn to Set Needle on/ Green on Lower Scale" handwritten on case: "PWO 3076" Sticker on case: "GASTECH/CALIBRATED/ Date 31-8-93/ Next Due/ 31-2-94/ Initials MW/ Serial no. 6479" Card attached by string, written in pencil: " PWO 3076/ Gas Detector/ Model no. 6479 [From the Howard Smith Collection]" -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tool - Brass balance 'Salters', c1900
In the 18th century, spring scales appeared. To produce these scales, a manufacturer would use the resistance of a spring to calculate weights, which could be read automatically on the scale’s face. The ease of use of spring scales over balance scales is what led most post offices to outfit their clerks with spring postal scales. One of the most common types of spring scales was the kitchen scale—also known as a family or dial scale. Designed for horizontal surfaces, these scales used the weight of goods in a pan at the top of the scale to force the spring down. Such scales were common in early-20th-century households and were sold by Sears and Montgomery Ward. Many had flat weighing surfaces but some were topped by shallow pans. Companies such as Salters, Chatillon, and Fairbanks made both. SALTER HOUSEWARES began in the late 1760 in the village of Bilston, England. At this time Richard Salter, a spring maker, began making 'pocket steelyards', a scale similar to the fisherman's scale of today. By 1825 his nephew George had taken over the company, which became known as George Salter & Co. and later established a large, well equipped manufacturing site in the town of West Bromwich. The business thrived throughout the 1900s, and in 1972 the company was purchased by Staveley Industries Plc. In 2002, the management team at Salter Housewares Ltd, backed by Barclays Private Equity, bought the company out from the group, to concentrate on its consumer businesses. In 2004 was sold to the US-based HoMedics company, and in 2006, Salter Housewares USA and Taylor Precision Products Inc (also owned by HoMedics) merged. A portable, brass balance scale , 'Salters' for weighing items. A steel ring holds a brass plate marked with graduations 0 – 26 to which is attached a steel hook. ( rope & arrow TM ) / SALTER / POCKET / BALANCE / MADE IN ENGLAND Graduated 0 – 26 / PATENT / No. 8 Base rope & anchor S (trade mark) pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, moorabbin, brighton, cheltenham, tools, craftsman, balance, scales, weights, imperial measure,, salter housewares pty ltd, west bromwich, england, salter george, salter richard, bilston england, -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1980
The RDNS Sister is visiting a lady in her own home to take and record her blood pressure reading. The Sister will assess if these readings are within normal limits and relay these readings to the lady's Doctor as necessary. The RDNS uniform worn by the Sister is a white short sleeve blouse under a royal blue V neck tunic style dress and a dark blue cardigan. The Trained nurses (Nurses) of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), later known as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), visited patients in their home and gave best practice care in many fields of nursing, and to people of many cultures, throughout its 130 years of expansion. Initial visits not only assessed the specific nursing situation but the situation as a whole. Their patients ranged in age from babes, children, adults to the elderly and referrals were taken from Hospitals, General Practitioners and allied Health facilities. Some of the care the RDNS Trained nurses (Sisters) provided is as follows: – Post-Natal care given to mother and babe, Wound Care following various types of surgery, accidents, burns, cancer, leg ulcers etc. Supervising and teaching Diabetic Care, including teaching and supervising people with Diabetes to administer their own Insulin, and administering Insulin to those unable to give their own injections. Administering other injections and setting up weekly medication boxes. The Sisters performed Catheterizations on adults suffering from conditions such as Quadriplegia, Paraplegia, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Motor Neurone Disease (MND) and Guillan-Barre Syndrome, and when required at school on children for e.g. those with Spina Bifida. The Sisters visited those requiring Cystic Fibrosis support and care; those requiring Haemo-Oncology care, including visiting children at school; those requiring Home Enteral Feeding care, and those requiring IV therapy at home and home Dialysis. Palliative Care was given including pain relief with the use of syringe drivers, personal care as needed, and advice and support to both patient and family. The Sisters provided Stoma management to those needing Urostomy, Ileostomy and Colostomy care and those requiring Continence care. HIV/AIDS nursing care was provided; visits to Homeless Persons were made. Personal care was given to patients ranging in age and with varying mobility problems, such as those with MS, MND, Guillan-Barre Syndrome, Poliomyelitis, Quadriplegia, Paraplegia, Acquired Brain Injury, to those following a Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke), those with severe Arthritis and those with a form of Dementia. When necessary the elderly were assisted with personal care and advice given on safety factors with the use of hand rails, bath or shower seats, and hand showers. Rehabilitation with an aim towards independence remained at the forefront of the Sister’s minds and when possible using aids and instruction on safe techniques enabled the person to become fully independent. All care included giving advice and support to the patient and their Carers. The Sisters liaised with the persons Doctor, Hospital and allied Health personal when necessary.A black and white photograph showing on the left, a Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister who has short dark curly hair and who has the ends of a stethoscope in her ears and with her left hand holding the other end below the blood pressure cuff on an elderly lady's extended right arm.. She is looking down at the blood pressure dial which is held in her right hand. The Sister is wearing her RDNS uniform of a white blouse, the peaked collar of which can be seen, under a darker V neck tunic style frock and a dark cardigan. The lady who has short grey curly hair, is watching the procedure. She is wearing a grey short sleeved frock with a broach at its neck and with dark long sleeves seen underneath. The lady is sitting in a patterned padded chair which has a carved wooden top. Long opened curtains with voile curtain in the centre can be see behind her. In the left background, part of a cabinet with ornaments can be seen, and in the left foreground part of a patterned lounge chair can be seen.royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns patient care - blood pressure check -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCalculator, Burroughs, Calculator (Adding Machine), c1935
The "Burroughs Calculator" was a non-printing key-driven machine introduced in 1912 in response to the success of the Felt & Tarrant "Comptometer". The first Burroughs key-driven machine was very similar to the Comptometer in its external appearance, but was quite different in its internal mechanism, with the register and carry mechanism based on a complex system of planetary gears. It was only about two-thirds of the weight of the Felt & Tarrant machine, and had none of the safety features. In particular, there was no protection against incomplete keystrokes in either direction. The register would simply advance in proportion to the depth of stroke, with no indication of error. However, the price was also about two-thirds of the Comptometer, which made it quite a popular (if dangerous) machine. (http://home.vicnet.net.au/~wolff/calculators/Burroughs/Burroughs.htm) The Burroughs Portable Adding Machine introduced in 1925 became the basic design for the adding machine for many years, until the ten key adder was introduced and started to replace it gradually. The key-driven type machine did not print, and while it was often used as an adding machine, it developed into a special purpose machine in later years. The machine was very fast . The efficient operation of these machines required an experienced operator who often received a high salary. The machine was produced over a very long period because of its unique capabilities and was often used to verify product delivery lists from delivery routes. Later models of the machine, called a duplex design, could hold a running total in a second set of dial wheels while the primary wheels continued to add and subtotal amounts that could be transferred at any time to the running total. A side note, Burroughs copied the Felt design for its first models and was sued for patent infringement by Felt and Tarrant who prevailed in the suit. As a result, Burroughs totally redesigned their machine and went on to compete with the Felt machine for decades. Info from (http://www.burroughsinfo.com/group_d.htm) Black metal low keyboard manual adding machine. The key-driven type machine did not print, and was exceedingly fast and experienced operators could easily outrun an operator on a full keyboard or 10-key adding machine. The adding machine has a brown leather carry case.calculator -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwaySmiths Setric Electric Clock, circa 1937
Electric Clock - Smiths Setric Clock From 1937 the trademark "Sectric" appears on their synchronous models.Usually on the dial but sometimes also on the back cover. Early clocks had a prominent "T" in sectric. Smiths English Clocks 1931 Smiths, then called S. Smith and Sons (Motor Accessories) Ltd, entered the domestic clock market and formed a new company, Smiths English Clocks Ltd, as the Clock and Watch division with Cricklewood as the main factory. Smiths were one of the first companies to produce synchronous electric clocks. These were put on the market towards the end of 1931. Smiths formed a subsidiary company called Synchronous Electric Clocks to produce these clocks as the first models carry this name. 1932 Smiths purchased English Clock and Watch Manufacturers of Coventry, and acquired the trade names Astral and Empire. 1934 Smiths produced a synchronous alarm clock which they named the Callboy. 1934 They bought the Enfield Clock Co. The Smith's 8 day Calotte clock made its debut at the British Industries Fair in 1934. Prior to this date calottes had been exclusively of foreign manufacture. Also that year, Smiths introduced the Batriclock which was intended for areas where the synchronous clock could not be used. 1935 They introduced the Synfinity, which Smiths described as "the clock that never stops". They said it was "the remarkable combination of a synchronous electric movement with the essential elements of a fine precision lever escapement". If the electric supply failed the clock would run for up to six hours and rewind when the power returned. Apparently the synchronous motor also corrected the mechanical time train at intervals. Smiths produced a synchronous electric chiming clock. 1937 The trade name Sectric appears on Smiths electric clocks. Also the introduction by Smith's of a calotte clock with an alarm movement.Historic - Smiths English Setric Electric Clock Electric Clock - Smiths Setric Clock It is round with the numbers one to twelve, three hands with a white face. Smiths Sectricpuffing billy, clock, time, smiths sectric -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Scale, Early 20th century
The basic balance scale has been around for thousands of years and its accuracy has improved dramatically over the last several centuries, the principle behind this tool remains unchanged. Its parts include a fulcrum, a beam that balances on it, a pan at the end of the beam to hold the materials to be weighed, and a flat platform at the other for the counter-balancing weights. Balance scales that require equal weights on each side of the fulcrum have been used by everyone from apothecaries and assayers to jewellers and postal workers. Known as an unequal arm balance scale, this variety builds the counterweight into the device. Counter scales used in dry-goods stores and domestic kitchens often featured Japanned or (blackened) cast iron with bronze trims. Made by companies such as Howe and Fairbanks, the footed tin pans of these scales were often oblong, some encircled at one end so bulk items could be easily poured into a bag. Seamless pans were typically stamped from brass and given style names like Snuff (the smallest) and Birmingham (the largest). Some counter scales were designed for measuring spices, others for weighing slices of cake. In the 18th century, spring scales began to appear and would use the resistance of spring to calculate weights, which are read automatically on the scale’s face. The ease of use of spring scales over balance scales. One of the most common types of spring scales was the kitchen scale also known as a family or dial scale. Designed for horizontal surfaces, these vintage kitchen scales used the weight of goods in a pan at the top of the scale to force the spring down rather than the balance system. Such scales were common in early 20th century households and were sold by many companies. Many had flat weighing surfaces but some were topped by shallow pans. Companies such as Salters, Chatillon, and Fairbanks were the most popular brands used. These scales are significant as they identify one of the basic preparation items for the weighing of foodstuff in the family kitchen to prepare everyday meals. This item is significant as it gives a snapshot into domestic life within the average home in Australia around the turn of the twentieth century and is, therefore, an item with social relevance. Black cast iron, medium weighing scales, with a fulcrum which the beam that balances on, there is as scoop at one end for the material to be weighted and a flat circular disc at the other end that holds the weights. Around the cast iron base is an embossed leaf pattern. All the weights have their weight embossed within the casting.There are 5 weights, marked 2 oz, 4 oz,8 oz,1 lb,2 lb, This scale does not have any visual markings on the arms to identify a maker or true balance. It is therefore assumed that these scales were made for domestic use only.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spring scale, scale -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional Object - Ticket punch, Railway Register Manufacturing Company, 1880's
Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. Bell Punch No. D1902. A heavy nickel plated steel ticket or fare strip cancelling / registering mechanism used on Melbourne cable trams. When a fare was sold, the bell would ring advising the passenger that their fare have registered. "An ingenious device resembling in principle the ticket punch of a railway porter. It is carried by the conductor who wears pinned to his coat a 'trip-slip'. He punches this once for every fare received; the action is simultaneously registered on a dial inside the punch and bell rings to appraise the passenger of the fact. The punch is provided with a patent lock, the secret of which is known only at headquarters and effective system of check is thus secured." (" A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System" - page 54). Used by the MT&O and MMTB until 1922/23 when replaced by the check ticket system. Manufactured by the Railway Register Manufacturing Company. Lock number IDMA - see btm6. Has "TB" - Tramways Board - stamped on one side along with patent dates. See also Reg Item 72 and 72.1 for other examples. See "A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System 11/11/1885 to 26/10/1940" C.N. Govett and A. E. Twentyman. Copy held in the Hawthorn Tramway Depot collection. See Notes on opening from the Hawthorn Tramway Depot collection - see related documents.Has "D 1902" punched above ticket entry slot (both sides), "1902" on handle, "TB" stamped on numbering registering face. trams, tramways, ticket punch, tickets, fares, cable trams -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional Object - Ticket punch, Railway Register Manufacturing Company, 1880's
72 - Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Co. Bell Punch No. D1335. A heavy nickel plated steel ticket or fare strip cancelling / registering mechanism used on Melbourne cable trams. When a fare was sold, the bell would ring advising the passenger that their fare have registered. "An ingenious device resembling in principle the ticket punch of a railway porter. It is carried by the conductor who wears pinned to his coat a 'trip-slip'. He punches this once for every fare received; the action is simultaneously registered on a dial inside the punch and bell rings to appraise the passenger of the fact. The punch is provided with a patent lock, the secret of which is known only at headquarters and effective system of check is thus secured." (" A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System" - page 54). Used by the MT&O and MMTB until 1922/23 when replaced by the check ticket system. Manufactured by the Railway Register Manufacturing Company. Lock number not known. Has "MT& ..." stamped on one side along with patent dates. 72.1 - as above but for punch number D1338 - added 17/12/12. See also Reg Item 6437 for another sample - punch No. D1902. see - \dbtext\museum\documents\htd242i.pdf for opening instructions. See "A story of the Melbourne Cable Tramway System 11/11/1885 to 26/10/1940" C.N. Govett and A. E. Twentyman. Copy held in the Hawthorn Tramway Depot collection. Has "D 1335" punched above ticket entry slot (both sides), "335" on handle, "MT& ..." stamped on numbering registering face. 72.1 - As above with number "D1338" punched in. The M.T.& Co" is more visible.trams, tramways, ticket punch, tickets, fares, cable trams -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageShip Log Rotor, 1930s
Thomas Walker & Son was internationally renowned in the manufacturing of ships logs, founding father, Thomas Walker (1805–1871), an engineer in Birmingham, patented a mechanical log in 1878 which was a recording instrument that attached to a rail at the stern of a vessel connected by a long cord with a rotor which was towed behind the ship. The instrument dial recorded the distance travelled. Thomas Walker first went into business to manufacture stoves at 58 Oxford Street Birmingham. Walker’s self-feeding stove was widely lauded at the Paris Exhibition of 1855, winning a prize medal and kick starting the first of many notable innovations for the Walker family's manufacturing business. However, it wasn’t until working on an earlier ships log model invented by his Uncle that Thomas Walker became interested in the further development of this device, used to ascertain a ship’s speed. Walker continued to improve on the common log for the company of Massey & Sons and these improvements were deemed revolutionary. This log became a firm favourite of the West India Association (British-based organisation promoting ties and trade with the British Caribbean). and the most common log in use for two generations. It took till 1861 for Thomas Walker and his son, Thomas Ferdinand Walker (1831-1921) to patent the first Walker log of many. Together, with the introduction of the A1 Harpoon Log two years later, they established the Walker Log Business as a force to be reckoned with. By the time of his passing in 1871, Thomas Walker Snr had not only founded a family business with considerable staying power but also instilled a tradition of public service. Having sat as a representative on the Birmingham Town Council for 15 years and played an active role in public works, he was soon given the nickname of ‘Blue Brick Walker’. Much like his father, Thomas Ferdinand Walker changed the face of the maritime industry. His patent of 1897, the ‘Cherub’ log, was a notable departure from the past providing a far more accurate reading and replacing the majority of logs of the age. They were the first to produce an electric log and the Walker factory was one of the first to introduce the 48 hour work week for employees. This ship log rotor was invented and made by a significant marine instrument maker and innovator of machinery. It demonstrates the huge leap taken to improve navigational accuracy at sea with an instrument that was in use for decades and still is today. Therefore it is a worthy addition to the Flagstaff Maritime collection as it demonstrates another aspect of maritime navigation.A Walkers Cherub III Patent mechanical ship brass rotor with with four vane's one marked with an anchor and "T. W. Cherub 441", The log is attached to a brass swivel with a short length of rope. Has T W Cherub 441 marked on a vane.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, log rotor, taffrail log, thomas walker, marine technology, marine instrument, navigation, ship speed, measurment
