Showing 3488 items matching "local people"
-
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph, HORNBY STUDIO - CLUNES
BLACK AND WHITE PHOTOGRAPH OF PEOPLE AT A PICNIC WITH THREE HORSES & SULKY.JACKY WOOLCOCK. JOHN WOOLCOCKlocal history, photography, photographs, events and celebrations -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph, HORNBY STUDIO
PEOPLE DRESSED IN VARIOUS OUTFITS ATTENDING A FUNCTIONBLACK AND WHITE PHOTOGRAPH MOUNTED ON BROWN MAT BOARD, FANCY DRESS BALL.local history, photography, photographs, events and celebrations, fancy dress ball -
 Emerald Museum & Nobelius Heritage Park
Emerald Museum & Nobelius Heritage ParkAdministrative record - Nobelius Nursery Cash book, August 1895 - October 1903, 12 July 1907 - 11 June 1910
The Cash Accounts contain the names and transaction details of all Gembrook Nursery clients. The cash account books are historically, and socially significant as the entries give an insight into the growth of the company and the details of payments from local and other government offices and overseas customers as well as significant companies associations and people. The earlier account books also detail wage payments.Hard cover cash book, brown leather binding, black cover. Starts 21 August 1895 and finishes 3 October 1903 Label affixed to spine: 'C. A. Nobelius'c. a. nobelius & sons, gembrook nurseries, horticulture, accounting, emerald -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Delegates to the 1893 Corowa Conference, Michele Matthews Collection, 1993
Michele Maslunka-Matthews B.A. (Hons). Dip.Ed. Local Bendigo Historian and teacher. Member of the Bendigo City Council's Sir John Quick Committee.a. Three page typewritten list of the seventy two delegates to the 1893 Corowa Federation Conference. The Bendigo delegates were A J Hampson (ANA), John Quick (ANA), J B Young (ANA). b. Two newspaper articles from the Bendigo Advertiser (3.8.1993) recording the presentation of a framed portrait of Sir John Quick to the people of Corowa. The presentation was made by Cr. John Balsillie on behalf of the bendigo City Council's Sir John Quick Committee. federation, corowa conference, paul keating, sir john quick, portrait -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Roll of Honour, State Forest Department
Honour boards and rolls were erected in many local schools, halls, churches and offices as a means of acknowledging the commitment made by the community to the military forces. The criteria used for inclusion of names on an honour board were determined by those creating the board and can vary. This board lists the names of 20 people from the State Forests Department who enlisted in WW1. The most significant name is Albert Jacka VC who was perhaps Australia’s finest fighting soldier, and has the honour of being the first Australian to be awarded the Victoria Cross during WW1, the highest decoration for gallantry in the face of the enemy. Most of the other names have been researched.Roll of HonourMembers of the Forest Service of Victoria who enlisted & went to The Great War 1914 - 1919forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph
MEMBERS OF THE FORD FAMILY, TAKEN IN FRONT OF TOTTY TREMBATH'S HOUSE IN 1910, FROM LEFT VIV, NELL, NELLIE, (MOTHER) DULCIE, FRONT ROW - ESME, HARRY, AND TOM WITH THOMAS (FATHER) SITTING IN CART, VIV IS HOLDING A WHALE'S BACK BONE, THEY HAD PICKED UP IN PORT FAIRY.1 FRAMED WITH GLASS PHOTOGRAPH OF THE FORD FAMILY IN 1910, WITH HORSE AND BUGGY. .2 HANDWRITTEN NOTE OF THE PEOPLE IDENTIFIED IN THIS PHOTOGRAPH, SEE BELOWTHIS PHOTO WAS TAKEN OF THE FORD FAMILY IN 1910. THEY CAME FROM DUNACH NEAR TALBOTlocal history, photography, photographs, trembath, perry, richard ford -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Property Binder, 931 Main Road, Eltham
Present day location of Nongkhai Thai Eltham restaurant Formerly the location of: Luther Haleys Bakery and General Store (Sep 1902-1917) - Hayley built this store, which was the first store erected in the present-day Eltham shopping district Hannah Lloyd's General Store (1917-c.Feb 1920) Various owners Staff's General Store (c.1939-Feb 1965) then demolished Ray Staff Eltham Big Star Food Centre (c.1965-1967) Eltham Big Star Food Centre (Staffs new building c.1965-1967) A Country Heritage Furniture and Homewares (?-2006) Newspaper advertisement: Leader Associated Newspapers, 100 Years of News Special Edition, August 27, 1997, p6; A Country Heritage Newspaper advertisement: Diamond Valley Leader, 4 September 2006, Closing Down Sale, A Country Heritage In February 1965, Staffs Railway Store, the oldest business premises in the Eltham shopping district was demolished. Formerly a self-service grocery, restaurant and electrical repair shop, the building for many years housed Eltham’s only ‘family’ grocer and feed store. Earlier it had appeared to have been the town’s bakery. The building had been purchased in late March 1939 by Mr Eric N. Staff. At the time of E.N. Staff’s purchase there were huge bakers’ ovens located at the rear and the building also had a well and four toilets for employees. When the ‘pictures’ came to Eltham with the opening of the Eltham Public Hall across the road in 1941, Mr E.N. Staff extended the business and opened a milk bar and sweet shop. Further extensions re-established the tea rooms of days gone by. Mr E.N. Staff conducted business for about 15 years before handing over the reins to his son, Ray Staff. When his son Ray took over, the milk bar and tea rooms were closed for several years but the milk bar and was later re-opened and subsequently became a greengrocers and later again, a restaurant. The tea rooms section was converted to an electrical repair shop about 1955. Electoral Roll records for 1967 record Raymond Charles Staff at 929 Main Road, Eltham, grocer, and in 1968 at Lot 4, Hillcrest Avenue, Eltham, taxi truck operator. Staff’s store appears to have occupied 929-933 Main Road and the Eltham Big Star Food Centre was centred around 931 Main Road. It would appear that Ray continued to run the business for approximately two years after the original store was demolished and a new supermarket was built. Today, 931 Main Road is the Nongkhai Thai Restaurant and is precisely where the original Staffs store stood. Even though the facade has been modified at eye level with new larger windows, the upper facade is identical to that of the new Eltham Big Star Food Centre of 1965/66. But how did the original building, the oldest premises in the 1965 era shopping centre come about? On August 12th, 1902 at the Eltham Courthouse, appearing before T. Smallman, Esq,. Police Magistrate, and Messrs. W. Duncan and W.J. Taylor, Justices of the Peace is Luther Haley, baker. Wilfred Henry Johnston, by his agent Stanley Ernest Elder had applied for a warrant of ejectment under the Landlord and Tenant Act 1890 against Luther Haley from the bakery premises at the corner of Main Road and York Street. From the evidence presented we learn that Mrs Burgoyne of Eltham had purchased the property some months earlier from Mr Johnston, which consisted of a store and bakery establishment at Eltham occupied by Mr. Luther Haley, and whose lease expired some little time back, and up to the present time, Mr. Haley was not prepared to leave. He informed the court that he is unable to secure at Eltham a suitable house in which to carry on his business, but was building a place near the railway station which he expected to be done in about three weeks time, and he is then prepared to give up possession of the premises he now occupies. Mr Smallman informed the defendant, Luther Haley, that he will have to quit the premises in three weeks from the present date, and that a warrant of ejectment would be issued. However he also informed Mr Haley that he would order the warrant to lie in the office for three weeks from that date. The premises under construction referred to by Luther Haley in court were situated on the western side of Main Road, near the railway station slightly opposite present-day Arthur Street. It was opened around September 1902 as a General Store, Bakery and Tea Rooms. This was the original building in the present-day shopping precinct. At the time the only thing nearby was the railway station. Luther Haley’s business appeared to prosper and he would have catered to not only the locals abut also day visitors by train on Sundays coming up from Melbourne, offering fresh baked produce, tea rooms and summer drinks. The fields across Main Road running between present day Arthur Street and Luck Street were known as Haley’s Paddock and at times were used for community festivities and picnics. A newspaper report on the annual State schools picnic held at Haley’s Paddock on March 11, 1904 described it as “quite close to the railway station, and is quite capable of holding comfortably 10,000 people. With its ample shade and hilly surroundings, it is an ideal place for any gathering.” Luther Haley successfully ran his general store, bakery and tea rooms until 1917 when he and his family departed the district and moved to Westgarth Street in Northcote where he changed careers and became a publisher. It was then taken over by Hannah Lloyd and became known as Lloyd’s Railway General Store from 1917 to 1920. From then it had a succession of owners, one as short as two months until March 31, 1939 when the Grocery Business formerly carried on by Mr. T.K. White of Eltham for the previous eight years was purchased by Mr Eric N. Staff of Research and became known as E.N. Staff’s Railway Store. The ownership timeline for the store is as follows: Luther Haley Sep 1902-1917 Hannah Lloyd 1917-c.Feb 1920 Messrs J.R. & N.E. Lee 1920-Sep 1922 A. & E. Copeland Sep 1922-Sep 1925 Mr Price Sep 1925-Nov 1925 Mr Warren Nov 1925?-Nov 1926 A.W.J. Edwards Nov 1926-1931 T.K. White 1931-Mar 1939 Eric Staff Apr 1939-c.1954 Ray Staff c.1954-Feb 1965 then demolished Ray Staff Eltham Big Star Food Centre c.1965-1967 THROWBACKTHURSDAY: ELTHAM BIG STAR FOOD CENTRE, MAIN ROAD, 1966 https://elthamhistory.wordpress.com/2020/04/16/throwbackthursday-eltham-big-star-food-centre-main-road-1966/eltham, businesses, a country heritage, property, shops, main road eltham, a. copeland, a.w.j. edwards, big star food centre, e. copeland, eric staff, general store, hannah lloyd, j.r. lee, lloyd's general store, luther haley, n.e. lee, price, ray staff, staffs general store, supermarket, t.k. white -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope
One of several letters sent to Mrs M MacDonald of Grey Street Wangaratta by soldiers during the second world war. This one is from Private Peter Alan ANDERSON VX 33905 Born 17/2/1910 Enlisted 21/2/1941 Served with 2/24th and 2/29th Battalions Prisoner of War - B Force / Japanese Died 25/2/1945 due to illness in Borneo - Labuan Memorial Malaya - POW No 282 Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with censor stamp and stickerTop left - By air mail Left side - AIF Censor stamp and sticker along fold "Opened by Censor" Right side - Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Rear VX33905 Pte P Anderson R.O.D A.I.F Malaya ww2, pow, private peter alan anderson vx 33905, 2/24th batt, 2/29th batt -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of palm tree and mountains.Top left - BY AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with sketch of palm trees and hut on left of scroll.Top left - AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Top left - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
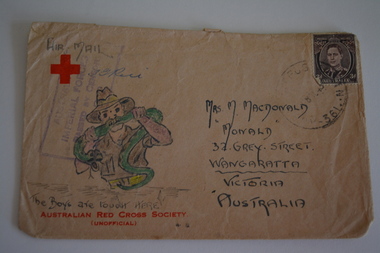 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of soldier holding green snake. Signature above sketchTop left - AIR MAIL and red cross Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Signature above sketch Below sketch - "The boys are tough here" / Australian Red Cross Society ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of three palm trees an ambulance and plane overhead with bomb exploding in distance.Top left - BY AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side - Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Bottom - "The good samaritan" 1943 ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with brown coloured sketch of palm tree with stick figure at base. Signature left of sketchTop left - AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Centre- AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Signature left side of sketch ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of a soldier pointing to a mosquitoTop left - BY AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp and signature Right side - Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Bottom - "Hey who let this thing in?" ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of Wangaratta Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of waterfall from mountainsTop left - BY AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side - Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with sketch of full moon over water and palm trees - to the left of this outline in blue of map of Australia with red shield in centreTop left - AIR MAIL above The Salvation Army Red Shield War Services Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Bottom left - " A Merry Christmas to you all" Right side Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
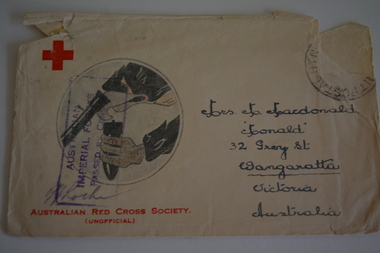 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes without letter sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with a circular sketch of an eagle holding shell/bomb Top left - Red Cross Top right - postage stamp Centre - AIF Censor stamp and signature Right side - Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Bottom Left - Australian Red Cross Society ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes without letter sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with sketch of two mountainsTop left - By Air Mail - ACF in red star Top right - postage stamp Centre - AIF Censor stamp and signature Right side - Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Bottom left - "They shall not pass" ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of Wangaratta Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with sketch of a soldier in bed and a nurseTop left - "The reason for not writing sooner" Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side - Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australi Rear - Red cross ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes without letter sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs McDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with sketch of three tall palm trees in front of mountainsTop left - By Air Mail Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side - Mrs M McDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
 Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.
Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Congregation of Kalorama Methodist Church 1911
Congregation gathered for photograph at front of Kalorama Methodist Church at FiveWays. The area was known as Mt Dandenong North until 1926 when the name was changed to Kalorama. The people assembled are all members of the local community. The church was built by the community in 1910.Black and white photograph showing a group of 31 people gathered in front of a wooden church building.kalorama, methodist church -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph - DISPLAY PANEL
COPIES OF DISPLAY PANELS DONATED TO THE PEOPLE OF CLUNES BY THE HUGH WILLIAMSON FOUNDATIONINTERPRETIVE DISPLAY PANEL DEPICTING HISTORY OF EBERHARD CORDIAL FACTORY, EARLY COLONIAL WINE MAKING UP TO PRESENT DAY WINE MAKING IN THE DISTRICT.local history, civic momentoes, presentations, williamson, hugh foundation -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph, John Street Rain Forest Revegetation Reserve, Lakes Entrance Victoria, 2000 c
Colour photograph of about 20 local residents listening to Bill Peel at the proposed John Street Rain Forest Revegetation Reserve John Street Lakes Entrance Victoriacoast, environment, people -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Cigar Cutter
This cigar cutter belonged to Dr.William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by his daughter, Bernice McDade. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.A chrome plated metal cigar cutter. Ruler measurements are marked along one edge. A swivel joint joins an internal blade at one end. Inscriptions are on moulded into the cutter. Made in Britain.The object is part of the W.R. Angus Collection. 'Ever-Ready BRITISH MADE'. Small ruler: 2 inches and 50 millimetres on the sides. Incised decorative pattern. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, cigar cutters, cigars, tobacco, smoking, w.r. angus -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Pistol Lighter
This pistol cigarette lighter belonged to Dr.William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by his daughter, Bernice McDade. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.A small pistol cigarette lighter. The object is part of the W.R. Angus Collection. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, smoking, lighters, novelty lighters, w.r. angus -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Sharpening Stone, Unknown
This sharpening stone belonged to Dr.William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by his daughter, Bernice McDade. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.A sharpening stone or whetstone set in a wooden box with lid. The object is part of the W.R. Angus Collection. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, sharpening stone, whetstone, medical, w.r. angus -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph, Lakes Entrance History Society 25th Anniversary 2002, 1/08/2002 12:00:00 AM
... Local History History Groups People Colour photograph ...Colour photograph of eight members of LERHS celebrating the Society's 25th Birthday in Society office, Marie Fish, Syd Skogh and Rev Heather Bryant, Marion Holding, Judy Davies, Des Thomas, Vera Bennett Lakes Entrance Victorialocal history, history groups, people -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Liz Pidgeon, Heritage Excursion; Eltham Lower Park, 1 July 2017
Civic Guide sign near the entrance of Eltham Lower Park with a map of the local area and an advertisement for Eltham College Newsletter No., 234, June 2017 Heritage Excursion - Saturday 1st July - Eltham Lower Park - Walk and Talk Eltham Lower Park has played an important part in the history of our area since the early days of European settlement when it was used by local residents as an informal racecourse. Prior to that its location at the junction of the Diamond Creek and the Yarra River made it an important meeting place for the Wurundjeri people. The park combines formal elements and sporting facilities with remnant bushland that is of environmental significance. It is home to sporting and horse riding clubs, popular play spaces and the Diamond Valley Miniature Railway, which attracts large numbers of visitors. The park will be the venue for our July excursion which will comprise a walk of about 3.5 km around the park and adjacent areas. Along the way we will discuss the history and natural history of the area. The path along the creek and the river provides a pleasant and scenic walk. This walk on Saturday 1st July is about 3.5 km in length and will take 2 to 2.5 hours. It will start at 2pm at the Main Road car park at the front of the park. (Melway ref 21 H 10). This sign was removed in about 2021 when works began on the building of an intersection to replace the roundabout at Fitzsimons Lane & Main Road. By May 2023 plantings in green spaces near Eltham Lower Park took place before the official opening of the new Eltham Gateway.Born Digitalheritage excursion, activities, eltham district historical society, eltham lower park, civic guide, eltham college, sign -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Liz Pidgeon, Heritage Excursion; Eltham Lower Park, 1 July 2017
Sign at the front of the park which includes a map. Newsletter No., 234, June 2017: Heritage Excursion - Saturday 1st July - Eltham Lower Park - Walk and Talk Eltham Lower Park has played an important part in the history of our area since the early days of European settlement when it was used by local residents as an informal racecourse. Prior to that its location at the junction of the Diamond Creek and the Yarra River made it an important meeting place for the Wurundjeri people. The park combines formal elements and sporting facilities with remnant bushland that is of environmental significance. It is home to sporting and horse riding clubs, popular play spaces and the Diamond Valley Miniature Railway, which attracts large numbers of visitors. The park will be the venue for our July excursion which will comprise a walk of about 3.5 km around the park and adjacent areas. Along the way we will discuss the history and natural history of the area. The path along the creek and the river provides a pleasant and scenic walk. This walk on Saturday 1st July is about 3.5 km in length and will take 2 to 2.5 hours. It will start at 2pm at the Main Road car park at the front of the park. (Melway ref 21 H 10). This sign was removed in about 2021 when works began on the building of an intersection to replace the roundabout at Fitzsimons Lane & Main Road. By May 2023 plantings in green spaces near Eltham Lower Park took place before the official opening of the new Eltham Gateway. The sig Born Digitalelection day, heritage excursion, activities, eltham district historical society, eltham lower park, sign -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupBook, City of Greater Dandenong, Living Treasures of Greater Dandenong. Heroes in our midst, 2000
... is a local project where people who have made a lasting impact ...Living Treasures is a local project where people who have made a lasting impact on the quality and nature of life for all of the City of Greater Dandenong community were named and honoured. The project was initiated as part of the city's celebrations for Australian Federation in 2001. In the lead up to federation, the City of Greater Dandenong honoured one of its residents as a Living Treasure each month from September 1998 until September 2000. This publication contains portraits of the initial living treasures - the project is ongoing. https://www.greaterdandenong.vic.gov.au/history-and-cultural-heritage/living-treasuresnon-fictionLiving Treasures is a local project where people who have made a lasting impact on the quality and nature of life for all of the City of Greater Dandenong community were named and honoured. The project was initiated as part of the city's celebrations for Australian Federation in 2001. In the lead up to federation, the City of Greater Dandenong honoured one of its residents as a Living Treasure each month from September 1998 until September 2000. This publication contains portraits of the initial living treasures - the project is ongoing. https://www.greaterdandenong.vic.gov.au/history-and-cultural-heritage/living-treasureswal turner, maurie jarvis, dandenong (vic.)
