Showing 390 items
matching wickham
-
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesNewspaper, Cairn marks plane crash, 1976
"On 5 July 1936, locals in Melton South saw a plane emerge from behind clouds above the railway station, in heavy wind and rain. Engine roaring, the plane went into a spin and disintegrated into pieces in mid-air, before crashing to the ground near Arnold’s Creek. The pilot, young Australian aviator Jimmy Melrose, and a passenger, Alexander Campbell, were killed.Jimmy Melrose was a popular figure in international aviation, having been the youngest and only solo pilot to finish the London to Melbourne Centenary Air Race in 1934. His death, at the age of just twenty-two, caused an outpouring of sorrow. He was honoured with a state funeral two days later at St Paul’s Cathedral in Melbourne, which was attended by thousands of people. Locals Maisie Arthur, Ted Wickham and Bill Cahill gave eyewitness accounts of the accident to the authorities, and an inquest found that it was the result of structural failure and poor weather. A cairn erected by locals near the scene was reconstructed by the Melton and District Historical Society in Brookfield, opposite the Melrose Memorial Reserve, on the 40th anniversary of the crash in 1976".Regional Gazette article of a cairn erected by locals near the scene of the plane accident which involved Jimmy Melrose, and passenger, Alexander Campbelllocal significant events, landscapes of significance -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - R.S.L. BENDIGO COLLECTION: ANNUAL R.S.L. BALL 1957
Three copies of the Bendigo Sub-branch R.S.S.A.I.L.A. Annual R.S.L. Ball held at the City Hall, Bendigo on 11th July 1957. Card is cream with gold print on the front and a gold RLS badge. Other printing is blue. The inside of the tri-fold card has a Dance Program of 28 dances and a space for Autographs. The other side has the Debutantes: Judith Binns, Dulcie Mildren, Joan Taylor, Judith Strauch, Rosalie Smith, Marilyn Smith, Gloria Wickham, Joyce Twigg and June Richardson. Trained by Mr Albert Osborn. Chaperone: Mrs H A W Morey. Partners: Robert Knight, Bernard Hinton, Ian Coulston, George Thompson, Robert Pollard, Jack Luke, Brian Thomas, Trevor Tonzing and Stan Rutland. President Bendigo Branch R.S.L. Col Sir George V Lansell, K.B., C.M.G., V.D. Secretary Ball Committee: Mr F C W Brown. M.C.: Mr G Hudson. Printed by Hocking & Sloan Print, Bendigo.Hocking & Sloan Print, Bendigoevent, social, annual ball, r.s.l. bendigo collection - annual r.s.l. ball 1957, judith binns, dulcie mildren, joan taylor, judith strauch, rosalie smith, marilyn smith, gloria wickham, joyce twigg, june richardson, mr albert osborn, mrs h a w morey, robert knight, bernard hinton, ian soulston, george thompson, robert pollard, jack luke, brian thomas, trevor tonzing, stan rutland, col sir george v lansell, mr f c w brown, mr g hudson, hocking & sloan print -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Textile - Casino embroidery, S.S. Casino
The SS Casino was a coastal trader of 450 tons gross, 160.4 feet in length, built at Dundee for the Newcastle and Hunter Steam Navigation Company. It had saloon accommodation for 35 people, fore-cabin 25 and carried 300 tons (425 tonnes) of cargo.The Casino called at Warrnambool on 30th May 1882 while on her delivery voyage and narrowly escaped being dragged ashore by gale force winds. While the ship was in Warrnambool the directors of the Belfast and Koroit Steam Navigation Company bought the ship. It was used as a coastal steamer solely on the west coast of Victoria run from 1882. On the morning of 10th July 1932 an attempt was made to berth the ship at Apollo Bay in heavy seas. Captain Middleton decided to take the ship out into the bay and wait until the seas abated, not realising that the anchor used to steady the ship as she was being manoeuvred had pierced her hull. The ship was put about and headed to the beach, but sank. The captain and four crew members were swept off the deck, and though one crew member was rescued, four drowned. The beaded picture was made by Mary Wickham, the grandmother of the donor. This item has significance linking a piece of handcraft and a local ship from the late 19th century.It has significant artistic value. Hand worked embroidery of black, white, maroon, gold & clear glass beads on a background of white polished cotton. The embroidery is in a black painted wooden frame. It is backed by a sheet of "War Cry" 26th April 1896. "Casino" in gold beading on bow of ship.the casino ship, warrnambool casino, warrnambool shipwrecks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBracket, On or before 1889, when the Newfield was built
This bracket was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perishedFlagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.‘L’ bracket, copper, 3 holes on one side, 2 holes on the other1893, shipwrecks, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, newfield, 1892, 28 august 1892, port campbell, nineteenth century, victorian shipwrecks, barque, norma bracken, peterborough, 29 august 1892, peter ronald, curdies river, bracket -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole, Before June 1892, when the Newfield sailed for Brisbane
This porthole frame was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.A porthole frame from the wreck of the Newfield. The porthole and glass are missing. It is encrusted, cracked and eroded. There are 8 retaining bolt holes with the remnants of 7 bolts remaining. On the inside are the remains of the hinge flange and the two release screws. Restored, good condition.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdie's river, newfield, nineteenth century, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, porthole, porthole frame, shipwrecks, victorian shipwrecks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole, On or before 1889, when the Newfield was built
This small porthole was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreckSmall porthole frame (inner), from the wreck of the Newfield. Glass missing, brass with 2 screw dogs lugs and one hinge. Restored, good condition.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdie's river, newfield, nineteenth century, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, porthole, shipwrecks, victorian shipwrecks -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Deep Rock Swimming Pool and Clubrooms on the Yarra, c.1925
The former Deep Rock Swimming Pool was about 500 yards [457 metres] above Dight’s Falls. It was there that the Deep Rock Swimming Club was established in 1906. This initial club was expanded in 1916 to incorporate a life-saving club. In 1918, John Wren, the president of the club offered the club £1000, and undertook to sponsor a patriotic carnival in March 1918, at which swimming champions would take part. The ‘pool’ was to achieve fame as the venue for a world record-breaking ‘swallow dive’ of 205 feet 9 inches [63 metres] by ‘Prince Wickyama’, [aka Alec Wickham], a Solomon Islander. The dive from a special platform on the west side of the Yarra was reputedly viewed by between 50,000-100,000 spectators, with funds going to the State War Council. The Herald, 25 March 1918, claimed that the wide area occupied by spectators made more precise estimates impossible. In the 1980s, the construction of the Eastern Freeway, and the consequent re-routing of the Yarra River led to the site of the Deep Rock Pool being obliterated. A small cairn and plaque on the Fairfield side of the river now marks its former site.Very rare early photograph off the Deep Rock swimming pool. The pool and its built structures are historically and socially important to the people of Collingwood, Fairfield and Kew. Small, faded, Gelatin Silver print positive photograph of the Deep Rock Swimming Pool situated on the Yarra at Collingwood and Fairfield. The famous diving tower is at the right of the photo. The built structures were constructed for the Deep Rock Swimming and Life Saving Club. People are sitting on the terraces above the river. "Bathing Club. Deep Rock on the Yarra. Studley Park Melbourne. Please credit E.J. Thomasson Collection"deep rock swimming pool, deep rock swimming club, deep rock lifesaving club, swimming -- river yarra, river yarra -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, 'Melton State School 430 Class Photo, 1916
Head Teacher Thomas Lang Miss Silke, Miss Lang Back Row L – R 1-16 Jongebloed, Julius son of Gottfried. Storekeeper 5-1 Jan 1907 Manning, Eric Frederick son of Thomas Hotelkeeper. 4-6 1906 not named Dodemaide - ? Raleigh, Albert son of Oliver. Hawker 5-11 1904 Whiteside, Thomas son of Edward 5-6 1904 7. not named 8. not named 9. not named 10. not named 11. not named Jongebloed, Claus could be Augustus 19-10-06 April 1911 Coburn not named Whiteside, Albert Ernest son of Alexander. Labourer 4-11 Oct 1905 16. not named 2nd Back Row L-R No 1-18 1. not named 2. not named McGuire, Leopold son of John. Carpenter 22-2-03 Jan 1911 MC 23/11/15 Dodemaide, ? 5. not named 6. not named Whittington, Henry son of Wm. Blacksmith. 17-4-05 Jan 1910. MC 74845 Coburn, Albert, son of Fredr. 4-8 July 1904 not named Wickham, Edward son of George. Carpenter. 7-4 July 1908 26/1/1916 11. not named Wickham, George son of George. Carpenter 7-4 July 1908 26/11/1915 not named not named Dodemaide ? 16…not named Watson, Donald son of Alexr. 6-5-05 1911 Trewin, James son of Willm. James 31-3-03 1910 2nd Front Row L –R No 1-14 not named McGuire, Monica, daughter of John Carpenter 22-4 Jan 1909 St Ambrose Brunswick ? McLennan, Bella McDonald Gladys, daughter of Donald 6-2 1906 Riddell, Annie daughter of Joseph 6-3 July 1903 Minns, Chesney daughter of Fredk. 5-5 Sept 1904 Watts, Alice daughter of James. Labourer 6-11 May 1906 Toolern Neal Margaret, daughter of John 4-3 April 1902 Barrie, Essie (not found), Myra daughter of Wm Henry 7-6 May 1905 Werribee Wilson, Lila daughter of Alfred George Farmer 6- Jan 1907 Robinson, Florence daughter of Thomas 5-10 Mar 1908 Burns, Caroline James 4-10 Mar 1907 Trewin, (Lena) Emily daughter of Thomas. Farmer 10-3 Jan 1904 Jessie McLellan daughter of Duncan Farmer 5-11-07 1912 ? Head Teacher Thomas Lang, Miss Silke, Miss Lang and a group of students in front of one of the school buildings. education, local identities -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole frame, ca. 1889
This porthole and porthole cover was removed from the stern of the Newfield wreck, on the starboard side. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreckPorthole frame, including porthole and porthole cover, from the wreck of the Newfield. Porthole secured by nine bolts. It was removed from the stern of the wreck on the starboard side. there is some marine growth on the porthole. The cover still opens. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdie's river, newfield, nineteenth century, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, porthole, porthole cover, shipwrecks, victorian shipwrecks, porthole frame -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Valve, or before 1889
This Non-return valve was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield. Non-return valves can be used to pump water out.of a vessel The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.A non-return valve used to connect to a hose on a bilge pump on a vessel. This valve is from the ship Newfield and was used to pump water out of the vessel. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdies river, newfield, nineteenth century, non return valve, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, shipwrecks, victorian shipwrecks, valve, bilge pump -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Black & White Postcard, Cheltenham Church of Christ 40th Anniversary Invitation, c1900
On his arrival from Scotland c 1857, James Keir commenced a communion service in his home on the Nepean Road. By 1859 the group-which included such other names as Allen, Brough, Cameron, Fairlam, Holdsworth, Le Page, Meeres, Monk, Organ, Penny, Perry, Potts, Sears and King-had built a small chapel near the corner of Wickham and Chesterville Roads. During 1858, a group had also begun meeting in the Charman family home on the corner of Charman and Balcombe Roads. Names associated with this group included Bodley, Charman, Fisher, Hayes, Hilliar, Judd, Moysey and Ruse. In 1860 they built a chapel on the corner of Charman Road and Patty Street. It was enlarged in 1866 and it became the meeting place of the two groups when they came together around 1870. They were able to buy land near the corner of Chesterville and Nepean Roads, and erected a new brick chapel on the site in 1878. This chapel, of course, continues to be an integral part of the life of the Southern Community Church and was one of the three worship venues for the 150th Anniversary celebration in 2007. The Southern Community Church was formed by the amalgamation of the Cheltenham, East Bentleigh and Hampton Street Churches of Christ in 1993, and a comprehensive new facility was designed and built to accommodate the ever-increasing activity of the amalgamated church. It was opened on 30th November 1997. ( Southern Community Church website 2019)c1878 - continuing The Church or Christ Cheltenham was one of the first places of worship established in Cheltenham by the early settlers. The settlers came together, in private homes at first, to support each other spiritually and physically and later built brick Churches for Sunday services and established social and sporting clubsBlack & White photograph as a postcard invitation to the 40th Anniversary of the Church of Christ corner Chesterville Rd and Nepean Highway Cheltenham ( ? 1900)Front Printed ; Church of Christ Cheltenham Back Printed ; POST CARD / One Penny Postage within Commonwealth / The address only to be written here/ One penny Stamp/ Sunday School Anniversary, / OCTOBER 27TH & OCTOBER 30TH / TO WHICH YOU ARE / CORDIALLY INVITED Handwritten in ink ; H.W. got the cramps in the pants. He took some pills then ran over the hills undatedearly settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, were j.b., o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards, keir james, lepage frank, lepage everest, holloway josiah, bruton henry, keys robert, judd clarence, fairlam percy, meeres william, southern community church, cheltenham, cheltenham church of christ -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDeck light, On or before 1889
This deck light was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield in 1973. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. Local man Peter Carmody was recognised for risking his life in order to help save the lives of the ship's crew. In 1893 he received a letter and accompanying limited edition of the Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea; 1872" medal and certificate from the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreckDeck light recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship “Newfield. Oval semi-spherical shape of clear thick glass.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdie's river, deck light, newfield, nineteenth century, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, shipwrecks, victorian shipwrecks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSteam-engine coupling, On or before 1889
This Steam Engine Coupling was recovered from the wreck of the Newfield and is thought to be part of a Donkey Engine (or steam donkey, or donkey winch), which is a small secondary steam engine with a cylindrical shaped boiler. In 19th century merchant sailing, a steam donkey was often used in marine applications such as to help raise and lower larger sails, loading and unloading cargo or for powering pumps. The barque Newfield left Liverpool on 1st June 1892 with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt for Brisbane. About six weeks later the ship ran into very heavy weather approaching the Australian coast. On 28th August at about 9pm her master, Captain George Scott, observed between the heavy squalls the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria, but due apparently to a navigational error (the chronometers were incorrect), he mistook it for Cape Wickham on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered course to the north expecting to run through the western entrance of Bass Strait, but instead, at about 1:30am, the ship ran aground about about 100 yards from shore, one mile east of Curdies River. The vessel struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with six feet of water in the holds. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreckCoupling is believed to be part of the Donkey winch's steam-engine. Threaded brass collar (with side outlet) attached to a copper pipe via a locking nut, and a four holed flange with bolts and coupling plate the other end.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, 1892, 1893, 28 august 1892, 29 august 1892, barque, curdie's river, donkey engine, newfield, nineteenth century, peter ronald, peterborough, port campbell, shipwrecks, steam engine coupling, steam donkey, victorian shipwrecks -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Plateway (Wheelway) Steel, circa 1885
By the later 1800s the dirt roads in the then out-lying areas of the City of Moorabbin became dangerous, and almost impassable due to huge potholes and muddy swampy areas. The heavily laden market gardener’s carts regularly broke axles and wheels, and horses foundered on their way to the Melbourne markets. Even worse, the heavier “iron maidens”, carrying their malodorous loads of sewage from Melbourne’s inner suburbs for dumping in the outlying areas of the City of Moorabbin, also got bogged in the mire. It was decided that a practical solution to this problem was to install a metal plateway on the side of the problematic roads. In about 1887 the Moorabbin Shire Centre Road, in the Brighton East area, two parallel metal rails were installed so that the wheels of carts could run along smoothly, the horse travelled in the filled, middle area between the rails. Point Nepean Road plateway was removed in 1930 and Centre Dandenong Road plateway was removed in 1934-35. The worn plateway along Centre Road, East Brighton (now known as Bentleigh), was gradually taken up in several pieces, commencing in the the1920s, when its condition deteriorated and it caused a hazard to bikes, pedestrians, motor-cycles and the few early cars. The early steel plateway, constructed by David Munro, and opened on 23rd March 1885 by Thomas Bent, was built along Nepean Highway, between Asling St. and Bay St. The Point Nepean Track was subsequently extended into Moorabbin with branches along Centre, Cumins, South, Wickham, and Keys Roads, the total length was 13 miles. In 1908-1909 plates were laid along Centre Dandenong Road to Ross Street Bentleigh This innovative solution proved successful and was used until gradually the main roads were upgraded, and motorised vehicles started to appear. Two parallel metal rails were installed in the right hand side of a few main roads in the Shire of Moorabbin so that the wheels of heavily-loaded market gardener's carts on their way to markets in Melbourne could run along smoothly. The horse pulling the carts travelled in the filled, middle area between the rails. The Steel Plateway was constructed by David Munro, and opened on 23rd March 1885 by Thomas Bent. The wheelway first only ran along Nepean Highway, but it soon extended from Centre Dandenong Road, along Nepean road to its junction with Chapel Street, St Kilda. Later branch lines were built along Centre Road, Bentleigh as far as Warrigal Road and, according to early photographs, along Wickham Road Moorabbin as well. This innovative solution proved successful and was used until gradually the main roads were upgraded, and motorised vehicles started to appear. There was a problem with the wheelway : there was only a single set of rails and this was established on the right-hand side of the Nepean Road, travelling towards the city. Traffic FROM the city travelled on the correct or left-hand side of the road. The exception to this rule was the malodorous iron-clads, heavily riveted iron carts, generally travelling in convoy, carrying several tons of human effluent out of Melbourne to be trenched-in in the sandy soil of the Moorabbin district. Moorabbin City Council donated and installed a small section of Plateway at Box Cottage Museum in 1984melbourne, brighton, moorabbin, roads, plateway, wheelway, transport, st kilda, bent thomas, munro david, market gardens, steelway, carts horse-drawn, iron maidens, point nepean track -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION; GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN EDUCATION 2000 LATROBE UNIVERSITY, BENDI
A laminated copy of the Graduate Diploma in Education 2000 La Trobe University, Bendigo. (The year 2001 has been changed to 2000). It displays a photo and the names of the recipients. They are - Les Lyons, Shannon Hubbard, Tony Speirs, Kirsten Colwell, Alex Vardy, Vanessa Smith, Gerard Hughes, Julian Watson, Kate Jones, Richard Wade, Luke Rowlands, Craig Coburn, Keith Hutchinson, Tom Esnouf, Prue Morrison, Chris Joyce, Alicia Sims, Cameron Barry, David Marriott, Matthew Ryan, Cameron Pickering, Fred Wierenga, Wilf Savage, Rosemary, Grubelnik, Maryanne Carroll-Keays, Michelle Smith, Rohan Lelliott, Deslee Joseph, Matthew Wickham, Tony Drummond, Denise Berry, Frank O'Neill, Emma Hards, Deborah Cordingley, Anita Morris, Bek Mifsud, Scott Alterator, Penelope Gilbert, Michelle Stokie, Tine Brok, Catherine McDougall, Kate Silverback, Wendy Jordan, Janine Sanderson, Charlotte Daniel, Meaghan Feldman, Steven Thorne, Kaye Porter, Brad Shone, Catherine Trimnell, Matthew Charles-Jones, Sheridan Clegg, Lyn Taylor, Michael Reeves, Caroline Foster, Wayne Repacholi, Phillip Payne, Wayne Blakeley, Andrew Pattison, Allison Umbers-Leitao, Renee Holland, Fran Eberbach, Rowena Wakefield, Caroline Steen, Sarah Siakew, Andrew Sutton and Ryan Kervin.bendigo, education, la trobe university bendigo, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, bendigo, education, teaching, teachers, students, tertiary education, graduate diploma, la trobe university bendigo -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Newsclippings, Folder of Newspaper Cuttings Relating to University of Ballarat and Federation University Australia, 2004 onwards, 2004 onwards
Folder of newsclippings, including: Ballarat Courier 03 November 1999 - Ballarat Sporting Heroes (Shayne Reese, Tony Lockett, Dennis Shaw, Tessa Molloy, Lisa Bruty, Kirst Benoit, Brett Hunter) Ballarat Courier 19 May 2001 - State revenue Office Ballarat Courier 02 MaY 2003 - Brian Howlett Kembla Lines September 2006 - Inside Steel at Port Kembla Weekend Australian 23-4 September 2006 - Adams Forges a Legacy in Steel by Robert Gottliebson - Bluescope Steel, Kirby Adams. Port Kembla Ballarat Courier 14 May 2003 - Alan Webb received Honorary Doctorate Ballarat Courier 07 July 2007 - Exhibition Showcases A Century of Artworks by Dorothy Wickham - outlines an exhibition highlighting 100 years of Art Lectures curated by Clare Gervasoni Ballarat Courier 23 December 2010 - Historical Sites Study Launched - Ballarat Industrial Heritage Wiki launched. Ballarat Courier 21 April 2014 - Unknown Soldier, tunnellers par of project's research: Wartime Connections Ballarat News 14 February 2019 - FedUni VC to speak at leadership forum. (Photo: Helen Bartlett) Ballarat News 10 June 2021 - Taking a closre look at contact tracing by Katie Martin. (Contact tracing during the Covid19 pandemic) Ballarat News 21 October 2021 - Hospital adds temporary Covid-19 triage tent by Edwina Williamsfederation university, university of ballarat, tony lockwood, alfred deakin place, state regional freight links program, nazareth house, ballarat technology park, state revenue office, wendouree parade, deer park bypass, geelong road caravan park, brian howlett, alan webb, honorary doctorate, arthur pickford, mosaics, john pickford, janet holmes a court, mount helen campus history, ballarat techncial art school, tony flude, joseph flude, humanities, nurture the humanities, clunes school of mines, ballarat school of mines 140th anniversary, david battesby, john mcdonald, kath white, catherine laffey, neil trivett, greg simmons, ballarat & district industrial heritage wiki, federation university art collection, ballarat school of mines honor book, clare gervasoni, henry sutton, sutton's music house, john smythe, david caro, david caro obituary, student union, new university name, merger, gippsland, mount helen campus, univesity of ballarat alumni connect, name change, science building, y building, ballarat equine centre, ballarat brewery, ballarat and united breweries, feduni, former ballarat gaol, ballarat gaol basement cells, federation college, sam henson, janet cowles, alexandra tascas, helen bartlett, graduation, pandemic, covid19, covid-19, corona virus -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION: BENDIGO TEACHERS' COLLEGE STAFF AND STUDENTS 1929
A very dark copy of a photo of the staff and students at Bendigo Teachers' College 1929. They are all dressed formally - the men with suits or jackets with ties.The women in frocks or skirts and all with short hair. The staff and students are listed in order from the back to the front row. Back row - R. Frankling, R. Jackman, K. Mitchell, A. Rebbechi, A.C. Macmichael, T. Condon, N. McLennon, C. Streader, R. Harry, T. Seymour, H. Brown, J. Leach, J. Day, A. Willey, H. Sergeant, A. Gomarsall. Second row - Misses B. Duggan, J. Mackenzie, O. Clarke, R. Nicholas, J. Bowling, B. Bradford, J. Metcalf, K. Fleischer, A. McInnes, L. Haines, M. Westwood, G. Stuart, B. Glasson, E. Kelly, M. Haydock, E. Armstrong, D. McKernan, N. Fraser. Third row - Misses J. Young, I. Collard, N. Comer, S. McKinnon, M. Roberts, M. Wickham, Miss Alice Smith, Mr. P. G. Samson, Miss D.A. Mackay, Mr. T. F. Scott, Miss M. McGawley, Misses W. Nixon, E. Liddell, M. Rowe, A. John, I. Lawson, V. Davis, G. Harris. Fourth row - J. Cunningham, F. Ryall, J. Hendry, J. Flanagan, W. Stephens, J.O'Dwyer, N. Wearne, G. Downing, L. Culhane, H. Parker, A. Elliott, E. Craving, S. Thompson, A. Keating. Absent - Miss A. Rosan. See 3320.100bendigo, education, bendigo teachers' college, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, bendigo, education, tertiary education, teaching, teacher training, bendigo teachers' college, photo, photos, photograph, photographs, photography, history miss j.c. burnett, mr. geoff. pryor, history, staff, students, r. frankling, r. jackman, k. mitchell, a. rebbechi, a.c. macmichael, t. condon, n. mclennon, c. streader, r. harry, t. seymour, h. brown, j. leach, j. day, a. willey, h. sargeant, a. gomarshall b. duggan, j. mackenzie, o. clarke, r. nicholas, j. bowling, b. bradford, j. metcalf, k. fleischer, a. mcinnes, l. haines, m. westwood, g. stuart, b. glasson, e. kelly, m. haydock, e. armstrong, d. mckernan, n. fraser, j. young, i. collard, n. comer, s. mckinnon, m. roberts, m. wickham, alice smith, p. g. samson, d.a. mackay, t. f. scott, m. mcgawley, w. nixon, e. liddell, m. rowe, a. john, i. lawson, v. davis, g. harris, j. cunningham, f. ryall, j. hendry, j. flanagan, w. stephens, j. o'dwyer, n. wearne, g. downing, l. culhane, h. parker, a. elliott, e. cravino, s. shompson, a. keating, a. rosan -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDocument - Speech, Bulletin Address. Legatee Kem Kemsley Tuesday 27 September 1983
An article from the Bulletin including the text an address by Legatee Kem Kemsley at a Legacy event on 27 September 1983. He discusses the beginnings of Legacy. He relates the approach made to Sir John Monash to be the first president. It was via Legatee Frank Meldrum who was playing tennis with Monash's son-in-law. It shows the nature of relations between high ranking ex servicemen. Monash suggested Colonel Harold Cohen. Initially Legacy was founded with 'one person from each profession or business who will represent that profession until such time as the Club has established itself on a wider basis.' For example there were 'two solicitors - Downing and Armstrong, Meldrum as dentist, George Worboys as plumber, Dr Gardener as the eye specialist, Doolan and Goodchild as Surveyors, Fred Wickham of the Premier's department who was regarded as very important, Baker from Myer's Emporium, Joynt from the printing world and Blackett the architect.' He also mentions a Police Strike and General Monash set up a special constabulary force. Cohen, Kemsley and many of the early legatees answered the call to help keep peace. By December 1923 there were 54 members of the new Legacy club. The name was under consideration as the Tasmanian club was called Remembrance Club. Pip Powell nominated the name of Legacy to be submitted for consideration, but it was Frank Selleck who moved the formal resolution. By the end of 1924 initial objectives were met. A picnic with widows and children was held at Heidelberg and then Beaumaris, (limited by the few legatees who had motorcars at the time). Following thoses successes Frank Doolan posed the question 'what does Legacy really mean?' and focus changed toward widows and children. Legatee Savige had a property at Balnarring and the first camps were started. For boys there was a Lacrosse team and football team. Also swimming classes and literary and debating classes, which were hoped to be interesting and develop their minds along the proper form of citizenship. Then classes for the widows and later the girls. The article was part of an album of past presidents from 1965 to 1989. The folder included biographical details and obituaries, eulogies and death notices of prominent Legatees. The items have been catalogued separately.A record of a speech made by Legatee Kem Kemsley a past president of Legacy about events in the early days of Legacy. The information was collected to record the lives of prominent legatees in a folder.Photocopy of 3 pages from Bulletin on an address by Legatee Kem Kemsley in 1983.Bulletin No. VAW 1209. 6.10.1983. Page No 8, 9 and 10.past presidents, speech, kem kemsley, history, police strike -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Pulley, Ca 1889
Wooden pulley wheel section from the wreck “Newfield”. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. See also other items in the Flagstaff Hill Newfield Collection.The report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. The Newfield collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criteria A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history This item is an oval-shaped brown and orange wooden shell from a ship’s pulley. The original wooden material is now petrified but the lighter coloured concentric rings of the wood's grain are still visible. A metal sheave or drum is fitted into the centre hole and some of the edge of its sheave’s collar has corroded and broken away. The collar has three holes of equal size that are evenly spaced around it. The bearing ring is now detached but still connected to the pulley with a string on which a label is attached. Most of the six cylindrical metal roller bearings are sand encrusted but some are still visible. Recovered from the wreck of the ship NEWFIELD.The pulley has a string through it that attaches it to the bearing. The label on the string bears the handwritten words “PULLEY WHEEL / NEWFIELD / PETER ROLAND”.block, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, peter carmody, carmody, newfield, shipwreck, pulley, wheel, pulley block, sheave, drum, peterborough, south west victoria, rocket, rocket crew, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hil maritime museum -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, post 1889
The photograph shows the three-masted iron and steel bark "Newfield" sailing in open seas. It event would have been between 1889-1892 during the ship's working life. ABOUT THE NEWFIELD The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. The report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. Black and white photograph of the three-masted sailing ship “Newfield” in the open sea, sails unfurled. The ship was built in 1859 by Alexander Stephen and Sons Limited of Dundee, Scotland. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, barque newfield, photograph, 1880s sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Ship Crew, 1889-1892
This black and white photograph shows the crew of the barque Newfield. They are pictured seated on a grassy slope and rock, a lifebuoy from the Newfield, Liverpool, resting on the men in the front row. The men are formally dressed, some with bowler hats, a bow tie and pipe, rather than in their sailing uniforms. ABOUT THE NEWFIELD The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck. The Letter accompanying the Medal for Bravery awarded to Peter Carmody is significant because the attempt to save lives is associated with the shipwreck Newfield. Black and white photograph of the crew of the sailing ship “Newfield”. The men in formal dress are seated on rocky slope with the ship’s lifebuoy showing the name “NEWFIELD, LIVERPOOL”. Photograph taken 1889-1892 flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, newfield, photograph, crew of the newfield, 19th century sailing ship, peterborough, cape otway, medal for bravery -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPamphlet, University of Ballarat Australian Studies Centre, University of Ballarat Conference Pamphlet, 12/1999
A conference in memory of Kevin Livingston to celebrate the role the Irish in Ballarat played in the formation of the nation..1) Light green tri-folded A4 pamphlet .2) Program for the 'Through Irish Eyes' Conference, A conference held in memory of Associate Professor Kevin T. Livinsgston by the University of Ballarat Australian Studies Centre, 3-5 December 1999. Speakers were: * Anne Beggs Sunter - 'irish Republican Echoes at Eureka * Jill Blee - 'Portrait of a Ballarat Irishman/woman * Dianne (Leonard) Cahir - 'The Irishness of Dunnstown * Dianne Campbell - Sir Henry Cuthbert * Dermot Clancy - Colonial Clergy - All Hallows College and the Australian Mission in the 19th Century. * Anne Cunningham - Dom bernard Smith's Australian Mission * Mella Cusack - Relations between the Young Irelanders and the Catholic Clergy in Australia * John Daykin - He that is Not With Me is Against Me: The Role of the Irish in the Defeat of conscription, Ballarat 1916-1917 * Dr Frances Devlin Glass - '[T]ouches of nature that make the world kin: Furphy, Race and Anxiety' * Helen Kinloch - Bernard O'Dowd,, and dreams of a Golden age in Australia' * Associate Professor Rederic Lacey - 'Exploring Pathways Towards reconciliation Through Encountering Our Shared Histories' * Dymphna Lonergan - 'Sounds Irish' * Dr David Lucy - ' Remarks on the Decline of Irish Language' * Patrick McCormack - The Irish Factor in the Campaign for Federation in New South Wales * Siobhan McHugh - 'In Search of Soul: One Irishwoman's Journey in Australia' * Ken Mansell * Dr Val Noone - 'the Irish in collingwood 1860-1900: Family Tree Meets historical Record * Ambassador Richard Anthony O'Brien * Terrence O'neill-FitzSimons - "Francis Thomas Cusack-Russell' * Professor Bob Reece - 'The making of the Eureka Film' * Edward O'Reilly - 'John Boyle-O'Reilly: Journeys and Monuments * Dr Chris Watson - 'Around the Boree Log and the identity of Irish Australians' * Dorothy Wickham - 'Saints or Sinners?: The Influence on Ballarat's Female refuge by Irish Women' * Christine Wright - 'A Stately Landmark: Adam Loftus Lynn .3) newspaper article on the conference from The Courier, 06/12/1999 - 'Irish Celebrate Their Role in City'Black print on light green paperaustralian studies, university of ballarat, kevin livingston, mt helen campus, "through irish eyes", jill blee, david james, rod lacey, val noone, dianne campbell, christine wright, terence o'neill-fitzsimons, helen kinloch, diane cahir, dorothy wickham, edward reilly, mella cusack, anne beggs-sunter, patrick mccormack, anne cunningham, shane carmody, dermot clancy, francis devlin-glass, chris watson, david lucy, dymphna lonergan, richard o'brien, bob reece, peter kennedy, gough whitlam, australian studies, university of ballarat, kevin livingston, mt helen campus, "through irish eyes", jill blee, david james, rod lacey, val noone, dianne campbell, christine wright, terence o'neill-fitzsimons, helen kinloch, diane cahir, dorothy wickham, edward reilly, mella cusack, anne beggs-sunter, patrick mccormack, anne cunningham, shane carmody, dermot clancy, francis devlin-glass, chris watson, david lucy, dymphna lonergan, richard o'brien, bob reece, peter kennedy, gough whitlam, genealogy, family history, irish australians, irish -
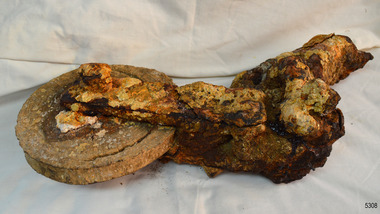 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Block, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
These remains of a block, shackle and wire are from the sailing ship Newfield. This would have been one of the hundreds of blocks and shackles used in the rigging of the vessel. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.This is what remains of a block, shackle and wire from the wreck of the sailing ship “Newfield”. The object is heavily encrusted. The exterior (cheeks) of the block is missing. The disc of the block has a channel part way around its face, about 2 cm from the edge. Two long, narrow plates are joined onto the centre of the disc’s face with a bolt through the centre. The other ends of the two plates join onto the elbow of the shackle. The elbow of the shackle is also joined onto a rod. At the other end of the rod can be seen the ends of thick wire strands.block, 1893, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, peter carmody, newfield, 1892, port campbell, shipwreck, ship, victorian shipwrecks, barque, ship wreck, peterborough, sailing ship, 29 august 1892, block and shackle, curdies river, bramley-moore medal -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
This large brass porthole is from the sailing ship Newfield this would have been one of the many port holes in the vessel used for light and ventilation. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Heavily encrusted large brass porthole, complete with glass intact object is a circular, thick glass window surrounded by a round brass frame and attached to a round brass porthole frame with 9 bolt holes. This porthole was recovered from the wreck of the NEWFIELD.Nonewarrnambool, peter carmody, newfield, port campbell, shipwreck, nineteenth century, ship, victorian shipwrecks, peterborough, peter ronald, dog screw, newfield porthole, bramley-moore medal, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, ship fitting, ship window -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Skylight frame, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
This skylight frame would have been fitted on the Newfield’s poop deck (or raised deck that forms the roof of a cabin at the aft or rear of the ship). It would have covered and protected a glass pane that allowed light to enter the area below desk. The glass pane from the skylight is missing. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Skylight, frame only. The heavily encrusted brass framework has eight bolts around the long side, and four metal bars forming two ‘v’ shapes across the centre. The frame is, slightly concave towards the inner side. The shorter ends of the frame each have a ‘U’ shaped bracket attached in the centre. The shorter ends are wider on one end and taper towards the other end to about a quarter of the thickness. The frame was recovered from the wreck of the NEWFIELD.Noneflagstaff hill maritime museum, newfield ship wreck, alexander stephen & sons, brownells & co, captain george scott, great ocean road ship wreck, peter carmody, bramley-moore medal, liverpool shipwreck and humane society, skylight cover, skylight frame, ship fitting, light cover, newfield -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHandle, c. 1859
This brass handle was found on Sea Elephant Bay beach in King Island, Tasmania, in 1913. The donor identified it as being from the wreck of the Newfield. It would could have been part of the fittings or amongst the cargo on the ship. ABOUT THE "NEWFIELD" The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. A report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. The Newfield collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criteria A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history Ornate brass handle, round plates each end, each with 4 round fixing holes. Found washed up on Sea Elephant Bay beach, King Island 1913, identified by donor as being from the wreck of the Newfield.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, barque newfield, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ornate handle, sailing ship fitting, sea elephant bay, king island -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Melton State School 430 honour board, 1970
HONOR BOARD Melton State School No 430 Supreme Sacrifice • BARRET, P Peter Maurice Barrett Number 5051 Rank: Private Unit: Private Date of death 18th August 1918 of wounds age 21 St Sever Cemetery Extension, Rouen, France Started school August 1904 5 years 10 months Previous school St Michaels Nth Melb Son of Maurice Barrett labourer Melton Brother of John Barrett • BLACK, William William M • EXELL, T S Number 2758 Rank: Trooper 3rd Battalion Imperial Camel Corps Date of death 30th November 1917 of wounds aged 20 years Cairo War Memorial Cemetery Egypt Started school September 1907 aged 10 Previous school Boisdale 3017 Son of George, farmer Melton Railway Station (Melton South) Year of 1918 • LANG, Horace Thomas Number 903 Rank: Corporal Unit: 24th Battalion Date of death: 5th May 1917. Court if enquiry confirmed Dec 1917. Aged 24 Date of birth 27th April 1893 Spring Hill – Kyneton Commemorated Villers-Bretonneux France Started school November 1997. Father: Thomas Lang Teacher Melton 430 Brother of Thomas Lang died 18th July 1918 buried Cairo • LANG, R William Roy Number 2818 Rank: Driver Unit: 1st Australian Light Horse Machine Gen Squadron Date of death 31st October 1917 of wounds Beersheba War Cemetery Israel Started school October 1899 Aged 9 Previous school Camperdown SS 114 Date of Birth: 24th Jan 1890 Son of William John and Mary Lang of Langlands Jandowae Queensland Nephew of Thomas Lang Melton • LANG, Thomas John Thomas NZ CC M Number 15/118 Rank: Lieutenant Unit: Army Pay Department Date of death 18th July 1918 of disease Cairo War Memorial Cemetery Started school November 1896 aged 16 years - Previous school Coliban 1920 Son of Thomas Lang, teacher Melton No 430 • McPHERSON Jas Mrs M: James Sept 1897 Previous Graham St Port Melb Son of Alexander farmer Melton • MISSEN, A P Frederick M Started school August 1899 age 7 years Son of Frederick, fruiterer Melton His sister Adelaide May 11years Previous Ascot Vale 2608 • NORTON, Lewis Thomas CC M Number 1809 Rank: Private Unit: 29th Battalion (Infantry) Date of death 30th September 1918 Cemetery Bellicourt British Cemetery, France Started school March 1901 age 9 years Previous school Galaquil Son of Thomas Norton of Parwan • O’CALLAGHAN, EJ Edward Edward M • O’CALLAGHAN, HT Thomas .. M Number 3859 Rank: Private Unit: 57th Battalion (Infanrty) Date of death 26th September 1917 Bedford House Cemetery, Belgium Started school 11th March 1901 Aged 10 years Father: John O’Callaghan farmer of Melton • PRATT, R H Robert Henry Number: 2203 Rank: Private Unit: 46th Battalion (Infantry) Date of death, 12th April 1917 Favreuil British Cemetery, France Started school in May 1903 aged 6 years Father: Matthew Pratt, Labourer Melton • RYAN J James or John David: RYAN J ? Started August 1896 Previous Christian Brother St Kilda John 11-5 or James 9-11 Charles 6-11 returned from WW1 Frank 8-5 returned Father Daniel Publican • WHITESIDE, John Edward M Number 2182 Rank: Trooper Unit 13th Light Horse Date of death 4th September 1918 of illness aged 29 years Alexandria (Hadra) War Memorial Cemetery, Egypt Started school July 1897 age 8 Son of Edward Whiteside Labourer Melton Brother of Edward. • WHITESIDE, W F Number: 3995 Rank: Private Unit: 22nd Battlion Date of death, 28th July 1916, died of wounds aged 21 years Puchevillers British Cemetery, France Started school in 1901 Year of birth circa 1895 Brother Edward died 4th September 1918 Father: Edward Whiteside. Labourer Year of 1917 • ANDREW. R H • BARRETT, J John Maurice • BLACK, Harold David • BLACKWOOD, Maxwell James A • BLACKWOOD, Roy .. • CAMERON David or (Donald) William M • CAREW, Edward Edward M • COLLINS, H John Henry H Thomas CC M • CANTLON, A Alfred CC • CHALMER, Frank Ernest CC M • COBURN, A Frederick CC M • COBURN, FS CC M • DODEMAIDE, Frank William • DODEMAIDE, Thomas .. • DODEMAIDE, W J William John M • FIELD, J • FORSYTH J • KEATING, WD William Edward M • KINNERSLY James Edward CC • KINNERSLY Norman Chas Edward CC • LANG Norman William • MINNS, J CC M • McCOLL R Alex R J. McColl • MOULSDALE Charles William M • McNULTY, Frederick James CC • McNULTY, W R CC • McPHERSON J which one? • NEAL, Elvine J Neal M • NEAL, Frank John M • NEAL, John William John M (husband of Isabella) • O’CALLAGHAN, Stephen Edward M • PRATT, David T Matthew CC M • QUINANE, David Peter • QUINANE, Peter .. • RIDDELL, William M • RYAN, Charles Daniel • RYAN Frank .. • SKINNER, Stanley John S’John CC M • SPRING, James George • TYLER, A • TYLER, George George • WATSON, Albert Ernest Alexander M • WADE, Howard James • WADE, Walter .. might be connected with CC • WILLIAMS, Percy Mr Williams • WICKHAM, George George M • WICKHAM, W M • WILSON, Stanley [ Alfred and Maude] M • WILSON, Gordon .. M SUPREME SACRIFICE Roll of Honor Melton State School No 430 Years of 1916,1917 and 1918 -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDocument - Speech, Foundation Day Address 1977. Legacy It's Beginnings. Past President Legatee Kem Kemsley
An article from the Bulletin including the text an address by Legatee Kem Kemsley at a Legacy event on 4 October 1977. He discusses the beginnings of Legacy. He starts with Legatee Savige's tip to Hobart and Sir John Gellibrand's Remembrance Club. Then a meeting of the 24th Battalion at Phair's Hotel in 1923 and the men there agreeing to start a similar club, he mentions Sandy Lowe as a member at the meeting in 1977 that was at the initial meeting in 1923. He also mentions other at that initial meeting were Savige, Frank Selleck, Ted Pittard, Bob Irving, and 'Babe' Norman. He relates the approach made to Sir John Monash to be the first president. It was when Savige was in Frank Meldrum's dentist chair that the plan was hatched for Meldrum, (who was playing tennis with Monash's son-in-law, Gershon Bennett), to approach Monash to be president. It shows the nature of relations between high ranking ex servicemen. Instead Monash suggested Colonel Harold Cohen. Initially Legacy was founded with 'one person from each profession or business who will represent that profession until such time as the Club has established itself on a wider basis.' For example there were 'two solicitors - Downing and Armstrong, Meldrum as dentist, George Worboys as plumber, Dr Gardener as the eye specialist, Doolan and Goodchild as Surveyors, Fred Wickham of the Premier's department who was regarded as very important, Baker from Myer's Emporium, Joynt from the printing world and Blackett the architect.' He also mentions a Police Strike and General Monash set up a special constabulary force. Cohen, Kemsley and many of the early legatees answered the call to help keep peace. By December 1923 there were 54 members of the new Legacy club. The name was under consideration as the Tasmanian club was called Remembrance Club. Pip Powell nominated the name of Legacy to be submitted for consideration, but it was Frank Selleck who moved the formal resolution. The speech mentions that Sir Gellibrand was appointed Patron of Legacy and later Monash and Sir Harry Chauvel were chosen. Frank Doolan posed the question 'what does Legacy really mean?' and focus changed toward widows and children. Citing some slightly different dates to those in a later speech about the start of Legacy (at 02029) he says it was July 1926 that they met with widows and a couple of weeks later 142 boys were to attend Anzac House for a Literary and Debating class. Ballarat and Geelong had formed clubs by 1925 and Legatee Hilmer Smith was transferred with his work to Sydney and started a Legacy Club there in 1926. The first Conference was held in November 1926. The first Government House Christmas party for children was held in 1926, when the Governor General of Australia was still residing there. His final words were about his war experiences and relates a speech made by Legatee Brian Armstrong on 28th February 1961 (02502) that also spoke of the area around the Pozieres Windmill that was part of the battle of the Somme in July/August 1916, where so many of the early legatees fought.. The article was part of an album of past presidents from 1965 to 1989. The folder included biographical details and obituaries, eulogies and death notices of prominent Legatees. The items have been catalogued separately.A record of a speech made by Legatee Kem Kemsley a past president of Legacy about events in the early days of Legacy. The information was collected to record the lives of prominent legatees in a folder.Photocopy of 5 pages from Bulletin on an address by Legatee Kem Kemsley in 1977.Bulletin 4.10.77. Page No 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.past presidents, speech, foundation day, kem kemsley, sir john monash, pozieres, somme -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBearing cap, (estimated); Before The Newfield completion in 1889
This bearing cap is thought to be from a donkey winch engine, (or steam donkey, or donkey winch), which is a small secondary steam engine with a cylindrical shaped boiler. In 19th century merchant sailing a steam donkey was often used in marine applications such as to help raise and lower larger sails, load and unload cargo or to power pumps. The bearing cap could have been used on the donkey engine to hold the rod of the winch gear wheel in place, or bolted to another bearing cap around the neck on the top of the boiler’s cylinder, connecting it to the flue. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody’s grand-daughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. The Bearing Cap joins other items in the Newfield collection.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Brass bearing cap from the wreck of the sailing ship “Newfield” is possibly from a donkey winch engine. The half-circle shaped cuff with a rectangular brass block attached to the outside of each end of the half-circle. Both blocks have a round hole in their centre and are approximately the same depth and width as the cuff. Midway around the half-circle cuff is another brass block that is about twice the depth of the cuff. It appears to have been a circular shape that has been modified to match the width of the collar, having had the sides of the circle cut off to leave straights edge parallel to the edges of the cuff. In the centre of this block is another hole, and there appears to be the head of a bolt inside this hole. The bearing cap is lightly encrusted.1893, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, warrnambool, newfield, 1892, 28 august 1892, port campbell, shipwreck, nineteenth century, ship, curdie s river, victorian shipwrecks, barque, ship wreck, 29 august 1892, 19th century, bearing cap, donkey engine, donkey winch, steam donkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAward - Medal, ca. 1872
This medal is the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society’s “Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea 1872”. The Society was formed in 1839. In 1872 Mr John Bramley-Moore donated £500 on condition that the medal have the specific inscription above on its reverse. The Bramley Morre medal was first awarded in 1874 and records show that since that time only one gold medal has been awarded, twenty-two silver medals and seventeen bronze medals, the last being in 1945. This Bromley-Moore medal was awarded to Peter Carmody for his bravery in saving lives on the Newfield shipwreck. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody’s grand-daughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. The Medal and Letter of Congratulations join other items in the Newfield collection.The Carmody Medal recognises the bravery of Peter Carmody in risking his life to rescue crew members of the Barque Newfield when it was wrecked near Curdies Inlet in August 1892. The ‘Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea, 1872’ was presented by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society. The medal and accompanying letter have local and international historic significance as they demonstrate both the difficulties associated with navigation and the dangers of shipping along the South West Coast of Victoria in the 19th century and the medal’s association with the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society and John Bramley-Moore, who provided £500 to found the Bramley-Moore medal. The medal is socially significant. It emphasises the importance of Peter Carmody in rescuing victims of shipwrecks with little thought for his own safety. The medal reminds us of the importance of local people to Victoria’s maritime history. The Carmody Medal and Humane Society letter were in the Carmody family until they were presented to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, by the grand-daughter and great-grandson of Peter Carmody, on the 25th May 2006. The medal is significant for its complete provenance recorded in the donation documentation. The medal is in very good condition and relatively rare with only 22 silver medals awarded between 1874 and 1945. The Carmody Medal and letter add a human element to the story of the shipwrecks. They give life and significance to the Newfield, its victims and its artefacts. Bramley-Moore medal from the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society, awarded to Peter Carmody. The round,silver medal is attached to a looped blue ribbon by a decorative, swivelling silver connector. The top of the ribbon has a silver pin bar threaded through it. The obverse of the medal has a design of a man kneeling on a floating part of a wreck. He is rescuing a child from the sea. There is a manned boat in the distance rescuing someone from the sea. In the far background there is a sailing ship. The top third of the medal has an inscription around it. The reverse shows a long-legged hen cormorant with extended wings holding an olive branch in its beak. The bird is surrounded by a wreath of oak leaves made from two branches. There is an inscription between the design and the rim that goes all the way around the circumference. There is a name engraved around the edge of the medal. The medal in embedded in a purple velvet panel that rests inside a brown, leather-covered case. The lid of the case has a gold embossed emblem in the cemtre. Both the lid and base have a rectangular gold border. The lid is attached to the base with two brass hinges. The base has a brass push-button catch. The box is lined with padded cream silk. The lining inside the lid has a gold emblem in the centre.The obverse has the words "LORD, SAVE US, WE PERISH". The reverse has the words "BRAMLEY-MOORE MEDAL FOR SAVING LIFE AT SEA" and "1872". Around the edge of the medal are the words "PETER CARMODY, FOR HAVING BEEN MAINLY INSTRUMENTAL IN RESCUING THE CREW OF THE BARQUE NEWFIELD, AUG 29 1892" The pin bar has the words “LIVERPOOL SHIPWRECK & HUMANE SOCIETY” written across it. The gold embossed emblem on the lid of the box has the words in the centre "SHIPWRECK AND …. …. ….FOUNDED 1839" The gold emblem on the cream silk lining has the words “BY APPOINTMENT ELKINGTON & CO” printed on it.medal, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, peter, peter carmody, carmody, bramley moore, newfield, liverpool shipwreck and humane society, 1892, 28 august 1892, august 1892, port campbell, bravery, shipwreck, rescue, nineteenth century, ship, curdie s river, victorian shipwrecks, barque, stuart bracken, norma bracken, gerard irvine, james mckenzie
