Showing 370 items
matching timber construction
-
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Schache, Scott, Bananacoast Railway Rails of the Coffs Coast: A Century Plus of Service 1906-2015, 2015
A history of the railways around Coffs Harbour in Northern New South Wales from 1906 to 2015 including the New South Wales Government Railways and narrow gauge timber tramways.ill, maps, p.88.non-fictionA history of the railways around Coffs Harbour in Northern New South Wales from 1906 to 2015 including the New South Wales Government Railways and narrow gauge timber tramways.railroad construction - new south wales - history, railroads -- new south wales -- coffs harbour -- history -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Dare, John, Timber, Spuds And Spa, 1978
A descriptive history and lineside guide of the railways in the Daylesford District 1880-1978.index, ill, maps, p.58.non-fiction A descriptive history and lineside guide of the railways in the Daylesford District 1880-1978.railroad operations - victoria - history, railroad construction - victoria - history -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryDare, John, Timber, Spuds And Spa - Revised and Enlarged Edition, 1993
A descriptive history and lineside guide of the railways in the Daylesford District 1880-1993.index, ill, maps, p.84.non-fiction A descriptive history and lineside guide of the railways in the Daylesford District 1880-1993.railroad operations - victoria - history, railroad construction - victoria - history -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBooklet, Turton, Keith, Farewell to the Timber Line, 1968
A brief history of the Heathcote Junction to Bendigo and associated railways issued in conjunction with the running of the last train to Heathcote on 9th November 1968 by the Australian Railway Historical Society.ill, maps, p.36.non-fictionA brief history of the Heathcote Junction to Bendigo and associated railways issued in conjunction with the running of the last train to Heathcote on 9th November 1968 by the Australian Railway Historical Society.railroad construction - victoria - history, railroad operations - victoria - history -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Anchen, Nick, Railways of the Yarra Valley, 2010
... Railway construction - Victoria - history Timber tramways ...A short history of the railways in the Yarra Valley including the line to Healsville and Warburton and narrow gauge timber tramways.ill, maps, p.96.non-fictionA short history of the railways in the Yarra Valley including the line to Healsville and Warburton and narrow gauge timber tramways.railway construction - victoria - history, timber tramways - victoria - history -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionAward - Royal Mint Building Award, JA Dodd Excellence in Construction
2002 Excellence in Construction AwardsFramed Award 2002 Excellence in Construction Awards, JA Dodd LTD, Excellence in Construction, (Existing Buildings) Under $2 million, Project: The Royal Mint Building, Architect: Robert Peck von Hartel Trethowan, Location: 280 William Street Melbourne, J A Dodd Ltd's refurbishment of the historic former Royal Mint Building delivered to the client's specification in retaining the features of this historic building, while at the same time providing modern office accommodation with state of the art facilities. New works have been defined by a modern style encompassing glass, stainless steel and flush surfaces, offering a stark departure from the ornate finishes of the original building. Traditional timber mouldings, tiles stonework and intricate paint methods have been used only where repairs to the existing building were required. The judges praised the superb job and made special mention of the exposed roof trusses. 38 master builder awards -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Presentation plaque from the "Woodpeckers"
In the post-war era from 1947 to the mid-1980s, the Forests Commission sponsored Australia's only military sawmilling unit, the 91 Forestry Squadron. It was a special reserve unit of the Royal Australian Engineers (RAE). Established and commanded by Commission forester and WW2 veteran, Major Ben Benallack, the "Woodpeckers" as they were known comprised a small pool of specialised soldiers capable of rapid mobilisation in the event of need. Several other Victorian departments such as the State Electricity Commission (SEC) did the same thing who supported a construction squadron based at Newborough in the Latrobe Valley. The scheme created a very active and capable part-time military group that completed many worthy projects across the State. In addition to their military training, the Woodpeckers operated bush sawmills, built timber bridges along the Murray River, the Snake Island Jetty, forest roads and performed various demolition tasks.Presentation plaque from the "Woodpeckers" Mounted on polished wooden burl forests commission victoria (fcv) -
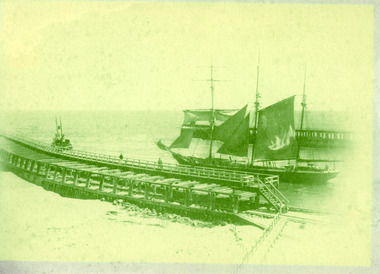 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Frank Guy, 1891
Frank Guy took timber and piles from Gippsland to Melbourne for wharf constructionSepia photograph of the masted barquentine Frank Guy with sails up being towed out the entrance by the S S Stormbird. Timber entrance piers quite distinct. Lakes Entrance Victoriawaterways, historic ships, piers -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Monash Bridge, Hurstbridge, 23 January 2008
Monash Bridge spans the Diamond Creek at Hurstbridge. It was built in 1917 for the Shires of Heidelberg, Eltham and Whittlesea. It is considered Nillumbik Shire's finest engineered bridge and was construced by the engineering company of Sir John Monash. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p117 Monash Bridge is considered the Shire’s finest engineered bridge and was constructed by the engineering company of that great Australian, Sir John Monash.1 The bridge spans Diamond Creek on the Hurstbridge-Arthurs Creek Road, linking Hurstbridge with Yarrambat and Arthurs Creek. Monash Bridge, also called Hurst’s Bridge, was built in 1917, by the Reinforced Concrete and Monier Pipe Construction Company Pty Ltd, for the Shires of Heidelberg, Eltham and Whittlesea. Although Monash was probably in action overseas during World War One when the bridge was designed and constructed, he evolved the basic design in the 1900s and it was a standard design for the firm. However J A Laing, a designer at the firm, was probably the designer, as his initials are on bridge drawings held by the Eltham District Historical Society.2 The bridge is an excellent early Australian example of an open spandrel reinforced concrete arch bridge and has a single span of 29 metres. It is unusual in Victoria, but similar to many reinforced concrete arch bridges in Europe and America, built from the late 19th century. In Victoria, Monash pioneered the use of reinforced concrete – then a revolutionary construction material. His company, Monash & Anderson, had the exclusive licence for the Monier patent for the system of reinforced concrete construction for Victoria and New South Wales. A well-known example of the Monier arch bridge is the Morell Bridge in South Yarra. The sweeping arch of the Monash Bridge combines grace and utility and blends with the surrounding rural landscape. Its design and construction have allowed it to carry increasing volumes of heavy traffic, but in modern times the one lane is considered by some to prevent easy passage through Hurstbridge. However others consider this an asset to deter too much more traffic, which would diminish Hurstbridge’s charming rural character.3 This is the third bridge across the Diamond Creek at this site. The original bridge was a log bridge upstream, constructed in the 1850s by early settler, Henry Hurst, after whom Hurstbridge was named. The bridge spanned the creek, where it divided his family’s property. In the 1880s a timber bridge replaced it, known as Hurst’s Bridge. However a more permanent bridge was considered necessary when the new railway arrived in 1912, bringing with it expectations of growth in the town and the surrounding fruit-growing district. Monash Bridge’s official opening on November 3, 1917 was a gala occasion, which took place before about 1000 spectators. Two who attended the opening had a particularly sound knowledge of the locality. One was Fred Hurst, Henry’s brother, who used to ford the creek at or near the bridge’s site more than 50 years before. The other was John McDonald of Arthurs Creek, who had built the old wooden bridge over the creek about 40 years earlier.4 Although John Monash was a fine engineer, his fame came from his brilliant war career, rather than from his engineering or his many other achievements. Monash was Corps Commander of the Australian Forces. His brilliance was recognised with his awards: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of St. Michael and St. George, and Knight Commander of the Bath. Monash was also decorated by the French, Belgian, and American Governments.5 After the war, Monash worked in many prominent civilian positions, the most notable as head of the Victorian State Electricity Commission. He was a leading and loved public figure, involved in many public and private organisations. He was president of the Australian Zionist Federation and involved in the Boy Scouts. Monash University is named after him. By the 1920s Monash was probably regarded as the greatest living Australian.6 Despite most of his life working as an administrator and leader, rather than a fighting soldier, he became integral to the ANZAC legend. Monash died in 1931.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, hurstbridge, monash bridge -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Former home of Professor William MacMahon Ball, York Street, Eltham, 24 May 2007
Situated at the eastern end of York Street, Eltham, 'Shinrone', the former home of Professor William (Mac) MacMahon Ball was one of the first in the Shire of Eltham to incorporate mud-brick. Professor MacMahon Ball, a political scientist, writer, broadcaster and diplomat and family moved to York Street, Eltham in 1945 into a timber cottage built around the 1890s and in poor repair. Mac asked Alistair Knox to renovate the home and he expanded the living area and added verandahs. In 1948 Montsalvat artist and sculptor Sonia Skipper supervised the building of most of the mud-brick studio. Neighbour Gordon Ford made the mud-bricks. Mac also asked John Harcourt, who had worked with him as a journalist in shortwave broadcasting, to build a pise (rammed earth) and stone addition to the largely timber house. Harcourt built two bedrooms - including an attic bedroom - a balcony with a shower and toilet, a nd a fireplace and chimney of local stone. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p141 At the eastern tip of York Street, Eltham, stands Shinrone, the former home of one of Australia’s intellectual leaders. Professor William Macmahon Ball, was one of the first to bring Asia as a foreign policy issue to the Australian public.1 He was a political scientist, writer, broadcaster and diplomat. The house was one of the first in Eltham Shire to incorporate mud-brick,2 because of the acute shortage of building materials after World War Two. Its novice builders later become leaders in Eltham’s built and garden design. Mac (as he was usually called), who was the son of a Church of England minister, was born in Casterton, Victoria in 1901 and died in 1986. In 1945 he helped establish the United Nations, as political consultant to the Australian Delegation at the San Francisco Conference.3 Then in 1946 Mac was appointed British Commonwealth Representative on the Allied Council for Japan, which is recorded in detail in his diary.4 In 1948 Mac led an Australian Government Goodwill Mission to South East Asia. However, Mac was perhaps most successful as an academic and public speaker.5 He was a commentator on the Australian Broadcasting Commission, from the early 1930s to the early 1960s. He was also Controller of the Short-Wave Broadcasting Unit during World War Two, which later became Radio Australia. From 1923 he taught at The University of Melbourne, then became foundation Professor of Political Science in 1949 and was Chair until his retirement in 1968.6 In 1942, as the government expected a Japanese invasion, Mac’s wife Katrine and their only child Jenny, moved from Kew to Eltham as temporary evacuees. However Mac and Katrine lived in Eltham for almost the rest of their lives. After staying with friends, they rented a house in Reynolds Road, where, as it was wartime, they needed to keep horses for transport and a cow and poultry for milk and eggs. In 1945 the family moved to the house at York Street, which was then a timber cottage, built around the 1890s and in poor repair. The underground well, cellar and part of the garden are all that remain of what stood on the original 18 acre (7.3ha) allotment. Thanks largely to Katrine’s hard work, the house was gradually renovated and extended. The long rambling house was partially built by several young neighbours, who were inspired by the cheap mud-brick and stone building style of Montsalvat, the Eltham artists’ colony. Mac asked Alistair Knox to renovate Shinrone, named after an Irish village near Katrine’s family home. Knox later popularised the mud-brick style of house construction, for which Eltham became known. He expanded the living area and added verandas. In 1948 Montsalvat artist and sculptor Sonia Skipper supervised the building of most of the mud-brick studio. Another neighbour, Gordon Ford, who was to have a major influence on the Australian garden style, made the mud-bricks. Mac also asked John Harcourt, who had worked with him as a journalist in short-wave broadcasting, to build a pisé (rammed earth) and stone addition to the largely timber house. Harcourt built two bedrooms – including an attic bedroom – a balcony with a shower and toilet, and a fireplace and chimney of local sandstone. With pioneering work naturally came mistakes, including one particularly dramatic incident when Harcourt was building walls with unsupported sections. Jenny Ellis, Mac’s daughter, remembers being awakened from sleep by a thundering shudder. The wall of her room had fallen down – fortunately away from her! In 1950 artist Peter Glass – another neighbour and later landscape designer – built Katrine a mud-brick pottery. As a result, the house features at one end Harcourt’s characteristic steep gable roof, while at the other the flatter construction characteristic of Knox. Mac referred to the home as the Eltham ‘experimental building site’.7 Surprisingly, the combination works, perhaps partly because it has the warm inviting feel of timber, mud-brick and stone.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, alistair knox, gordon ford, john harcourt, mudbrick construction, pise construction, professor macmahon ball, shinrone, sonia skipper, york street -
 Victorian Railway History Library
Victorian Railway History LibraryBook, Chambers, Don, Wooden Wonders: Victoria's Timber Bridges, 2006
A history of wooden bridges in Victoria, rail, road and pedestrian.index, ill, maps, p.207.A history of wooden bridges in Victoria, rail, road and pedestrian.bridges - victoria - design and construction, bridges - victoria - history -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncBook, Eltham War Memorial Trust, A favourite book of country recipes / compiled by the Women's Auxiliary of the Eltham War Memorial Trust, 1958
46 page book produced by the women of the Shire of Eltham as a fundraising project for the construction of the WW2 Eltham War Memorial. Contents: I. Fish, II. Meat, III. Puddings and desserts, IV. Bread and scones, V. Cakes and biscuits, VI. Jams, marmalades and chutneys, VII. Salads, dressings and sauces, VIII. Drinks. 47 p. : ill., b&w., ; 19 cm. a. & s. davis pty ltd, a. boyd-graham, a. lyon, a. mezner, a. uglow, a.m. lynes, b. clark, b. rothwell, b. thomas, b.j. brinkkotter, b.m. gresford, b.w. morrison, betty p. metcalfe, briar hill timber & trading, c. may, c. pelling, c. smith, cold comfort farm, commercial bank of australia, cook-book, cooking, d. garratt, d. richards, d. warner, d.g. wills, draffin bros pty ltd, e. egan, e. hoppner, e.i. rains, e.s. rothwell, eltham home supplies, eltham hotel, eltham motor garage, eltham real estate & business agency, eltham war memorial trust, f.j. burgoyne, g.b. gresford, gas and fuel corporation of victoria, george lovitt & co pty ltd, guest's biscuits, h.w. downing, heidelberg district bakery, i. putnam, j. & j. burgoyne, j. kimber, j.m. attiwill, jack burgoyne, kraft cheddar, l. carter, lyon bros garage, m. banks, m. battye, m. black, m. erswell, m. foletta, m. johnson, m. roletta, m.h. bucknell, m.j. loosli, millett's foodland, n.h. baxter estate agent, n.h. baxter, new bridge building supplies, m. banks, m. battye, m. black, m. erswell, m. foletta, m. johnson, m. roletta, m.h. bucknell, m.j. loosli, millett's foodland, n.h. baxter estate agent, n.h. baxter, new bridge building supplies, o. holland, o.a. brown, p. moore, p. pease, p. peel, p. reece, presswell's eltham east auto service, r.j. scully, rains, recipes, research meat supply, research post office and general store, s. littlehales, stanley s addison, t. sawyer, t.e. & e.m. moran, v. addison, v. hughes, valley furniture, women's auxiliary, cookery, fundraising -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPrint - Framed print, The Great Grey Raider
On the night of August 24, 1941 HMS Kanimbla, with 300 Indian troops on board led a flotilla in a surprise attack on the Iranian port of Bandar Shahpur capturing eight German and Italian merchant vessels all containing valuable cargoes, as well as two Iranian gunboats and a floating dock. Kanimbla went alongside the burning Italian tanker Bronte and fought the fires while engaging a train with her main armament and with her 3-inch guns. She remained in the region until October 11, supervising the port and carrying out salvage work on the captured vessels, including salvage work on the German freighter Hohenfels. After further work in Indian waters during the latter part of October and November, Kanimbla proceeded to Singapore and escorted the first convoy out of that city after the Japanese attack on Malaya. She arrived in Melbourne on Christmas Day. She carried out further convoy work off the Australian coast and in both the Indian and the Pacific Oceans. At the end of the war HMAS Kanimbla was employed in repatriating Australian servicemen from the Pacific Islands and also in returning Dutch dependents to the East Indies (Indonesia). Between October 1946 and June 1948 she sailed between Australia and Japan transporting British Commonwealth Occupation Forces. MS Kanimbla was unique for many reasons, she was the only passenger liner in history to have a fully operational radio broadcasting station built into the ship at the time of construction. The equipment was manufactured by AWA in Australia and had been shipped to Ireland for installation whilst the ship was still under construction.Brown timber frame housing white mount and dark blue print with grey ship in the centre above list of names below and top right and left corners.THE GREAT GREY RAIDER Captured 22 Ships, / Floating Dock, / 1Train Ships captured: Weissenfels, Wildenfels, V. Mayakovsky, Sheng Wha, Marienfels, Karakoram, Hathor, Winford, Sturmfels, Hohenfels, Store Nordiske, Tonjer, Chahbaaz, Barbara, Talisman, Corona, Carboto, Dah Pu, Sygna, Gabon, Bronte, Agnes Pre War: M.V. Kanimbla, McIlrath McEachern Line, 12000 Tons War: Commissioned as H.M.S. & Later H.M.A.S as armed Merchant Cruiserkanimbla, great grey raider, hohenfels, bronte, ww2, 1941 -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph - Framed photograph, Le Dawn Studio Pty Ltd Photography & Framing, Life Member Gordon Barnard
Joined R.A.A.F. 1943. Served in Australia and S.W.P.A with the 8th Airfield Construction Unit. Joined Wangaratta Sub-Branch in 1947. Served as RSL State Councillor, Past President of 34th Dist. Board and member of Legacy for ten years. Made life member in 1987Timber framed photo of Life Member - Gordon BARNARDGORDON BARNARD Joined R.A.A.F in 1943. Joined Wangaratta Sub-Branch in 1947. Served on the committee for many years and was made a Life Member in 1987gordon barnard, 8th airfield contruction unit -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Alistair Knox Park, Eltham, 2008
Alistair Knox Park, an oasis of peace and beauty. Covered under National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Landscape Significance and Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p173 It is hard to imagine that the Alistair Knox Park, an oasis of peace and beauty beside busy Main Road, Eltham, was once the township’s rubbish dump. It was only in the 1970s that the tip was transformed into this beautiful six hectare space, which later earned it a National Trust Landscape classification. Before its life as a dump, the area was used for small farms. Thanks largely to the foresight and efforts of local environmental builder Alistair Knox, the park was designed sympathetically with the character of the wider Eltham landscape. Then, appropriately, the park was named after Knox, who was an Eltham Shire Councillor from 1971 to 1975 and Shire President in 1975. The park designers were four major forces in the urban bush landscape garden –Knox, landscape designer Gordon Ford, artist Peter Glass and landscaper Ivan Stranger. The National Trust citation for the park, originally called Eltham Town Park, includes the Eltham railway trestle bridge and the Shillinglaw Cottage. The citation states ‘the semi-natural setting of the parkland provides a landscape which is evocative of the history of the area’. Manna Gums (Eucalyptus viminalis) and Candlebarks (Eucalyptus rubida) are significant features. Most of the park’s construction was directed by Bob Grant, Superintendent of the Parks and Gardens Department for the Eltham Shire Council. First plantings occurred in Arbour Week in 1973, then the lake and botanic area were completed in 1975, with Federal Government funding, and the toilet block in 1978. Bounded by the Eltham railway line, Panther Place, Main Road, Bridge and Susan Streets, the park is in a valley about a kilometre wide overlooked by steep hills at the east and west. The Diamond Creek flows through it and the picturesque historic timber trestle railway bridge edges the north. Informal plantings of Australian indigenous and native species in open and undulating grassed settings blend with the natural landscape of the Diamond Creek to the west. The bush-style plants, particularly around the creek, balance with open lawns, paths and a cascade flowing from a small lake to another below. A footbridge over the creek leads to the park’s west. The park includes an adventure playground and barbecue areas. The park stands on part of the land bought from the Crown in 1851 by Josiah Holloway, who subdivided it into allotments and which he called Little Eltham. Most of the land was subdivided into residential lots, but the creek valley, on which the park stands, was subdivided into farm-size lots, used mainly for orchards and grazing. One of the earliest owners was John Hicks Petty, who in 1874 bought a plot from Holloway. Other families who owned properties in that area, included Rees, Clark, Waterfall, Graham, Hill and Morant. In 1901 the railway was built through the area. Jock Read, an Eltham resident since around 1920, remembers several farms in the 1920s and ’30s that occupied the site of today’s park. A poultry farm, which extended from present day Panther Place, was owned by the Gahan family. Next to that farm was another for grazing cattle owned by Jack Carrucan. Beside this was land owned by John Lyon. A doctor lived beside this, and at the north-west corner of Bridge Street and Main Road stood a memorial to the soldiers who died in World War One, which was later moved to the RSL site. Mr Read also remembers other farms and orchards west of the creek In the early 1960s the Eltham Council began buying these farms and in the late 1960s turned the areas east of the Diamond Creek into a garbage tip. When this was filled above the creek’s flood plain, the tip was moved to the west of the creek.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, alistair knox park, eltham -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Bridges, Lakes Post Newspaper, 1991
This photo appeared in the Lakes Post Newpaper 24 July 1991Black and white photograph looking under the decking of the new Princes Highway concrete bridge over Toorloo Arm, showing the support pier shaped to fit the camber of the curved bridge. Timber bridge in left of image still in use. Toorloo Arm Victoriabridges, construction -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, Mason, John
Captain John Mason came from Stirling in Scotland, arriving at Port Fairy in 1844. One year after James Atkinson obtained his Special Survey of the area. Thus his life covers all the history of Port Fairy when it was known as Belfast. He married Jane Murray in Portland in 1846 and they had 5 children, Jane died in 1855 and ten years later he married Ann Brown widow of Abijah Brown. They had no children and she died in 1887. In due course he became known as Captain Mason, he was not a sea captain, but captain of the Belfast Volunteers, a Rifle Corps formed in 1859 as a consequence of the Crimean War, and later reconstituted as the Belfast Volunteer Corps. For 40 years he displayed a remarkable versatility in his various occupations. Starting as an Innkeeper - he took over the Stag Inn from Captain Saunders in 1852, for 3 years. He then became a carpenter, stonemason, architect, estate agent honorary technical advisor to the Borough and treasurer to the Shire, and Savings Bank Secretary. They thought so well of John mason in Belfast that they elected him to the first Roads Board in 1853 and to the first Municipal Council in 1856. He was Chairman four times and with Councillors David Talbot and Joseph Whitehead designed the Council's Common Seal and the Motto "Commune Bonum".He was the first Mayor of the Borough in 1863 for a period of 7 weeks. He was responsible for the design, supervision or construction of many of the buildings in the town; most still standing today. He built the Rosebrook Bridge in 1855 and the first official Post Office ( a timber structure in Bank Street) in 1857, replacing it with a stone office in 1865. he built the Court house in 1859 and completed the breakwater between Rabbit Island and Griffith Island started by James Atkinson and John Griffith in 1849, also the first bridge over the Moyne river which connected with Battery Lane and the Bay. Among the many buildings associated with John Mason are Gobles Mill, Tynemouth Villa, 10-12 Princes Street, the Mechanics Institute, the Commercial Hotel, Yambuk and Mickey Bourke's Pub in Koroit. However, he did not build "Riverdale" in Gipps Street as is thought. He had a store and workshop on this site but sold the property in 1872 before the house was built. After an almost uninterrupted term as Councillor starting with the Municipality in 1856, John resigned from the Council in 1873. He well deserved the illuminated address they gave to him and the toast that they drank in the Bank Hotel champagne. Within the year he was working for the Borough as its engineer., surveyor, general supervisor and advisor of public works, simply as the man to whom all difficult problems were referred and at very little expense. John Mason was a great worker for his town and devoted himself unsparingly to the community. That his work was appreciated was shown by the way in which people rallied to his aid when, in the end, he found himself in financial difficulties and his reputation was challenge; arrested for embezzling from the Savings Bank of which he was the actuary in 1882. The money was repaid and the charges found not proven at his trial. He was an early member of the Loyal Prince Albert Lodge, and a founding member of the smaller Loyal Belfast Lodge in 1863. He was also a member of the Horticultural Society. Captain John Mason Died on the 14th of October 1891 (see also 62-04-046 photo)Sepia photograph on heavy cardStevenson & McNicoll photo. 108 Elizabeth Street Melbourne copies can be obtained at anytimedefence, captain, mason, carpenter, councillor, mayor -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Radio Transcript, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Wireless talk - "inside information regarding tramcars", Jul. 1926
Radio transcript - 12 foolscap sheets, typed. Although not named, appears to have been prepared for or by Mr. Strickland describing "inside information regarding tramcars". Notes cable trams, conversion, sale of trailers and dummies or grip cars, the variety taken over from the trusts, design of new cars (180 in service at the time of the report), open cars vs closed cars, seating and standing capacity, speed, braking system, step heights, destination signs, lifeguards. Gives a description of Preston Workshops, finishing soon, description of the tramcar construction, roofing, painting, sourcing of materials, timbers, cost per tram of 3250 pounds, depots, breakdowns, overhauls, workshops, collision repairs in 1925, construction of 10 safety cars. Vicsig.net gives that X1 461 entered service in Sept. 1926. Pinned to the file by Robert on the rear of TMSV Raffle ticket is a note "Electrical Engineer 15/7/26 p35 "C. H. Wickham gave recent address broadcast on 3LO"In blue pencil in top left hand corner appears to be "Wickham"trams, tramways, tramcars, preston workshops, new trams, sale of trams, cable trams, destination roll, tram brakes, tramcar equipment, x1 class, w class, depots, radio stations -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Untitled - "SW6 class", May. 1939
Report - 7 quarto typed sheets - untitled, but gives a detailed description of the design basis and construction of the SW6 class tram. Dated May 1939. Details the design after Bell's overseas trip the previous year. Details dimensions, seating, ventilation, seating, doors, structure, construct, timber, materials, door engines, cab equipment, PA system, interior appearances, flooring, colours, lighting, conductor's bell / signals, trucks, bolster, wheels, brake shoes, braking, motors, acceleration, performance, controllers, contactors, compressor. Gives a detailed list of the specifications.Has a note in pencil about a typographical error on the bottom of the sheet.trams, tramways, sw6 class, specification, tramcars, tram controllers, tram equipment, tramcar design -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumAlbum - Photo Album, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Construction of depots and workshops, mid 1920's
Photo Album - brown manila card sheets as covers, containing 20 blue card sheets trimmed with white binding tape and held by two brass clips, containing the following photographs: South Melbourne depot - substation, construction, steelwork, inspection pits, offices, girders. overhead stores Preston Workshops - body shop, timber sheds, machine shop, steelwork, crane runways Sydney Harbour bridge steelwork. Three loose photos. For individual photo images of each page see: \dbtext\hawthtramcoll\photo collections\htd5526 - KC Painter Material /Early MMTB Depots-album images KCP01 to KCP20 KCP01_MMTB-depot-construction_cover.jpg KCP02_SouthMelbourne-1.jpg KCP03_SouthMelbourne-2.jpg KCP04_SouthMelbourne-3.jpg KCP05_SouthMelbourne-4.jpg KCP06_SouthMelbourne-5.jpg KCP07_PrestonWorkshops-1.jpg KCP08_PrestonWorkshops-2.jpg KCP09_PrestonWorkshops-3.jpg KCP10_PrestonWorkshops-4.jpg KCP11_PrestonWorkshops-5.jpg KCP12_PrestonWorkshops-6.jpg KCP13_PrestonWorkshops-7.jpg KCP14_PrestonWorkshops-8.jpg KCP15_PrestonWorkshops-9.jpg KCP15_PrestonWorkshops-10.jpg KCP16_Kew-extensions-1.jpg KCP17_Kew-extensions-2.jpg KCP18_OverheadDepot_SouthMelbourne.jpg KCP19_WaterTower_SouthMelbourne.jpg KCP20_SydneyHarbour-Unknown.jpgLetter "MMTB", "R T Alsop"? and "7" in ink on front cover as well as list of the photographs.trams, tramways, photo album, south melbourne depot, preston workshops, kew depot, sydney, substation, construction, buildings -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s, 1926
Black and white photograph of Preston Workshops, possibly soon after construction or during construction. Looking from the St Georges Road gate,. or North East. The overhead has been put up, tracks laid using wooden sleepers. The traverser between the Paint shop and the body shop can be seen. Prior to the timber store being constructed. C1926trams, tramways, preston workshops, construction, trackwork -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Slab Kitchen
A slab construction cottage built in Ripplebrook in 1880 as a home for a single female landowner by the name of Ada Donaldson, and later relocated to Labertouche. It was donated to Old Gippstown by the Mason-Brook Pastoral Co. of Labertouche. A small building of horizontal timber slabs. It has a verandah over the front entrance and the front porch, a main living area with a cast iron stove in the fireplace and a separate room (probably a bedroom). There is a stone chimney on the back wall and the roof is shingled. Originally a cottage in its own right, the slab kitchen is now a part of the Bushy Park display.Medium local historic significance.A small building of horizontal timber slabs. It has a verandah over the front entrance and the front porch. There is a stone chimney on the back wall and the roof is shingled. This building was built in 1880sout kitchen, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, timber slab cottage, ripplebrook, labertouche, mason-brook pastoral co., baw baw shire, latrobe valley, old gippsland heritage park, gunaikurnai, latrobe city council -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchMixed media - Framed Map and Newspaper, Peter Muncey, 23/7/1943
Sketch Map of Bulldog-Wau Road New Guinea drawn to scale by 2/1 Aust Fd Coy dated 23.7.43 and signed by soldiers together with related newspaper article. Hand sketched by Peter Muncey VX10042 a Draughtsman who served in the Middle East Ceylon and New Guinea with the 2/2 and 2/1 Field Coy Royal Australian Engineers. The sketch contains 26 signatures including:- S/Sgt Raymond Hector Ibbotson NX14112 who served in the Middle East and New Guinea Lt Col Jack Graham Wilson NX 130646Bulldog Track also known as Bulldog-Wau road was longer, higher, steeper, wetter, colder and rougher than Kokoda Track. In 1943 Australian Army engineers; the 2/1 and 2/16 Field Company RAE, 9th Australian Field Company (AIF), veterans of Syria, Palestine, Egypt, Greece and Crete, the 1st and 3rd Australian Pack Transport Companies and local Papuan labour cut the road with pickaxes and dynamite over a period of eight months. During five months of operations over seventy per cent of the 2/1 Australian Field Company contracted malaria.Seventeen bridges were constructed; mostly single, but at least one with multiple spans. More than two thousand Australian army personnel and over two thousand Papuans and New Guineans were involved during nine months of construction. Thus the road, acclaimed as the greatest military engineering feat ever, was completed and for the only time in history motor vehicles crossed the high rugged mountains of Papua New Guinea. Carved brown timber frame with cream mount containing hand sketched map with soldiers signatures and two newspaper articles.Sketch Map of Bulldog-Wau Road 23.7.43 2/1 Aust Fd Coy Newspaper - Diggers pushed on with pick and shovelbulldog-wau road, map, new guinea, ww2, 2/1 aust field coy -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook - Aircraft construction, Materials of Aircraft Construction
... Aircraft construction Alloys .Corrosion Timbers Varnish ...Overview of aircraft construction materials for designer, users & students of aircraft & aircraft engines, circa 1942non-fictionOverview of aircraft construction materials for designer, users & students of aircraft & aircraft engines, circa 1942alloys, .corrosion, timbers, varnish, glues, rubber, fabric & dopes, material selection -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Water Tower Picture Frame
The Water Tower is a major landmark of High Street, Wodonga. Construction of the Water Tower was completed in early 1924 and after thorough testing throughout that year, the completed new water system for Wodonga was officially opened on 4th December 1924. It was decommissioned in 1959. It stood unused until the lower section was modified and put to use as “ The Tower’s Cobbler’s Inn” in 1962. In 1972 Wodonga City Council proposed to demolish the Tower. Their suggestion received an unfavorable response from the city’s citizens, so the Tower still stands today. The community celebrated its centenary on 4th December 2024. This picture frame was created from timber taken from the ladders that were inside the Tower, allowing access to the water tank itself and the external balconies. It was donated to the Wodonga & District Historical Society at the Centenary Celebration.This item is significant because it is made from timber from the original ladders inside the Wodonga Water Tower.A timber frame made from sections of timber from the ladders once part of the Wodonga Water Tower.On sign at base on frame: In 2012, the company I worked for won the contract to replace the wooden internal ladders in the Wodonga Water Tower. The disposal of the ladders was included in the contract. Realising the significance (and age) of the wood, I decided to keep most of it. In 2018, I had Trent Keller of TKEL Furniture in Wodonga design and make a Wine Rack from the ladders. Trent's amazing design kept the "ladder-style" look and produced a beautiful Wine Rack. This Photo Frame has been made from the last remaining rungs. it is both mine and Trent's pleasure to donate this amazing piece of our town's history. Scott Fraser and TKEL Furniturewodonga water tower, landmarks wodonga -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionTool - Joiner or Jack Plane, c.mid to late 1900
A timber plane , or jack plane (or fore plane) is a carpenters or cabinet makers tool that is used for dressing timber down to the correct size in preparation for truing and/or edge jointing.A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that is still in use today. It gives context of how furniture and other finishes were created on timber by the use of cutting edged hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship of the era but also highlights craftsmanship needed to produce a even finish.Carpenters Plane also referred to a Joiner or Jack Plane. Long rectangular shaped timber block with carved timber grip handle, timber block support and blade. Square shaped opening Infront of block and blade, tapers to a small slot to the bottom to allow for the timber shaving to fall through. Stamp mark on metal plane blade: MITCHLL A........(Unable to distinguish further writing) Stamp is in a horse shoe shape with the Mitchll curving around the stop and the word starting with 'A' along the bottom.capenter, wood work, construction, box plane, cabinet maker -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Beauville Avenue, 9, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer Bev Baxter. See also 2104A-12 & 2104A-13.City of Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan Vol 2 p79 (this is p84 of the pdf version) – HO12 Beauville Estate and environs, Murrumbeena: The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. Colour photograph of white rendered house with a second timber storey and the word "Nine" on the front wall. Other features include a curved flat roof above the porch, tiled roof, striped awnings, an unpainted low fence pillar in the foreground and an overgrown side fence. murrumbeena, houses, beauville avenue, architectural styles, 1930's, inter war style, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, brick houses, beauville estate, porches, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, architectural features, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, striped awnings, brick fences, porthole windows -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - LONG GULLY HISTORY GROUP COLLECTION: LONG GULLY, 1976
BHS CollectionCopy of a Bendigo Advertiser 20/11/1976 article titled Historically Speaking A gully with a past - and a present - Long Gully with Amy Huxtable. Mentioned is a study carried out by the consultants Ashton and Wilson, the people who settled in the areas and the houses and miners' cottages. Photos include a miners cottage with a hip and valley roof construction, the Truscott Family home, Rutland House, built for the Koch Family during the quartz era of Bendigo's mining days is now Crusade House, a timber miner's cottage with a kangaroo roof construction and a cottage in William Street. There are also advertisements from various businesses on the page.bendigo, history, long gully history group, the long gully history group - long gully, bendigo advertiser 20/11/1976, amy huxtable, bendigo city council, commonwealth government's national estate program, ashton and wilson, henry koch, truscott family, rutland house, hip and valley roof construction, kangaroo roof construction, vahland villa, helen lang's beauty salon, cane & kitchen, bazulas, myer, kangaroo flat newsagewncy, margaret kean, corrigan's pharmacy, w p bissett, rob vains, golden hills motel, gale's carpet steam cleaners, ray gale, dungey's bendigo travel service -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge Collection
The Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge was constructed by the Country Roads Board in 1939. The date was recorded on a small plaque attached to one of the trestles. The bridge is an important reminder of one of the industries Wodonga was built on — cattle. It was constructed to develop a new stock route between Albury and Wodonga which would direct cattle away from the main bitumen roads and traffic bridges to the Wodonga Saleyards, where thousands of sheep and cattle were sold each month. It is a moderately tall timber trestle road bridge consisting of nine spans, with a deck length of 76 metres and deck width of 4.5 metres, and a maximum span length of 8.5 metres. The substantial timber deck featured decking laid horizontally and longitudinal running planks laid on top of it. The bridge also has timber side safety rails to discourage livestock from straying over the side. The bridge also became the centre of summer social activity for the young people of Wodonga as the area became a gazetted swimming area before the Wodonga Swimming Pool was constructed in 1959. In 1980 the Wodonga Saleyards were relocated to Bandiana to the east of the city. This meant that Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge was no longer needed for its original purpose. Although listed as a significant site by the Victorian Heritage and National Heritage Trust on 3/08/1998, the bridge fell into disrepair and also suffered damage from several floods. A suspension Bridge was constructed beside the Stock Route Bridge in 2013 and the old bridge was closed to traffic. Major damage caused by several floods, including a major flood in 2022 has resulted in the bridge being unsafe and its future is uncertain. The model of the Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge in our Collection made by Mr John Wild, depicts its current condition.The Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge is significant for technical, historic and social reasons and has been registered at the State Heritage level. It is of technical significance as a nine span bridge with tall timber trestles. Large bridges of this type are now very rare in Victoria. It is of historic significance as a surviving structurally authentic bridge designed specifically for livestock and drover use, on a historic stock route. The Stock Bridge is of social significance for its location at a popular riverside leisure spot since its construction in 1939.A collection of photographic images depicting the Wodonga Creek Stock Bridge. It contains both black and white and coloured images taken at different times in the Stock Bridge's history. A model of the Bridge made for Our Society is also included.wodonga creek stock bridge, wodonga heritage -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessels, Sail and Steam Ships, c. 1972-1975
Andy Clapham owned and operated a boat yard on the Maribyrnong River in Footscray, Victoria. The river runs into Port Phillip Bay (sometimes known as Hobson’s bay) at Williamstown, an area with a history of trades associated with the shipping and construction industry. Andy Clapham’s photographs include those of the Reginald M and one of Polly Woodside, another vessel restored and used as a maritime exhibition. Andy Clapham’s letter of 1972 was posted in a and envelope with an early Australian decimal currency stamp showing the profile portrait of Queen Elizabeth II, and valued at 7 cent. Andy offered invaluable advice to the Flagstaff Hill Historic Park Planning Board regarding the purchase a vessel suitable for use as an exhibit once Flagstaff Hill was opened. The Planning Board was set up by the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce and approved by the City Council and State Government. Flagstaff Hill was investigating vessels in Adelaide and Tasmania as well as Melbourne. Andy looked at several vessels in 1972-1973. He also serviced the Reginald M among other vessels belonging to Captain Julian Dyson of Yarra Ferries, who had casually offered the vessel to Flagstaff Hill as a price that was unattainable at the time. Flagstaff Hill later requested photographs of the hull to discern the dimensions and also the condition of the timbers as well as wanting advice on its seafaring capability. In 1972 the Flagstaff Hill Historic Park Planning Board – Chairman J. (John) S. Lindsay (1972-1980), Secretary J. (James) Mark – wrote a letter of appreciation to Mr A. (Andy) Clapham of 3 Charles Street Footscray ... “Dear Mr. Clapham, The Board has asked me to write to you to express our appreciation for the assistance you have offered us through our Chairman John Lindsay. The information you have already given us has been invaluable, in that is shows us that we have not been setting out to do something that is impossible. We look forward to receiving further information from you as it becomes available and we appreciate that you must be busy enough without our problems. Members of our Board hope to call and see you on a trip to Melbourne in the near future. The Board is optimistic about the future of Flagstaff Hill as a Maritime Museum and look forward to you visiting Warrnambool to examine what we believe will be an ideal site. Yours faithfully, James Mark.” ABOUT the vessel “Reginald M” The vessel “Reginald M” was a two-masted, timber coastal vessel built by John Henry Murch in Birkenhead, Port of Adelaide, South Australia. It was named after Reginald Murch. (It was occasionally referred to as the Reginald “Emm”). Its construction took approximately 6 months using many materials and fittings from salvage yards. It is believed that the keep was hewn from two telegraph poles! Reginald M was launched at Largs Bay in 1922. Reginald M was approximately 30 metres long and was fore-to-aft ketch rigged with an ‘auxiliary’ motor to support any loss of sail power. The Reginald M was built to service the coastal ports of South Australia to Port Victoria on the York Peninsular, Spencer Gulf. It freighted cargo from port to port cheaply and efficiently. It had a very shallow draft and a flat bottom, enabling it to come close to shore and sit high and dry at low tide, or to be beached on the sand. It could easily skim over reefs due to its flat bottom. Wagons could be loaded and unloaded directly from the side of the vessel. Over the years her cargo included guano, barley, wool, horses, cattle, timber, explosives, potatoes, shell grit and gypsum. The Murch brothers from Port Adelaide were owners of the Reginald M and Richard Murch as the Captain. On April 9, 1931, Reginald M weathered a large storm in St. Vincents Gulf, SA, suffering much damage; the mast snapped and the crew laboured for four hours to free it up by severing the mast and rigging. The crew patched it up and slowly returned to Port Adelaide with only a portion of the insured cargo being damaged. The crew members at that time were owner Mr John Henry Murch of Wells Street Largs Bay, Skipper Mr R Murch – John’s brother, Murray – son of Captain Murch and Seaman John Smith. At some stage it seems that the Reginald M was used as a Customs vessel “H.M.C. No. 3, Pt Adelaide” as shown in a photograph in Flagstaff Hill’s collection. In 1969 Reginald M’s last freight trip left Marion Bay, carrying grain, wool and explosives. In late 1970 it was sold to the Mount Lyall Mining and Railway Clompany and used as a barge to carry explosives. In 1972 The Navy League of Strahan, Tasmania, purchased the vessel for use by the Strahan Sea Cadet Unit at Macquarie Harbour; it was renamed “T.S. Macquarie”. (This plan did not come to pass.) In 1974 Mr Andrew Rennie of East Brighton, Melbourne, brought Reginald M for shipping purposes, He sailed it from Strahan to Melbourne, planning to use it for pleasure sailing. The Reginald M was later sold at auction to Captain Julian Dyson, owner of Yarra Passenger Ferries in Melbourne. Later in 1975 funds became available to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village to purchase the Reginald M. It was then restored and used as an exhibit here for many hears. Flagstaff Hill’s collection also includes various objects related to the Reginald M: - Photographs of Reginald M over the years in various aspects of its use - a life buoy with the inscription of “Pt. Adelaide” - helm section that was removed and replaced during restoration - a bullet found in pieces of timber during the 1979 restoration ABOUT THE POLLY WOODSIDE On the bow in the Polly Woodside's photograph is the word "RONA". the Polly Woodside was built at Belfast in 1885. In 1904 the vessel was sold to A.H. Turnbull of New Zealand and renamed "RONA". The letter and photographs are significant for their association with the Reginald M, an Australian built coastal trader now on the Australian Register of Historic Vessels (number HV000562). The letter and photographs are also significant as part of both the history of Flagstaff Hill and the history of the vessel “Reginald M” that has been on display in the lake for many years. Objects retained from this boat are included in Flagstaff Hill’s collection of maritime history.Packet with photographs and negatives in a KODAK envelope. The photographs are of two sail and steam vessels; twelve (12) black and white photographs of the 'Reginald M', and one (1) colour photograph of the Polly Woodside, plus six (6) negative strips. Included int he packet is a letter in stamped and postmarked envelope addressed to Mr A Clapham of Footscray. The envelope postmarked 9 Dec 1972, with the Warrnambool postcode 3280, A 7c Australian postage stamp in attached to the envelope. They are associated with Flagstaff Hill’s acquisition of the vessel “Reginald M”. Envelope "9 DEC 1972 / 3280" Postage stamp "7c" "Australia" Inscriptions on one Reginald M;; "REGINALD M" and "Pt ADELAIDE H.M.C. No. 3" Inscriptions of the Polly Woodside; "RONA / MSC" "MHI / NO. 1" Ball point ink, reverse of photograph "POLLY WOODSIDE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, vessel reginald m, reginald emm, t. s. macquarie, h.m.c. no. 3, pt adelaide, australian register of historic vessels (number hv000562), boat building trade, jack murch, john henry murch, birkenhead, port adelaide sa, largs bay sa, coastal trader south australia, 1920 ketch reginald m, marion bay produce, mount lyall mining and railway company, navy league of strahan, tasmania, melbourne ferry company, flagstaff hill historic park planning board, john lindsay, james mark, andy clapham of footscray, andy clapham boat builder, kodak photograph packet envelope, kodak super-size prints, kodak australia pty ltd, australian postage stamp 1972 - 7c
