Showing 744 items matching "triangle"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Badges, Warrnambool Racing Club Membership, 1950s
These badges all marked W.R.C. appear to come from the Warrnambool Racing Club. The first race meeting in Warrnambool was held in 1848 at Jetty Flat. The first meeting at the present race course was held in 1858 with Warrnambool Racing Club established in 1873.The main event in Warrnambool horse racing today is the May Racing Carnival which features the Grand Annual Steeplechase. It has 33 jumps, the most hurdles of any race in the world over 5,500 metres. These badges are of minor interest as ones that belonged to members and supporters of the Warrnambool Racing Club.1 Silver coloured metal diamond shaped badge fixed to a silver coloured metal horizontal bar. The centre of the diamond has intertwined letters R W C The reverse has a pin clip attached to the bar with numbers. .2.1 and .2.2 Silver coloured metal badge In rectangular shape with extended arcs on top and bottom and triangular extensions on the sides. R W C and other text is raised . The reverse has a pin clip The numbers on the reverse of the badges are different. .3 Rectangular silver coloured metal badge. The sides of the rectangle have extended points. The letters RWC are raised. Under these letters is a scroll with text. There is a pin clip on the reverse and numbers. .4 Triangular gold coloured metal badge with R W C raised and a scroll underneath with text. The upper corners of the triangle feature decorative spirals.There is a pin clip on the reverse with numbers. .5 Rectangular gold coloured badge with raised WRC attached to a gold coloured metal horizontal bar. There is a pin clip on the reverse and numbers. .1 RWC A 121 . 2.1RWC B7 LADY SEASON 1958 /59 STOKES .2.2 RWC B93 LADY SEASON 1958/59 STOKES .3 RWC LADY B123 SEASON 1956/57 STOKES MELB .4 RWC LADY B106 SEASON 1957/58 STOKES MELB .5 WRC A 125 STOKES MELB -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomMedal
The 1914–1918 Commemorative War Medal (French: Médaille Commémorative de la Guerre 1914–1918, Dutch: Oorlogsherinnerinsmedaille 1914–1918) was a Belgian commemorative war medal established by royal decree on 21 July 1919 and awarded to all members of the Belgian Armed Forces who served during the First World War that were eligible for the inter-allied victory medal.The Belgian 1914–1918 Commemorative War Medal was struck from bronze, it was 47 mm high by 31 mm wide, triangular shaped and with rounded sides. On its obverse, the relief left profile of a helmeted soldier within a 29 mm in diameter circular recess, the helmet adorned with laurels. Between the circular recess and the bottom left corner of the medal, the relief date "1914", in the lower right corner, the relief date "1918". In the upper point of the triangle, above the circular recess, the relief images of a lion rampant with an oak branch to its left and a laurel branch to its right. On the reverse, near the top, the relief image of a crown surrounded by the same branches as the lion on the obverse, below the crown, the relief semi circular inscription in French on two rows over the large relief dates "1914 – 1918", "MEDAILLE COMMEMORATIVE / DE LA CAMPAGNE", the inscription repeated in Dutch below the dates "HERDENKINGSMEDAILLE / VAN DEN VELDTOCHT" (COMMEMORATIVE MEDAL OF THE 1914 – 1918 CAMPAIGN).medal, belgium, ww1 -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Jane ANNOIS, Jane Annois, Evolution, 2006
Jane Annois had a long involvement with Potters Cottage in Warrandyte, where she taught for many years. Potters Cottage was established in the late 1950s in Warrandyte as an artist co-operative. Founding members included Reg Preston, Phyl Dunn, Gus McLaren, Artur Halpern, Sylvia Halpern and Elsa Ardern. These talented artists had the ingenuity and foresight to create a teaching studio, gallery shop and restaurant to experiment, make, promote and sell predominantly domestic wares of the time. These activities helped financially sustain each member’s individual creative practice. Potters Cottage was influential in the development of contemporary ceramics, building and developing practices that experimented with traditional ceramic processes, raw materials and locally sourced clay. The group mentored and nurtured many interested in the art of ceramics, producing alumni and teachers such as Peter Laycock, John Dermer, Greg Daly and Jane Annois. Jane Annois is a ceramic artist who has lived and worked locally in Warrandyte for many years. She focuses primarily on exploring the art of Japanese raku, adapting the technique to develop the typical characteristics of crackle glazes and lustres, with contrasting areas of black. Jane also applies a fine slip called terrasigillata which gives soft, warm ochre colours. This technique was once used by the Greeks over 2000 years ago to seal and decorate their pots. She is also strongly onfluenced by the French potters, particularly in the style of terre vernissee, a decorative form of terracotta tableware. Three piece stoneware and raku fired ceramic sculpture. The first piece is a hollow, dome shaped object. It is orange (terracotta slip) in colour with a copper metallic band and a black edge on one side with a small yellow glazed rounded triangle and metallic strip of colour on the otherside. The second piece is shaped like a traditional vase. It is orange (terracotta slip) in colour with white crackle on the inside. It has a yellow slip edge with a dark glazed square on one side and on the other side a black thick edge that mirrors the contour of this shape. The third piece is shaped loosley in the form of the letter 'z'. It compliments the second piece with a yellow slip edge and black glazed square to its lower left side and top right as well as on its' other side a black thick edge that mirrors the contour of this shape. This piece has a very small skewed square opening at its' top. All three pieces have elements of crazing and variations of colour and lustre, caused by the raku process. 2006.52.1VA has the artist name/signature 'J. Annois' inscriped small (with fine point ceramic tool?) on the front of the piece, bottom right; 2006.52.2VA has the artist name 'Jane'? inscribed (unlegible - with fine point ceramic tool?) underneath; 2006.52.3VA has the artist name/signature 'Jane Annois' inscriped (with fine point ceramic tool?) inside its hollow form. evolution, raku, stoneware, terrasigillata, terracotta, glazes, slip, terre vernissee -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, Circa 1971
The Vogt LO150 is a sailplane first produced in 1954. Designed in Germany by Alfred Vogt, the LO150 is of wood construction. It has a two piece wing of 15 metre (49 feet) span and a fuselage of monocoque design. The first of the type to be imported into Australia arrived in late 1955. In January 1956 this aircraft type was used to create a world speed record of just under 75 km/h for speed around a 300 km triangle and went on to win the Australian National Gliding Championships. The Museum’s LO150 (VH-GUC) – serial number EB71 was imported from Germany in 1971 by the late Frank Erdmann and an ownership syndicate formed. Following Erdmann it has had a number of owners. Much of its usage was at Bacchus Marsh and Horsham with excusions elsewhere for competition. This Vogt LO150 was last flown on 3 January 1988. Overall, since arriving in Australia, it has flown 315 hours from 273 launches, which is a commendable average performance of over an hour per flight. VH-GUC was donated to the Museum by Warren Mayfield in 2002. Substantial glue deterioration was discovered in one wing and, as a result, a decision has been made not to restore the glider to an airworthy condition. In due course the glider will be repainted and further prepared for display. This exhibit is an example of the Vogt LO150 semi-aerobatic competition sailplane.Single seat competition sailplane of wood construction.Builder's serial number EB71australian gliding, glider, sailplane, vogt, lo-150, erdmann, mayfield, geelong gliding club -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratJournal of Australasian mining history 2007, Australian Mining History Association, 2007
Periodical/journal: "Embracing all aspects of mining history, mining archaeology and heritage." Articles by various contributors Copper Triangle’s Spanish Legacy: Leaching the Waste Dumps at Moonta Mines 1901-1944. Australian Geochemical Mineral Exploration: It all began at Moonta through V.P. Sokoloff. Hegemony, localism and ethnicity: The ‘Welsh’ mining communities of Currawang and Frogmore in southern New South Wales. A Thirsty and Confusing Diggings: The Albert Goldfield, Milparinka-Tibooburra, north-western NSW. ‘Another Broken Hill’: The Mount Deddick Silver-Lead Field. Michael Dineen O’Keeffe: Union Leader - a ‘colourful personality. Radium Hill: Bindi To Boom Town. Tragedy on the Strickland: Jack Hides and the Investors Ltd Expedition of 1937 COMMENTS Observations on the History of the Blackwater Gold Mine. Comment on Brian R. Hill, ‘A Reinterpretation of the History of the Acquisition of the Blackwater Gold Mine’, Journal of Australasian Mining History, vol. 4, September 2006, pp. 156-165. BOOK REVIEWS Bullfinch and the Yilgarn Goldfield, Hesperian Press, Victoria Park, Western Australia, 2007; xvi +265pp Reviewer: Lenore Layman, Murdoch University Fool’s Gold: Myths and Legends of Gold seeking in Australia, Lothian Books, Sydney, 2006. Reviewer: Philip Payton, Exeter University Relevant to Australian and New Zealand history, particularly around miners and mining.Paperback. Front cover: crème coloured background; black and white photo; red and black lettering; 180 pages.Front cover: title and publisher.btlc, ballarat trades and labour council, ballarat trades hall, history - mining, moonta mines, albert goldfield, milparinka-tibooburra, mount deddick, michael dineen o'keeffe, radium hill, strickland, investers ltd, blackwater gold mine, bullfinch, yilgam goldfield, gold -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Collars and box
Detachable collars enclosed in a leather box such as this one were used in the 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly by men in the business and clerical professions. The collars were attached by studs or buttons to a shirt. The collars were removed prior to shirt washing the shirt. The leather box was most useful for travelling. Detachable collars could still be used today particularly by clergymen. Two are named E R Twomey.This box and collars are retained as an example of vintage men's wear. It will be useful for display.A brown leather cylindrical case with a strap and buckle. It has white thread stitching around the rim and upper edge of the lid, the slot for the buckle, the rim and lower edge of the base . Inside are four detachable white winged collars for wearing with a shirt. Each has three holes, one for a button and two for a stud or for buttons at the front, two wings and a curved slot at the back.They are made of very fine cotton and linen.002215.1 J.T. MADE IN ENGLAND ESPECIALLY FOR Buckley & Nunn Ltd. MELBOURNE 002215.2 A stamped lion, WELCH MARCETSON 7 CO. LTD. 4 THE ALATUS TRADE MARK DES M 9 M 520 1 3/4 x 1/2 T14 002215.3 MADE IN ENGLAND FOR BUCKLEY & NUNN MELBOURNE EXTRA QUALITY , A deer head with antlers in a pointed elipse E.R. THOMEY a red inverted drawn triangle two dots Lindum 2x 151/2 002215.4 MADE IN ENGLAND FOR BUCKLEY & NUNN MELBOURNE EXTRA QUALITY, A Deer head with antlers in a pointed elipse . T indecipherable . E.R.T.4 indecipherable. Lindum 2x15 002215.5 E.R. THOMEY Indecipherable Lindum 2x 15 ? warrnambool, detachable vintage collars, detachable men's shirt collars -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Kitchen Equipment, meat platter 'CETEM WARE', c1930
The Maling Pottery of Newcastle upon Tyne, England, was in production from 1762 to 1963. In its heyday it claimed to be the biggest pottery in the world. The first Maling pottery was established at North Hylton, near Sunderland, in 1762 by William Maling. William’s descendants who moved to the Newcastle area and built a succession of larger works. The last of these – the Ford B pottery – was begun in 1878 and occupied a 14 acre site... Maling’s stock in trade was everyday white ware – marmalade jars for Keillers and Coopers, crockery for railways, shipping lines and hotels, and a huge variety of domestic kitchenware. With a significant export trade in the 1920s they had showrooms in Australia, New Zealand and Denmark. Mary Ford, daughter of an Edinburgh glass manufacturer, married Christopher Maling. Christopher Thompson Maling’s initials form one of the company’s early factory marks – the letters CTM inscribed vertically inside a triangle. The Maling name (which had first appeared with the castle mark in the 1920s) and extended to the trade name “Cetem Ware” when the company adopted its well known trademark of a castle in the early years of this century. The “Cetem” name continued to be used into the 1930s. the Maling name continued to be used as a trademark until the factory finally closed in 1963 The outbreak of World War 11 in 1939 marked the beginning of a long decline. Many of the factory’s workers were called up for military service, and wartime restrictions prevented decorative ware being produced for the home market.A larger oval china platter with blue garland around the rim ‘ CETEM WARE’ EMPIRE c1930 On base ; CETEM WARE / over a Castle / EMPIRE / Rd No 519757 china, pottery, cetem ware, maling pottery co ltd., maling william, maling christopher thompson, ford mary, newcastle upon tyne uk, crockery, north hylton sunderland uk, moorabbin, bentleigh, market gardeners, early settlers, cheltenham, world war 11 1939-45, cooking -
 Footscray Community Arts
Footscray Community ArtsConverge - Collins Street Window Reflection, Greg Considine, 2005
MEDIUM: Photographic print. DESCRIPTION: A photograph of abstract architecture. Black outer frame with glass front panel and white board inner frame. An abstract collection of building faces meeting towards a left off centre vertical line collision point. This picture is a meeting of mirrors, how many remains a mystery. Where one mirror or building starts and another ends, to the viewers eye is met with some uncertainty. Following lines, the clearest meeting of mirrors is where the building on the left appears to be the same and collides with a variety of other buildings coming horizontally in a distinct vertical line to the top of the image. The bulidings on the right have somehow through the skill of the photographer captured a bermuda triangle of walls. The mirroring angles of the walls being from either several different buildings, or from several different mirrors. This creates a strange collecetion of imagery, the viewer unable to make clear distinctions of where something starts or ends or from where it is coming from. The tonal shades and shadows created also play a role in creating an interesting collage of shapes and lines. This piece essentially speaks of lines, angles, geometric shapes, meeting points, shadow and light. Signed and dated on white board inner frame, directly under left corner of image.photograph, st, considine, converge, collins -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Black and White photocopy, Travis Jeffrey, 1959 or 1960
Negative No. N378 and black and white print made by a laser printer (stored in folder) of Ballarat No. 17 outbound in Bridge St. for Victoria St. in 1959 or 1960. Photo taken after tram has passed. Has Bourne liquid plastic ad on rear of tram. Two small triangles in corners. Car number over headlight. Photographed by tram stop, with Coles store in background. A few parked cars and some cars on the streets. Date of photo on folder - 11/6/1960. Note: Reg Item 858 of Ron Fluck of 31/12/58 shows tram number to the side of the headlight while Wal Jack (Reg. Item 396) of 23/1/61 shows tram fitted with dash canopy lights. Large print of this photo made for display 1995c. Item updated when negative added to collection - 11/5/2003. Hi -Res Image available for this photo, on CD ex Harris House of Photography see Reg Item - 4457. Original negative rescanned 24/5/2020 and image file updated. Paper print of original photo in folder 73.Paper folder that contained the negative had "NR34A" in red ink, "BA5" in pencil, date stamp of "11 Jun 1960" on front, and on rear date stamps "26 Sep 1962" and "6 Oct 1962".trams, tramways, ballarat, coles, victoria st., bridge st., tram 17 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageChest of drawers, early 20th century
This medical bureau / cabinet shows several signs of being used for a different purpose before being a medical bureau. It once had the words "GENUINE PURE QUALITY" lettered across the top of the front, as can been still seen from the impression left behind in the stained timber. On each drawer above the handle is a faint impression of something long and rectangular, as though there had been a label attached. The front panel of the drawers is made of the same wood as the rest of the outer cabinet, most probably blackwood. The handles on the drawers are not the original handles either. There are 3 filled-in holes that would form the corners of a triangle, apex at the top, around the perimeter of the current handles. The sides of the drawers are made from plywood and the base made from alternating lengthwise strips of oak and beech wood pressed together, rounded corners at the back and joined to the front panel with metal brackets. The backs of the base of the drawers have four round impressions in them. Along the back edge of the base, in the centre, is a rectangular hole. Between the front pair of round holes is a faint black rounded marking, like the impression made by rubber. The cabinet may have once been a filing cabinet, with the drawers used as document drawers, each with a spring-loaded clamp attached to the back of them to secure documents within. The original handles could have been the half-cup type used for filing cabinets. The construction and use of plywood could place this cabinet in about 1950's.Chest of drawers (or Medical Bureau, or Apothecary Chest, or Filing Cabinet) wooden, dark stained, with 30 small drawers (10 rows, 3 columns). The outer wood of cabinet is possibly blackwood and the edges of top and sides have carved wood decoration. Drawer fronts have bevelled edges and round silver-coloured metal knobs. Drawers have plywood sides, and oak and beech wood bases/, Each drawer has four round depressions (in a square-shaped arrangement) at the back plus a small rectangular hole cut in the centre back of base. A faint impression from previous lettering is evident in the wood stain across top front of cabinet.Impression of previous lettering across top front of cabinet "GENUINE PURE QUALITY". flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, drawers, bureau, cabinet, chest of drawers, furniture, bedroom furniture, household storage, medical bureau, apothecary cabinet, document drawers, filing cabinet -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1963
The Skylark 4, the final in the Slingsby Skylark series, dates from 1961. The design heralded a trend towards the use of plastics in the construction of gliders. Slingsby incorporated GRP (glass reinforced plastic) panels to achieve a streamlined fuselage nose and cockpit area while retaining the more traditional wood techniques for the rest of the aircraft. Another notable feature was the smooth wing surface that was obtained using a Gaboon ply skin across the ribs. Best glide performance of 1:33 was found to be comparable with the early full GRP glider designs. The Museum’s example (VH-GTB – C/N 1382) was built in 1963 and originally owned by Chuck Bentson of the UK. It was brought to Australia in 1967 by Jeremy Picket-Heaps and flown at various places including Benalla, Cooma and Gundaroo. In 1970 the glider was transferred to the New England Soaring Club. Many flights were made from Armidale and Bellata in Northern New South Wales. On one occasion, the glider was kept aloft for 8 hours 45 minutes and on another the pilot took it around a 500 kilometre triangle in nearly 8 hours. In 1980 it was sold to Ralph (“Feathers”) Crompton and was flown extensively in South Australia until 1988. The final owner before the glider was given to the Museum in 2004 was Ross Dutton of Melbourne. The last recorded flight occurred in 1992. The glider at that point had logged over 2000 hours flying time from about 2000 launches. The airframe is currently being restored to flying condition. Technically this aircraft represents the state of the art at the stage that sailplane design was changing from traditional wood construction to composites (GRP) The Slingsby Skylark 4 is high wing single seat sailplane of mainly wooden construction with plywood and fabric covering. However, the cockpit and forward part of the fuselage consists of glass reinforced plastic which was innovative at the time that the type was designed. The cockpit provides for a semi reclining position for the pilot protected with a full Perspex canopy. The wings are made up of a centre section with constant chord and tapered wing tips. The aircraft has a conventional arrangement for the tail stabiliser / control surfaces. The sailplane bears construction number 1382 and is registered in Australia as VH-GTBaustralian gliding, glider, sailplane, skylark, slingsby, bentson, picket-heaps, crompton, new england soaring club, dutton -
 Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.
Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.Photograph - Digital, Clare Kathleen Gervasoni, St Mary's Kinglake, 2012, 15/12/2012
The images depict the newly completed fourth Catholic Church at Kinglake. The previous three churches having been destroyed by 'Black Saturday' bushfire. The painting is oil on canvas. The historical continuity is expressed by the continuity of the skyline and the disconnectedness of the colours. it is not a literal depiction of each church, but a recognizable and symbolic image conveying resilience of faith of the local community. The first church was burnt down in a bushfire, the second burnt down by vandals, and the three burnt down in the 2009 bushfires known as 'Black Saturday'.The white cross and black fence at the lower left commemorated the remarkable fact that these remained intact after the 2009 bushfires. The red-orange can be the colour of the kinglake soil or the fires. The return of new life is indicated by the green growth on the burnt gumtrees. The presence of the Holy Trinity is shown above the entrance to the church. The return of new life is indicated by the green growth on the burnt gumtrees. The presence of the Holy Trinity is shown above the entrance to the church. The Holy Sprit is symbolized by the sulphur crested cockatoo, an Australian bird instead of the white dove. The symbol for the father is above the church in the triangle which has God's Holy Name (I AM) as given to Moses from the Burning Bush, written in Hebrew. Christ is represented by the cross above the entrance. The previous church was destroyed in the 2009 bushfires. The area is surrounded by 22,000 hectares of Kinglake National Park, the largest National Park close to Melbourne. The park was established in 1928 to protect native flora and fauna. Kinglake takes its name from Alexander Kinglake who travelled through the area in 1870. Photographs showing the newly built St Mary's Catholic Church at Kinglake. .1) Interior of Church .2) Painting of the Four Churches of Kinglake by Judy Racz .3-5) Views from the Church windows to the adjoining landscape .6) St Mary's Church groundskinglake, bushfire, black saturday, church, catholic, racz, st mary's catholic church kinglake -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALBERT RICHARDSON COLLECTION: SECRETARY FOR MINES ANNUAL REPORT 1911
Three page typed report titled ' Notes on diagram showing pitch lines, Bendigo'. Longitudinal sections along the lines of reefs or anticlines within the 8 mile block at Bendigo are shown in a diagram' (diagram not included with notes) Mines and reef lines mentioned in the report are : New Chum line, New Chum Railway mine, Catherine United mine, Hercules and Energetic mine, Garden Gully, Hustlers and Redan, Sheepshead Reef, Sea Mine, Garden Gully, Miller's line of reef and Bendigo Development Mine. The 'old stacks' or chimneys, on Bendigo are described. 'Among the earliest of the stacks built at Bendigo in connexion with Quartz crushing plant, are the two figured in this Annual report No 1 was situate in Sailor's Gully but was demolished about three years ago. This, if not the first, must have been one of the first built, for it had a stone inserted on which chiselled the date 1854. It was built altogether of rough masonry. The other, No. 2, is still standing at the Sheepshead line and was apparently of later date, the upper portion being of brick. They are intersting landmarks of an era that is rapidly passing.' Map attached to report showing location of stacks. Stack at Sailors Gully was near the corner of Murchison Street and Lester Street. The stack at Sheepshead ( Deborah Triangle area) was near the intersection of Belle Vue Road and Adam Street.bendigo, mining, pitch lines bendigo -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Pikeman's Dog Statue by Charles Smith and Joan Walsh-Smith, 21/05/2017
A sculpture unveiled on December 3rd 1999, the Anniversary of the Eureka Stockade Rebellion, in Ballarat, Victoria commemorates the Pikeman's Dog . The centerpiece of the sculpture is the bronze Irish Terrier. His stance, is a direct expression of his forlorn anguish, as he sits at the base of a symbolic bronze Pike, his head turned towards the place where once his master stood. The Pikeman's Dog statue was relocated from inside the Eureka Centre to a more prominent position within the Eureka Stockade Memorial Park. The new memorial was unveiled at a ceremony on December 3, 2014 - the 160th anniversary of the Eureka Stockade. The new memorial consists of 22 large golden stockade posts – representing the number of diggers killed in battle – erected in a triangle behind the statue of Wee Jock, on high ground outside the Museum of Australian Democracy at Eureka. The triangular shape of the monument is metaphorically symbolic. The V shape can be interpreted as symbolising victory, and the 22 golden posts represent the 22 diggers who were killed. The Pikeman`s Dog (known as Wee Jock), a little terrier, showed great devotion and bravery at the death of his master at the Eureka Stockade on 3 December 1854. As a result of the attack on the miners by Crown forces, five British soldiers and some thirty miners died. Among the miners lay a Pikeman, mortally wounded with some 15 wounds. Guarding his body throughout the hours it lay unclaimed at the battlefield, and later accompanying it on the death cart as the remaining bodies were transferred to the cemetery, was this small dog. According to reports the dog howled continuously and could not be separated from his master. The dog was awarded the RSPCA`s Purple Cross which Honours exceptional behaviour in serving humans in 1997.Colour photographs of the Pikeman's Dog statue in the Eureka Stockade Memorial Gardens. pikeman's dog, eureka stockade, statue, charles smith, joan walsh-smith -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyBadge - Badges, 31 Badges relating to ANZAC Day, WW1, Red Cross etc. c 1914-1918, c. 1914 - 1918
Most badges would have been collected during WWIBadges, varying in size from diam 2.2cm to diam 3.2cm. Total 31 badges. Each has a picture on the front and a plain metal back slightly rusting, with a sharp metal pin fastener. ANZAC DAY (2); Hospital Day; British/Red Cross; King George's Day (Copyright); Allies for Freedom and Life; Australian Red/Cross Appeal/1918; I will help until the war is won (2); Hospital/Day/1918; Our fighting men/Australian Comforts Fund; Same 3.2cm diam; Wattle Day (3); Hospital Day/for charity; Discharged Soldiers' Fund/For our Returned Soldiers; French Red Cross; For/Our Own (2); Red Triangle/King/God/Country; Our/Day/Nation/& Honour; Servia/Syria/Armenia; Our Sailors' Day (2); Italian/Red Cross; For Our Fighting Men; ANZAC/Remembrance Day; Our/Day/Nation/& Honor; Three enamel badges:; 1. Red Cross/'Australian Red Cross Society'. Red Cross on white surrounded by annular blue enamel. Crown on top. Diam 1.7cm.; 2. 'Fathers'. Centre of badge brass on red enamel background. Reg No 20169 over 494. Diam 2.6cm.; 3. ARP 'Victoria/ARP/AG121/WARDEN. Crown on top. On rear: 'Issued by State Emergency Council'. H 3.0cm x W 2.6cm.Refer photograph. -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratArtwork, other - Public Artwork, The Pikeman's Dog Memorial by Charles Smith and Joan Walsh-Smith, 2014 (re-commissioned memorial, original dog sculpture commissioned in 1999)
This memorial commemorates the ideas of mateship through using the legend of the Pikeman’s Dog. According to the legend, the Pikeman's Dog 'Wee Jock' stayed by his masters side during the Eureka rebellion and stood guard over his body and grave. The dog was awarded a Purple Cross by the RSPCA for service to humans in 1997 and a bronze life-size sculpture commemorating him was unveiled on December 3rd 1999 at the Anniversary of the Eureka Stockade Rebellion, in Ballarat, Victoria. The bronze Irish Terrier has an expression of his sadness with his his head turned towards the place where once his master stood. This statue was relocated from inside the Eureka Centre to a more prominent position within the Eureka Stockade Memorial Park when the Museum of Democracy at Eureka (M.A.D.E) was constructed. The new memorial was unveiled at a ceremony on December 3, 2014 - the 160th anniversary of the Eureka Stockade. The new memorial consists of 22 large golden stockade posts – representing the number of diggers killed in battle – erected in a triangle behind the statue of Wee Jock, the work could be viewed from the cafe area of the Museum of Australian Democracy at Eureka. The triangular shape of the monument is metaphorically symbolic. The V shape can be interpreted as symbolising victory, and the 22 golden posts represent the 22 diggers who were killed. At the time of awarding the building the new memorial in July, the sculpture artists Charles Smith and Joan Walsh-Smith were quoted: “This ‘new incarnation’ will be a much more significant memorial than the original, and much more accessible to the public,” they said. “We have set the golden stockade post/poles in a graphically precise angle to each other, which both leads the eye to the dog and the pike, while, at the same time, creating a sense of controlled visual ‘unease’. Essentially, the impression is one of ‘controlled collapse’ while suggestive of purpose and final victory.”The memorial is of historic and aesthetic significance to the people of BallaratA small bronze dog surrounded by gold-coloured metal polespikemans dog, eureka stockade -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaWork on paper - Methodist Order of Knights, Page's Degree symbol
The number seven enclosed in an equilateral triangle was the General Mark of the Order. The number seven is the perfect number used in scripture. The Methodist Order of Knights was the official youth organisation of the Methodist Church of Australasia. It originated in Hurstville, NSW, on the 4th October 1914 by the then Mr and later Rev Alex Bray. Alex Bray was a Sunday School teacher and spoke to his class of the Knights of the Round Table. In 1917 the Order of Knights was officially recognised by the Sunday School Dept of the NSW Methodist Conference. Courts spread thoroughout Australia. In 1927 the High Court of NSW called for designs for a badge and in 1929 the General Conference of the Methodist Church of Australasia recognised the Order as an approved Organisation. In 1938 the Senior Section was organised into Degrees of Sincerity, Service and Sacrifice; the Junior Section into Pages' Degree with advancement to Esquire. In 1954 the Junior Section was reorganised into two groups: Pages 8 to 11 years and Esquires 12 to 15 years. The Knight's Motto: "Live Pure, Speak True, Right Wrong, Follow Christ the King, else wherefore born?" Courts of the Order: General Conference Department of the Christian Education - General Court - Provincial High Court - District Court - Local Court - Senior Court - Intermediate Court - Junior Court . Regalia: All members of the Intermediate and Senior Courts wore regalia consisting of a cloth shield superimposed by a cross of light and dark blue ribbons, and supported by a cloth collar. Esquire and Degree of Sincerity regalia: White collar and white shield. Degree of Service regalia: Green collar and shield. Degree of Sacrifice: Scarlet collar and shield. District Court regalia: Blue collar and gold shield. High Court regalia: Gold collar and purple sheild. General Court regalia: Purple collar and shield. Officers of the local courts wore their symbols as part of their regalia. Square cardboard and black ink general mark of the order symbols.On the back of MOK214.2: Sticker with the words "FRAMED BY BALLARAT GLASS COY. Glass and Glazing, etc. 54 HUMFFRAY ST. NTH. BALLARAT"methodist order of knights -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Metal Case, To. Jindudo, Mid-20th century
The purpose and contents of the case are unknown. However, the word "Kwairobai" has been used in a group of words listed as solid fuels - coal, coke, fire wood, charcoal and spunk and ‘Kwairobai’ - in a 1939 book 'Consular Reports Issue 31' in reference to the publication of Japanese Trade-marks. This particular Trade-mark, No. 53, is a "cross in a triangle". the maker was To. Jinjudo of Osaka, Japan. This case belonged to Dr William Roy Angus and is now part of Flagstaff Hill’s comprehensive W.R. Angus Collection, donated by the family of Dr W R Angus, 1901-1970, surgeon and oculist. The W.R. Angus Collection: - The W.R. Angus Collection includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. It includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Force. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Both Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This case is an example of objects belonging to Dr. W. R. Angus, 1901-1970, surgeon and oculist. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800s.Case, a rectangular brass case neatly covered in brown velvet fabric with a paper label attached. It has a long sliding cover with three rows of cutout stars with a red background, and a decorative brass thumb grip at one end that has three Japanese characters on it. Inside are three cylindrical rolls of white fabric with unknown contents. The label has English and Japanese text, and a logo with three Japanese characters. It was made by To. Jimjudo in Osaka Japan. This object is part of the W. R. Angus Collection.On the label and thumb grip; [unknown] Japanese characters On the label; “KWAIROBAI / KIMIGASODE / MANUFACTURED BY TO. JINJUDO / OSAKA JAPAN”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, dr w r angus, dr ryan, w.r. angus collection, metal case, velvet covered case, kwairobai, kimigasode, to. jinjudo, osaka jap -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PORTRAITS, Paramount Photo. J. Solomon, Jerusalem, Photos of Jack Parsons in the Middle East
Photos/postcards are addressed with much affection to "Thel". 1. B & W portrait of soldier with peaked cap. Aust Rising Sun is on the cap and he is wearing a great coat. He has a moustache. 2. B & W studio portrait of soldier seated. He has his slouch hat folded down with the chin strap on. He has a triangle colour patch on right shoulder, He is wearing leather leggings. 3. B & W portrait of Jack Parsons in a type of Arabic costume. Tents in background. On rear it states "Middle East - Jack Parsons 1940." The moustache has gone. 4. B & W full length portrait. Jack Parsons in uniform with an Arabic style head-dress. Tents in background. 5. Seated portrait of Jack Parsons in uniform. He has a peaked cap, jersey and an MP armband. 6. B & W photo of soldier standing beside a vehicle which has the bonnet up. On the rear is written 25/11/40 to Thel from Jack. Palestine. 7. B & W portrait of soldier standing at ease. He has a peaked cap. Uniform shorts, long socks & shoes. He is wearing a pistol holster on his left hip. On the the back is written "Jack Parsons, Middle East 1940," 8. B & W photo of Jack Parsons in civilian attire, dark shirt & tie. A jacket with light trim. Light coloured trousers. No moustache. On the rear is written "Jack Parsons, Bankstown". 2. The green ink has run. From " Alexandria - Egypt."photos, ww2 -
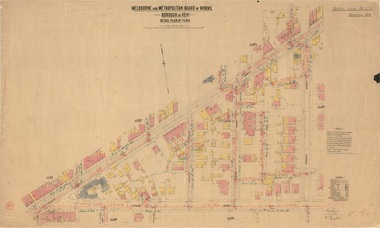 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan, Melbourne & Metropolitan Board of Works : Borough of Kew : Detail Plan No.1588, 1904
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) plans were produced from the 1890s to the 1950s. They were crucial to the design and development of Melbourne's sewerage and drainage system. The plans, at a scale of 40 feet to 1 inch (1:480), provide a detailed historical record of Melbourne streetscapes and environmental features. Each plan covers one or two street blocks (roughly six streets), showing details of buildings, including garden layouts and ownership boundaries, and features such as laneways, drains, bridges, parks, municipal boundaries and other prominent landmarks as they existed at the time each plan was produced. (Source: State Library of Victoria)This plan forms part of a large group of MMBW plans and maps that was donated to the Society by the Mr Poulter, City Engineer of the City of Kew in 1989. Within this collection, thirty-five hand-coloured plans, backed with linen, are of statewide significance as they include annotations that provide details of construction materials used in buildings in the first decade of the 20th century as well as additional information about land ownership and usage. The copies in the Public Record Office Victoria and the State Library of Victoria are monochrome versions which do not denote building materials so that the maps in this collection are invaluable and unique tools for researchers and heritage consultants. A number of the plans are not held in the collection of the State Library of Victoria so they have the additional attribute of rarity.Original survey plan, issued by the MMBW to a contractor with responsibility for constructing sewers in the area identified on the plan within the Borough of Kew. The plan was at some stage hand-coloured, possibly by the contractor, but more likely by officers working in the Engineering Department of the Borough and later Town, then City of Kew. The hand-coloured sections of buildings on the plan were used to denote masonry or brick constructions (pink), weatherboard constructions (yellow), and public buildings (grey). This plan shows the original configuration of the Kew Post Office, Court House and Police Station, which had opened in 1888. This configuration was to essentially remain until the purchase of the Court House and Police Station by the City of Boroondara in 2007 and its subsequent renovation. Interestingly, the MMBW surveyors incorrectly labelled parts of the complex. In the triangle in front of the Post Office, before the erection of the Kew Cenotaph in 1925, was located a lawn and the Queen Victoria Jubilee Fountain. While many of the shops on the south side of High street had been constructed by 1903 a number of sites were still used as vegetable gardens. Further along High Street, on the corner of Charles Street, the Salvation Army Barracks can be seen on the plan. These Barracks predate the later Citadel and ‘Young People’s Hall’ that were opened in 1919. At 22 Charles Street can be seen the house of James Venn Morgan. Hailed as the ‘father of Kew’, Morgan arrived in Melbourne in 1840. He was first engaged as a bookmaker, but a fortunate venture on the goldfields enabled him to purchase land in Kew. He conducted a market garden and dairy in Kew for many years.melbourne and metropolitan board of works, detail plans, maps - borough of kew, mmbw 1588, cartography -
 Woodend RSL
Woodend RSLUniform - Great coat, 1967
It is a woolen khaki green great coat, with inter shoulder lining of khaki green canvas. There are back belt loop holes in the interior, lined by the same canvas. The pockets are made of the same canvas and are not sew to the interior of the coat at the bottom. The insides of the sleeves are lined with a more beige khaki green material. There is a split flap that is 500mm long in the middle at the bottom of the coat, which is fixed shut with two brown plastic buttons and a metal hook and eye at the bottom. The construction of the jacket is four panels and has been taken in at the waist for form above both pockets. The jacket has a back pleat from below the triangle stitching below the nape of the neck. The back belt has three metal insignia buttons, and the backside is lined with canvas. On both shoulders, there are epaulettes which have one metal insignia button each. On the front, there are three metal buttons on each on flap, and when the jacket is done up, the left flap goes on top. It has three button holes on the left flap and one button hole on the right flap for a large brown button on the inside of the left flap. There are two outer pockets on either side of the jacket. Beneath the jacket lapels, on either side there are metal buttons, and there are button holes for them in the middle of the bottom lapel. Where the upper and lower lapels are split, there is a hook and eye. There is a brown plastic button on the underside of both the upper lapels, which is where the extra flap of fabric on the inside of the left jacket flap, can be fixed as a face protector. The tag on the inside reads; DAVID KLEIN PTY. LTD. Victoria 1967 An arrow (Department of defence symbol) SIZE 6 CLASS 8405 66.012.0494 REGIMENTAL NO................... NAME......................... The regimantal number section had a number filled in but then scribbled out and another number written above, which is 359282. The name section was filled in with B.R.MIER. The name and regimental numbers were done in black marker pen. All the metal buttons are decorated with the medical corps symbol, which is a serpent-entwined rod (Rod of Asclepius) surrounded by a laurel wreath and above the rod is a crown (St Edward’s Crown). On the outside of the upper sleeves, just below the shoulder, there is two patches that signifies the rank of Staff Sergeant. The top patch is an embroided St Edward’s Crown and represents the staff rank. It is 47mm wide and 45mm. Below this there is a patch depicting the three stripes/ chevorns of the sergeant rank. The chevorn’s points face down, and the sides measure 66mm, while the depth down to the point is 86mm. The bottom lengths is 100mm on both sides and the top lengths are 9mm. coat, trench coat, great coat, medical corps, staff sergeant, b.p. mier, 359282, david klein pty. ltd., 1967 -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, Boxmoor, 1.Minute Book of the Berry Growers Section Victorian Fruit Growers Central Association. 2.Minute Book of the Berry Growers Association of Victoria, 1921 and 1929
These blank books were used by 1. Minute Book of the Berry Growers Section Victorian Fruit Growers Central Association. 2. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of book 1. were taken 1st July 1921 in Lilydale and the last minutes were on 14.8.1929. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of book 1. were taken 1st July 1921 in Lilydale and the last minutes were on 14.8.1929.Two large green fabric covered Minute Books with tan leather tape on the spine and two tan leather triangles on the corners of each of the front and back covers. Both books at the top of the spine have a red label with gold lettering Minute Book 1. has brown marbled end papers with blue tape along the spine for added strength inside both covers. Book 2. has burgundy marbled end papers with green tape along the spine for added strength inside both covers. Both books have coloured marbled edges to the pages. These blank books were used by 1. Minute Book of the Berry Growers Section Victorian Fruit Growers Central Association. 2. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of Book 1. were taken 1st July 1921 in Lilydale and the last minutes were on 14.8.1929. The book is filled with Minutes of meetings. 2. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of Book 2. were taken on Wed August 14th at 8pm 1929 in the Silvan Hall and the last minutes were on 26.7. 1945. The book is filled with Minutes of meetings. 170 out of 190 pages used. At the back is a handwritten note on faded and foxed lined paper for the 25th Report for the Association which did not have a formal page entry between the 24th and 26th and final entry. The details are noted in the photograph.non-fictionThese blank books were used by 1. Minute Book of the Berry Growers Section Victorian Fruit Growers Central Association. 2. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of book 1. were taken 1st July 1921 in Lilydale and the last minutes were on 14.8.1929. Minute Book of the United Berry Growers Association of Victoria. Minutes of the first meeting of book 1. were taken 1st July 1921 in Lilydale and the last minutes were on 14.8.1929. meetings, reports, proceedings, minutes of meetings -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionCeremonial object - Mayoral chain, Blashki, City of Sandringham Mayoral Chain, c. 1954
This chain was part of the official regalia worn by the Mayor of the City of Sandringham before the amalgamation into Bayside City Council in 1994. The chain was seen as an outward sign of power, authority, and responsibility and was a formal, full-dress type of regalia that was worn by the mayor over their robes at ceremonial functions. The large central drop medallion features the design of the council sea, and the links of the chains are made of cutwork initials of each Mayor. The Sandringham seal was designed by Sans and McDougal had been selected in 1917, by a special committee and its main features are the Sandringham pier and breakwater, with a yacht in full sail as an inset, supported by two dolphins. The motto reads 'Omni Opere' which translates to ‘With all earnestness.’9 carat yellow gold mayoral chain for the City of Sandringham. Consists of two concentric circles of 57 small oval links, with an Australian Coat of Arms as a centrepiece and a large 'drop' medallion of the City of Sandringham seal below. Each oval link is made up of the cutwork initials of a mayor, the surrounding oval border has an inscription above the initials which gives the mayor's name; an inscription below gives dates of office; the earliest is Cr. B.J. Ferdinando 1917-18, and latest is Cr. S.T. Russell 1993-94. The ovals are surrounded by decorative scrolls and are joined by small curb chains. The outer circle contains 31 links, while the inner contains 26. On both shoulders sit decorative bars, joining the front of the chain to the back. The main medallion has an oval central panel that features the coloured Sandringham seal in enamel depicting two sailboats in the water, a pier protruding from the left, a coastline on the right with two pine trees. Above the scene are decorative triangles in light blue and yellow, above which is another section in dark blue containing a third sailboat. The seal is flanked by two engraved dolphins and above it sits an engraved St Edward's gold crown filled with red enamel. Below the seal, there is a ribbon containing the Latin motto 'OMNI OPERE' which is engraved and filled in dark blue enamel. The pendant is surrounded by cutwork lettering reading 'CITY OF SANDRINGHAM / 1919' and leaf decorations. The medallion is inscribed on the reverse with important dates in Sandringham's history. A fleur-de-lys joins the medallion to the Australian Coat of Arms centrepiece above. The Coat of Arms features a shield, depicting symbols of Australia's six states, in enamel, flanked by an engraved kangaroo on the left and emu on the right. Below it sits a ribbon engraved 'ADVANCE AUSTRALIA'.mayoral chain, ceremonial wear, seal, medallion, mayor, coat of arms, crest, bayside, blashki & sons, city of sandringham, sandringham, omni opere, blashki, mayoral regalia, motto, st edward's crown, sans and mcdougall -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomFlag, 173rd Airborne Brigade (US)
173 AIRBORNE BRIGADE (SEPARATE) US ARMY 1 RAR BATTLE GROUP BIEN HOA 1965-1966 On May 5, 1965, the Brigade deployed to South Viet Nam as the first US Army ground combat unit in that war. Upon arrival, the 1st Battalion of the Royal Australian Regiment (1 RAR) and a battery from New Zealand (161Royal NZ Artillery) were attached to the Brigade -- making the 173d Airborne the only multi-national combat unit in the war. Initially headquartered in Bien Hoa, the Brigade operated in the four provinces around Saigon. (Xuan Loc, Long Khanh, Phuoc Long & Phuoc Tuy), but (in its roll as a "Fire Brigade") also went to the Central Highlands (Pleiku / Kontum) to fight Viet Cong. The 173d also conducted constant operations against the southern stronghold of the VC Main Force in the legendary Iron Triangle in War Zone D. The brigade was organized as a balanced airborne combat force consisting of two infantry battalions, an artillery battalion, a support battalion, an engineer company, a cavalry troop, an armour company, and a headquarters company. Upon activation, it became the first and only separate airborne brigade in the United States Army. This was the beginning of a long series of "Firsts" for the Brigade. On 5 May 1965, it became the first US Army ground combat unit committed to the war in South Vietnam, where further organizational changes were to take place. Australians attached to the Brigade were: 1st Battalion, of the Royal Australian Regiment (I RAR) and support troops of the 4/19th Prince of Wales Light Horse Regiment (1Troop), 105 Field Battery Royal Australian Artillery, 161 Field Battery Royal New Zealand Artillery, 3 Field Troop Royal Australian Engineers, 161 Reconnaissance Flight, Royal Australian Army Air Corps, 1st Australian Logistical Support Company. The Brigade's two infantry battalions, the First Battalion of the 503' Infantry (1/503`d) and the Second Battalion, of the 503`d Infantry (2/503`) and the attached Australians of 1 RAR constituted the infantrymen available to the Brigade. Their mission was to protect the Bien Hoa Air Base and to close with and destroy or capture the enemy. This was in fact the first operational ground force formed under the ANZUS Defence Treaty. ANZUS was a mutual defence treaty signed in 1951 between Australia, New Zealand and the United States of America. In 1965 the spirit of this treaty appeared as 173d Airborne Brigade (Sep) a tri-national brigade. The only such tri-national fighting force formed during the Vietnam War. On deployment to South Vietnam in 1965, 1 Troop A Squadron, 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment was part of the US 173rd Airborne Brigade combat group. Flag, two colours divided vertically, hoist half mid blue, fly half red. Badge of 173rd Airborne Brigade (730 x 490 mm) in centreflag, 173rd airborne, south vietnam -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph (black & White), Major General, Sir William Penn Symons - South Africa
William Penn Symons' first combat experience was in South Africa during the Ninth Xhosa War, 1877-78. In 1879 he took part in the Zulu war. He then served during the Burma Expedition (1885-89). In 1889 he received the Companion of the Order of the Bath. In 1898, following other campaigns, he was awarded the Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath. In 1899, Symons was given the staff rank of brigadier general and was to be General Officer Commanding of Natal. He was asked by the War Office to advise on the number of troops required to safely garrison the Natal from the threat of invasion from the Boer Republics of the Transvaal and Orange Free states. Cabinet decided to send ten thousand extra troop abut they also appointed Lieutenant General Sir George White to supersede Symons as Generat Officer Commanding in Natal. Penn Symons, on his own authority deployed one of his brigades to Dundee, a town north of Ladysmith. The position of Ladysmith anad Dundee was precarious as they stand in a triangle of Natal, Orange Free State and Transvaal. White wanted to recall the Dundee garrison to Ladysmith but because of political pressure from Sit Walter Hely-Harrison, the Governor of Natal, he agreed to leave them there. The Boers declared war on 11 October and began crossing the Natal borders the following day. On 20 October 1899 Boer troops on the nearby Talana Hill proceeded to open fire on the town. The British guns moved to return fire as the general surveyed the Boer positions and gave orders to his commanding officers. Symons believed in old fashioned military tactics of close order but these formations were not designed to be used against lonf range bolt action rifles and Symons' brigades would be the first of manyin this war to pay the heavy cost ofthe mistake, as many generals would repeat it. The infantry battalions set off from the east of the town. The first part of the advance went well and they reached a small wood at the foot of the hill where they found shelter. Beyond the wood was a wall and then open ground. Symons rode up to the wood to find out why the attack had halted. He ordered the men to proceed, rode through the wood then walked through the gap in the wall. After a few moments he returned and was helped to remount his horse. He rode back from the front lines until he was out of sight of his troops before he asked for assistance from the Indian stretcher bearers. He had been shot in the stomach. Symons was taken to the field hospital at Dundee. After a few wasted days Symons' replacement, Brigadier General Yule, decided to abandon the town and the worst-wounded to the Boers and steal away at night to Ladysmith. Symons became a prisoner of war along with many others. He felt betrayed by Yule and just before he died he implored the medical officer, Major Donegal, to "tell everyone I died facing the enemy". Individual image from photographed poster of tobacco and cigarette cards.william penn symons, south africa, ninth xhosa war, companion of the order of the bath, knigt commander of the order of the bath, general officer commanding in natal, dundee, ladysmith, orange free state, transvaal, sir walter hely-harrison, governor of natal, boers, brigadier general yule -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Knowth and New Grange, Ireland, World Heritage Centre
The Megalithic Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth, Fourknocks, Loughcrew and Tara are located in the present day County Meath in Ireland's Ancient East. The Boyne Valley Mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth were built around 3200BC making them older than Stonehenge in England and the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Built by Neolithic farming communities about 5000 years ago, the passage tombs have clear astronomical alignments such as the Winter Solstice Sunrise at Newgrange and the Equinox Sunrise at Loughcrew. Judging from the splendour and magnificence of Newgrange and Knowth it is likely that these temples of the ancestors were places of astrological, spiritual, religious and ceremonial importance, much as present day cathedrals are places of worship where dignitaries may be laid to rest. There is a lively debate about whether these wonderful megalithic structures were built primarily as burial tombs, sacred temples or astronomical observatories. While passage tomb is the traditional description for Newgrange and similar structures, chambered cairn or passage mound are the descriptions favoured by those who consider the passage tomb description too narrow. The large stones surrounding and inside the Passage Tombs are decorated with Megalithic Art such as spirals, concentric circles, triangles, zigzags and images which have been interpreted as the sun, moon and the human face. Irish passage tombs tend to occur in clusters traditionally described as a Necropolis or cemetery. The Boyne cluster includes Newgrange, Knowth, Dowth and Townleyhall. The other great clusters in County Meath are on the hills around Loughcrew. The ancient Boyne Valley passage tomb mounds at Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth have been designated World Heritage Site status by UNESCO and attract 200,000 visitors per year. The sites and Visitor Centre are managed by the OPW (Office of Public Works). Newgrange is best known for the illumination of its passage and chamber by the winter solstice sun. The site is open to the public with controlled access to the passage and chamber. Tours of Newgrange start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre located near the village of Donore, Co. Meath. Knowth has two passages and is surrounded by seventeen satellite cairns. The site is open to the public; however there is no public access to the interior passages and chambers. Tours of Knowth also start at the Brú na Bóinne Visitor Centre. Dowth is the only one of the three large Brú na Bóinne Passage Tombs which is not accessible from the Visitor Centre situated on the south bank of the river. Visitors to Dowth must drive directly to the site on the north bank, a couple of miles from the Slane / Drogheda road. Fourknocks with its short passage leading into a wide pear shaped chamber is in similar style to Tombs in Portugal. Just inside the main chamber to the left of the entrance is one of the few representations of a human face from the Neolithic Period in ancient Ireland. Entrance to Fourknocks Megalithic Passage Tomb. Megalithic Art - Loughcrew, Co. Meath Loughcrew Cairns form the largest complex of Megalithic structures in Ireland. The Cairns contain symbolic engravings similar in style to Newgrange. Like other Passage Tombs in ancient Ireland, they have clear astrological alignments.Tara was the seat of the High Kings of Ireland in the first millennium A.D. however Tara is also the site of a Passage Tomb known as the Mound of the Hostages that was built about 2,500 B.C. knowth, newgrange, megalith, ireland, world heritage, neolithic
