Showing 1549 items
matching 1855
-
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph, Black & White, John Box 1841-1913 and Document re Will, a) c1900 b) 1928
John Box 1841 - 1913 was a member of the George Box family who migrated from Sussex England 1855 and established market gardens in Parish of Moorabbin, County of BourkeJohn Box was a pioneer settler 1855 in Moorabbin Shire, County of Bourke and established a market garden and raised his family.a)Black & White photograph of John Box standing at his home in North Road East Bentleigh c1900 b) Document - letter regarding the Estate of John Box 1928a) nil b) as printedbox george,b 1808, box john1841 - 1913, box william, box elizabeth smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, early settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationNewspaper - Clipping, The Sun, Going back to 1850s, 19.11.1971
This article anticipates the opening of the new Tower Hill centre. It compares the 1855 landscape of Tower Hill painted by Eugene von Guerard with the today's landscape - very different indeed.p 16tower hill, von guerard, walsh st library -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Nicholas Dunstan, Copy of original photograph made 1999
Copy of black and white photograph of man, three quarter face, clean shaven chin but heavy beard below chin. Wearing dark jacket, white shirt."Nicholas Dunstan, Born Stithians- Cornwall about 1823 or 1824-Arrived Sth Australia 1855 aboard "Hooghley"- with wife Catherine and son John Henry-spent several years at Linton Vic-settled at Moonta S.A. about 1873-Buried Moonta cemetery".nicholas dunstan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Safe, W. Marr, Circa 1855
This strong, heavy bank safe was made by W. Marr in London. It was formerly owned by the ANZ Bank in Portland, Victoria. Portland’s ANZ Bank was originally a branch of the Bank of Australasia, which first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. Portland’s Bank of Australasia began in a bluestone building built on the north corner of Julia and Bentinck Streets by stonemason William Robb in 1855, around the time of Australia’s Gold Rush. Eventually, in 1951, the Bank of Australasia merged with the Union Bank to become the Australia & New Zealand Bank, known as the ANZ. Portland’s branch of the Bank of Australasia then moved into the old Union Bank building at 44 Percy Streets; both bank buildings were built around the same. The maker of this safe, W. (William) Marr, obtained a patent in 1834 for what is believed to be the first fire-retarding patent, building this into the lining of strong boxes. Others made further design improvements such as hardening the metal plates used to make the boxes. In about 1840 Thomas Milner, a Sheffield tinsmith, made the earliest safes that could safely protect their contents from a surrounding fire. This was achieved by including tubes of a substance between the inner and outer walls of the safe that would react to the heat and the contents would put the fire out. In 1851 an Exhibition at London’s Crystal Palace included fire-proof safes from different vendors. William Marr was listed under Fireproof Box Makers in the 1842 London Trades Directory, at 33 Broad Street, and 52 Cheapside. William Marr & Son were appointed to supply Her Majesty’s National Debt Office and other departments in 1860, with the address 9 Walbrook, Vulcan Safe Works, Skin Yard, Bankside, Southwark, London. 1n 1870 the address for William Marr listed under Safe Makers and Agents in the London Trades Directory was 67 Cannon Street. The manufacturer, W Marr, is significant as an inventor of a way to make a strong box fireproof, then patented his secure safe. This invention indicates that security of money was of great importance in the mid-1800s as it continues to be today. The secure safe would have given much comfort to those with investments and savings, as well as to the bank itself, the custodian of other people's money. This safe was made in London and exported to colonial Australia, giving significance to the safe as an item that was high in the list of the needs of the early Australians and their businesses. The safe has local historical significance as it was used by the original Bank of Australasia in Portland, which was built in 1855 and went on to become the ANZ Bank, still in operation today. The bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Victoria.Safe; heavy metal bank safe, painted green. Double doors each have top and bottom external hinges, and two front panels; the top panels are arched. The thick doors have five sliding locks. Inside is a fixed metal compartment with a locked sliding metal drawer, and several fitted shelves plus some temporary removable shelving. Both doors have a decorative brass knob near the centre opening. Left door has an oval artificial keyhole and a space where another fitting has been attached. The right door has a second brass knob and an oval keyhole. The top panels of the left door has an oval plaque with an inscription; the right door has evidence that there was an oval attachment. Made by W. Marr, London.Text embossed on plaque: "W. MARR / PATENTEE & MANUFACTURER / 52 / /CHEAPSIDE / LONDON" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, safe, bank safe, vault, security, finances, anz bank, portland bank, w marr, william w marr, financial institution, savings, gold exchange, loans, investments, safety, safe maker, lock maker, iron box, strong-room -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, ca 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or Muntz metal has been recovered from the sea at the wreck-site of the ship SCHOMBERG. . It has been damaged by the reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and has other damage that has caused the edges to break away or fold over. Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in seawater and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUTH THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its dayCopper sheathing or Muntz metal recovered from the shipwreck Schomberg. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, coppper sheathing, ship building, sea worm -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, ca. 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three-masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the cover and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its dayCopper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. The sheet was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. It is irregular in shape with nail holes and slight encrustation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, late 19th century sailing ships -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ARTICLES FOR RHSV BENDIGO BRAND NEWSLETTER AUG 1973
Articles for RHSV Bendigo Brand Newsletter Aug 1973. 1. Market Square - reference to Messrs Reid & Co.; pudlers' activity on that area; Hunter's puddling machine in area; weighbridge 1855; vegetable market; hay and corn market; wood market; City Fire Brigade; City Retail Market; City Lock-up; City Hall (1885). 2. Typewritten article ''Looking Back'' (see Mosaic #6545). 3 Handwritten notes on ''The Pearl mine'' - see Mosaic # 6543document -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. THE CHINESE ON THE GOLD FIELDS, c1850s
Diggers & Mining. The Chinese on the Gold Fields. Slide: Shows map of Victoria and part of South Australia and New South Wales. South Australia Act. Of 1857 repealed I 1861. New South Wales Act. Of 1861 repealed I 1867. Victoria Residence tax abolished in 1862. Act. Of 1855 repealed in 1865. The declining numbers of Chinese in the three colonies allowed all restrictions to be lifted in the 1860's. Markings: 2 2. Used as a teaching aid.hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Archive - Mines of Bendigo Government Gazettes Books 1 and 2, 1871
Founded as a sheep run in 1840, the city’s official name was Sandhurst until 1891, when it was formally changed to Bendigo. It was declared a municipal district in 1855 and a shire in 1863, Bendigo became a city in 1871.Government gazettes. Books 1 and 2, Bendigo Mines. Excel Spreadsheet on CDbendigo, mining, sandhurst, mines in bendigo -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph
FRANCIS AND JANE CLARK (NEE RANKIN). FRANCIS BORN IN NAIRN, SCOTLAND. HE ARRIVED IN CLUNES 1855, AGED 15 YEARS. DIED IN CLUNES APRIL 1921. JANE DIED IN MAY 1921.PHOTOGRAPH OF FRANCIS AND JANE CLARKE (NEE RANKIN)local history, photography, photographs, clark family -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph, C 1870
FRANCIS AND JANE CLARK (NEE RANKIN). FRANCIS BORN IN NAIRN, SCOTLAND. HE ARRIVED IN CLUNES 1855, AGED 15 YEARS. DIED IN CLUNES APRIL 1921. JANE DIED IN MAY 1921.PHOTOGRAPH OF FRANCIS AND JANE CLARK (NEE RANKIN) C.1880local history, photography, photographs, clark family -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper sheathing, c. 1855
This object is a piece of Muntz or copper sheathing, a sheet of metal used for lining a ship's hull as protection from sea worm or muntz worm. It has been salvaged from the Schomberg ship wreck. The muntz has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea. It also has encrustations from the sea such as sand. Other damage, such as movement of the sea or objects in the sea, has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ The hulls of early timber sailing ships had a problem of being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries ships were built with their hulls sheathed in sheets of copper or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing remained effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. This piece of muntz sheathing is representative of building methods and materials used in late 19th and early 20th century ship building. The munts is also significant for its association with the Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or Muntz metal in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, copper sheathing, muntz, muntz metal, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, 19th century sailing ships -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph
The Stag built 1848-1853.Land was purchased from Atkinson by John Sanders to serve as Licensed premises. The Bank of Australasia was built around 1855-57, designed by Nathaniel Billing and built by McKenzie and McCowan .Black and white Photograph of Two story bluestone Bank of Australasia in centre, two story Rendered Stag Hotel on left and 2 story Bank hotel on righthotel, bank, stag, australasia, nathanial billing, mckenzie, mccowan, john sanders -
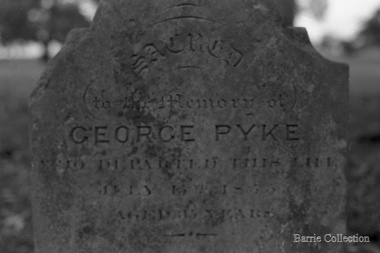 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, George Pyke headstone, 1970
Brothers William and George arrived in Melton in 1838, George was born in 1819 and died in 1855 at 35 years old. Edna Barrie was involved with the restoration of the Pykes Grave (using EW Barrie earthmoving equipment) George Pyke's headstonepioneer families, local identities -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, Pt Fairy Hospital looking east 1890, 1890
The land for this building was granted to the Benevolent Society by James Atkinson in 1850. Tenders were called for a new "Benevolent Asylum" in 1855, the foundation stone having been laid and by 1856 the first part of the Hospital was completedBlack and white photograph New addition to the hospital with i’ts bay windows. 5 women and two men posed to the sidehospital, health service, nurses, bay window -
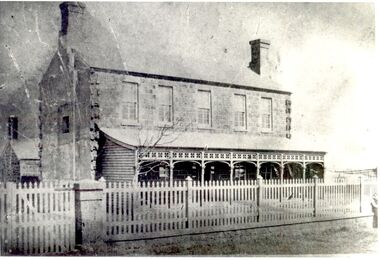 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph
The land for this building was granted to the Benevolent Society by James Atkinson in 1850. Tenders were being called for a new "Benevolent Asylum" in 1855, the foundation stone having been laid and by 1856 the first part of the Hospital was completed. This photo taken in 1860 shows the very first building made from local bluestone. The hospital is thought to be the first such building in VictoriaBlack and white photograph of Bluestone 2 story building with verandah and paling fencehospital, institution -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Short stories, Jolly, Emily, A wife's story and other tales by the author of "Caste", "Safely married", &c., &c. : in three volumes : Vol. I, 1875
Volume I contains three stories: 'A wife's story' ; My first and last novel ; 'Annie and her master'312 p. : includes preface with letters written by Charles Dickens. Plain green coverfictionVolume I contains three stories: 'A wife's story' ; My first and last novel ; 'Annie and her master'fiction, emily jolly, short stories -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Short stories, Jolly, Emily, A wife's story and other tales by the author of "Caste", "Safely married" &c., &c. : in three volumes : Vol. III, 1875
Volume contains two stories: 'Daisy's Trials' and 'I do not love you'.296 p.fictionVolume contains two stories: 'Daisy's Trials' and 'I do not love you'.fiction, emily jolly, short stories -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyArticle, John Gibson, Plenty Gorge Park dig May 2015, 23/05/2015
Account of a dig carried out by Heritage Victoria at the site of the Thomas flour mill, a three-story building with a small cottage built in 1855, which ceased operation in 1863. Article written by GHS member John Gibson.5 p., black text and photographsmoses thomas, flour mill, plenty river -
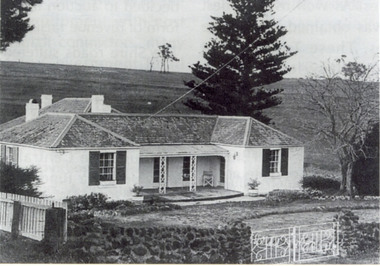 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Somerset Inn, Bannockburn
The Somerset Inn was built for Edward Carter Holmes by carpenter Isaac Sutherland and his two sons in 1855/1856. Situated on Bruce's Creek on the Shelford - Bannockburn Road. Bruce's Creek was the original name for current day Bannockburn. Black and white photograph of a house with slate roof and window shutters. The front fence is stone. The house is the former Somerset Inn (later a private residence). This building is located on the Leigh River at Bannockburn and was the home of Edward Carter and Sarah Holmes. Verso in blue ball point pen. "Somerset Inn on Leigh river Bannockburn. Home of Edward C. & Sarah Holmesholmes, leigh river, sarah holmes, ec holmes, holmes family collection, chatham-holmes family collection, edward carter holmes, farm, bannockburn -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratCutherts: A Ballarat Institution, 2016
Cuthberts was a law firm in Ballarat that was established by Sir Henry Cuthbert in 1855. In 2013, the firm amalgamated with another law practice, Harwood Andrews. The book tells the story of the firm from its beginning up until the 2000s.Of interest to the history of Ballarat and its institutions.Hardback, paper; red and brown cover; golden lettering.Title: gold lettering on front. Author has signed the title page. The book is number 187 of 200 copies.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat regional trades and labour council, blee, jill, cuthberts, law, law - history, law - firms, cuthbert, sir henry, harwood andrews -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Information folder - Grace Vosper
Research carried out to ascertain history of sampler donated to Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society by Helen Gibson.Folder containing information pertaining to Grace Vosper, creator of the sampler now hanging in the original St Martins Anglican Church, Belgrave Heights, Victoria. Contents: -marriage certificate, Dennis Rock and Grace Vosper, 1st September 1855, Melbourne, Victoria -family tree, showing descendants of Grace & Dennis Rock, hand-written -printed Register chart, William Vosper, showing descendants -printed Descendancy chart, William Vosper, showing descendants -printout, 1881 British Census, Vosper family members (2 sheets)vosper, grace, vosper family, rock family, gibson, helen, original st martins church, southern sherbrooke historical society -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Photo of William Plummer
Black and white photo of William Plummer (1855-1924). He was a solicitor at Thompsitt & Co, Oakleigh, and handled all Sir Matthew Davies' (1850-1912) legal work. He and his wife, Mary Ellen Plummer, nee Crowhurst, holidayed at "Lockwood", a Davies property, with their daughter Eva Victoria Crowhurst Plummer. The photo shows Matthew apparently sitting outside at a small table. He is pouring a drink into a glass from a small jug held in his left hand. He is smoking a pipe and is dressed in a suit and tie. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. DIGGERS AND MINERS, c1855
Diggers & Mining. Diggers and miners. Like this quartz mine on the Black Hill, Ballarat (1855) with its crushing machine at the base of the hill - - - Slide: Shows dwellings one made from timber with chimney, one made from canvas, with a veranda and what appears to be a round metal chimney. 2 men in the for ground have some timber and could be contemplating a timber dwelling. There are a couple of other dwellings in the background. Not many trees left on the hill. Markings: 26 994:LIF I. Used as a teaching aid.hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyPhotograph - Digital image, John Gibson et al, All Saints Anglican Church Greensborough, 1935c
The original wooden building of All Saints Anglican Church Greensborough, seen from rear. First services were held in this church in 1855. All Saints still operated from this site in Church Street, but from a new building.Digital copy of black and white photographluxford family, all saints anglican church greensborough -
 City of Whittlesea
City of WhittleseaInstrument - Weighing instruments, Weights and measures
Weights & Measures, partially in wooden boxConsists of 10 parts as follows: 4 lb 1866; 8 oz 1803; 4 oz 1855; 2 lb 1866; 7 lb 1866; 1 lb 1866; Imperial Standard Gill 1826; Imperial Standard Pint; Imperial Standard Quart; Imperial Standard Half Gallon -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Folder, O'Keefe, Richard (Charles)
Dr Richard (Charles) O'Keefe arrived in Australia on the Hastings, 17 March 1855 with his wife and family. Six and a half months later, he registered in the Medical Register of Vitoria 1 October 1855 (number 415), as a British graduate of Dublin University and a Licentiate of the Dublin Society of Apothecaries, conferred 27 April 1849. In 1856, he was on the electoral roll in the district of Evelyn as a surgeon and resident of Eltham. By the end of May 1858 he was living in Gunning NSW. Contents Email: Brett Lowe to Eltham District Historical Society, 1 December 2013, seeking information about the two years Dr O'Keefe was in Eltham.Newspaper clippings, A4 photocopies, etcrichard (charles) o'keefe, eltham doctors, dublin society of apothecaries, dublin university -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Machine - Clothes Mangle, C1820
From an item in the Nunawading Gazette on Weds ,15th Nov 1972 , this item was a gift of Mrs. Jennie Wagg and that it was given to her mother, Mrs. L.L.Bruce, when she was married 93 years ago(ie.1879). It is understood that it was purchased in 1855.Solid iron frame with three wooden rollers. Pressure is on the rollers obtained from an adjustable worm drive to a five leaf spring set(similar to a car leaf spring). Large reduction gearing from handle. Used for pressing sheets, towels, table clothes, etc.GH+G NICHOLL BANK STREET 1820domestic items, laundering -
 Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.
Mt Dandenong & District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Francis Matthew Child and Family, c1886
Francis Matthew Child was 15 when he came to the Valley with his father, Matthew Child in 1855. He married Martha Jeeves (born 1857) in 1875. They had 6 children. Harry, May, Edward, Alice, Bert, Eva.Posed photograph of Francis Matthew Child, his wife Martha (nee Jeeves) and six children, all well dressed with background of bushes. Handwritten inscription on back by John Lundy-Clarke.F.M. Child and Family about 1886. Back Row Martha (nee Jeeves), Harry, May, Francis Mathew, Edward (Ted). Front Row Alice (Petty), (Bert), Eva.francis matthew child, martha child, martha jeeves, eva child, bert child, harry child, alice child, may child, ted child, edward child -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Raglan Hotel, Unknown
Lord Raglan Hotel (‘The Raglan’) built by Strachan 1855 in Unitt Street, was moved to High street. The owners of the hotel included Kilpatricks and Richard Manning. The hotel was a major coach staging point, with large stables to accommodate the teams. Demolished in 1927. Mr and Mrs Kilpatrick with their children outside the front of the hotel.local architecture
