Showing 3312 items
matching ancient
-
 School of Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT University
School of Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT UniversitySculpture - Statue, Fu Xi
伏羲 中国神话中人类的始祖,上古三皇之一。所处时代约为旧石器时代中晚期。在医 学方面,传说他发明了八卦,演示阴阳学说,成为中医理论的基础,同时又发明了九 针,为针灸学之始祖。 Fu Xi First of the three mythological emperors of ancient China and the earliest ancestor for humans according to Chinese legends. He is said to have lived in the mid to late stages of the Old Stone Age. Medically, legend tells he discovered the famous Chinese eight trigrams (bagua), developed yin-yang theory which became the principal of traditional Chinese medicine. Fu Xi is the pioneer of acupuncture and invented the nine classical needles.Small silver coloured metal sculpture on sqaure wood base with Chinese script along front. fu xi, chinese medicine, yin-yang, bagua, acupuncture, rmit chinese medicine collection -
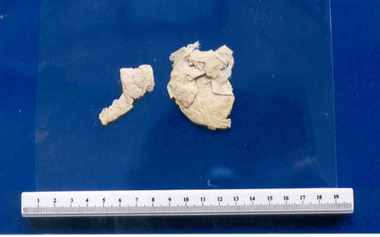 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Caul associated with Private Robert Powning Holbery, World War I
Label written by Dr Frank Forster documents that this item belonged to Private RP Holbery, who carried the caul as a good luck charm when he served in the Australian Imperial Forces (AIF) during WWI. Refer to supplementary file for War Records at Cat no: 34 A caul is a small slightly yellow coloured membrane that can cover the newborn baby's face. After birth, the caul can be removed and laid on a piece of paper to dry. Superstitions regarding cauls are very ancient, and believers in superstition thought that babies born with a caul would never drown. They were traditionally sold to sailors to bring good luck. Lawyers or advocates in the legal profession would buy cauls as they believed it would confer the "gift of the gab". Cauls were also carried by servicemen during the early part of the 20th Century. World War I pushed up the price of cauls. They were often carried in silver cases engraved with commemorative inscriptions. Other names used for a caul are "Coif", "Sillie", "How" (Hood) or "Hallihoo" (Holy Hood).Caul, consisting of yellowed membrane in two pieces. Caul has tissue paper like appearance and is folded upon itself.world war i -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Bituminous Coal, Unknown
Bituminous coal is the most common type of coal, abundantly found in ancient coal deposits which can be dated back millions of years. Often referred to as soft or black coal, this specimen exhibits a high carbon content, ranging from 76-86%. It also holds a relatively high energy density (27 MJ/kg) meaning that it releases significant amounts of energy when burned. Bituminous coal is most commonly used for electricity generation, as well as in the production of steel. This particular piece of coal was collected as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria in the nineteenth century. It originates from Cape Paterson, a seaside village located in South Gippsland, Victoria (located on Bunurong Country). The discovery of bituminous coal in this locality was first made in 1826 by explorer William Hovell. More discoveries were gradually made over the following decades and in 1859 the Victorian Coal Company commenced the first active coal mining operations in the state by sinking a number of shafts and bores near the area of Cape Paterson. Evidence of this coal-focused past can be found today at the State Coal Mine Museum in the nearby town of Wonthaggi. This specimen is significant as it was collected from the locality of Cape Paterson in Victoria, an area that has since become historically instrumental in the mining of coal and other substances in the state of Victoria. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A solid hand-sized piece of bituminous coal with a shiny black-grey surface and jagged edges.Existing Label: BITUMINOUS COAL / Locality: Cape / Patterson, VIC. burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, state coal mine museum, wonthaggi coal mine, victorian coal company, bituminous coal, coal victoria, coal energy generation, william hovell, cape paterson, coal specimen -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Samuel Bolton in Druid's regalia, 1950
Samuel Bolton of 244 Union Road, Surrey Hills in his 'Druid's Collar' in 1950. Samuel and his son-in-law Patrick Burns were staunch Druids. The Lodge met monthly in the Rechabite Hall in Canterbury Road. The United Ancient Order of Druids (UAOD) was founded in Victoria around 1862. An account is included in Ken James' book 'Surrey Hills Friendly Societies'. This is based on Box Hill Reporter articles and material in relevant files at PROV. Summary: The Surrey Hills Lodge was established in 1890. The trustees were Ernest W Opperman (newsagent), James H Corstorphan (grocer) and Thomas White (plasterer). Opening night was 27 November 1890 and early meetings were held in Br Corstorphan's home in Canterbury Road on Tuesday evenings. By 1891 the ledge had 80 members. Samuel (1978-1951) was a butcher who came to Surrey Hills from Euroa some time between 1926-1931. His shop was at the Mon Albert terminus. After he sold it, it became part of the supermarket on the north side of Whitehorse Road. He was married in 1879 to Elizabeth Beatrice Maker (1881-1963).A black and white photograph of a man with regalia collar around his neck.(mr) samuel bolton, union road, surrey hills, druids, rechabite hall, clothing and dress, united ancient order of druids, druid's regalia, regalia, friendly societies -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Kitchen Canister set, Late 19th to early 20th century
This set of kitchen dry food canisters is made of metal; each container has a different height, width and capacity. The rolled thin metal has created a strong, round design with decorative rings on the circumference. The base and close-fitting lid protect the contents from vermin and most insects, and the handle on top aids in the removal of the lid. Metal containers like these are reusable and can be re-purposed, which is advantageous when living in regional or rural areas. The type of manufacture indicates that the set was made in the late 19th to early 20th century. Gradually, colourful and attractive plastic kitchenware began to replace metalware. One of the canisters is labelled 'coffee'; coffee plants and seeds were transported from Brazil into Australia in 1788 when the First Fleet arrived although their growth was unsuccessful. However, by the 1920s, a tenth of the Australian population was drinking readily stored coffee. Large quantities of harvested grains such as maize, wheat and barley were protected from pests by being stored in airy buildings, often raised from the ground. This was an age-old practice used by civilizations such as the ancient Egyptians and early Hebrews. Smaller quantities of food for short-term use in the homes were stored in woven baskets or clay pots.This set of kitchen food containers is an example of colonial food storage used in a domestic setting to store and preserve dry ingredients. These canisters give a snapshot of early domestic life in Australia. Canister set; four cylindrical cream coloured metal canisters with domed lids that have lift-up handles on top. They are made from rolled metal and the bases and lids have a side seam. Each canister is a different size and displays a label for different contents. The adhesive labels are vertical, and a gold colour with black vertical text. The cream paint has brush strokes and small areas have exposed green paint under the cream. The insides of the bases are painted dark grey but the lids have no paint underneath. The empty canisters can fit one inside the other. Labels, in descending order: "FLOUR" "RICE" "SAGO" "COFFEE"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, canister set, kitchen storage, food storage, metal canisters, dry food storage, food packaging, kitchen container, vintage, flour, rice, sago, coffee, kitchenalia, late 19th to early 20th centuries, nesting canisters -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyEphemera - Invitation - wedding, Invitation to wedding of Miss Swindles and Mr John Nicholson 1867, 1867 (original)
The Argus, 27 September 1867 p4 - MARRIAGES: NICHOLSON—SWINDELLS.—On the 12th inst., at Christ Church, St. Kilda, by the Rev. D. Seddon, John, eldest son of the late Hon. W. Nicholson, to Gertrude Sarah, youngest daughter of the late James Swindells, Esq., of Manchester. No cards. https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/5779002 Barham House was built in 1850 by Edward Bernard Green (1809-1861) a successful land speculator. It was a magnificent residence built in the regency style to the design of architect John Gill and set in landscaped grounds of nine acres and included an ancient Swiss cottage. When Green died in 1861, his executor was his neighbour, William Nicholson (1816-65) who owned Fernleigh immediately to the north in Grey Street, but actually lived in Barham House during his time as Premier of Victoria 1859 - 1860 until his death in 1865. In 1866 Richard Twentyman purchased Fernleigh from the Nicholson Estate and a year later he married Nicholson's widow, Sarah. Both remained at Barham House until June 1870. In 1871 the building was substantially remodelled and re-named Eildon. It is one of the larger surviving 19th century houses in Melbourne.Black and white photocopy of invitation, wedding breakfast menu and envelope(handwritten) Original in possession of Lady Johnston. (handwritten) Gerty's marriage? Invitation: Mr and Mrs Twentyman request the pleasure of [unclear] Johnstone's Company at Breakfast on Thursday the 12th at 1 o'clock. Miss Swindells Mr John Nicholson. Ceremony at Christ Church St Kilda, at 12, Noon Barham House, Grey Street, St Kilda Sept. 2nd. 1867 The favour of an early answer is requested Menu: Déjeuner Barham House, St Kilda, 12. September, 1867. Menu items listed on following page Envelope: [unclear] Johnstone Esq Care of J C Johnstone Esq Sunburybarham house, christ church, st kilda, 19th century, eildon house, grey street -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - Dunn's Rock Eppalock, 2012
The low rolling hills of the Kimbolton countryside consist of ancient, hard and fractured Ordovician rock up to 65 million years old, which was originally deposited deep under the sea. Rocks mainly are sandstone, mudstone, black shale and quartz conglomerates. Marine fossils can be found in the area. Around seven million years ago a basalt flow buried the original bedrock along the along the Campaspe River. Ongoing weathering, wind and water movement over the following years has produced younger clay, sand, silt and gravel deposits throughout the area. Patches of White Hills Gravel are also found in the area. Another unique geological feature of this area is the Permian Glacial Pavement rocks north and south of Eppalock and glacial sediments (such as “Dunn’s Rock” and “Kellams Rock”). During the ice age (up to 280 million years ago) large glaciers moving over the countryside, scoured out sediments, pulverized bedrock, polished and cut grooves into bedrock in the direction of ice movement. When the ice melted boulders etc where left behind in areas of entirely different rock types, such as a 100 Tonne granite block known as ‘The Stranger’ near Derrinal. Dunn's Rock (Glaciated Pavement) Eppalock - Photos of the rock and a field group collecting date with Lake Eppalock (Knowsley) in the backgroundhistory, bendigo, dunn's rock eppalock, kimbolton forest, lake eppalock, gately collection -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Cloak, Dr Deanne Gilson, Campfire Gathering, Meeting Place Cloak, 2022
Standing proud, still here, the spirit of ten ancestral matriarchs adorned in contemporary ceremonial cloaks. Representing our women past, present and future, her Spirit, our culture, our Country (spelt with a capital for its importance and this is part of First Peoples protocols on acknowledging Country, our strength, our resilience and healing towards a sustainable future). The circle and diamond pattern are ancient symbols used by Wadawurrung people dating pre-colonisation on possum skin and kangaroo skin cloaks, other artefacts like spear heads (carved), wooden shields, stone tools and caves were painted with blood, ochre and bound with grass tree sap, black wattle tree sap and kangaroo fats. The diamond pattern was a strong design used by men on shields and women on baskets and adornments. Shields were taken from the tree in the colder months when the tree was cold as the wood came off cleaner. Ochre colours of red, white, yellow and charcoal were often used to colour in and decorate the skin side of possum skin cloaks, wooden shields, spear heads, baskets and some coolamon bowls.The design for this cloak has been simplified from the original artefact design.Cloak with black and white diamond and circle design on outer cloak and coral and white line pattern within lining. Trimming is solid black. Cloak is machine sewn and handstitched with hand stitching on shoulder seam.deanne gilson, wadawurrung, first nations, cloak -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyProgramme - Document, programme, The Shrine Forecourt. Dedication by Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth the Second, 1954
The order of service of the ceremony to dedicate the Shrine Forecourt by the Queen on 28 February 1954. It was the official commemorative document of the occasion. The Queen lit the Eternal Flame as part of the ceremony. The design of the Forecourt was part of a competition that was run to find a suitable memorial. The Forecourt is cross shaped. The Cenotaph is 65 feet high and rises as a focal point to the Forecourt, it is balanced on the other side by three 70 foot high flagstaffs. The sculpture at the top of the Centoph is "carved in Footscray basalt. It represents six men in battle dress of the Navy, Army and Air Services, carrying a bier on which lies the figure of a dead comrade draped with the national flag. Its simple symbolism harmonises with the great shrine itself and sums up with dramatic power the whole message of the monument - the debt of the living to the dead, the eternal bond between the fallen and those who enjoy the fruits of their sacrifice." Also from the souvenir booklet: "In front of the Cenotaph, surrounded by a protective railing, the Eternal Flame which burns continually in its great bronze bowl. The eternal flame is an ancient symbol signifying at times the continuing spirit of a city, at others the constancy of man to an ideal, and again as they symbol of continuing faith." The document was in a file with other documents concerning the Shrine and it's history (01181 - 01190).A record of the dedication of the Forecourt at the Shrine of Remembrance by the Queen. There was an effort to record historical events for the "Archive Committee" which collected this and other documents relating to the Shrine together in a file (see items 01181 - 01190)Booklet x 12 pages with sepia photos and brown text in a cream card cover for the dedication of the Shrine Forecourt on 28 February 1954.memorial, wreath laying ceremony, royal visit, shrine of remembrance -
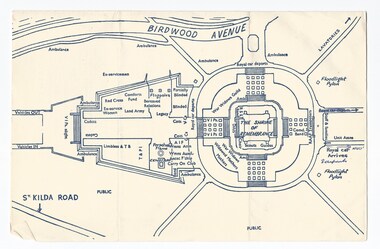 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyProgramme - Document, programme, Dedication of the 1939-1945 War Memorial by Her Most Gracious Majesty Queen Elizabeth the Second, 1954
The order of service of the ceremony to dedicate the Shrine Forecourt by the Queen on 28 February 1954. The Queen laid a wreath and lit the Eternal Flame as part of the ceremony. The design of the Forecourt was part of a competition that was run to find a suitable memorial. The Forecourt is cross shaped. The Cenotaph is 65 feet high and rises as a focal point to the Forecourt, it is balanced on the other side by three 70 foot high flagstaffs. The sculpture at the top of the Centoph is "carved in Footscray basalt. It represents six men in battle dress of the Navy, Army and Air Services, carrying a bier on which lies the figure of a dead comrade draped with the national flag. Its simple symbolism harmonises with the great shrine itself and sums up with dramatic power the whole message of the monument - the debt of the living to the dead, the eternal bond between the fallen and those who enjoy the fruits of their sacrifice." Also from the souvenir booklet: "In front of the Cenotaph, surrounded by a protective railing, the Eternal Flame which burns continually in its great bronze bowl. The eternal flame is an ancient symbol signifying at times the continuing spirit of a city, at others the constancy of man to an ideal, and again as they symbol of continuing faith." The document was in a file with other documents concerning the Shrine and it's history (01181 - 01191).A record of the dedication of the Forecourt at the Shrine of Remembrance by the Queen. There was an effort to record historical events for the "Archive Committee" which collected this and other documents relating to the Shrine together in a file (see items 01181 - 01191)Cream paper program with blue print, single page folded in half, order of service for the dedication of the Shrine Forecourt on 28 February 1954.memorial, wreath laying ceremony, royal visit, shrine of remembrance -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bottle, c. 1850's - 1900's
Glass bottles and glass jars are in many households around the world. The first glass bottles were produced in south-east Asia around 100 B.C. and the Roman Empire around 1 AD. America's glass bottle and glass jar industry were born in the early 1600s when settlers in Jamestown built the first glass-melting furnace. The invention of the automatic glass bottle blowing machine in 1880 industrialized the process of making bottles. In 2019, plans were made to re-introduce milk glass bottle deliveries to Auckland in early 2020 The earliest bottles or vessels were made by ancient man. Ingredients were melted to make glass and then clay forms were dipped into the molten liquid. When the glass cooled off, the clay was chipped out of the inside leaving just the hollow glass vessel. This glass was very thin as the fire was not as hot as modern-day furnaces. The blowpipe was invented around 1 B.C. This allowed molten glass to be gathered at the end of the blowpipe and blown into the other end to create a hollow vessel. Eventually, the use of moulding was introduced, followed by the invention of the semi-automatic machine called the Press and Blow. In 1904 Michael Owens invented the automatic bottle machine. Before this time most glass bottles in England were hand blown. This is one of four bottles in our Collection that were recovered by a local diver from the quarantine area just inside the Port Phillip Heads. Ships were required to pull into this area to check for diseases etc before they could head up to Melbourne. Quite often they would drink and throw the bottles overboard. Handmade glass bottle, manufactured in the 1850s-1900s. The bottle gives a snapshot into history and a social life that occurred during the early days of Melbourne's development and the sea trade that visited the port in those days. 1850's Pontiled Black Glass Stout/Porter/Ale Beer Bottle, solid colour brown glass,concave base with Pontil scar, tapering slightly wider towards shoulder then inwards towards neck; ring of glass just below opening cork and wire type.Label "c.1850's "Stubby ale" hand made in England flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, brown glass bottle, handmade glass bottle, handmade beer bottle, handmade late 19th century bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Compass Saw, Mid to late 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture. Compass saw blade with wooden handle attached with wingnut.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Compass Saw, Mid to late 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture.Compass saw with wooden handle and metal blade. Small teeth. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool, compass saw -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Compass Saw, Mid to late 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture. Compass saw with wooden handle broken and metal blade. Small teeth.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool, compass saw -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Saw, Mid to late 20th century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone. The subject item at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, as the maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture around the mid to late 20th century.Wood hand saw with wooden handle attached to saw by 4 rivets. No blade markings Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, handsaw, wood saw, carpenders tools, cabinet makers tools, wood cutting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Saw, Mid 20th Century
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard-toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power sources. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic. In ancient Egypt, open (unframed) saws made of copper are documented as early as the Early Dynastic Period, circa 3,100–2,686 BC. Many copper saws were found in tombs dating to the 31st century BC. Models of saws have been found in many contexts throughout Egyptian history. As the saw developed, teeth were raked to cut only on the pull stroke and set with the teeth projecting only on one side, rather than in the modern fashion with an alternating set. Saws were also made of bronze and later iron. In the Iron Age, frame saws were developed holding the thin blades in tension. The earliest known sawmill is the Roman Hierapolis sawmill from the third century AD used for cutting stone.The subject item is believed to date from around the mid to late 20th century and is regarded as a modern item. The maker is unknown but the pattern or design and type of wood used indicate it is a tool of modern manufacture. Compass saw blade with wooden with open handle blade attached with wingnut lever at side to adjust long narrow blade Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood cutting, wood saw, cross cut saw, cabinet makers tools, wood working tools, tool -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art Collectionartwork, Pwerle, Minnie, 'Untitled' by Minnie Pwerle
Minnie PWERLE (c1910-2006) Atnwengerrp/Utopia Minnie Pwerle's Dreamings consist of elements of 'Bush Melon' and 'Awelye'. Awelys-Atnwengerrp' is depicted by a series of lines painted in varying widths and colours. These patters represent the lines painted on the top had of women's bodies during ceremonies in Minnie's country of Atnwengerrp. 'Bush Melon' is depicted using linear design of curves and circles in different colours creating a very loose and bold design. This dreaming tells the story of this lovely sweet food that comes from a very small bush and is only found in Atnwengerrp. Once very abundant and fruiting in the summer season, the Bush Melon is now hard to find. Minnie and other women used to collect this fruit (that was green in colour and then ripened to a brown colour) and scrape out the small black seeds. They would then eat the fruit straight away or cut it in pieces and skewer them onto a piece of wood to dry then to be eaten in the coming months when bush tucker was scarce. These artistic symbols carry potent spiritual meanings.. The physical creation of these Dreamings in an important part of the continuation of an ancient and rich cultural heritage. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Awelye & Bush Melon Dreaming, 2004 Acrylic on canvas, over three panels art, artwork, minnie pwerle, aboriginal, anmatyerre language, atnwengerrp country -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Round Metal Shaker
The history of metal packaging began in Bohemia in the 1200s. Metal has been produced for a very long time. But the first metal used for packaging was tin. In particular, it was the process of tin plating that was invented in Bohemia. Before this no other metal was economically able to be used for packaging. Later, in 1667 Andrew Yarranton, and English engineer, and Ambrose Crowley brought the method to England. Here it was improved by ironmasters including Philip Foley. Then by 1697, John Hanbury had a rolling mill at Pontypool in South Wales. The method they developed involved rolling iron plates using cylinders. This process enabled more uniform blank plates to be produced than was possible by just hammering the tin. https://www.shilohplastics.com.au/history-of-metal-packaging/ Fuller's Earth is any clay material that has the capability to bleach or dissolve oil or other liquids without the use of harsh chemical treatment. Modern uses of Fuller's Earth include as absorbents for oil, grease, and animal waste (cat litter) and as a carrier for pesticides and fertilisers. Minor uses include filtering, clarifying, and decolorising; active and inactive ingredient in beauty products; and as a filler in paint, plaster, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Fulling is an important step in the production of woollen garments, and can be traced back to ancient times. Cuneiform texts from Mesopotamia mention a raw material, which was delivered to fullers for the finishing of cloth. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuller%27s_earth The use of tin to protect and store items, revolutionised the world. Fuller's Earth is a widely used product.Container of cylindrical sheet metal with perforated lid, used by Duerdin and Sainsbury Ltd, Sellers of Franbert's Fuller's Earth. Colour printed paper deteriorating. ‘Nett Contents 3½ oz.’ Ingredients still inside.Tin very rusty.'Franbert's Fuller's Earth. For the Toilet and Nursery. Protects the skin & Improves the Complexion. Nett Contents 3½ oz.'flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tin, tin plating, containers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bottle, 1850's - 1900's
This bottle is sometimes referred to as a black glass 'Gallon' bottle. It is used for storing and transporting liquor such as stout, porter or ale. Glass bottles and glass jars are in many households around the world. The first glass bottles were produced in south-east Asia around 100 B.C. and the Roman Empire around 1 AD. America's glass bottle and glass jar industry were born in the early 1600s when settlers in Jamestown built the first glass-melting furnace. The invention of the automatic glass bottle blowing machine in 1880 industrialized the process of making bottles. In 2019, plans were made to re-introduce milk glass bottle deliveries to Auckland in early 2020. The earliest bottles or vessels were made by ancient man. Ingredients were melted to make glass and then clay forms were dipped into the molten liquid. When the glass cooled off, the clay was chipped out of the inside leaving just the hollow glass vessel. This glass was very thin as the fire was not as hot as modern-day furnaces. The blowpipe was invented around 1 B.C. This allowed molten glass to be gathered at the end of the blowpipe and blown into the other end to create a hollow vessel. Eventually, the use of moulding was introduced, followed by the invention of the semi-automatic machine called the Press and Blow. In 1904 Michael Owens invented the automatic bottle machine. Before this time most glass bottles in England were hand blown. This is one of four bottles in our Collection that were recovered by a local diver from the quarantine area just inside the Port Phillip Heads. Ships were required to pull into this area to check for diseases and other medical issues before they could head up to Melbourne. Quite often they would drink and throw the bottles overboard. Handmade glass bottle, manufactured in the 1850s-1900s. The bottle gives a snapshot into history and a social life that occurred during the early days of Melbourne's development and the sea trade that visited the port in those days. Bottle, glass, solid dark brown (black), round, matt surface. Glass ring below mouth, neck is slightly bulbous, seam line around shoulder, body tapers slightly inward from shoulder to base. Base is concave with pontil mark. Bottle has a white mark down the side. No inscription. Generally used for storing stout, porter or ale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, handmade bottle, handmade english beer bottle, pontil bottle, black glass, gallon -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Kitchen Equipment, china meat platter, c1900
Wedgwood was founded on 1 May 1759 by Josiah Wedgwood and in 1987 merged with Waterford Crystal to create Waterford Wedgwood, an Ireland-based luxury brands group. After the 2009 purchase by KPS Capital, Wedgwood became part of a group of companies known as WWRD Holdings Ltd, an acronym for "Waterford Wedgwood Royal Doulton." In 1765, Josiah Wedgwood created a new earthenware form which impressed the then British Queen consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz who gave permission to call it "Queen's Ware"; this new form sold extremely well across Europe. Wedgwood developed a number of further industrial innovations for his company, notably a way of measuring kiln temperatures accurately and new ware types Black Basalt and Jasper Ware. Wedgwood's most famous ware is jasperware. It was created to look like ancient cameo glass. It was inspired by the Portland Vase, a Roman vessel. Wedgwood had increasing success with hard paste porcelain which attempted to imitate the whiteness of tea-ware imported from China. High transportation costs and the demanding journey from the Far East meant that the supply of chinaware could not keep up with increasingly high demand. In 1812 Wedgwood produced their own bone china which, though not a commercial success at first eventually became an important part of an extremely profitable business. An oval white china platter with blue flowers and fruit. Back is marked WEDGWOOD CHRYSANTHEMUMOn base ; CHRYSANTHEMUM / i / W / 7 / WEDGWOOD china, pottery, crockery, england, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, kitchenware, wedgwood josiah -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1850's - 1900
This bottle is sometimes referred to as a black glass 'Gallon' bottle. It is used for storing and transporting liquor such as port or madeira. Glass bottles and glass jars are in many households around the world. The first glass bottles were produced in south-east Asia around 100 B.C. and the Roman Empire around 1 AD. America's glass bottle and glass jar industry were born in the early 1600s when settlers in Jamestown built the first glass-melting furnace. The invention of the automatic glass bottle blowing machine in 1880 industrialized the process of making bottles. In 2019, plans were made to re-introduce milk glass bottle deliveries to Auckland in early 2020. The earliest bottles or vessels were made by ancient man. Ingredients were melted to make glass and then clay forms were dipped into the molten liquid. When the glass cooled off, the clay was chipped out of the inside leaving just the hollow glass vessel. This glass was very thin as the fire was not as hot as modern-day furnaces. The blowpipe was invented around 1 B.C. This allowed molten glass to be gathered at the end of the blowpipe and blown into the other end to create a hollow vessel. Eventually, the use of moulding was introduced, followed by the invention of the semi-automatic machine called the Press and Blow. In 1904 Michael Owens invented the automatic bottle machine. Before this time most glass bottles in England were hand blown. This is one of four bottles in Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum collection that were recovered by a local diver from the quarantine area just inside the Port Phillip Heads. Ships were required to pull into this area to check for diseases and other medical issues before they could head up to Melbourne. Quite often they would drink and throw the bottles overboard. Handmade glass bottle, manufactured in the 1850s. The bottle gives a snapshot into history and a social life that occurred during the early days of Melbourne's development and the sea trade that visited the port in those days. Bottle, glass, solid dark purple (black), round, matt surface. Glass ring below mouth, neck is slightly bulbous, body tapers slightly inward from shoulder to base. Base is concave with pontil mark. Bottle has no inscription. Generally used for storing port.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, handmade bottle, handmade english beer bottle, pontil bottle, black glass, gallon, purple bottle, ale bottle, porter bottle -
 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesDiplomatic gift, St Mark's Mallet
The mallet was given to the College by the staff of St Mark’s Hospital, London to celebrate the inauguration of the Proctological (later Colonic and Rectal) Section, on 28 May 1963. It was presented by J.C. Stewart to Alan Lendon, then Vice-President and Chairman of the Court of Examiners. Although it is usually described as a gavel, the form of the piece is in fact that of an ancient stonemason’s mallet. The action required to use it is a straight up-and-down motion, unlike that of a normal gavel, which is handled like a hammer. Made of black bean, 22.5cm high and 12cm in diameter, the mallet rests in a wooden stand made of Queensland walnut, with a square base of English oak. The mallet and stand are housed in a travelling case covered in red leather and lined in red velvet and white satin. On the front of the stand are four crests, those of St Mark’s Hospital, the Royal College of Surgeons of England, the Royal Society of Medicine, and the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons. St Mark’s was founded in 1835 as a specialist hospital for the treatment of fistula in ano, a common condition in the days of travelling on horseback, and other anorectal disorders. Over the years the hospital developed into a centre for gastroenterology, colonic and rectal surgery, and many Australians went to further their training there. Some noted Fellows of the College, including Robert Officer, James Guest, Reg Magee, Brian Collopy and Adrian Polglase, and three Presidents, Mervyn Smith, Sir Edward Hughes and Russell Stitz, are alumni of St Mark’s. This mallet is a reminder of the establishment of a significant surgical section within the College, and is a fitting gift from an institution with which so many eminent Australian surgeons formed close ties.GAVEL ON STAND WITH PAINTED COATS-OF-ARMS IN RED LEATHER PRESENTATION BOXPLAQUE ON GAVEL: "PRESENTED BY THE STAFF OF ST. MARK'S HOSPITAL TO COMMEMORATE THE FOUNDING OF THE PATHOLOGICAL SECTION OF THE RACS 28TH MAY 1963" -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Mitiamo UC Centenary & Rev. V. Raymond Hicks 11/11/1984, 11/11/1984
Victor Raymond Hicks (11/8/1903–19/11/1995) born at Ballarat. Trained at Otira and accepted as candidate for the ministry in 1927. Ordained 1934. Married Lillian Harvey, 4 children. Appointments to Mitiamo, Matimuk, Woomelang, Wodonga, Kerang, Springvale, Brunswick, North Fitzroy, Geelong West, Kyneton and Brown Hill (Ballarat). Chaplaincy in WW2 and at Box Hill hospital. The article about the Mitiamo church: "Fifty years ago the Rev. Raymond Hicks was minister at Mitiamo as it celebrated its Golden Jubilee. He returned for the centenary this year and powerfully preached on 'Lengthen your cords, and strengthen your stakes' (Isaiah 54:2). He spoke of the great need of the church today to have a passion to lead men and women to Christ. Also sharing in the service were the Rev. Ray Scholl, a Mitiamo member before entering the ministry, and present minister, the Rev. M. Thalheimer. The centenary weekend began with an old fashioned tea meeting and concert. The Sunday school hall housed a comprehensive display of photos and historical records dating back to the Bible Christian days of 1884. Mrs Thirza Phelan has researched and written the church history. FOOTNOTE: The first minister, Mitiamo's the Rev. Daniel Daley, preached at the Golden Jubilee service—Mr Hicks has followed an ancient tradition."Colour photograph of Rev. V. Raymond Hicks standing outside the front of a wooden church porch.C&N identification.rev raymond hicks, home missionary, methodist ministry, otira -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital Photograph, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotland, 10/2016
St Giles, also known as the High Kirk of Edinburgh is the principal place of worship for the Church of Scotland. It is very interesting for the mason's marks found on its many stone columns inside the church, and for its connections to the graveyard outside. According to wikipedia, "There is record evidence of a church here, very likely on the present site, in the year 854. In 1120 King Alexander I, rebuilt the church in the Norman style. Of this building characteristic features survived until 1798. During the fourteenth century, Edinburgh was captured and plundered by the English under Edward II. and Edward III., and twice St Giles was laid waste. After restoration, the church was more thoroughly ruined at the Burnt Candlemas in 1387, when Richard II. sacked the city. The western part of the fabric was soon in use again ; but the restoration of the choir and transepts, which were much enlarged, lasted on into the sixteenth century. In 1467 the city endowed St Giles as a collegiate church. It now became usual to speak of the nave, where the stonework was ancient, as the Old Kirk, while the eastern part of the building was called the New Kirk. When the movement for reform drew large crowds to St Giles, separate services began to be regularly held in the Old and New Kirks. Soon this was not enough, and the great church was partitioned off into smaller sections. In 1571 St Giles was seized by Kirkcaldie of Grange, and held by him as a stronghold for Queen Mary. This resulted in serious damage to the structure.Colour photograph of St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotlandst giles cathedral, edinburgh, scotland, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital Photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Interior, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotland, 10/2016
St Giles, also known as the High Kirk of Edinburgh is the principal place of worship for the Church of Scotland. It is very interesting for the mason's marks found on its many stone columns inside the church, and for its connections to the graveyard outside. According to wikipedia, "There is record evidence of a church here, very likely on the present site, in the year 854. In 1120 King Alexander I, rebuilt the church in the Norman style. Of this building characteristic features survived until 1798. During the fourteenth century, Edinburgh was captured and plundered by the English under Edward II. and Edward III., and twice St Giles was laid waste. After restoration, the church was more thoroughly ruined at the Burnt Candlemas in 1387, when Richard II. sacked the city. The western part of the fabric was soon in use again ; but the restoration of the choir and transepts, which were much enlarged, lasted on into the sixteenth century. In 1467 the city endowed St Giles as a collegiate church. It now became usual to speak of the nave, where the stonework was ancient, as the Old Kirk, while the eastern part of the building was called the New Kirk. When the movement for reform drew large crowds to St Giles, separate services began to be regularly held in the Old and New Kirks. Soon this was not enough, and the great church was partitioned off into smaller sections. In 1571 St Giles was seized by Kirkcaldie of Grange, and held by him as a stronghold for Queen Mary. This resulted in serious damage to the structure.Two colour photographs of the interior if St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotlandst giles cathedral, architecture, mason's marks, stonemasons, church of scotland -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital Photograph, Stonemason's marks, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotland, 10/2016
St Giles, also known as the High Kirk of Edinburgh is the principal place of worship for the Church of Scotland. It is very interesting for the mason's marks found on its many stone columns inside the church, and for its connections to the graveyard outside. According to wikipedia, "There is record evidence of a church here, very likely on the present site, in the year 854. In 1120 King Alexander I, rebuilt the church in the Norman style. Of this building characteristic features survived until 1798. During the fourteenth century, Edinburgh was captured and plundered by the English under Edward II. and Edward III., and twice St Giles was laid waste. After restoration, the church was more thoroughly ruined at the Burnt Candlemas in 1387, when Richard II. sacked the city. The western part of the fabric was soon in use again ; but the restoration of the choir and transepts, which were much enlarged, lasted on into the sixteenth century. In 1467 the city endowed St Giles as a collegiate church. It now became usual to speak of the nave, where the stonework was ancient, as the Old Kirk, while the eastern part of the building was called the New Kirk. When the movement for reform drew large crowds to St Giles, separate services began to be regularly held in the Old and New Kirks. Soon this was not enough, and the great church was partitioned off into smaller sections. In 1571 St Giles was seized by Kirkcaldie of Grange, and held by him as a stronghold for Queen Mary. This resulted in serious damage to the structure.Colour photographs of tonemason's marks, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotlandmason's marks, st giles cathedral -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Stonemason's marks, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotland, 10/2016
St Giles, also known as the High Kirk of Edinburgh is the principal place of worship for the Church of Scotland. It is very interesting for the mason's marks found on its many stone columns inside the church, and for its connections to the graveyard outside. According to wikipedia, "There is record evidence of a church here, very likely on the present site, in the year 854. In 1120 King Alexander I, rebuilt the church in the Norman style. Of this building characteristic features survived until 1798. During the fourteenth century, Edinburgh was captured and plundered by the English under Edward II. and Edward III., and twice St Giles was laid waste. After restoration, the church was more thoroughly ruined at the Burnt Candlemas in 1387, when Richard II. sacked the city. The western part of the fabric was soon in use again ; but the restoration of the choir and transepts, which were much enlarged, lasted on into the sixteenth century. In 1467 the city endowed St Giles as a collegiate church. It now became usual to speak of the nave, where the stonework was ancient, as the Old Kirk, while the eastern part of the building was called the New Kirk. When the movement for reform drew large crowds to St Giles, separate services began to be regularly held in the Old and New Kirks. Soon this was not enough, and the great church was partitioned off into smaller sections. In 1571 St Giles was seized by Kirkcaldie of Grange, and held by him as a stronghold for Queen Mary. This resulted in serious damage to the structure.Three photographs of stonemason's marks, St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotlandmason's marks, st giles cathedral -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image, Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne, c1934, 1934
The design for the Shrine of Remembrance was selected by competition among Australian artists and architects. Eighty-three designs were submitted and the winning design was by two Melbourne returned-soldier architects, Philip Hudson and James Wardrop. The inspiration for the external outline came from one of the seven wonders of the ancient world—the mausoleum at Halicarnassus to Mausolus, King of Caria in South West Asia Minor. Although the country was faced with frightful unemployment and financial difficulty in the late 1920s and the 1930s, so great was the gratitude of the people that the huge amount required to build the Shrine was raised or promised within six months from the opening of the appeal in 1928. (https://www.shrine.org.au/About-Us/History) Lodge Bros were commissioned to build the Shrine of Remembrance in St Kilda Rd in the late 1920s. In 1947, Lodge Bros were manufacturing a further stage at the Shrine of Rememberance, that being the carving and fixing of the bluestone servicemen on the top of the 1939-1945 War Memorial at the Eternal Flame. When funding became available for the new undercroft development at the front of the Shrine in 2001, the Shrine Trustees were eager to explore the possibility of the original stonemasons who built the Shrine, to complete the new development. This came to fruition in 2002-2003 when Lodge Bros constructed all the exterior walls of the undercroft development. Phil Luchetta (Managing Director) was able to source and secure the use of the same granite from Tynong Victoria that was used in the original works of the 1930s.Photograpic image of Melbourne's Shrine of Remembrance.shrine of remembrance, melbourne, war memorial, lodge brothers, world war one, remembrance -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Adze, Ward & Payne Ltd, Between 1843 to Mid 20th Century
An adze is an ancient and versatile cutting tool and has been in use for thousands of years. Adze are similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. They have been used since the Stone Age. Adzes are hand tools used for smoothing or carving wood. The subject item was made by Ward & Payne of the Limbrick Works at Hillsborough, Sheffield England manufacturers of hand-forged tools. Their trademark registered in 1850 was a Letter "W" & "P" stamped into the steel. The firm was established by David Ward (1767-1822) in 1803 the company became David Ward & Sons, in 1837 after Ward's son Edward joined the firm. In 1845 Henry Payne the founder's son-in-law became a partner but died in 1850 after which the company reverted to the Ward family. The business then concentrated on making carving tools, chisels and gouges. In 1882 David Ward's grandson David Ward Jr. (1835-1889) purchased land and built a factory at Sheffield North known as the "Limerick Wheel". For a time Wards operated from both 106-114 West Street Sheffield and at Limbrick Road, Hillsborough on the river Loxley. By 1911 they had expanded into making spades, forks, sheep shears and many other types of edged tools including drills and wood planes. In 1967 Wilkinson Sword purchased all the company's share capital and continued to sell Ward & Payne tools until 1970 when a fire burned the factory down and housing development was built on the site.The subject item is significant as it gives a snapshot of the technological development of sailing ships and their operation before steam-powered vessels took over around the world. Tools such as the subject item demonstrate the traditional craftsmanship and skill of the shipwright and the aesthetic quality of the timber ships designs of the time. Adze with wooden handle curved painted green with patent number and maker's name inscribed on inside curve of blade. Inscribed "Patd 561 Ward" "2w". flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, smoothing tool, hand tool, carpenders tool, adze, coopers tool, woodworking tools -
![Ceramic, Malcolm Boyd, Untitled [Male Form] by Malcolm Boyd, 1977](/media/collectors/530576742162ef0fa09a2288/items/556e8b9f2162f1015460fbfb/item-media/62a9b7295a061b9db7f1e053/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic, Malcolm Boyd, Untitled [Male Form] by Malcolm Boyd, 1977
MALCOLM BOYD Born Gippsland, Victoria In 1977 Malcolm Boyd graduated with a Diploma of Visual Arts from the Gippsland Institute of Advanced Education. It was at this time that he presented this work to the Jan Feder Memorial Ceramics Collection. Over thirty years later he still has a passion for ceramic history and design. Boyd operated the Black Cockatoo Pottery from around 1980-1995, starting in Essendon, then moving to Ascot Vale, Stratford, Bairnsdale and finally Fernbank in Gippsland. His handbuilt stoneware pots and clay sculptures are wood fired at his East Gippsland studio. He often uses ochre coloured dam banks on his property at Fernbank. The local clays are crushed, screened and blended with a white stoneware body to produce a number of shades and textures. All Malcolm Boyd's pot's are hand built using moulding, coiling, slabbing, and modelling techniques, and are high temperature fired (1300C) to allow some of the very ancient oriental glazes to mature. All works spend at least 20 hours in the wood fired kilns. This work is part of the Jan Feder Memorial Ceramics Collection which was amassed with funds raised by Jan Feder's student peers at the Gippsland Centre for Art and Design in the mid 1980s after Jan Feder passed away. Although many of the works are donated the intention of the collection was to purchase from visiting lecturers who became leading ceramic artists around the world, as well as from many of the staff who taught at the Churchill Campus. This work is part of the Jan Feder Memorial Ceramics Collection. Jan Feder was an alumna of the Gippsland Campus who studied ceramics on the campus. She passed away in the mid 1980s. Her student peers raised funds to buy ceramic works in her memory. They bought works from visiting lecturers who became leading ceramic artists around the world, as well as from many of the staff who taught there.malcolm boyd, ceramics, artist, artwork, jan feder memorial ceramics collection, gippsland campus, alumni
