Showing 464 items
matching warrnambool 1905
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Screen, Thomas Hope, 1905-1913
The fire screen was part of the original furnishings of the Lighthouse Keeper's Quarters in Merri Street, Warrnambool. It was made by Lighthouse Keeper, Thomas Hope. Thomas served two terms as an assistant lighthouse keeper in Warrnambool. His first term was from 1905 to 1907. He later returned from 1910 to 1913, when he was appointed as Keeper five months after the untimely death of his predecessor Peter Quinn. Woodworking was one of Thomas Hope’s hobbies, and the three-panel fire screen he made as a lighthouse keeper is now in the Flagstaff collection and is displayed in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage. Thomas Hope 1857 - 1928 Thomas James Hope was born in Camden, Surrey, England in 1857. His father, also called Thomas, was reputed to be a member of the Royal Family, and Thomas Hope Junior his illegitimate son. Thomas was subsequently brought up on the estate of the Earl of Hopetoun in Somerset and it was thought that Thomas was the Earl’s grandson. Against the wishes of those in charge of Thomas, he joined the navy at an early age, seeing much of the world until he settled in New Zealand at the age of twenty-four. After some years in New Zealand, he came to Australia to live. One of the jobs Thomas Hope had prior to becoming an assistant lighthouse keeper in 1896 was as a cook in the Lunatic Asylum at Sunbury, Victoria. He served as an assistant keeper at Shortlands Bluff, Gabo Island, Split Point and Warrnambool, retiring in 1918. He bought a house in Nicholson St, Warrnambool and died in March 1928. He is buried in the Warrnambool cemetery. Thomas Hope is recorded in family history as being of short stature and, not surprisingly given his alleged aristocratic connections, possessed a beautiful speaking voice. He and his wife Elizabeth nee Waters, whom he married in New Zealand, had six children (Thomas, killed in World War One), Ellen (Nell), Nora (who was married at the Warrnambool lighthouse keepers cottage), William (who died in Warrnambool), Marion and Alan. Joseph Hoover (Dec 29, 1830, to Aug 7, 1913) Joseph Hoover, the printer of the pictures on the screen, was born in Baltimore, of Swiss-German heritage. He was trained as an architectural woodturner. In 1856 Hoover moved to Philadelphia and began producing elaborate wooden frames in his wood-turning and framing business. By 1865 Hoover had started to produce popular prints for publishers and artists, which included noted Philadelphia artist James F. Queen. In the 1880s Hoover set up a complete plant specialising in chromatography, the process of producing colour prints from lithographic plates. The coloured prints he produced were affordable to business and private customers. In 1893 his son Henry L., a trained lithographer, joined the company as overseer and it was called J. Hoover & Son. It became one of the largest in America by the turn of the century. Hoover won a medal for Excellence for his Chromolithographs of James Queen’s works. In 1904 Joseph’s other son, Joseph W, joined the business as a partner and the company was called Jos. Hoover & Sons. Hoover died of a heart attack in 1913. He was survived by his wife and six children: two sons who were also his business partners, and four daughters. The firm continued in production until around 1985. Hoover’s prints included scenes, still life and landscapes of America and other locations. They were sold in America and overseas to countries including Canada, Germany, Mexico and England. The three-panelled screen in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage was made by the Assistant Lighthouse Keeper, Thomas Hope during one of his two terms at the Lighthouse Keepers' Quarters. It is the only object in the collection known to be connected to Hope. The Lighthouse Keeper's Cottage is part of the Lady Bay Lighthouse Complex, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register for being of historical, scientific (technological) and architectural significance to the State of Victoria.Fire screen comprising three black wood framed panels hinged together. Each panel contains a glass-encased print depicting a rural landscape. Ornate stencil cut wood edging and quilt-inspired parquetry sits above each panel. The central panel is taller than those either side. Screen is lined in black-painted cardboard.Printed at the base of each of the three prints “COPYRIGHT 1896 BY J. HOOVER & SON, PHILAD’’A.”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, firescreen, thomas hope junior, ellen (nell) hope, nora hope, william hope, marion hope, alan hope, jos. hoover & sons of philadelphia, lighthouse keeper, assistant lighthouse keeper, carved screen, merri street, lighthouse keeper's cottage, lighthouse residence, lighthouse, wood carving, lighthouse complex, lady bay lighthouse, fire screen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Table, Johann A. Landmann, 1853
This decorative octagonal inlaid table was made by Johann Landmann as a wedding present to his wife and was donated to Flagstaff Hill by the wife of Landmann's great-grandson. Landmann (or Landman, also known as August Landmann) was born in 1826 in Ganhor, Silesia, Prussia. At the age of 20, he travelled through Europe, working from town to town as a cabinet maker. At 26 years old he returned to Germany, married Anna Rosina in Wahlstatt, Prussia, and on the same day sailed for Australia on the Wilhelmsburg in 1853, the year the ship was registered. The Wilhelmsburg was a three-masted, square-rigged sailing ship built at Reiherstieg, Hamburg, and registered in Hamburg on 27th April 1853. On her maiden voyage in 1853, the ship sailed from Hamburg, Germany, to Australia with 510 passengers on board, including emigrants under the Bounty Scheme. Johan Landmann was one of the passengers. The Wilhelmsburg arrived in Hobson’s Bay, Melbourne after sailing for 100 days. Johann spent a week in Melbourne then travelled to Warrnambool aboard the Merry Kitty, arriving fourteen days later. Johann had landed in Melbourne with only 16 shillings in his pocket and by the time he arrived in Warrnambool, he only had one shilling and sixpence left. He also had very limited ability to speak English. He settled in the Allansford area, near Warrnambool, together with other families from Germany and went on to play a significant role in the history of Warrnambool. Johann worked as a cabinet maker in Warrnambool, making the first coffin in the Warrnambool cemetery. He also worked as a general merchant. He built many of the earliest shops in Warrnambool, and the first paddle boat used on the local Hopkins River. He made models of Warrnambool’s Ozone Hotel and Presbyterian Church; the model of the Hotel is now in the Warrnambool Art Gallery, and the model of the Presbyterian Church has been in the care of the Warrnambool & District Historical Society since around 2017. One of Landmann's residences was a two-storey building in Henna Street Warrnambool where he, lived upstairs and operated his business downstairs. After he retired Landmann built a ‘handsome stone residence’ at 30 Mickle Street, Warrnambool, where he lived until his death in June 1920; he was aged ninety-five. “Landmann Street” in Warrnambool has been named after Johann and appears on a map in 1872. He has also been honoured on Warrnambool’s Pioneer Memorial Board which is displayed at the Warrnambool and District Historical Society. Landmann's son Adolph Fritz Landmann (Fritz Landmann) born in 1861, was a Councillor from 1905 to 1915, and Mayor of Warrnambool from 1912 to 1915. The Wilhelmsburg sailed from Hamburg in 1863 heading for Queensland, Australia, but in December the vessel was wrecked off the coast of Holland during storms, with the loss of 247 lives.The table is significant as an early Warrnambool historical artefact with a connection to the maiden voyage of the ship Wilhelmsburg a vessel that holds the record for the number of passengers carried in one journey on a small vessel. Johann Landmann is regarded as a significant and historical figure in the development of Warrnambool as one of the earliest pioneers, not only as a businessman but the civic duties he undertook. First as a councilman and later the mayor of Warrnambool.Table, wooden, inlaid octagonal, two tiered with eight pillar supports and seven turned legs (one leg missing). Two large cracks in table top. A handwritten inscription is beneath the table top.Inscription is indecipherable. shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, warrnambool, table, octagonal table, inlaid woodwork, wilhelmsburg, johann landmann, augustus landmann, fritz landmann (warrnambool mayor), ozone hotel warrnambool, inlaid table -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Trinket Box, Johann A. Landmann, 1853
This trinket box was made by Johann Landmann during his journey on the sailing ship Wilhelmsburg and was donated to Flagstaff Hill by the wife of Landmann's great-grandson. Landmann (or Landman, also known as August Landmann) was born in 1826 in Ganhor, Silesia, Prussia. At the age of 20, he travelled through Europe, working from town to town as a cabinet maker. At 26 years old he returned to Germany, married Anna Rosina in Wahlstatt, Prussia, and on the same day sailed for Australia on the Wilhelmsburg in 1853, the year the ship was registered. The Wilhelmsburg was a three-masted, square-rigged sailing ship built at Reiherstieg, Hamburg, and registered in Hamburg on 27th April 1853. On her maiden voyage in 1853, the ship sailed from Hamburg, Germany, to Australia with 510 passengers on board, including emigrants under the Bounty Scheme. Johan Landmann was one of the passengers. The Wilhelmsburg arrived in Hobson’s Bay, Melbourne after sailing for 100 days. Johann spent a week in Melbourne then travelled to Warrnambool aboard the Merry Kitty, arriving fourteen days later. Johann had landed in Melbourne with only 16 shillings in his pocket and by the time he arrived in Warrnambool, he only had one shilling and sixpence left. He also had very limited ability to speak English. He settled in the Allansford area, near Warrnambool, together with other families from Germany and went on to play a significant role in the history of Warrnambool. Johann worked as a cabinet maker in Warrnambool, making the first coffin in the Warrnambool cemetery. He also worked as a general merchant. He built many of the earliest shops in Warrnambool, and the first paddle boat used on the local Hopkins River. He made models of Warrnambool’s Ozone Hotel and Presbyterian Church; the model of the Hotel is now in the Warrnambool Art Gallery, and the model of the Presbyterian Church has been in the care of the Warrnambool & District Historical Society since around 2017. One of Landmann's residences was a two-storey building in Henna Street Warrnambool where he, lived upstairs and operated his business downstairs. After he retired Landmann built a ‘handsome stone residence’ at 30 Mickle Street, Warrnambool, where he lived until his death in June 1920; he was aged ninety-five. “Landmann Street” in Warrnambool has been named after Johann and appears on a map in 1872. He has also been honoured on Warrnambool’s Pioneer Memorial Board which is displayed at the Warrnambool and District Historical Society. Landmann's son Adolph Fritz Landmann (Fritz Landmann) born in 1861, was a Councillor from 1905 to 1915, and Mayor of Warrnambool from 1912 to 1915. The Wilhelmsburg sailed from Hamburg in 1863 heading for Queensland, Australia, but in December the vessel was wrecked off the coast of Holland during storms, with the loss of 247 lives.The trinket box is significant as an early Warrnambool historical artefact with a connection to the maiden voyage of the ship Wilhelmsburg a vessel that holds the record for the number of passengers carried in one journey on a small vessel. Johann Landmann is regarded as a significant and historical figure in the development of Warrnambool as one of the earliest pioneers, not only as a businessman but the civic duties he undertook. First as a councilman and later the mayor of Warrnambool. Trinket box, wooden, with inlaid timber patterns and images. The design includes a mirror with a hidden compartment inside the hinged lid, a removable inner tray divided into compartments, and a fitted brass lock. The trim around the base is angled to widen the base. Images on the lid and three sides represent sailing vessels and a building. The lid and corners have a rope-edge design. Panels of the top and three sides have an intricate inlaid pattern featuring various wood grains. Images are framed by lines etched into the wood. The inside corners of the frames have inlaid quarter-circles of contrasting woods, resembling photograph corners.shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, warrnambool, trinket box, inlaid woodwork box, wilhelmsburg, landmann, johann landmann, augustus landmann, landman, fritz landmann (warrnambool mayor), presbyterian church warrnambool, 30 mickle st warrnambool, ozone hotel warrnambool, johann carl augustus landmann, jewellery box -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket set, John Dennett, ca. 1860s
This rescue line-throwing rocket set was made for the Dennett rocket system, which was used by the Rocket Rescue crews in South West Victoria from around the 1860s to the 1890s. John Dennett - John Dennett was from Carisbrooke, in the Ilse of Wight, UK. In 1826 he invented, patented and demonstrated an improved method of rocket powered, line firing rescue equipment for saving lives. The rockets had a longer range than the mortars being used, they were lighter, needed less preparation time, only needed one line for repeated shots, and fewer people were needed to move the equipment. Very favourable reports of Dennett’s rockets were received by those in charge of His Majesty’s Naval and Military services. In 1832, Dennett’s rocket-thrown line was sent out to the wreck of the ‘Bainbridge’, and was responsible for nineteen survivors coming ashore in two boatloads, along the fired line. Dennett’s rocket received national fame, and a one-year contract to supply rockets to the Coastguards. He became known as ‘Rocket Man’ and his rockets were used in rescues at least until 1890, when his son Horatio was running the business. A rocket weighing 23 lb would have a range of about 250 yards (228 metres), on average. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The first use of a lifesaving rocket rescue system is often credited to Captain Manby and his invention of a life mortar, first used in 1808 to fire a line onto a ship to rescue lives. Henry Trengrouse’s invention of 1820 was the first to use a sky rocket’s power to throw a line, and his invention included a chair for carrying the shipwrecked victims to shore. In 1832 John Dennett invented a rocket specifically for shore to ship rescue. It had an iron case and an 8 foot pole attached and could shoot the line as far as 250 yards (about 230 metres). From the 1860s the rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. Colonel Boxer, who had invented an early line-thrower, designed a rocket in 1865 with a range from 300 to 470 yards. It was the first two-stage rocket, with two rockets placed one in front of the other in a tube that carried the rescue line. The hemp line was faked, or coiled, in a particular way in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired, and the angle of firing the rocket was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol around 1920, which used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. Victoria’s Government adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain, which used Colonel Boxer’s rocket apparatus rescue method. The British Board of Trade published instructions in 1850 for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line attached, then firing it across the stranded vessel. A tally board was then sent out with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the continuous whip line and attach the whip block to a mast or sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a heavier hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser is then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rocket system could also be used from one ship to another.The Dennett rocket set is quite rare - there are not many examples in existence and little information is available. This Dennett's rocket set is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.A Dennett rocket set in six parts; the rocket head, three shafts (poles) and two rocket-head toting boxes. The rocket head, mounted on one of the shafts, is a long, red painted, iron tube with rounded ends and a protruding fitting around each end. The wooden rocket shafts are octagonal, with a metal sheath at the ends, carved elongated slots towards each end, and a scribed channel above the black foot. The rocket head toting boxes are thick timber, covered in fabric and painted black. They have a hinged wooden lid that slants downwards from back to front, and a metal closure. Small deliberate holes, in groups of four, on the box’s sides, indicate missing attachments, likely to have been handles. Impressed one a shaft "8"flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, irish hand barrow, rocket head toting box, explosives, rocket shaft, rocket pole -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rocket Launcher, John Dennett, 1860s
This rocket launching machine is used in conjunction with the Dennett Rocket Set. Both are part of the rocket rescue equipment that launches the line-throwing rescue rockets. A light line is threaded through the carved holes in the 8 foot long shaft and attached to the scribed channel at the base of the shaft. The rocket head is fitted to the shaft and inserted into the machine. The machine is set at an angle determined by the person in charge of the rescue crew, and the legs and base of the machine are adjusted accordingly with the use of the quadrant, or protractor, and plumb-bob on the side of the machine. The rocket is then ignited and fired across the vessel in distress. John Dennett - John Dennett was from Carisbrooke, in the Ilse of Wight, UK. In 1826 he invented, patented and demonstrated an improved method of rocket powered, line firing rescue equipment for saving lives. The rockets had a longer range than the mortars being used, they were lighter, needed less preparation time, only needed one line for repeated shots, and fewer people were needed to move the equipment. Very favourable reports of Dennett’s rockets were received by those in charge of His Majesty’s Naval and Military services. In 1832, Dennett’s rocket-thrown line was sent out to the wreck of the ‘Bainbridge’, and was responsible for nineteen survivors coming ashore in two boatloads, along the fired line. Dennett’s rocket received national fame, and a one-year contract to supply rockets to the Coastguards. He became known as ‘Rocket Man’ and his rockets were used in rescues at least until 1890, when his son Horatio was running the business. A rocket weighing 23 lb would have a range of about 250 yards (228 metres), on average. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket launcher machine is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket launcher, named a Rocket Machine, and storage box. Launcher has a long open metal channel with a spike at the base, and narrow, rectangular device, which is the line-firing rocket machine, at the top, all painted blue. Two hinged wooden legs are attached where the channel and machine meet. The side of the machine has an oval cut-out window and an attached quadrant, or protractor, with a plumb-bob on it. The quadrant has angles marked in degrees. The long protective box has white stencilled letters along the side. Its lid has three hinges and is fastened with two metal latches.On box “ROCKET MACHINE” On quadrant “10” “20” “30” “40”flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, protractor, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Hand Barrow, 1860s
This hand barrow, sometimes called a Welsh hand barrow, was used to transport a load of marine rescue equipment from the beach cart to the rescue site, particularly over hilly, uneven or rough terrain. Hand barrows were in common use in the 19th century. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This hand barrow is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Hand barrow; a transporting device carried between two people walking one in front of the other. A wooden ladder-like frame with two handles at each end, blue painted body with unpainted handles. Seven equal-length slats are joined at equal distance between two parallel poles, and two longer slats are attached diagonally between the first and last slats as a brace. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, hand barrow, manual transport, welsh hand barrow -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Sheet Music, Enoch & Sons Ld., music publisher, The Parade of the Tin Soldiers, ca 1911
This sheet music is "The Parade of the Tin Soldiers', the original German title, composed by Leon Jessel as a solo piece for the piano in 1905. The work is also known as "The Parade of the Wooden Soldiers". In 1907 the orchestra version was published, Opus 123. (Op. 123, as written on the cover). The sheet music was published by Sole Publishers for the British Empire, Enoch & Sons Ld (1890-1927) of 58 Great Marlborough Street, London, W. Versions for all other countries were published by Neinrichshofen's, Verlag, Magdeburg. Orchestral and Military arrangements of the music were published by Hawkes & Son, Denman St, Piccadilly Circus, London, Leon Jessel (Jan. 22, 1821 to Jan. 4, 1942) was a German composer who was born a Jew and converted to Christianity in 1894. His works included a wide variety of music including 'The Parade of Tin Soldiers' (Die Parade der Zinnsoldaten). Jessel was also a music conductor and bandmaster. The instrumental piece 'Die Marokkanische Patrouille' (The Moroccan Patrol) was published in 1911, Opus 227. He was also known for his operettas 'Schwarzwaldmädel'(Black Forest Girl), presented in 1917, and 'Die Postmeisterin' (The Postmistress), presented in 1921. In December 1941 he was arrested and then tortured by the German Gestapo; he died in January 1942. In the early 1920s, The Parade of the Tin Soldiers became very popular; it was presented as part of a show and was re-titled The Parade of the Wooden Soldiers. It was also made into a film and its recording was a hit single record. The music continues to be played and presented and is a Christmas-time favourite.This music is significant for its connection with the German composer Leon Jessel, a victim of the Germans for being born a Jew, even though he converted to Christianity in his youth. It is also significant as a popular work of music composed in the early 1900s and later used for a variety show and a film. The music an example of entertainment in the early 20th century that has endured to current times and often played at Christmas celebrations.Book of sheet music for four tunes. The thin softcovered book has eight pages, with the front cover featuring colourful graphics of soldiers marching and others on horseback. The four tunes are: - The Parade of the Tin Soldiers, (piano solo), Composer: Leon Jessel. Ballade de la Lune, Enjolement, Lentement, document, tendrament, Publisher: for the British Empire, Hawkes & Son, Denman St, Piccadilly Circus, London, Sole Publishers for the British Empire, Printer: Enoch & Sons Ld. 58 Great Marlborough Street, London, W. Printer: Lowe & Brydone Printers Ltd. London N.W. 10 Publisher, for all other countries: Heinrichshofen's, Verlag, Magdeburg. Printed: in England by Heinrichshofen's Verlag Copyright: 1911 by Heinrichshofen's VerlagOther print on the cover includes: ALSO KNOWN AS "THE PARADE OF THE WOODEN SOLDIERS" "Op. 123" "Characteristic Piede" "SOLE PROPRIETORS FOR THE BRITISH EMPIRE" "NEW SUCCESS BY THE SAME COMPOSER 'MOROCCAN PAT(ROL) (CH)ARASTIC PIECE" "PIANO SOLO" "SIMPLIFIED" "DUET" "VIOLIN & PIANO" "Orchestral & Military Arrangements" On the bottom of pages: "E & S 4370" "Copyright 1911 by Heinrichshofen's Verlag" flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, leon jessel, composer, operetta composer, the parade of the tin soldiers, the parade of the wooden soldiers, musical march, music conductor, music director, bandmaster, 19th-century classical composers, 19th-century german composers, 20th-century classical composers, 20th-century german composers, sheet music, music book, piano music, jewish composer, world war ii victim, composer: leon jessel., ballade de la lune, enjolement, lentement, hawkes & son, for all other countries: heinrichshofen's, verlag, magdeburg., book of sheet music, enoch & sons ltd london, lowe & brydone london, heinrichschofens verlag, marching music, 1911, early 20th century -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Sanctuary Lamp, ca. 1944
The sanctuary lamp was part of the original furnishings of St Nicholas Seamen's Church, Williamstown, Victoria. The church was operated by the Missions to Seamen organisation. The lamp was donated by Miss C. Roberts to St Nicholas Seamen's Church, Williamstown, as a memorial to Edward Roberts, who passed away on August 7th, 1905, as stated on the plaque. THE MISSIONS TO SEAMEN (Brief History: for more, see our Reg. No. 611, Set of Pews) The Missions to Seamen was an Anglican charity that served seafarers of the world since 1856 in Great Britain. It symbol is a Flying Angel, inspired by a Bible verse. Today there are centres in over 200 ports world-wide where seamen of all backgrounds are offered a warm welcome and provided with a wide range of facilities. In Victoria the orgainsation began in Williamstown in 1857 as a Sailors’ Church, also known as ‘Bethel’ or the ‘Floating Church’ in an old hulk floating in Hobson’s Bay, Port of Melbourne. It soon became part of the Missions to Seamen, Victoria. In the year 2000 the organisation, now named Mission to Seafarers, still operated locally in Melbourne, Portland, Geelong and Hastings. The Ladies’ Harbour Lights Guild was formed in 1906 to support the Missions to Seamen in Melbourne and other centres such as Williamstown. Two of the most significant ladies of the Guild were founder Ethel Augusta Godfrey and foundation member Alice Sibthorpe Tracy (who established a branch of the Guild in Warrnambool in 1920). The Guild continued its work until the 1960s. In 1943 a former Williamstown bank was purchased for the Missions to Seaman Club. The chapel was named St Nicholas’ Seamen’s Church and was supported by the Ladies’ Harbour Lights Guild, the Williamstown Lightkeepers’ Auxiliary and the League of Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Friends. It ceased operation in 1966. A Missions to Seamen Chapel and Recreation Room was a significant feature of ports during the late 1800s and into the 1900s. It seemed appropriate for Flagstaff Hill to include such a representation within the new Maritime Village, so the Melbourne Board of Management of Missions to Seamen Victoria gave its permission on 21st May 1979 for the entire furnishings of the Williamstown chapel to be transferred to Flagstaff Hill. The St Nicholas Seamen’s Church was officially opened on October 11, 1981, and closely resembles the Williamstown chapel. The lamp is socially significant as a lasting memorial to Edward Roberts. It is also significant historically for its origin in the St Nicholas Mission to Seamen's Church in Williamstown, established in 1857 to cater for the physical, social, and spiritual needs of seafarers. It originated in Bristol, England when a Seamen's Mission was formed in 1837. The lamp is historically significant for its connection to the Ladies Lightkeepers’ Auxiliary, an organisation of women, formed to support seafarers. The connection of this lamp to the Mission to Seamen highlights the strong community awareness of the life of people at sea, their dangers and hardships, and their need for physical, financial, spiritual and moral support. Sanctuary Lamp, brass six-sided lamp supported by three chains to a main disc, with single chain above. Ring on base. Ruby glass bowl on top. Inscribed glass plates on sides. Lamp bowl is lit by electric lamp. Made in England.Marked on plates "In Loving Memory of Edward Roberts who passed away 7 August 1905 Nearer My God To Thee"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, religion, religious service, sailors rest, bethel sailors’ church, bethel floating church, ladies harbour light guild, harbor lights guild, joy club for fighters, ladies lightkeepers’ auxiliary, missions to seamen victoria, mission to seafarers, flying angel’s club, st nicholas seamen’s church williamstown, st nicholas mission to seamen church williamstown, mission to seamen williamstown, st nicholas seamen’s church flagstaff hill, 139 nelson place williamstown, sanctuary lamp, electric lamp, church lighting, pendant lamp, edward roberts, memorial plaque, 7-08-1905, c. roberts -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chest of Drawers, British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, 1905-1927
This early 20th-century chest of drawers is unique. It was made from recycled timber kerosene boxes and metal tins. The case was made in South Australia between 1905 and 1927 by the British Imperial Oil Company Ltd, which was the first business to import bulk petroleum products into Australia. Before this, ships carried crates of kerosene as cargo. Items salvaged from the 1880 wreck of the vessel Eric the Red included kerosene boxes. Kerosene replaced plant and animal-based fuel, such as whale oil, for lighting in homes and for the lamps in lighthouses and on marine vessels. It was also used for cooking and heating and as engine fuel. The last kerosene-fueled lighthouse lamp was transferred to solar power in 1985. The chest of drawers is one-of-a-kind. The original uses for the components of the chest of drawers, the wooden box and metal tins were for containing and transporting kerosene. Kerosene was used from the late 19th century for fuel in lamps, heating, and cooling. Previously whale oil was used for the lamps in lighthouses. The company providing the kerosene was the first to import it into Australia in bulk quantities. The set of drawers is one of the many ways that inventive Australians were able to repurpose materials.Chest of drawers; wooden frame and rails, metal drawers with vertical metal handles. The frame has been constructed from the wooden panels of a vintage oil and kerosene box. The three drawers have been created from empty kerosene cans that were cut in half from top to bottom, some with the round opening closed over. Inscriptions from the original box and cams are stencilled on the top and base of the frame and impressed or painted on the metal cans. The frame has provision for a further drawer. The wooden case and metal tins were made in Australia.Top and base of frame; "THE BRITISH IMPERIAL OIL CO. LTD." "OIL ENGINE KEROSENE" "CASE ANDTINS AUSTRALIAN MADE" On tin; "POWIRIN" "BIOCO LTD" Logo [cross} with inscription on horizontal bar "CROSS" Impressed in timber drawer dividers (indecipherable text) Side of drawer, painted in orange on black; "TY -, REG U S - TIDE - "flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, antique, domestic equipment, chest of drawers, tool box, furniture, storage, recycled tin, recycled box, kerosene, fossil fuel, lighthouse lamp fuel, british imperial oil company ltd. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ports and Harbours, Ports and Harbours, Tender for Warrnambool Light, 24-06-1904
The document confirms that the Tender for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light, also known as the Lighthouse, by the Warrnambool Gas Works was successful. The Tender was issued by the Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for a the period ending 30th June 1905, at the offered rate of 10/- (ten shillings) per 100.0 c/f (cubic feet). The Manager of the Warrnambool Gas Works expected to follow this acceptance with a visit to the Collector of Customs to sign the Conditions of Contract and Bond. The light of Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse was originally powered by oil. Later it was converted to gas, followed by electricity, then solar power, and finally to battery power. The Warrnambool Gas Company operated the gas works from the 1870's to the late 1920's.This document connects Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse to the Warrnambool Gas Works during the first decade of the 20th century. It documents to process of a Government department requesting Tenders for the supply of goods to operate a service, the the formal documentation required at that time.Pale cream rectangular paper with template text printed in black and completed in black ink script. Letterhead of the Department of Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, and addressed to the Gas Works, Warrnambool, dated 24th June 1904, for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light until 30th June 1905 at the cost of Ten Shillings per 100 cubic feet."24th [June] 1904" Warrnambool [Light]" "Manager W'bool Gas Wks" "supply of gas to" "1905" "10/- per 100.0 c/f" "Collector of Customs" " The Manager / Gas Works / Warrnambool" [Signature] "for" [Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours]flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, department of ports and harbours, ports and harbours, ports and harbours melbourne, warrnambool light, warrnambool lighthouse, warrnambool gas works, w'bool gas works, gas works, gas supply, early 1900s, early 20th century, shillings, cubic feet, collector of customs, customs, warrnambool customs, engineer in charge, lady bay lighthouse, warrnambool gas company -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Coastal Scene, Joseph Jordan Photographic Studio, Lady Bay and Breakwater, Warrnambool, circa 1907
The Port of Warrnambool - In the early years the Port of Warrnambool was a busy port. Steamships and sailing ships were frequent visitors to the port. Steam navigation companies were plentiful, carrying passengers and freighting cargo such as coal, timber, food, livestock, furniture, hardware and haberdashery between Melbourne and the ports along the southwest coast of Victoria, including Warrnambool. The carts would take their loads into the township for distribution. The Breakwater was built (using 32 ton blocks of concrete) between 1874 and 1890 to provide ships with greater protection from the Southern Ocean. The Lifeboat and Rocket House - The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Joseph Jordan - Joseph Jordan was born in 1841 in Leicester England. When he was 16 he joined the 7th Queen's Own Hussars and was sent to India at the outbreak of the mutiny. He took part in the relief of Lucknow and remained in India for eleven years. It was during this time, he became interested in photography. He was posted to New Zealand and later came to Victoria, becoming a sergeant major of the Mounted Rifles. In the mid 1880s he came to the Western district where he was responsible for establishing units of the Mounted Rifles in various country towns such as Dunkeld, Mortlake, Panmure, Bushfield, Koroit etc. He resigned from the army in 1889 and set up a professional photography studio in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. He became very well known in the Western District for family photographs, official photographs of local councillors and groups as well as views of local scenery. In 1891 he photographed the wrecked barque "Fiji" at "Wrecks Beach" near Princetown. His business was taken over by his son Arthur around 1917. Joseph was a keen rifle shot and in 1924 he donated the "Jordan Shield" as a prize to the Victorian Rifle Association. He was made a "Life Honorary Member" of the Warrnambool Returned Soldiers League and in 1933 he was recognised as being the oldest living soldier in Victoria. Joseph died in 1935 aged 95.This photograph is significant for its association with the Port of Warrnambool and the Warrnambool Breakwater as it shows a point in time when shipping activities were an important part of Warrnambool's commerce and social development. It is also a record of the Warrnambool Lifeboat and Rocket house which was important in aiding ordinary citizens, harbour employees and the volunteer boat and rescue crew in saving the lives of sailors and passengers due to the high number of shipwrecks that occurred along the coastline. Joseph Jordan is a significant figure in Warrnambool history as he helped to establish early units of the Mounted Rifles (G Company) in local towns during the late 1880's and later, photographed local scenes, groups and citizens of early Warrnambool. Sepia photograph showing the beach and the Breakwater in Lady Bay Warrnambool, two ships (a steamship and a barque), a small sailboat, and the Lifeboat and Rocket House plus two smaller sheds.Front of photo - BREAKWATER, WARRNAMBOOL, VICTORIA Back of photo - "From: P Gregory / 365 Beach Road / BLACK ROCK 3193"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, warrnambool, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, lifeboat and rocket shed, steamship, barque, photograph of lady bay, rocket house, shipping, joseph jordan, lady bay, views of warrnambool, jordan photography -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Water Canteen and Ladle, mid-to-late 19th century
The horizontal water canteen has been carefully designed to fit snugly on the hip when worn with the straps diagonally across the body. The ladle allows quick and easy scooping of the contents to refresh the lifeboat and rocket launching crew, and the survivors of the disaster Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. This water canteen is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Water canteen and ladle; blue painted oval metal cylinder with a removable round threaded lid. Two adjustable leather shoulder straps are attached to the canteen through metal rings on the sides of the lid. A blue-painted copper ladle with a fixed, 45-degree angled handle is attached to the canteen with a length of string. The water canteen is designed to be carried horizontally.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, survival canteen, rescue canteen, dipper, cup, canteen and dipper, canteen and ladle, water canteen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Canvas Bag, mid-to-late 19th century
This drawstring canvas bag is amongst the Rocket Rescue equipment. It could have been used to carry equipment, clothing or provisions between the crew on the shore and the victims of a shipwreck or other rescue need. It could be worn on the shoulder or as a backpack or winched out to a vessel on the block and pulley system. The strong canvas could be weatherproof and waterproof to a large extent, provided the drawstring was pulled tight. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in a wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. This canvas bag is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Canvas bag; thick beige canvas bag, cylindrical with a round base. The top has a thin rope in a drawstring closure. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, survival kit, rescue kit, canvas bag, storage bag, carry bag, equipment bag, drawerstring bag -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The History of Northcote
Warrnambool Public Library The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. SIGNIFICANCE The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. The History of Northcote Author: William George Swift Publisher: The Leader Publishing Co Pty Ltd Date: 1928Label on spine with typed text RA 994.51 SWI warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool library, the history of northcote, william george swift -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, How To Collect Books
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1942 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. How To Collect Books Author: J Herbert Slater Publisher: George Bell & Sons Date: 1905 Label on spine with typed text PAT 020.75 SLA Pastedown end page has sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, pattison collection, warrnambool library, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, how to collect books, j herbert slater -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Lasseters Last Ride
About Ion L Idriess Ion Llewellyn Idriess was born in Waverley, Sydney, New South Wales on 20th September 1889 and passed away on 6th June 1979 in Mona Vale, Sydney, New South Wales at the age 89. After Idriess finished school he worked in the assay office of Broken Hill Proprietary mine. Both Idriess and his mother had typhoid fever when Ion was about 15 years old and it caused his mother’s death. After spending time with his Grandmother in Sydney he found work on a paddle-steamer and had a relapse of the fever. He then went into the western district of New South Wales where he worked in many different itinerant jobs, including rabbit poisoner, boundary rider, drover, sandalwood harvester, shearer, dingo shooter and opal miner. While opal mining at Lightning Ridge he wrote short stories, about life on the opal fields, for the Bulletin using the name “Gouger”. Idriess then moved to North Queensland in search of gold, tin and sandalwood. He travelled over a great deal of the Cape York Peninsula spending a lot of this travel time with local indigenous people; thus began his lifelong interest in their customs. He then spent time on cattle stations in the Gulf of Carpentaria. In 1914 Idriess travelled to Townsville and enlisted in the 5th Light Horse as a trooper. He became a specialist in sniping and was a spotter for the noted sniper Billy Sing. He saw service in Palestine, Sinai and Turkey. Idriess was wounded at Beersheba and after fighting the Battle of Gaza he was invalided home in March 1918. After recovering from his wounds Idriess again travelled to Cape York Peninsula where he worked with pearlers and missionaries in the Torres Strait Islands. He then went gold mining in Papua New Guinea, buffalo shooting in the Northern Territory of Australia and then exploring in Central and Western Australia. LITERARY WORKS OF IDRIESS In 1928 Idriess settled in Sydney and published the first of his 47 books. In 1931 - “Lasseter’s Last Ride”, became his first best seller. In the years 1932 and 1940 he published three books in each year. “The Cattle King” (1936) and “Flynn of the Inland” (1932) have gone through reprinting forty to fifty times. His last book was published in 1969. Idriess’ books where in general non-fiction and were written in a colourful and immediate story style, taken from life experiences gained during his travels. Idriess was appointed an Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (OBE) for his service to literature in 1968. Warrnambool Public Library The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison SIGNIFICANCE The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. Lasseters Last Ride First published in 1931 Author: Ion Idriess Publisher: Angus & Robertson Label on spine with typed text R.A. 994.03 IDR warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, great ocean road, book, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, warrnambool public library, lasseters last ride, ion idriess, indigenous people -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Knights of The Boomerang
WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. Knights of The Boomerang Author: Herbert Basedow Publisher: The Endeavour Press Date: 1935Label on spine with typed text RA 572.94 BAS Pastedown front endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, knights of the boomerang, herbert basedow -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Reference, Australian Aborigines
WARRNAMBOOL'S MECHANICS' INSTITUTE Warrnambool's Mechanics' Institute (or Institution as it was sometimes called) was one of the earliest in Victoria. On 17th October 1853 a meeting was held where it was resolved to request the Lieutenant Governor of the Colony to grant land for the erection of a Mechanics' Institutes building. A committee was formed at the meeting and Richard Osburne chaired the first meeting of this committee. The land on the North West corner of Banyan and Merri Streets was granted but there were no funds to erect the building. The Formal Rights of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute's encompassed its aims and these were officially adopted in1859; "This Institution has for its object the diffusion of literary, scientific, and other useful knowledge amongst its members, excluding all controversial subjects, religious or political. These objects are sought to be obtained by means of a circulating library, a reading room, the establishment of classes, debates, and the occasional delivery of lectures on natural and experimental philosophy, mechanics, astronomy, chemistry, natural history, literature, and the useful and ornamental arts, particularly those which have a more immediate reference to the colony." The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute opened its first reading room in November1884 in the National School building at the corner of Banyan and Timor Streets. The Institute was funded by member subscription, payable on a quarterly, half yearly or yearly basis. Samuel Hannaford, the Manager of the Warrnambool Bank of Australasia, was the first Honorary Secretary of the Mechanics' Institutes, and an early President and Vice-President. He also gave several of the early lectures in the Reading Room. Another early Secretary, Librarian and lecturer was Marmaduke Fisher, the teacher at the National School. Lecture topics included The Poets and Poetry of Ireland', 'The Birth and Development of the Earth', 'The Vertebrae - with Remarks on the pleasures resulting from the study of Natural History' and 'Architecture'. In 1856 the Reading Room was moved to James Hider's shop in Timor Street, and by 1864 it was located in the bookshop of Davies and Read. In the 1860's the Mechanics' Institute struggled as membership waned but in 1866, after a series of fund raising efforts, the committee was able to purchase land in Liebig Street, on a site then called Market Square, between the weighbridge and the fire station. A Mechanics' Institute building was opened at this site in August 1871. The following year four more rooms were added to the main Reading Room and in 1873 the Artisan School of Design was incorporated into the Institute. The same year Joseph Archibald established a Museum; however it deteriorated when he was transferred to Bendigo in 1877. In 1880, with Archibald's return to Warrnambool, the Museum was re-established, and in 1885 a new building was built at the back of the Institute to accommodate the re-created School of Design, the Art Gallery and the Museum. In 1887 the Museum section was moved to the former court house in Timor Street (for some time the walls of the building formed part of the TAFE cafeteria but all is now demolished)). In 1911 the Museum was transferred back to the original building and the management of the Mechanics' Institute was handed over to the Warrnambool City Council. The Museum and Art Gallery became one and housed many fine works of art, and the Library continued to grow. The building was well patronised, with records showing that at the beginning of the 20th century there were between 500 and 800 visitors. During World War One the monthly figures were in the thousands, with 3,400 people visiting in January 1915. The Museum was a much loved Institution in Warrnambool until the contents of the Museum and Art Gallery were removed to make room for the Warrnambool City Council Engineers' Department. The contents were stored but many of the items were scattered or lost. When the original building was demolished the site became occupied by the Civic Centre, which included the new City Library. (The library was temporarily located in the old Palais building in Koroit Street.) In the process of reorganisation the Collection was distributed amongst the community groups: -The new City Library took some of the historic books and some important documents, historic photographs and newspapers. -The Art Gallery kept the 19th Century art collection and some of the artefacts from the museum. -The Historic Society has some items -The State Museum has some items -Some items were destroyed -Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village has old newspapers, Government Gazettes, most of the Mechanics' Institute Library, ledgers and documents connected to the Mechanics' Institute Library, some framed and unframed art works and some photographs. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Library book collection is deemed to be of great importance because it is one of the few collections in an almost intact state, and many of the books are now very rare and of great value. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. Australian Aborigines Has hand written "Presented to the Warrnambool Mechancis Institue and Free Library with compliments from The Author 1881" Author: James Dawson Publisher: George Robertson Date: 1881 Label on spine with typed text RA 572.9945 DAW Front loose endpaper has a sticker from Warrnambool Public Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool public library, australian aborigines, james dawson, indigenous people -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Waverley Novels Vol 6 The Antiquary
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1942 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. Warrnambool Public Library The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. Waverley Novels Vol 6 The Antiquary 2 Author: Sir Walter Scott Publisher: Fisher, Son and Co, London Date: 1836Label on spine with typed text PAT FIC SCO Pastedown end page has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library Front loose endpaper has a sticker Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, pattison collection, warrnambool library, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, waverley novels vol 6 the antiquary, sir walter scott -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Cattle Chosen
The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance Cattle Chosen Author: E O G Shann, M.A. Publisher: Oxford University Press Date: 1926Label on spine cover with typed text R.A. 994.1 SHA Pastedown end paper has a sticker from Warrnambool Public Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, warrnambool library, cattle chosen, e o g shann -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Scallop
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1942 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Scallop Studies of a shell and its influences on humankind Eight authors edited by Ian Cox Publisher: The Shell Transport & Trading Co Ltd Date: 1957Label on spine cover with typed text PAT F 704.94 SCA Pastedown end page has a sticker from Warrnambool Public Library Front loose endpaper has a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, pattison collection, warrnambool library, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, the scallop, ian cox -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Land of Byamee
WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Land of Byamee Australian Wild Life in Legend and Fact Author: Keith C McKeown Publisher: Angus & Robertson Date: 1938 Label on spine cover with typed text RA 398.200994 MAC Pastedown end page has sticker from Warrnambool Public Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool library, the land of byamee, keith c mckeown -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Proceedings of The Royal Society of Victoria Vol 17
Proceedings of The Royal Society of Victoria Vol 17 Containing Papers read before the Society during the months of August, September, October, December 1904 Publisher: Royal Societys Hall Date: 1905Label on spine cover with typed text R.A. 506 ROY Pastedown end page has sticker from Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, proceedings of the royal society of victoria vol 17, the royal society of victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Australian Annual Digest 1954
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1942 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Australian Annual Digest 1954 A digest of the reported decisions of the Australian courts and of Australian Appeals to the Privy Council Editor Jean Malor Publisher:The Law Book Comp of Australasia Date: 1955 Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 346.94 AUS Front pastedown end page has sticker from Warrnambool Public Librarywarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, pattison collection, warrnambool library, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, the australian annual digest 1954, jean malor -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Maritime painting, The La Bella, 1980s
This painting of the “La Bella” is associated with Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the wreck of the “La Bella”. It was painted around the 1980s by maritime artist Philip J. Gray. Some 15 – 17 ships are believed to have sunk in Lady Bay, but only two have been discovered on the seafloor; the “La Bella” and the “Edinburgh Castle”. Both wrecks are popular diving sites and are preserved as significant historical marine and marine archaeological sites. The Kosnar Picture Framing and Mirrors Shop identified the "GRAY 3135, Y04/111" as their job number for the framing and said that the label "ANOTHER KOSNAR FEATURE" was last used before about 1990. About artist Philip J. Gray “Philip is one of Australia’s leading maritime artists and his meticulous research and social commentary paintings of ships, such as, the Loch Ard and Schomberg form an important part of Warrnambool’s Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum.” [Dr Marion Manifold, Artist and Art Historian, 2014] Philip James Gray was born in London but has lived most of his life in Australia. He graduated from a London school of art as an illustrator, specialising in technical and scientific illustration as well as other commercial and applied art. He was also a student for a time of Fyffe Christie - British figurative artist, mural painter and humanitarian – who had a great influence on his career. Philip has always worked as a professional artist and illustrator. Many publications on maritime history have featured his work. His paintings have been released and sold all over the world as limited edition prints. The State Library of Victoria’s ‘Latrobe Collection’ holds two of his paintings. His street painting of ‘The Ashes Contest’ decorates the brick wall of Old Bakery Laneway in Sunbury and a Sunbury café owner commissioned him to paint the ‘Sunbury Pop Festival’ as a remembrance of local history. Philip has been an active member of the Sunbury Art Society in Victoria for several years, serving on the committee for some of that time and being involved in exhibitions. He enjoys helping new artists and sharing his skills and experience. About the “La Bella” The wreck of the La Bella lies at the bottom of the Warrnambool Harbour in Lady Bay. Some 15 ships are believed to have been wrecked there but only two have been discovered on the sea floor; the La Bella and the Edinburgh Castle. Both wrecks are popular diving sites and are preserved as significant historical marine and marine archaeological sites. The story of the final voyage of the La Bella is summarised as follows … The ship from which the sailors were rescued was the three-masted, iron and steel barquentine the La Bella, built in Norway in 1893. She was one of two iron and steel ships by Johan Smith, the company being one of the leading shipping families in Tvedestrand, Norway. She was significant to Norwegian shipping, being one of only 27 iron and steel ships ever built in Norway. La Bella was registered in New Zealand and engaged from 1902 in inter-colonial trading of timber in the pacific, between New Zealand and Australia and was often in Port Phillip Bay, Victoria. On 5th October 1905 the twelve year old La Bella left Lyttleton, New Zealand carrying a cargo of timber bound for Warrnambool, Australia . She was manned by a crew of twelve: the Master, (Captain Mylius, previously 1st Mate of La Bella, appointed Captain to La Bella on 6th February 1903) 2 Mates, Cook, six able seamen, one ordinary seaman and a boy. Bad weather en-route caused her to shelter at Burnie on Tasmania's North West coast. On November 10th, the 37th day of her journey, La Bella approached Warrnambool. Captain Mylius steered her towards Lady Bay Channel in heavy south-west seas and evening mist. He ordered the helmsman to steer for the light. As the ship came round, a tremendous sea struck her on the port quarter, causing her to breach broadside in a north-westerly direction into breakers. The helm was brought round twice more, but each time heavy seas broke over her, the third time throwing the La Bella on to a submerged reef in Lady Bay now known as La Bella Reef (about 100 yards from the Warrnambool breakwater). The sea was so rough that it even wrenched a one-and-a-half ton anchor from its fastenings and into the sea. As Captain Mylius headed to the steel wheelhouse, intending to send up a rocket flare, a huge sea slammed the steel door into him (resulting in massive bruising front and back) Despite his injuries he still managed to set off a blue light, which he held up in his hands. La Bella’s lifeboats were filled with sea water and broke up on their chocks. The blue light was the first indication to people on shore that there was a ship in distress. The Harbour Master, Captain Roe (who lived in the Harbour Master’s House opposite Flagstaff Hill), organised a group of volunteers to crew the lifeboat because the trained crew was unavailable; the crewmen were working on a steamer in Port Fairy at the time. He then poured oil onto the water to try and smooth the sea. At around 11pm three of the crew took shelter in the steel forecastle but the sea crashed into it and broke it up. While the rest of the crew and onlookers watched helplessly in the moonlight the bodies were washed away into the sea, never to be seen again. Some of the crew lashed themselves to the weather rail to keep from being washed away. Watson, the ordinary seaman, became tangled in the rigging lines and was too weak to move, so the 2nd Mate, Robertson, put a line onto him so that he wouldn’t wash off. Around 11pm three of the crew were unconscious from exhaustion. The situation on La Bella was becoming dangerous. The 2nd Mate moved to the ‘house’ and soon afterwards the ship slipped in the heavy sea. The lashings of the 1st Mate and the ‘boy’ Denham had kept them safe until about 2am when they were washed overboard; no one was able to help. One by one, the exhausted crew were being washed overboard, too weak to hold on any longer. During the night the La Bella had broken into two and the deckhouse ran out towards the sea. Two more men drowned when trying to reach the lifeboat. By sunrise the only survivors of the twelve were the Master, 2nd Mate and three seamen. Early in the morning Captain Roe used the rocket apparatus on shore to try and shoot a line to the ship for a safer rescue but each attempt fell short of the target. Several attempts were made by the lifeboat to rescue the stricken sailors, but the rough conditions made this difficult for the boat to get close enough to the ship and the lifeboat had to return to shore. During a final attempt to reach the ship Captain Mylius ordered his men to jump into the sea. Leonard Robertson, 2nd mate, jumped and swam towards the lifeboat, taking hold of the boat hook offered to him. Oscar Rosenholme managed to reach the boat floating on a piece of timber from the ship’s load and a third survivor, Noake, also made the boat. Along with the lifeboat rescue crew, 25 year old William Ferrier rowed his small dingy through the heavy seas and managed to rescue the Captain, whom he landed on the breakwater. Ferrier then returned to the ship to attempt a final rescue, losing his oars and rowlocks into the high sea. Using just a spare paddle he skulled towards the La Bella, reaching her stern in time to cut loose the lone surviving sailor, Payne, from the lashing that held him to the ship; the terrified sailor dropped from the ship and into the dingy. Shortly after the last man was rescued, the La Bella was lifted by a huge wave and crashed back down on the reef; she broke up and sank. The ordeal had lasted ten hours. The survivors were taken to the nearby Bay View Hotel and gratefully received warm food and clothing, medical attention and a place to sleep. In the following days an unidentified body of a young person was washed ashore; it was either Watson or Denham. The body was buried in the Warrnambool cemetery with an appropriate gravestone and inscription. William Ferrier became a national hero as news of the daring rescue spread. In recognition of his bravery in the two daring rescues he was awarded the Silver Medal for Bravery by the Royal Humane Society and was honoured in the letter from the Prime Minister and the Parliament of the Commonwealth, telegrams and a cheque for £20 from the Governor General, over £150 subscribed by the public, including Warrnambool and district and readers of The Argus, and a gold medal from the Glenelg Dinghy Club of South Australia. Ferrier’s rescue efforts are one of the most heroic in Victoria’s shipwreck history. (William Ferrier’s son, Frank, received a similar award almost fifty years later, when he helped rescue four members of the crew on the yacht Merlan, after it ran on to a reef near the Point Lonsdale Lighthouse. ) The wreck of La Bella now lies on her port side in 13 metres of sheltered water inside the reef she struck. The bow section is relatively intact and part of the stern has drifted north-easterly towards the mouth of the Hopkins River. The reef the La Bella struck now bears its name. Those five rescued from the La Bella were Captain George Mylius, Leonard Robertson (2nd Mate, 21 years old), R. Payne, Oscar Rosenholme and Jack Noake. Those seven who lost their lives were Mr Coulson (1st mate), Charles Jackman (cook) Gustave Johnson, Pierre Johann and Robert Gent (all able seamen), Harry Watson (ordinary seaman) and Jack Denham (ship’s boy). Captain Mylius was found guilty of careless navigation; he had sailed into the bay without the services of a pilot. His Master Certificate was suspended for twelve months. Later he was also charged with manslaughter of one of the crew who had died when the La Bella was wrecked, but found not guilty. The event’s adverse publicity and damage to his career took a toll on his health and he died of a heart attack six months after the wreck; he was only thirty-seven. His body was buried in the Melbourne General Cemetery. The La Bella was “the best documented of all sailing ships owned in New Zealand”. Her record books, ship logs, correspondence and supporting papers are still available. At the time of the tragedy she was owned by Messers David C.Turnbull and Co. of Timaru, New Zealand timber merchants and shipping agents, who had purchased her on 13th December 1901. A detailed account of the last journey of La Bella can be read in “Leonard Robertson, the Whangaroa & La Bella” written by Jack Churchouse, published in 1982 by Millwood Press Ltd, Wellington, NZ.This painting of the La Bella by Philip J. Gray is part of the La Bella Collection and is significant at both a local and state level. Its connection to the La Bella shipwreck and the rescue of five survivors highlights the dangers of Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast. The painting connects with other objects and artefacts associated with the wreck of the La Bella. This painting is significant because of its association with the sailing ship “La Bella” . the “La Bella” is of local and state and national significance. It is one of the only two shipwrecks discovered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool, out of the 15-17 shipwrecks in the bay. Large framed painting of the three masted barquentine "La Bella" fully rigged. Painted by Phillip J Gray. A fine printed line squares off the painting. Beneath painting and line is a gold plate with black copper plate designating "La Bella" is encased in glass, surrounded by a silver-metal frame. Yellow and brown paper label is adhered to back of painting. Picture framed by Kosnar in Melbourne."The La Bella" on gold plaque Logo of "K" inside a brown square. "GRAY 3135, Y04/111", "ANOTHER KOSNAR FEATURE" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, painting, la bella, artist phillip j gray, maritime painting, lady bay warrnambool -
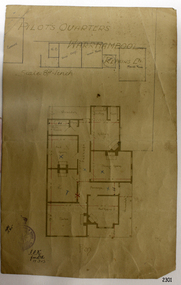 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Plan, Pilots Quarters Warrnambool
Warrnambool was officially made a Port of Entry in 1855 and by the 1870s had became the dominant port in the Western District. Sadly, due to an increasing problem with silting in the harbour, by the 1890s only small vessels could navigate the harbour. Men with the position of Pilot and Harbourmaster in Warrnambool were employed by the government to enforce government regulations and to help guide vessels safely into the port of Lady Bay, which was difficult to navigate. Some of the Pilots and Harbour Masters of Warrnambool were – - Captain Christopher Gwatkin, the first Harbourmaster for Warrnambool (1857 - his death in 1859). - Captain Helpman was Warrnambool’s second Harbourmaster 1859-1869 - James Nicol was Harbourmaster in Warrnambool for a time, including 1906 (b. 1840 – d. 1926) - Thomas Smith Drewett (1853 - 15-3-1905) past Captain of the Helen Nicoll, Pilot and Harbourmaster of Warrnambool. Warrnambool’s Tourist Guide of 1888 advises that “At the Port of Warrnambool there are two Leading Lighthouses. A licensed sea pilot, Captain Drewett, is stationed at the Port.” In 1915 plans for the Pilot’s Quarters were drawn up for the Department of Public Work. It was at that time, when personnel was short due to the First World War, that apparently the Pilot and Harbourmaster was also responsible for maintaining the light (lighthouse). The new Pilot and Harbourmaster’s house would be built on the site at 88 Merri Street, overlooking Lady Bay and right beside the Flagstaff and the Lady Bay Upper Lighthouse. Other Pilot and Harbourmasters were - - James Menzies was the Pilot and Harbourmaster at Warrnambool in 1929 . In 1932, he was appointed to the position of Acting Secretary to the Warrnambool Harbour Board. A hundred or so years later Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village has fully renovated the former Harbourmaster’s quarters, changed the name to Lighthouse Lodge, and is now allowing guests to stay in the home, which is still neighbour to the operational Lady Bay Lighthouses, now over 150 years old. The association of the old Pilot and Harbourmaster’s Quarters (currently renamed as Lighthouse Lodge) with the Port of Warrnambool, and its maritime activities, is historically significant. The Pilot’s quarters are connected to a time when access to Warrnambool’s Port was important to the colonial settlers for income and supplies. Plan of Pilots Quarters, Warrnambool. Printed and handwritten plan shows house, garage, out buildings and maid's room. The plan's lower left corner has an official stamp and text beside the stamp. Department of Public Works, Melbourne, Victoria, March 11th, 1915. "PILOTS QUARTERS WARRNAMBOOL" "Department of Public works, Melbourne, Victoria I.P.K. , 11.3.15"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plan, pilot's quarters warrnambool, pilot and harbourmaster's quarters warrnambool, pilot and harbour master's quarters warrnambool, port of warrnambool, department of public works victoria, lady bay lighthouses, warrnambool ports and harbours -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Traveller pulley block, 1860s
The life saving breeches buoy was attached to a traveller block such as this one. The assembly was sent from shore to ship and back to transport the stranded people and goods safely to shore. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them.This traveller block is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost. Wood and brass pulley block or 'traveller', used in conjunction with the Breeches Buoy. The block has double brass inline sheaves and brass rollers on each cheek of the pulley. Each shell is scored for the strop. The thimble on the strop has a wooden slat attached for quick release of the Breeches Buoy. A portion of rope is connected.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, petticoat breeches, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, life jacket, traveller, traveller block, running block, block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, faking board, italian hemp, quadrant, protractor, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, welsh hand barrow, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, government of victoria, harbour master, l.s.r.c., lsrc -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Case, Early 20th century
This small case is lined with a metal insert and shows remnants of a carry strap. It could have been used for storing and carrying fuses or cartridges for the life saving Rocket Launcher machine. The protective metal insert would help keep the contents dry or cool and protect from flame. It is part of the collection of rescue equipment in the Rocket House used by the life saving rescue crew. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This small leather carrying case is significant for its connection with the rocket rescue equipment, local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Leather case, brown with contrasting stitching, protective metal insert divided into two compartments. Rectangular shape. Roller buckle on front with remnants of the matching strap. Also remnants of a leather strap on the side, possibly a shoulder strap.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, line throwing cartridge, l.s.r.c., lsrc, leather case, cartridge case, fuse case, ammunition case -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageUniform - Arm Bands, c. 1860s
Members of the Life Saving Rescue Crew would wear scarlet arm bands such as these as part of their uniform, with each member having a different number. The crew would work as a team to haul in the victims of the shipwreck. The leader of the crew would call out one or several member's numbers to give them a break during the rescue, while other members took their place. All members would then be relieved at some time during the rescue. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This set of scarlet arm bands is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Arm bands; three scarlet flannel arm bands with black cotton backing and a metal buckle on one end. White cotton embroidery forms letters and numbers, with each arm band having a different number. Part of the uniform of the Life Saving and Rescue Crew.Embroidered on front "L.S. 1 R.C." "L.S. 8 R.C." "L.S. 13 R.C." flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, arm band, armband, scarlet arm band, l.s.r.c., lsrc, red arm band -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Life Jacket, General Naval Supply G.N.S.), 1940
This life jacket was issued by the Australian Government's General Naval Store in N.S.W.. It was inspected in 1940. Life Jackets - Life jackets were part of the equipment carried by the Life Saving Rescue Crew of South Western Victoria, including Warrnambool, from around 1858 until the 1950s. The purpose of a life jacket is to keep the wearer afloat until he or she is rescued from the water. Life jackets were first invented in 1854 by Captain Ward of the Royal National Lifeboat Institution in Britain. The early life jackets were filled with cork, which is very buoyant. However, many times he cork caused the jacket to rise up quickly with a force that caused unconsciousness, sometimes turning the person face down in the water , causing them to drown. After the tragic loss of the ship RMS Titanic in 1912 and the lost lives of those onboard, a woman named Orpheus Newman designed the Salvus life jacket (Salvus means safe), which was filled with kapok instead of cork. Kapok comes from seed pods of the Ceiba Pentandra tree and is waterproof as well as buoyant. These Salvus jackets were used by the Royal Navy until new synthetic materials became available around the time of World War II.This life jacket is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Life jacket, canvas covered, with two padded compartments filled with kapok. Designed to slip over the head. it has shoulder straps and straps for tying under the arms. An inscription and symbol is stamped on one shoulder strap. The life jacket was supplied by the General Naval Store, Defence Department, N.S.W., and inspected in in 1940.Inscription "G.N.S. [crown symbol] N.S.W / 12 JUN 1940 / INSPECTED".flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, g.n.s., general naval store, 1940s life jacket, captain ward, royal national lifeboat instution, cork, kapok, life jacket, orpheus newman, salvus jacket, life saving, rescue, rescue crew, l.s.r.c., life saving equipment, marine technology, lifeboat, shipwreck victim, vintage
