Showing 11132 items
matching line
-
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumMap, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Melbourne's tramway routes and timetables - MMTB, 1925
Map of the MMTB Tramway routes 1925 with a list of first and last cars, along with photographs of Wattle Park, Luna Park, and Studley Park. Provides information for the Prahran and Malvern lines, Hawthorn, Footscray, Essendon, Coburg, Kew, St Kilda, cable tram routes, and buses. Also provides information for passengers. The cover photo is of the front of W 296, with the destination of Esplanade. The map is dated by the opening of the line to West Brunswick as far as Albion St, the City Road to St Kilda line via Sturt St lines, and the electric line in Flemington Road which were all opened during mid to late 1925. See Reference. Shows a number of buildings and locations by a numbered reference list, including the Federal Parliament house. The map has advertisements around the outside of the map for Kiwi Shoe or boot polish.Yields information about the Melbourne tramway system in 1925 and demonstrates the methodology the MMTB used to provide information to travellers. Shows both cable and electric tram lines and the development of the Melbourne system.Map book - 15 fold paper titled "Melbourne's tramway routes and timetables"trams, tramways, mmtb, tramway maps, wattle park, studley park, timetables, cable trams, w class tram, tram 296, kiwi shoe polish -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionEricsson 'Commonwealth' wall telephone Model AB535
The Commonwealth Ericsson Wall Telephone was adopted in 1901 by the Post Master General as the standard magneto telephone throughout Australia. It was designated by the Australian Post Office as: "Telephone No.1 - Magneto Wall, Commonwealth Type" The No1 was widely used in country areas and new installations of this type continued throughout the 1920s. Although classified as obsolete in 1951, several were still in service in country areas into the mid-1960s before the phone systems were fully automated. The phone was originally connected to a 'party' line (several connections to a common wire), and the winder was turned in various combinations of long and short turns (being the codes unique to each individual connection) to alert the other party of an incoming call. Anyone could listen in on a party line, although courtesy prevented it occurring most of the time. Central telephone exchanges rendered the party line obsolete. Vintage wall telephone The case originally housed two No6 dry-cell batteries to power the speaker (early models used a pair of Leclanche-like wet-cell batteries - the drawing from 1911 indicates that wet-cell batteries were still in use at that time). Batteries became obsolete when the phone was connected to a central exchange. A plastic speaker horn was fitted in 2025 - the original was missing on front - L M ERICSSON & Co STOCKHOLM inside - serial number: 496018 H 5 (this serial number identifies the phone as being manufactured in 1904) inside - slip of paper identifies date of manufacture as 1904 inside aftermarket writing - F.W.31forests commission victoria (fcv), communications -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Fred Rochow Railways Collection - Driver George Sandford, C. 1970s
The Fred Rochow Railways Collection incorporates photos related to the operation of the Wodonga Railway Station including different types of trains and railways staff C. 1930 – 1990. It was donated to the Wodonga Historical Society by Fred Rochow, a railwayman who spent many years based in Wodonga. He joined the Victorian Railways on 17th June l947 and retired in 1988. For some time, he was a member of the Australian Federated Union of Locomotive Enginemen and served a term as a member of the Trades Hall Council. He had an extensive knowledge of the struggles that took place to achieve better conditions for railway workers. Fred worked for many years as a fireman and then worked his way up the ranks to driver, experiencing many changes from the days of steam locomotives through to diesel trains, locomotives and even the modern XPT train. He worked throughout Victoria at different stages of his career, with his final working years focused on the northeast of Victoria and the Albury to Melbourne line. After his retirement, Fred continued to share his love of steam miniature trains with the community.This collection has local and statewide significance as it captures images of trains, locomotives and personnel who operated the railway services in Wodonga and throughout Northeast Victoria. The railways played a critical role in opening up Victoria and connecting Australia for trade, business, social communication and transport.Driver George Sandford on Locomotive K153 George joined Victoria Railways on 4th June 951. He started cleaning at Seymour on 21 February 1955. George passed his Driver qualification on 18 May 1960. He was based at Cressy from 1966 to 1968 followed by Wodonga from 1966 to 1982. K Class Locomotives - One of VR's most successful classes of loco they were built over a 24 year period. A general purpose, light lines loco the K class had a very long career in all sorts of service from branch line passenger and goods work to pilot and banker duties and roadside mainline service. The K class is credited with working virtually every line in the VR system and hauling almost every kind of train. The majority of the class lasted into the 60's. K153 entered service on 9 September 1940, initially allocated to the Benalla locomotive Depot It is now owned by VicTrack and managed by Steamrail Victoria. When in Melbourne, it is regularly used on suburban shuttles and on day tours to Geelong and similar-length trips. At various stages it has been withdrawn from service for preservation work. Throughout its preservation career (starting from 1974), the engine has been painted all-over black with some details picked out in white or yellow (such as handrails and the staff exchanger horn, welded in the raised position) to meet modern safety standards. It most recently returned to service in 2003.railways wodonga, fred rochow, wodonga railwaymen, george sandford, locomotive k153 -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Barnes Railway Station, Moama, NSW, c.November 1962, 1962
The railway reached Echuca in 1864 and transformed the town into a major river port, with a famous wharf and substantial urban growth in the 1870s. In 1876 the Deniliquin and Moama Railway Company opened its 71 km (44 mi) private railway northwards to Barnes and Deniliquin, and the line at Echuca was extended across the Murray River into Moama to join the railway. This section was taken over by Victorian Railways in 1923, as part of the 1922 Border Railways Act. Barnes station was closed in 1979. Deniliquin railway line https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deniliquin_railway_lineDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybarnes railway station, echuca, george coop collection, moama -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayStation Sign - Puffing Billy Direction Trains to Belgrave - Emerald & Lakeside
Station Sign - Puffing Billy Direction Trains At Menzies Creek, a Puffing Billy train has had to pass another train since 1966, due to a single line in operation from Belgrave or Emerald / Lakeside / Cockatoo / Gembrook to enable more trains to operate. When two trains passed at Menzies Creek, to assist passengers to travel on the correct train, this sign was erected. The arrows pointed towards the direction of travel as well as the locomotive that was hauling the train. This sign dates from 1975 when the line was re-opened to Lakeside. Historic - Puffing Billy Railway - Station Sign used at Menzies Creek to show next station directionStation Sign - Puffing Billy Direction Trains to Belgrave - Emerald & Lakeside Large rectangle wooden sign Puffing Billy Trains to BELGRAVE Trains to EMERALD & LAKESIDEpuffing billy, menzies creek, station sign -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumLetter - from Alwyn Marshall Toolamba to Wal Jack, Alwyn Marshall, 1958 & 1959
Wal Jack had an extensive range of correspondents throughout Australia and the world. This set are two letters from Alwyn Marshall of Toolamba, who travelled extensively. His first letter discusses tramways in Sydney, the type of trams in use, Brisbane tramways, NSW Railways on the Sydney to Brisbane line, Queensland railways, the Sandy Hollow line and the wooden trestle bridge near Nayook. He used a motor bike for his Australian travels. The second letter discusses the Frankford lines in Philadelphia and sending maps of the system.Demonstrates some of the correspondence that Wal Jack received from around the world.Set of two typed letters on quarto paper from Alwyn Marshall to Wal Jack 4 Dec 1958 - two sheets Friday, May 1 (no year), single sheet - based on the calendar most likely 1959) letters, wal jack, railways, photography, tramways, sydney, brisbane, qgr, nswgr, philadelphia, alwyn marshall -
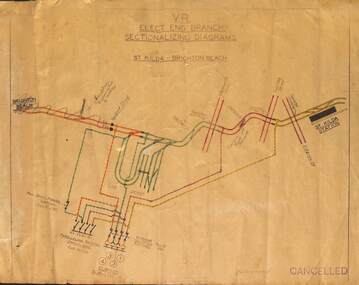 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDrawing, Victorian Railways (VR), "Sectionalizing Diagram - St Kilda - Brighton Beach", c1957
Drawing shows the power supply arrangement to the overhead for the VR St Kilda Brighton tramway, including Elwood depot and substation. Has been marked up for removal of the line south of Elwood Depot to Brighton and Dickens St crossover. Shows the isolating and paralleling switches and their pole numbers. Not known when the original drawing was prepared. The tramway or electric street raikway operated from 1906 to 1959, the section south of Elwood depot closing in two stages during 1956. See reference for history of the line.Yields information about the power supply arrangements for the St Kilda Brighton tramway.Drawing dyeline print and hand coloured with a cloth back sheet with two punch holes on the left hand side to enable filing.Has numerous pencil inscriptions that updated the drawing to c1957 and a "Cancelled" stamp in the bottom right hand corner.tramways, vr, victorian railways, power supply, electrical switching, electrical engineering, st kilda brighton tramway, elwood depot -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Case, Early 20th century
This small case is lined with a metal insert and shows remnants of a carry strap. It could have been used for storing and carrying fuses or cartridges for the life saving Rocket Launcher machine. The protective metal insert would help keep the contents dry or cool and protect from flame. It is part of the collection of rescue equipment in the Rocket House used by the life saving rescue crew. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This small leather carrying case is significant for its connection with the rocket rescue equipment, local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Leather case, brown with contrasting stitching, protective metal insert divided into two compartments. Rectangular shape. Roller buckle on front with remnants of the matching strap. Also remnants of a leather strap on the side, possibly a shoulder strap.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, line throwing cartridge, l.s.r.c., lsrc, leather case, cartridge case, fuse case, ammunition case -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Tally Board, 1860s
The boards each have instructions adhered to each side, printed in four languages (English, French, Dutch and German). At the beginning of a shore-to-ship rescue the instructions are sent to the distressed vessel after the first rocket line was received by them. The stranded people on the vessel follow the instructions to assist the life saving rescue crew in saving their lives. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest themThis pair of tally board is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Tally boards, two, rectangular wooden boards, both with a hole drilled into one short end. Instructions are glued onto the boards. They were printed in light letters onto dark canvas in four languages (English, French, Dutch and German). Text (English) "MAKE THIS HAWSER FAST ABOUT 2 FEET ABOVE THE TAIL BLOCK. CAST OFF WHIP FROM HAWSER. SEE ALL CLEAR AND THAT THE ROPE IN THE BLOCK RUNS FREE, AND SHOW SIGNAL TO THE SHORE."flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, breakwater, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, lifeboat warrnambool, beach apparatus, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, beach rescue set, rocket set, tally board, rescue instructions -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Sand peg set, Mid-19th to mid-20th Century
This set of Victorian era wooden sand pegs was part of the equipment used by the Rocket Rescue Crew when attending a shipwreck. The broad pegs were designed to give a strong grip on soft sand and soil. The pegs could be used with the sand anchor as well as to give a stronger hold on the tripod holding the hawser. The same design is still available today and is used by the Army and by campers. The rocket rescue crews used a sand anchor at a beach rescue site to weigh down the rescue apparatus. The crew would connect the shackle to the other cable on the anchor and to the loose steel cable to form a triangle with the cable lengths. They would then bury the anchor in about a 0.75-meter trench, keeping the free end of the cable above the surface. This end of the cable was then connected to a block that was attached to the heavy hawser line. The block and a crotch pole were used to keep the hawser line high and taught as the survivors were hauled to shore on a line or in a breeches buoy. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s, the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This set of sand pegs would have been used with sand anchor that is part of the rocket rescue equipment . It is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Peg or spike; set of twelve wooden pegs, painted red. Pages have a long, thick square shank with bevelled side edges, flat top with broad hook on one side of the top and a point at the other end. A small hole goes from one side to the other side near the centre of the shank, on the face without the hook. flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket equipment, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, whip line, endless whip, harbour board, sand anchor, rocket set, anchor backer, beach anchor, backer, steel cable, wire cable, sand peg, wooden tent peg, army peg, military peg -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Chisel
Cold chisel; long metal rod with round flat head, six sides with one being slightly indented. Shank tapers to a flat end with a narrow blade. Inscription impressed into metal with a deliberate indented line on it. Size 1/2 inch. " - - CT STEEL" flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, chisel, cole chisel, forging tool, hand tool -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaLetter - Correspondence, 1947
Quinn CollectionTwo-page, double-sided letter on unlined paper (0359.a1-a2) written on board S.S.Morgenster, dated 19/10/47 with blue-lined, stamped envelope (0359.b). Envelope bears United States postage two stamps.Envelope has been re-addressed to 140 Brunswick Road, Brunswick, Victorialetters-from-abroad, quinn, s.s.morgenster, 1947 -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumLetter - LETTERS of SYMPATHY, Sgt D.P. Pullen, DEC 41
Letter of Sympathy from RAAF Unit for Dental Surgeon "Mervyn Clive Townsend", lost on HMAS SYDNEY on 15 /11/41. Refer Cat No. 2313P for Townsends service.Letter of Sympathy from Sgt D.P. Pullen. White faded paper, lined with emblems on top of each page for YMCA, Salvation Army, A.C.F. and Returned Sailors and Soldiers League. Both pages same structure with handwritten message in black writing.Listed from “401581, Sgt Pullen D.P. No.1 ED RAAF”hmas sydney, sympathy letters, mervyn clive townsend -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - AMMUNITION BOX - VICKERS MACHINE GUN, c. 1939 - 45
Box would contain a belt of .303 ammunition for a Vickers machine gun - one belt of 250 rounds. Yellow lining included to make the box gas tight to avoid ammunition being corroded.Metal box with double hinged lid. Two leather handles rivetted to each side of the box. Two leather straps on one end for fastening. Inside of lid lined with yellow coloured felt padding. Box originally painted dark green.Stamped on opposite end to fastener: "RPL" above a circle.ammunition box, vickers machine gun, ww2 -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Letter Book Presbytery of Mortlake, Early 20th century
This letter book (1922-6) was found in the old Mackay Taylor building in Kepler Street. The Secretary of the Presbytery of Mortlake in the early 1900s was George Mackay who established his legal business in 1891 and merged with the business of James Fletcher in 1893 to form Fletcher and Mackay. In the 1920s J. Taylor joined the business which was known from then on as Mackay and Taylor and this firm existed until the 1990s. George Mackay was prominent in Warrnambool civic and community affairs and was Secretary of St. John’s Presbyterian Church for many years. The Presbytery of Mortlake was an administrative district committee established in 1862 and included the Presbyterian churches of Port Fairy, Tower Hill, Wangoom, Allansford, Warrnambool, Woodford, Hexham, Caramut, Mortlake and Terang. The committee consisted of the local ministers, some elders and other church representatives and met monthly or quarterly to discuss church business that affected the region. This letter book is of some significance as it indicates the type of business carried out by a district church council – properties, missions, individual church problems etc. It also shows the community work of George Mackay, a prominent Warrnambool resident at the time, and the book contains his signature, many times over. The book will be of interest to researchers. This is a ledger with dark blue binding and binding reinforcements on the spine and corners. The inside covers are lined with thick paper in a mottled blue and black coloured pattern. There are 250 pages with entries up to page 54. The letter copies are typed with an alphabetical listing at the front.Front Cover: Label with typed title ‘Presbytery of Mortlake’ Spine: ‘Letter Book’ presbytery of mortlake, george mackay -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Cap, scouts, Circa 1950
This cap belonged to Mark Pullen, a cub scout from Highton, Geelong, Victoria. No information is available on Mark Pullen. In Warrnambool there are three scout groups – Allansford, Norfolk (scout hall at the corner of Raglan Parade and Kepler Street) and Tooram (scout halls at the corner of Timor and Banyan Streets and in Otway Road). Cub scouts in Victoria are aged between 8 and 10. This cap has no known local provenance but is a useful item for display.This is a cap made of dark green wool with narrow gold braid dividing the crown into six sections. A button is missing from the top. The badge on the cap is a circular patch with the scout emblem in yellow and green. The cap is lined with black material with a white centre.Hills Hats Size 7 Name: Mark Pullen Group: 1st Highton Fabric Content all wool Scout Approved Product Made Expressly for the Scout Association of Australia Made in Singapore scouting in australia, scout association of australia, mark pullen, highton, geelong, fleur de lis, fleur de lys -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPostcard - Memorial Card, Lisa Widdop - Celebration of Life
Verso of memorial card with an illustration of a yellow and black tail with a red tuft inscribed with "Oh the Places You'll Stand. Also a 32 line verse beginning with 'Oh , where will you go?' attributed to Jill Revelli. Black writing on a fawn background. -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchCommunications Head Set
Head set used for communications equipment. Consists of two earpiece receivers attached to a head band with a flexible cable for connection. The cable terminates in a two pole line plug. The earpices have a protective rubber shroud and one has a cloth cover.The ear receivers have the following, 'ANB-H-1 MADE IN USA BY UTAH-CHICAGO'radio, ww2, communications, headphones, radio, ww2, communications, headphones -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFur Collar, 1930’S
The donors of this fur collar believe the collar to be between 80-90 years old. It was worn by the donor’s grandmother and mother as an accessory to Warrnambool and district balls and dances. It may have also been worn for warmth! The donors believe the fur would have been purchased in either Melbourne or Toorak. This fur could have been worn by either men or women. This fur collar is representative of fashion accessories in Warrnambool and District in the 1930’s.Fur collar, 1930’s. Rabbit fur collar, wide lapels, very soft fur with dyed pattern of light and dark brown stripes. Collar is lined with a heavy dark green woollen fabric. Between the fur and the lining there is a felt interfacingflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, fur collar, fur stole, fur accessory, clothing 1930’s, fashion 1930’s, fashion accessory, rabbit fur -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaLetter - Correspondence, 1949
Quinn Collection Three sheets of cream-coloured, lined paper (0800a1-3). Each sheet is written on one side only. Letter dated 1.01.1949 and headed Willoughby. The envelope (0800b) bears a lilac-coloured Australian stamp priced at one shilling and sixpence.0800.b is addressed to M.S.Fenris C/- Thor Ekerka Co. , 19 Rector Street, New York, post-marked 25-01-1949 and franked with the slogan 'Road carelessness kills'letters-from-abroad, quinn, 1949 -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaMedal - Medal in box, Royal Mint, Civil Defence Long Service Medal
Charles worked in the Merchant service. After enforced retirement due to injury he was active in Civil Defence. Donated by the estate of Mr Charles Page. Commemorative cast alloy/silver-coloured oval medal with attached ribbon and pin. One side of medal depicts profile of QEII, while the other side depicts three shields with acorns. The medal is housed in a small blue velvet lined case.On box: "Civil Defence Long Service Medal"charles page, medal, civil defence -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAccessory - Sash belonging to Syd Cuffe, Portland Town Crier, n.d
Blue velvet sash, gold fringe, lined with blue fabric. Approx 250 badges collected by Syd Cuffe on trips around Australia and overseas to participate in competition as a Town Crier. Earliest date on a badge 1985. The badges cover 50 % of the sashtown crier, championships, world travel, badges, sash, syd cuffe, portland -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionFunctional object - Fishing floats, c. 1950
Four various sized cork floats, egg shaped wooden 'pencil', rod through middle, protruding both ends. Top section painted white, bottom green, the two sections separated by a red line Identification numbers 7570a-d -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAccessory - Shoulder Patch - Portland Junior Basketball Association, c. 1980
Oval cloth shoulder patch, white background, black print 'PORTLAND JUNIOR BASKETBALL ASSOCIATION' around edge, line drawing of basketball ring and basketball in centre, 'RUNNERS UP UNDER 12 COMPETITION 1980' beneath. Badge bound in yellow.portland basketball, recreation, junior sport
