Showing 2957 items matching "stage"
-
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchGrenade
Production stages for an M26 Grenadeammunition, army -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Ian McCann, Main Street - Gold Reef Mall, c 1987
Working ofn the mall Stagegold reef mall -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, 'No, No, Nanette, 1968
Stage production at Mechanics Hallmisc., local identities -
![Photograph (Framed), Diamond Valley Community Hospital [site], 1942c](/media/collectors/4f729f5697f83e03086015b8/items/53f81ce52162f11310859ab2/item-media/53f81ea02162f1131085a77a/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyPhotograph (Framed), Diamond Valley Community Hospital [site], 1942c
The Diamond Valley Community Hospital was established in 1942 in Grimshaw Street Greensborough. Prior to the hospital, health services had been limited.The Hospital closed in 2000.A photograph of the house on the Diamond Valley Hospital site. This area on Grimshaw Street now houses many medical services in what was once the Diamond Valley Community Hospital.Black and white photograph of house with two people walking past."In 1942 this dwelling became the first stage of the Diamond Valley Hospital".dvch, grimshaw street greensborough, diamond valley community hospital -
 Bialik College
Bialik CollegePhotograph (Item) - Jewish Arts Festival 1988
Sunday 27 March, 1988 the Jewish Festival of the Arts was held in Caulfield. It was estimated by a journalist from the Australian Jewish News that between 7000 and 10 000 people were in attendance. Bialik Dance Troupe performed during the six hour event, sharing the stage with soloists, duos, bands, and choirs. The moto for the event was "In One Voice". judaism, bialik college, dance, 1988, 1980s -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomPhotograph, 1980's
A colour photograph of the 4th/19th PWLH Band on stage. The stage is an arched formation. The Bandmaster is shaking hands with the MC. There is no indication of location.band -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: BAND ON STAGE
Colour photograph. Band members on stage in large marquee. Hessian facing on stage. Some audience visable. Banjo, guitar, lute.entertainment, music, bush band -
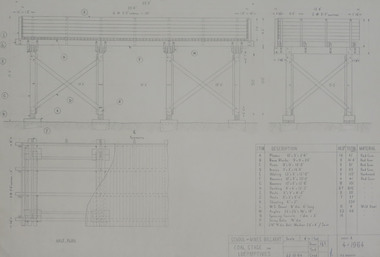 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDrawing - Engineering drawings, Technical drawings, 1964
pencil on paper student's technical drawings .1) Coal stage for locomotive - assembyy .2) Coal stage for locomotive - connection detailstechnical drawing, p. j. shedden, school of mines ballarat -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph
Phillip Island Cemetery dates from 1870Photograph of early stage of Garden of Remembrancelocal history, photography, photographs, slides, film, phillip island cemetery, garden of remembrance, coloured photograph -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesDocument, Concept Proposal VCAH - Burnley, 1984
Proposal for Stage 1 building developmentvcah, burnley -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPhotograph - Image, Dusk view of 1992 Carols by Candlelight, 24/12/1992
Twilight descends as the crowds light up the Sidney Myer Music Bowl as the Carols by Candlelight performance begins in 1992.Col. photograph of Carols by Candlelight stage.carols by candlelight, royal victorian institute for the blind, fundraising -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, No, No, Nanette, 1968
Stage production held at Mechanics Hallmisc., local identities -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c 1989-1990
A set of 12 photographs of the 'Enterprize Project' showing the different stages of the rebuilding of the historic schooner 'Enterprize' which brought early setters to Victoria from Tasmania in 1834. George Evans who settled in Sunbury was one of the schooner passengers.A coloured photograph of the early stages in the reconstruction of the schooner 'Enterprize'. The ribs of the hull are exposed and some of the boards around the sides of the hull have been fitted. The structure is on a raised scaffold under an open shed. A painted sign 'Enterprize Project' shows details of the project is under a wooden stairway.schnooner 'enterprize', evans, irene, south wharf - melbourne, enterprize project, shire of bulla, george evans collection -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Murals with descriptions inside the Town Hall 1930
Details of a decorative murals taken from The Weekly Times Diamond Jubilee Celebrations. The decorative mural is on the righthand side of the town hall stage. Three smaller images (floral) are on the right hand side of the mural. The artist of the murals was Will Rees.Enlarged black & white photograph of a mural with a woman seated holding a musical instrument. The image is an enlargement of the righthand panel beside the stage in the town hall. The enlargement taken from the Weekly Times newspaper cutting of the Stawell Diamond Celebrations The paper was handed on to the Society by Stawell Athletic Club.stawell -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph
BLACK AND WHITE PHOTOGRAPH OF OFFICIAL PARTY. CATHOLIC BALL. TAKEN ON STAGE AT CLUNES TOWN HALL. FATHER O'SHANNASY SEATED ON LEFT OF STAGE.local history, photography, photographs, events and celebrations -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: BAND ON STAGE
Black and white photograph. Band on stage in tartan waistcoats people dancing and watching below the stage. Peter Ellis playing with Wedderburn Oldtimers.entertainment, music, bush band -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - CAC Collection - Technical Information - ATAR 09C Turbojet Engines
Compressor Rotor Fatigue Test on 1st 3rd and 4th Stage Blades -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Ringwood Anzac Service. c1950's
Black and white photographImage shows Cr Lavis and other personalities on stage at the Anzac Service. -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Portland Library, 13/01/2000
Coloured photo. Portland Library. Woman and young girl standing in front of mock 'stage'. The stage has yellow curtains with an orange velvet border.Front: '00 1 13'portland library, community, council services, event, amateur dramatics -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CASTLEMAINE GAS COMPANY COLLECTION: PHOTO PEOPLE
Unknown Male on stage making a speech at a Gas and Fuel event, a second male on stage - Date and Location Unknown - Several people sitting at tables.Fujiorganization, business, gas and fuel -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Ruth Swan's Entertainment - undated
Large group on stage (adults and children) in costumeCatalogue card reads, "Ruth Swan's Entertainment - undated". -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Film - Film, DVD, Australian Entertainers, Luscombe Bowl, Nui Dat - Vietnam, 1968-1969
Actual footage of some 'entertainers' performing on stage.entertainers - vietnam war, luscombe bowl -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph, RSL Hall Murchison, 1941-1946
Hans Walter von Gruenewaldt was a German POW who used his artistic ability to paint several large mural caricatures while he was held at Camp 13 at Murchison. The technique he used was colourful house paint, painted directly onto the walls of the German mess hut, reading room and recreation hall in compound 13D. The paintings were completed over a duration of six years (1941-1946). Colour photo of stage of the RSL Hall Murchison.hans walter von gruenewalt, german pow's, camp 13 murchison, pow camps, caricatures -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Realia, 1995
Certificate of First Stage of Museum Accreditation Certificatestawell -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPhotograph - Image, Free Lending Library of the Blind building opening, 1919
In 1894 the Victorian Braille Writers Association was established in order to create a braille lending library. Such an endeavor also meant a need of space for storage. At first the library was accommodated in the home of Mrs May Harrison before moving to the home of Mrs Dickinson two years later. Eventually, with the help of donors, a space was rented in the Block Arcade to house the 1300+ volumes it held and the yearly increase produced by its braille transcribers. Fortunately in 1918 the Trustees of the Edward Wilson Estate provided 4000 pounds to pay for a new building in Commercial Road. Despite some misgivings from the RVIB at the time, this building was home to both braille volumes and talking books (albums and cassettes) for many years.1 b/w photograph of people on a stageFree Lending Library for the Blind. Senator G. Fairbairn, on behalf of the Edward Wilson Trust, presenting the key of the building to Miss Aston, a Braille reader, representing the Braille Writer’s Association. 26th April 1919. (Label on mount board)tilly aston, braille and talking book library -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: MUSICIANS ON STAGE
Colour photograph. Musicians on stage. Other people sitting on chairs in front of stage facing audience. Piano accordion. Lute. Violin. Harmonica. Mouth organ.entertainment, music, bush band -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - CAC Collection - Technical Informations ATAR 09B And 09 C Turbojet Engines
Compressor Rotor Improvement Of The Operational Behaviour On Compressor Rotor 3rd Stage Blades -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White, Bill Durant (probably), Mount Helen Campus, 1970, c1970
This photograph was most probably taken by lecturer Bill Durant who was a staff member on the Mount Helen Campus from 1970Views of the Stage one buildings on the Mount Helen Campusfederation university, federation university australia, feduni, ballarat institute of advanced education, durant -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Reclamation, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, reclamation -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Stage & Foundations, Port Melbourne Town Hall, Port Melbourne City Council, 1916
Plan - details of stage and foundations for the 1915 Town Hall.port melbourne town hall, built environment - civic, city of port melbourne engineering dept
